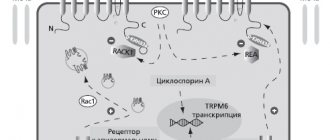
Based on modern ideas about the mechanisms of development of ischemic stroke, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital identify 2 main directions of pathogenetic therapy: improving the perfusion of brain tissue (the passage of blood through them) and neuroprotection (a set of measures aimed at improving the biochemical and restorative properties of the nerve cell).
Complex therapy of ischemic cerebral stroke
It is known that in the absence of adequate therapy, approximately 2 million neurons die within ten minutes of ischemia. Each stage of the ischemic cascade is a potential target for therapeutic intervention. The earlier neuroprotective treatment is started, the greater the chances of success, the less the degree of damage to the brain substance.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin complex therapy for ischemic stroke immediately after the patient is admitted to the neurology department and an accurate diagnosis is established. Neurologists draw up treatment regimens for patients with cerebral infarction individually, taking into account which vessel has impaired blood flow, the size of the ischemic focus, and how damaged the nerve cells around the area of cerebral infarction are. Due to the fact that the clinic conducts research on modern drugs for the treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents, patients at the Yusupov Hospital have the opportunity to receive the most modern drugs.
Drug treatment of acute ischemic stroke includes basic and specific therapy. Basic therapy consists of:
- measures to support respiratory and circulatory functions;
- correction of metabolic disorders and the volume of circulating fluid;
- blood pressure control.
The main goal of intensive care is to prevent oxygen deprivation of brain tissue and the associated increase in brain damage. To ensure adequate water-electrolyte balance and blood flow, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide infusion therapy to patients with ischemic stroke. The purpose of infusion therapy is:
- achieving blood thinning;
- maintaining adequate cerebral perfusion pressure (a physiological indicator characterizing the level of blood supply) not lower than 70 mm Hg. Art. to eliminate ischemia and oxygen starvation of neurons;
- correction of electrolyte disturbances, primarily high or low sodium levels in the blood.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital achieve a normal level of cerebral perfusion pressure in patients with ischemic stroke by increasing systemic arterial pressure and decreasing intracranial pressure. To increase blood pressure, crystalloid solutions and sympathomimetics are administered intravenously.
In case of ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital maintain the patient’s circulating blood volume at the proper level and prevent the development of hypovolemia, which increases the risk of low blood pressure and reduces central perfusion pressure. These changes in the equilibrium of the internal environment of the body lead to vasodilation and increased intracranial pressure.
To maintain the overall water-electrolyte balance and ensure sufficient blood flow in the cerebral vessels, patients with ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic are administered 30-35 ml/kg/day of fluid. Patients who, upon admission to the Yusupov Hospital, have low blood pressure, elevated hematocrit, dry mucous membranes and no decompensated heart failure, are prescribed infusion therapy in a volume of 1000-1500 ml of Ringer's solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Patients with developed cerebral edema are maintained in a negative water balance.
How do chemotherapy drugs work?
Despite their different mechanisms of action, all chemotherapy drugs work in the same direction: they disrupt the cell cycle, stop the proliferation of cancer cells and cause their death.
Due to the fact that tumor cells multiply rapidly, they are an ideal target for chemotherapy. But healthy cells of the body are also affected, although to a lesser extent. The organs in which cell division processes occur most intensively are most affected: red bone marrow, skin (including hair and nails), mucous membranes (oral cavity, intestines). Chemotherapy drugs have numerous side effects, and special supportive therapy helps to cope with them.
Treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke with neuroprotectors
Currently, there are many drugs that have a neuroprotective effect. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use only neuroprotectors, the effectiveness of which has been proven by scientific research, to treat ischemic stroke. One of these drugs, which has the most versatile mechanisms of action in relation to oxidative stress (damage to brain cells as a result of oxidation) and a wide evidence base for ischemic stroke, is EMHPS (ethyl-methyl-hydroxypyridine succinate).
