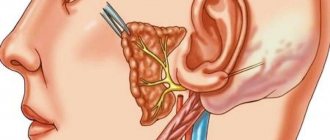
Often people experience pain that does not confirm the presumptive diagnosis. Pain in the back, chest, nose or eyes. The patient thinks that the heart, teeth.
Such complaints may indicate neuralgia, namely the nasociliary nerve, or Charlin's syndrome, the symptoms and treatment of which will be discussed in the article.
What is neuritis, nerve neuritis?
Neuritis is a lesion of the spinal or cranial nerves, manifested by syndromes of irritation and (or) loss of their functions in the corresponding area
innervation.
Neuritis occurs during acute and chronic viral and bacterial infections (influenza, pneumonia, dysentery, focal infections). Nerve damage is relatively rarely inflammatory in nature; various degenerative changes are more often found.
Classification of the disease
Charlin's syndrome occurs in two forms:
- Typical neuralgic - occurs when the main nerve trunk is damaged. The clinical picture is classic, that is, the symptoms correspond to the disease. Watery eyes, soreness in the nose and eye area;
- Erased hyperpathic . The nasociliary nerve has a main trunk and small branches. When these nerve endings become inflamed, the picture becomes blurred. Symptoms become atypical. Sensitivity may simply be lost or perception may increase.
Neuralgia can also be unilateral or bilateral. It is divided into acute, subacute and chronic forms.
Neuritis symptoms
The clinic of neuritis is characterized by dysfunction of the innervated structures. Since most nerves are mixed, when they are damaged in the innervation zone, flaccid paresis (paralysis), muscle atrophy, decreased and loss of reflexes, impaired sensitivity and autonomic disorders (swelling, cyanosis, increased sweating, depigmentation, hair loss) occur.
With neuritis of the facial nerve, damage to the root or trunk of the facial nerve occurs at various levels, manifested by homolateral paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles.
Treatment methods
When treating neuralgia, the cause must be eliminated. Therefore, the patient is sent for consultation to a dentist and otolaryngologist.
Next, the neurologist prescribes antidepressants with an analgesic effect . They have an analgesic effect based on reducing impulse transmission.
Local anesthetics help relieve pain at the site of application. Typically these are ointments or solutions that are applied to the skin.
Vitamins of group B and PP have a therapeutic effect . Drugs from the group of H-anticholinergics are also used. They act on membrane receptors, blocking access to the nerve impulse. Then there is no pain.
For erased hyperpathic form, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are effective. They reduce pain and eliminate local inflammation (which forms in one place).
Prescribed as eye drops and nasal spray. If such remedies do not help, corticosteroids are used.
In the presence of primary infections, such as pulpitis, periodontitis, sinusitis, antibiotics are prescribed . Physiotherapy is also used. These are ultrasound, vibration massage, diadynamic currents.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
The following procedures apply:
- SMT or DDT as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
This method is more often used for neuralgia after the flu. The temporal artery and stellate ganglion are affected for 2-3 minutes. For bilateral inflammation, a half mask is used. - Electrophoresis . Depending on the cause of neuralgia, different drugs are used. Novocaine, iodine, diphenhydramine, platyphylline.
- Exposure to ultrasound for 5-20 minutes . This reduces pain, improves blood circulation and tissue nutrition.
- Face massage . Light movements for 5-6 minutes. It shouldn't cause pain.
- Exposure to diadynamic current . Eases pain. The procedure lasts 20 minutes.
Causes of neuralgia
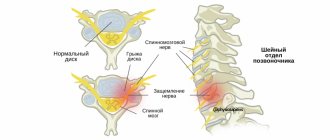
The causes of neuralgia are inflammatory, traumatic, toxic, infectious-allergic, and metabolic effects. Compression of nerves in the bone, musculoskeletal and osteoarticular canals, prolonged microtrauma, especially in combination with hypothermia, and foci of focal infection also play an important role.
In the mechanism of pain syndrome, irritation of peripheral nerve fibers and central changes are important. In various suprasegmental parts of the nociceptive system, a generator of pathologically enhanced excitation may arise, which causes paroxysmal pain of a central nature.
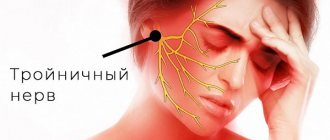
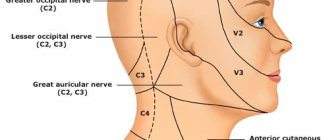
There are neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve, its ganglia and main branches (nasociliary, auriculotemporal nerves, pterygopalatine ganglion), glossopharyngeal nerve, occipital neuralgia, neuralgia of the facial nerve.
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases, an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders: facial hyperemia and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, hypersalivation, possibly increased blood pressure, chill-like tremors, difficulty breathing. Detailed information on trigeminal neuralgia.
There are primary (idiopathic, essential, typical) and secondary (symptomatic) trigeminal neuralgia.
With primary neuralgia (mainly of central origin), attacks occur for no reason or are provoked by any movements of the facial muscles. Secondary neuralgia is usually a complication of the primary disease, has a predominantly peripheral genesis and is often caused by pathological processes in the dentofacial area. The pain is almost constant, periodically intensifying in the form of attacks lasting up to several hours.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on symptoms, medical history, and research:
- The doctor talks with the patient, finds out the symptoms. Finds out what the pain is and where it is located. Are there any infectious diseases in the head area? For example, otitis media, sinusitis, tooth extraction, adenoiditis.
- Then he examines and palpates the damaged area. The presence of swelling and redness is detected.
