September 24, 2019
59253
0
3.8 out of 5
The presence of occipital neuralgia is indicated when, as a result of irritation by certain factors of two large or two small occipital nerves, severe headaches occur. Attacks can reach such a frequency that they completely deprive a person of his ability to work.
But you can cope with the disease if you consult a neurosurgeon. The doctor will be able to accurately determine the causes of neuralgia and select the most appropriate treatment tactics in a particular case, including surgery. SL Clinic specialists have extensive experience and knowledge in the field of neurological disorders and are able, using modern treatment tactics, to significantly improve the patient’s quality of life or achieve complete elimination of signs of neuralgia. The price of a specialist consultation is available to everyone and is given in the price list.
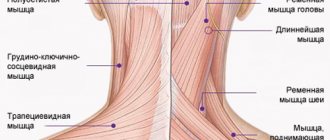
Anatomy of the occipital nerve
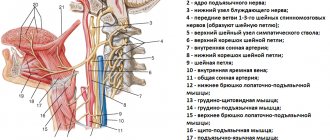
There are 2 major and 2 minor occipital nerves. They are symmetrically located in pairs on both sides of the back of the head. The large ones are responsible for the innervation of the skin of the back of the head and are formed from the posterior branches of the second cervical spinal nerve. They pass under the lower edges of the oblique muscle of the head, in the thickness of the semispinalis, along the trapezius tendon and branch into branches of different sizes in the skin of the occipital and part of the parietal zone. The greater occipital nerves are not responsible for innervating muscle fibers.
The minor occipital nerves are responsible for the sensitivity of the lateral surfaces of the head, the area behind the ears and partially the auricles. They are formed from the anterior branches of the 2nd and 3rd spinal nerves and pass under the sternosubclavian muscle.
Knowledge of the location of nerve fibers allows a neurologist to correctly diagnose the cause of pain through manual manipulation of special points. With neuralgia, this provokes a sudden attack of pain.
Causes of occipital neuralgia
Neuralgia becomes a consequence of irritation of nerve fibers at any part of their passage. This could be a consequence:
- degenerative-dystrophic processes of the cervical spine, provoking the formation of osteophytes, thinning of cartilage tissue, deformation of the intervertebral discs, which leads to pinched nerves (osteochondrosis, herniated discs, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis);
- receiving neck injuries;
- formation of tumors of various nature in the area of passage of the occipital nerves;
- severe spasm of the neck muscles resulting from prolonged stay in a static forced position;
- hypothermia;
- anomalies of the craniovertebral junction;
- diabetes mellitus, spinal tuberculosis, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
In these cases, it can be considered as a symptom of an existing disease, since its elimination leads to the elimination of headaches. Due to the nature of their professional activities, office workers and drivers belong to the risk group.
There is also spontaneously occurring neuralgia of the occipital nerve, called Arnold's neuralgia. Its presence is indicated in the absence of other factors that can lead to compression or irritation of the nerves, i.e., the idiopathic nature of the development.
Prognosis and prevention
You can prevent the development of the disease simply by following a few simple rules:
- Maximum protection against blowing and hypothermia.
- Taking vitamins needed by the body.
- Be careful in your movements. Injuries to the neck, back and back of the head should not be allowed.
- Physical activity. You don't have to be a master of sports. You just need to keep yourself in shape and do daily exercises.
- When the first signs of illness appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Proper nutrition, sufficient physical activity and a medical examination once a year are the cure for all diseases.
Don't ignore even the slightest headache . Small problems can become big ones. Take care of your body and it will take care of you in return.
Symptoms of the disease
The main manifestation of the disorder is attacks of pain. They can occur with different frequencies and be of different nature. But the pain always initially appears in the back of the head and radiates to the neck and ear area. More often it is unilateral, in some cases there is bilateral damage.
The pain can be lumpy, electric-like, or pulsating. It is always acute and can reach painful intensity, intensifying with head movements and coughing. A patient can experience from one attack to hundreds per day, which completely deprives him of the joy of life. The duration of each varies from a few seconds to a couple of minutes.