In this case, based on clinical experience in the use of EMGPS, the following scheme for its administration is used:
- at the prehospital stage, 400 mg is administered intravenously as a bolus once;
- in the acute period of ischemic stroke (up to 14 days), 5 mg/kg/day is administered intravenously, but more than 800 mg/day;
- during the recovery period (within 14 days), 400–800 mg of the drug 2-3 times a day is administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
One of the mechanisms of the damaging effect of ischemia is cholinergic insufficiency. With pathology of cerebral vessels, the number and size of cholinergic neurons in brain structures decreases. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the following regimen for the use of choline alfoscerate for acute ischemic stroke: for the first 3-7 days, 1000 mg is administered intravenously 2 times a day, and from the second week they switch to taking 400 mg of the drug per day 2 times a day (course of treatment - 2 month).
The combination of ethyl-methyl-hydroxypyridine succinate and choline alfoscerate in the context of ischemic stroke allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to fully influence the fundamental mechanisms of the development of clinical symptoms associated with ischemia and cholinergic insufficiency.
Drugs with proven effectiveness in ischemic stroke include the cerebroprotector Citicoline. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use it for both primary and secondary neuroprotection. Primary protection of brain cells begins from the first minutes of ischemia and continues during the first three days of stroke, especially active during the first twelve hours. Secondary neuroprotection reduces the severity of long-term consequences of ischemia. Neurologists begin it 3-6 hours after the onset of a stroke and carry it out for at least seven days.
Results of trials of a new drug for stroke
It turned out that when the protein is injected into the brain of animals that have suffered a stroke, it restores 99% of motor abilities in the hind limbs. When protein was administered through the nose, the resumption of motor activity was recorded in 70% of cases. To conduct this experiment, scientists were able to simulate the occurrence of a stroke in a group of experimental animals. Like humans, the rats had half their bodies immobilized.
Approximately 1 month after the onset of the disease (in humans this period is one year), TGFA . 30 days after this, the experimental rats completely resumed all movements in the damaged part of the body.
In the group of rats not exposed to TGFA , the resumption of movements was observed in only 1/3 of the experimental subjects.
In a second experiment, scientists injected this protein into the animals' brains through the nose, while slightly changing its structure to facilitate delivery to the brain. After 1 month, in 70% of cases, movement in the damaged half of the body was restored in the experimental rats.
“It is already becoming obvious that the brain has enormous reserve capacity for its own restoration. Our task is to correctly direct this process ,” says one of the authors of this technique about the results of the work.
Drugs after ischemic cerebral stroke
In order to prevent recurrent acute cerebrovascular accident. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe antihypertensive drugs to patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke. During your stay at the neurology clinic, cardiologists individually select the most effective drug and its dose. In some cases, it is recommended to take combination antihypertensive drugs.
If there is a depressive state, antidepressants are prescribed. They not only eliminate the patient’s feeling of fear, but also eliminate the negative symptoms that develop as a result of cerebrovascular accidents. If the patient has no contraindications, he is prescribed antiplatelet agents. These include:
- acetylsalicylic acid and its derivatives (Trombo-AS, Aspirin Cardio, Acecardol, Cardiomagnyl, Aspicor, CardiASK);
- ADP receptor blockers (Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine);
- phosphodiesterase inhibitors (Triflusal, Dipyridamole);
- glycoprotein receptor blockers (Lamifiban, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban, Abciximab);
- inhibitors of arachidonic acid metabolism (Indobufen, Picotamide);
- medicines based on the Ginkgo Biloba plant (Bilobil, Ginos, Ginkyo).
Some plants also have an antiplatelet effect: horse chestnut, blueberries, green tea, ginger, garlic. Vitamin E also falls into this category.