- When the doctor roughly presents the diagnosis, he examines for the presence of diseases with similar symptoms. That is, differential diagnosis is carried out. Refers for examination to a dentist and otolaryngologist.
- To determine the diagnosis, there is a method of applying a solution of cocaine hydroxide to the mucous membrane of the front of the nose. If the patient stops feeling pain, then this is inflammation of the nasociliary nerve.
- Next, instrumental studies should be carried out. Ophthalmoscopy, MRI of the head, biomicroscopy, anterior rhinoscopy.
- Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed.
With the help of additional examination, neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve is differentiated from other diseases. And they establish an accurate diagnosis.
Biomicroscopy of the eye
It is performed using a slit lamp , the main part of which looks like a large slit. The device examines the structure of the eye, the back and front walls. This method allows you to see any damage, foreign body, and detect the disease at an early stage. Biomicroscopy allows you to see the condition of the retina and optic nerve.
Ophthalmoscopy
The fundus of the eye is examined using an ophthalmoscope . With the help of an eye mirror you can see blood vessels and nerves. Identify changes, redness, swelling.
Anterior rhinoscopy
This is done using a nasal speculum . The anterior part of the nasal cavity is examined by inserting the device into the nostrils. The most suitable for this procedure is the Hartmann mirror. The doctor holds the device in his left hand, slightly dilating the nostril.
In this case, the nasal septum and passages are visible. This is how redness, curvature, atrophy and hypertrophy are noticed.
Sometimes it is possible to examine the nasal cavity using reflector lighting. It is used to examine children, as they may be frightened by an unknown object.
MRI of the head
To accurately confirm the diagnosis, an MRI of the head is performed . X-ray radiation is not used here. The examination is carried out using magnetic fields, which create an energy change in the examination area. This is how photographs are taken without the use of contrast. A cross-sectional image is displayed on the computer monitor.
Neuralgia treatment, how to treat neuralgia, intercostal neuralgia treatment, neuritis treatment
Complex treatment of neuritis and neuralgia (Saratov, Russia) includes a variety of effective techniques. Sarklinik knows how to treat and cure neuralgia neuritis !
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Jabiru | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Depression, treatment of depression, how to get out of depression in Saratov
Trigeminal nerve, inflammation, treatment, trigeminal neuralgia, symptoms, how to treat
Polyneuritis, treatment of polyneuritis, alcoholic polyneuritis, polyradiculoneuritis
Neuroses, neurosis, treatment of neurosis, neurasthenia, how to treat
Hypersomnia, doubtfulness, pathological increased sleepiness, treatment
Comments ()
What diseases should not be confused with?
Differential diagnosis - excluding diagnoses with similar symptoms. Charlin's syndrome should be distinguished from:
- inflammation of the sinuses, nasal cavity;
- ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion (the pain goes away when the back of the nasal cavity is lubricated with a cocaine solution. And with inflammation of the nasociliary nerve in the front part);
- neuralgia of the maxillary nerve (burning pain under the eye and upper jaw);
- ganglionitis of the ciliary ganglion (pain radiates to the forehead, temple, root of the nose, forearm, neck).
Prevalence
Neuralgia is quite common in the practice of a neurologist. Examples of prevalence depending on the type of pathology:
- trigeminal nerve - up to 50 patients per 100,000 population, more often in women aged 50–70 years;
- intercostal – about 12 people per 100,000, typical for middle-aged and elderly people.
Neuralgia is more common in the elderly, but this does not mean that middle-aged and young people are not susceptible to the disease.
Differences between neuritis and neuralgia
In medicine, there are 2 concepts that sound similar, but have different meanings - neuritis and neuralgia.
Neuritis is characterized by deeper damage to the nerve, affecting the nerve sheath, in which muscle twitching and changes in sensitivity are observed.
Neuralgia is accompanied by the involvement of sensory fibers in the process, so pain is always present. Numbness is observed less frequently, there are no muscle manifestations
Survey
Diagnosis of neuralgia is the competence of a neurologist or therapist.
Neuralgia is not confirmed using laboratory or instrumental research methods. In most cases, characteristic attacks allow a diagnosis to be made. To exclude other diseases and confirm inflammation, the doctor may prescribe:
- ECG, chest X-ray, ultrasound of internal organs - if intercostal nerves, solar plexus are affected;
- general, biochemical blood tests - detect inflammation;
- ENMG (electroneuromyography) - shows the extent of nerve involvement in the process, as well as whether there are disturbances in the conduction of impulses to the muscles.
Causes and risk factors
First of all, the following reasons lead to the occurrence of neuralgia:
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- viruses (primarily herpes, which causes neuralgia after the exacerbation of shingles subsides);
- pinching by tight clothing, crutches;
- hypothermia;
- injuries, sprains;
- tumors;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases – tuberculosis, brucellosis.
Risk factors that increase the risk of neuralgia:
- diabetes;
- antisocial lifestyle;
- age over 50 years;
- frequent hypothermia.
It is believed that stress and overwork also increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Lack of treatment for the acute form risks its development into chronic neuralgia.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable . That is, the disease can be cured and recurrences can be avoided.
A feature of neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve is the subsidence of pain. The patient thinks that the disease goes away on its own and no treatment is needed. Here lies the danger. Even if the pain decreases, treatment is necessary.
Prevention measures include:
- treat ENT diseases in a timely manner;
- prevent the development of infections in the mouth;
- maintain eye hygiene;
- Follow safety precautions to avoid injury.
Inflammation of the nasociliary nerve is a rare pathology . And it occurs more often as a secondary disease. That is, against the background of other infections in the head area. Timely treatment of sinusitis, caries, otitis, and sinusitis will help avoid neuralgia.