Attacks occur spontaneously, more often after sudden movements, sneezing or coughing. A distinctive feature is that patients try to take a forced position with their head slightly pulled back and to the side. This further increases tension in the neck and can make attacks more frequent.
Additionally there may be:
- nausea and vomiting;
- lacrimation;
- feeling cold;
- photophobia;
- intolerance to loud sounds;
- hair loss on the back of the head;
- redness or paleness of the skin in the affected area.
Between attacks, usually nothing bothers the person. Although in some cases it is possible to retain a dull, aching pain in the occipital region, a sensation of goosebumps, burning, and tingling.
A decrease in the sensitivity of the skin of the occipital region is often observed. The patient does not feel touching it, and when injected he only has a slight sensation of touch. But this is only true if you don’t touch the so-called trigger points.
Why is ultrasound control needed?
Did you know that blockades for back pain, joint pain, and neuralgia in the vast majority of cases are performed “blindly” without technical control? This means that the doctor works according to traditional superficial guidelines, and the manipulation itself occurs according to the feelings of the doctor and the patient.
With this method, erroneous delivery of the drug “to the wrong place” will, at best, lead to the ineffectiveness of the procedure; at worst, punctures of the pleura, erroneous administration of the drug into the subarachnoid space, or erroneous intravascular administration. In many cases, these mistakes can end sadly.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing occipital neuralgia is not difficult. This can usually be done at the first consultation with a neurosurgeon. Pain in the skin of the back of the head or numbness are clear specific symptoms of the disease. The doctor can finally confirm its presence by influencing special trigger points located along the greater or lesser occipital nerve on the affected side. This:
- Impact on a point located on a conventional line passing between the mastoid process and the occipital protuberance. If you divide it into 3 parts and press on the point located on the border of the upper and middle third, the patient will feel severe pain due to neuralgia of the greater occipital nerve.
- Pressure on the site at the junction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle with the mastoid process when the lesser occipital nerve is damaged causes an attack of pain.
But the main goal of diagnosis is to search for factors and diseases that caused its development. Otherwise, any treatment will be ineffective, and painful attacks will become more frequent, longer and more frequent. To detect the causes of the development of occipital neuralgia, a vertebrologist may prescribe to the patient:
- radiography;
- MRI;
- CT;
- UAC;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test.
If during the studies no pathological abnormalities are found, neuralgia is recognized as primary, which determines further tactics for treating the disease.
Treatment of occipital neuralgia
Without influencing the cause of the disorder, it is impossible to completely eliminate its manifestations. The only case where therapy is purely symptomatic is idiopathic occipital neuralgia.
Until research results are obtained, all patients are prescribed symptomatic therapy. Once the root cause is known, treatment is supplemented with remedies aimed at eliminating it.
In most situations, neuralgia can be dealt with directly using conservative therapy. It assumes:
- drug treatment;
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy.
If left untreated, occipital neuralgia can lead to destruction of nerve tissue and the development of complications, including hair loss and depressive disorders.
Drug therapy
Depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations and causes of nerve irritation, patients may be prescribed:
- muscle relaxants - a group of drugs that help eliminate muscle spasms;
- NSAIDs are drugs that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties;
- corticosteroids – have powerful anti-inflammatory properties, prescribed in short courses when NSAIDs are insufficiently effective;
- anticonvulsants – help reduce muscle tone;
- antidepressants – necessary to normalize the psycho-emotional state of patients;
- B vitamins - necessary to improve the condition of nervous tissue and impulse conduction.
In case of a severe attack of pain, a blockade can be performed, which involves pinpoint injections of anesthetics at certain points along the affected nerve.
Physiotherapy
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, patients are recommended to undergo courses of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UVR method involves exposure to mid-wave ultraviolet rays. This leads to an intensification of the release of specific neurotransmitters, which has a beneficial effect on the transmission of nerve impulses. Typically, the course of treatment includes 10 procedures.
- UHF - the procedure is based on the action of high frequency currents, which provoke an improvement in the quality of blood circulation and restoration of the sodium-potassium membranes of nerve cells. Treatment duration is from 15 to 20 sessions of 15 minutes each.