In order to receive treatment and rehabilitation after an ischemic stroke with modern drugs, call us by phone. You will make an appointment with a neurologist, who, after the examination, will select an individual treatment regimen. The collective decision on the choice of treatment method for the most severe patients with ischemic stroke is made by doctors of the highest category, candidates and doctors of medical sciences on an expert council.
Scientists have tested a new cure for stroke
Drugs that can cure a person from the consequences of the disease in a short period of time are not known today. If a person has a stroke, doctors do not know many methods for rehabilitating the patient. However, scientists from the University of California managed to quickly restore the motor functions of limbs paralyzed due to a stroke in rats.
Scientists have discovered previously unexplored properties of one protein, which is called transforming growth factor alpha (TGFA) . In the human body, such a protein takes part in the formation of all tissues throughout life.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: “advanced” chemotherapy drugs
The ability to study the molecular genetic characteristics of cancer has led to the emergence of a relatively new group of anticancer drugs— targeted drugs . These “snipers” act on specific molecules that malignant tumors need for growth, survival, and protection from the immune system. Unlike classical chemotherapy drugs, targeted drugs do not act on healthy cells and are less likely to cause severe side effects.
Modern scientists and oncologists place great hopes on immunotherapy drugs. These drugs use the power of the immune system to destroy cancer cells.
The development of oncology does not stop. Scientists continue to work on creating new anticancer drugs. Some drugs are currently undergoing clinical trials. Unfortunately, creating and testing new drugs is a long and expensive process. However, there is progress, which means there is hope for cancer patients.
What is personalized chemotherapy?
In recent years, approaches to the classification of malignant tumors have changed somewhat. Previously, scientists could only examine cancer cells under a microscope; now it is possible to study their molecular genetic characteristics. Cells can look the same but have a different set of gene changes. They produce different substances that help them survive, reproduce, and protect themselves from immune aggression in different ways.
If we consider cancer at the molecular genetic level, it turns out that there are practically no two identical tumors. Each patient is individual, each needs his own approach when choosing a combination of chemotherapy drugs. This type of treatment is called personalized. It is the most effective, since it implements the most important principle of medicine: “to treat not the disease, but the patient.”
Currently, molecular genetic studies that help prescribe personalized chemotherapy are not available in every clinic. But they are the future of oncology.
Side effects of using chemotherapy drugs
Chemotherapy causes various side effects. Symptoms may occur some time after the start of treatment and even after completion of the course. Some of them pass quickly, others persist for a long time. The degree of their severity also varies; it depends on many factors, such as age, health status of the patient, type, dose and method of administration of the chemotherapy drug, and concurrent use of other medications.
Doctors at Euroonko prescribe maintenance treatment, which helps to cope with most side effects and comfortably undergo chemotherapy. The patient receives detailed recommendations regarding lifestyle, and is told which symptoms should promptly consult a doctor if they occur.
You can learn more about the possible side effects of chemotherapy drugs on this page.
Types of Chemotherapy Drugs
Chemotherapy drugs are divided into groups depending on their chemical structure and mechanism of action. The same drug can work in different ways and belong to different groups. Knowing which group a chemotherapy drug belongs to, the doctor can predict therapeutic and side effects and correctly plan the course of treatment.
Cytostatics and cytotoxic drugs
Traditionally, anticancer drugs are divided into two groups:
- Cytostatics (cytostatics) stop the proliferation of cancer cells and trigger the process of programmed cell death in them - apoptosis . This group includes, in particular, fluorouracil, cisplatin, and doxorubicin.
- Cytotoxic (cytotoxins) damage the nucleus, membrane and other components of the cell, leading to its death.
Currently, there are also targeted drugs that disrupt the vital activity and proliferation of tumor cells by affecting certain target molecules, and immunotherapy drugs that use the resources of antitumor immunity.
Alkylating agents
The oldest group of chemotherapy drugs. They are so named because they can alkylate a variety of molecules, including DNA, RNA and proteins. The drug binds to the DNA molecule and causes it to break during duplication during cell division. As a result, the process of programmed cell death is triggered - apoptosis .