- Electrophoresis is a procedure during which painkillers or other drugs are injected directly into the affected area using an electric current. Traditionally, 10 procedures are prescribed, performed every other day.
- inductometry;
- Laser therapy is a method based on the positive effect of the thermal energy of laser beams on nerve fibers. This effect reduces their sensitivity, which reduces the degree of their irritation and the frequency of attacks. Patients are recommended 10 procedures of 4 minutes each.
- Diadynamic currents - the procedure involves fixing electrodes on trigger points and passing Bernard current through them. This is an ultra-high frequency current, the impact of which provides a rapid decrease in the pain threshold and inhibition of the transmission of nerve impulses. The duration of the treatment course is 5 sessions, performed every other day.
- Spinal traction is a procedure aimed at increasing the size of intervertebral discs and normalizing the position of the vertebrae. It can be performed using dry or underwater methods. Its duration ranges from several minutes to an hour, and the course of treatment includes about 15 sessions. With the dry method, traction is carried out under the influence of its own weight in a vertical or horizontal position. When underwater, the procedure is carried out after the patient is immersed in water. The second method has a more gentle effect on the spine.
Additionally, patients may be recommended reflexology sessions. It has long been noted that targeted effects on biologically active points provoke increased blood circulation, improved lymph flow and a decrease in the severity of pain.
Massage
A properly performed massage helps eliminate pressure on nerve endings, improve blood circulation in the head, and eliminate muscle spasms. The mastoid process and the area under it are exposed to manual intervention. It is important that the procedure is carried out by a qualified specialist. Otherwise, you may accidentally hit trigger points, which will provoke a new attack of pain.
Traditionally, a course consisting of 12–14 procedures is prescribed. The duration of each of them is about a quarter of an hour.
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Regular exercise therapy classes according to individually designed programs will help normalize the functioning of the cervical spine. They are especially important for osteochondrosis, as they allow you to accelerate the processes of natural restoration of cartilage tissue and eliminate the prerequisites for compression of nerves.
For each patient, a set of exercises is selected separately, taking into account the characteristics of existing diseases. They should be performed daily at least once a day. On average, one physical therapy session takes about 20–30 minutes.
All exercises are performed carefully, without sudden movements. If a new attack of neuralgic pain or discomfort in the cervical spine occurs, you should immediately stop exercising and consult a doctor as soon as possible to understand the causes of pain and change the nature of the exercises to a more gentle one.
Surgical treatment of occipital neuralgia
For idiopathic neuralgia, as well as when conservative treatment is ineffective, patients may be offered surgical treatment. It may consist of:
- microvascular decompression;
- radiofrequency ablation;
- neurostimulation.
Patients may also be recommended surgeries aimed at eliminating the cause of neuralgia. Most often, they lie in disturbances in the structure of the cervical spine, which is why surgical interventions are performed in this same area with high frequency.
Microvascular decompression
Microvascular decompression allows complete preservation of the nerve. It can be used when a nerve fiber is compressed by a nearby passing blood vessel, from which blood pulsations are transmitted to it, which causes pain.
The operation is performed openly under general anesthesia. Its essence is to separate the vessel from the nerve at its junction and install a Teflon gasket between them. This is a reliable means of eliminating pain and leads to complete recovery, provided that neuralgia was a consequence of irritation of the occipital nerve by pulsation of a blood vessel.
But this method of surgical treatment requires great caution from the operating neurosurgeon, since it can easily damage the nerve fiber. This will result in loss of sensation in the entire area it innervates. Therefore, you can trust its implementation only to a highly qualified neurosurgeon.
Radiofrequency ablation
The procedure is characterized by minimal trauma and a high level of safety. Its essence consists in introducing a thin needle through the skin under the control of an image intensifier. It is brought directly to the nerve, after which the active or damaging electrode is immersed through the cavity in it. It is connected to a generator, due to which, after turning on the device, current is supplied to the non-insulated end of the electrode. By acting on the nerve fiber, it is destroyed, which leads to the elimination of pain.
For neuralgia of the occipital nerve, the use of current with a frequency of 100 Hz is indicated. This leads to heating of the tissue around the bare end of the electrode to 42°C. The ablation itself lasts about 2 minutes, and the extremely low temperature effect eliminates the risk of thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
Because the procedure does not require significant tissue damage, the patient can move and return to daily activities almost immediately afterward. No hospitalization required.