Alkylating agents attack cells at any stage of the cell cycle. Chemotherapy with these drugs is effective for many types of cancer: lung, ovarian, breast, as well as sarcomas, multiple myeloma, Hodgkin's disease, lymphoma, leukemia.
Representatives of the group : cisplatin, carboplatin, dacarbazine, chlorambucil, oxaliplatin, temozolomide.
Antimetabolites
These drugs attack tumor cells at the stage of chromosome duplication during division. They disrupt the synthesis of new RNA and DNA, taking the place of nucleotides - the “links” that make up the chains of nucleic acids. Antimetabolites are effective as chemotherapy for colon, ovarian, breast, and leukemia cancer.
Representatives of the group : 5-fluorouracil, 6-mercaptopurine, capecitabine, gemcitabine, methotrexate.
Antitumor antibiotics
They resemble antibacterial drugs that are used to treat infections. These chemotherapy drugs damage the DNA of tumor cells and interfere with their reproduction. There are different groups of antibiotics for chemotherapy, one of them is anthracyclines . These drugs interfere with the function of enzymes that are necessary for DNA duplication.
Representatives of anthracyclines : doxorubicin (Adriamycin), epirubicin, daunorubicin, idarubicin.
Representatives of antitumor antibiotics that are not anthracyclines : bleomycin, mitoxantrone, mitomycin-C, actinomycin D.
Topoisomerase inhibitors
The DNA molecule consists of two chains twisted into a spiral. In order to copy it during cell division, the helix must be “unraveled.” topoisomerase, is responsible for this function . There are chemotherapy drugs that block it, thereby disrupting the processes of cell division. Topoisomerase inhibitors are effective against cancer of the stomach and intestines, ovaries, lungs, and leukemia.
Representatives of the group : topotecan, irinotecan, etoposide, teniposide, mitoxantrone.
Mitosis inhibitors
Chemotherapy drugs from this group are of plant origin. They block cell division, disrupting the function of microtubules and some enzyme proteins. Mitosis inhibitors are used to treat breast cancer, lung cancer, myeloma, lymphoma, and leukemia.
Representatives of the group : docetaxel, paclitaxel, vinblastine, vincristine.
Vinkaalkaloids
The first mitosis inhibitors in this group, vinblastine and vincristine, were isolated from the rose periwinkle plant (Vinca rosea). Then, based on vinblastine, semisynthetic compounds for chemotherapy were created - vinorelbine and vindesine. The main mechanism of action of these drugs is that they bind to the protein tubulin in microtubules and prevent it from polymerizing. Cell division stops.
Vinca alkaloids also disrupt other cellular processes: they change the metabolism of amino acids and some other substances, affect the synthesis of nucleic acids, fats, and cellular respiration.
Taxanes
These drugs have been widely used for chemotherapy since the 90s of the last century. Paclitaxel was first obtained in the 1960s from an extract of the Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia). In the 1980s, a more powerful drug, docetaxel, was isolated from an extract of European yew needles (Taxus baccata).
Taxanes also affect microtubules, but not in the same way as vinca alkaloids. On the contrary, they accelerate the polymerization of tubulin and subsequently prevent its depolymerization and the disintegration of microtubules. Because of this, cell division is also disrupted.
Glucocorticosteroids
Glucocorticosteroids, or glucocorticoids, are preparations of adrenal hormones. They have many functions, in particular, they take part in the regulation of metabolism, suppress immune reactions and inflammation. These drugs also have antitumor properties. Sometimes glucocorticoids are used for maintenance therapy. They help eliminate nausea and vomiting caused by anticancer drugs and prevent allergic reactions.
Representatives of the group : methylprednisolone, prednisone, dexamethasone.
Chemotherapy drugs that do not belong to any groups
Some chemotherapy drugs are not included in any group and have their own mechanisms of action. For example, the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, the enzyme L-asparaginase.