Radiofrequency ablation is performed under local anesthesia, so choosing it completely avoids the risks associated with general anesthesia. The duration of the procedure is about half an hour. Almost always it leads to complete recovery and immediate pain relief.
The method is also used if the cause of pain is spondyloarthrosis, which is not amenable to conservative treatment. In this case, the essence of the procedure is the same, but the damaging electrode is immersed under the control of the image intensifier into the soft tissue in the immediate vicinity of the affected joint.
Neurostimulation
The essence of the procedure is to implant electrodes under the skin that generate electrical impulses, which helps reduce pain. A total of one or two 8-pin electrodes are installed. The quantity depends on whether the process is one-sided or two-way.
Electrodes are installed in the area of the greater and lesser occipital nerves. They are connected to a generator with the ability to recharge and are equipped with a remote control. Patients can independently turn on the supply of electrical impulses when an attack occurs, which allows them to completely get rid of the painful sensations.
Operations aimed at eliminating pathologies of the cervical spine
Since one of the causes of the development of occipital neuralgia is degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the cervical spine, patients may be prescribed surgical interventions aimed at eliminating them. The type of operation depends on the nature of the detected deviations. It can be:
- Microsurgical methods for the treatment of intervertebral disc protrusions (cold plasma, radio wave, laser nucleoplasty) - make it possible to reduce the size of the disc protrusion by sclerosing part of the nucleus pulposus with cold plasma, thermal laser energy or high-frequency current. They are not performed under local anesthesia, allow you to immediately return home and do not leave scars on the skin, since all the necessary instruments are inserted into the patient’s body through a thin cannula.
- Microdiscectomy is an operation to remove a herniated intervertebral disc, performed under general anesthesia through an incision, usually on the side of the neck, up to 3 cm in size. It requires a short hospitalization and compliance with a number of restrictions during the recovery period, but has a significantly lower risk of relapse. At the same time, with the help of microdiscectomy, hernias of almost any size can be removed.
- Endoscopic surgery is performed for herniated intervertebral discs, but is carried out through a pinpoint puncture of soft tissue up to 1 cm in size. It has a more gentle effect on the body, which facilitates the rehabilitation period. It is also indicated for severe spondylosis. In such cases, excess bone tissue is removed, the intervertebral disc is moved or removed, and, if necessary, implants are installed.
What worries you?
- Headache
- Pain in the face
- Pain in the spine
- Shooting pain and numbness in the arm/leg/hand
- Joint pain
- Pain due to cancer
- "Phantom" pain
Expectation of pain during manipulation may cause refusal or delay in seeking medical help.
People's pain threshold is very variable, so some people are able to endure pain, while others feel ill just in front of the doctor's office at the mere thought of the upcoming manipulation. Surely you remember the varied feelings of your classmates when you stood in line to get vaccinated at school. Of course, the main component of the fear of the “prick” is the languid anticipation of physical suffering, while the very sensation of pain is ultimately simply insignificant and only a hundredfold increased by our psychology! Relieving you of pain from the very threshold is our main task. It has long been known that the main pain sensation during manipulation is puncture of the skin. Almost the entire volume of pain is created by a huge number of pain receptors located on the surface of the skin. This is how nature wisely ordered - the signal about damage must come from the surface in order to give us the opportunity to prevent damage deeper. Before carrying out the main intervention, it is especially important to thoroughly anesthetize the skin.
To try to cheat nature a little when numbing the skin, we use the finest needles. The pain they cause is comparable to a mosquito bite. Using these needles, we infiltrate the most superficial layers of the skin with a solution of local anesthetic, causing pain signals to be completely blocked. After this, any manipulation deep into the anesthetized area turns out to be practically painless! Ultrasound navigation of the further procedure allows you to prevent punctures of the nerve trunks, and bring solutions of anesthetics and drugs as close as possible to them in order to completely relieve you of pain that lasts for days, months or even years!
Dear friends, pain should not become an obstacle to our active life and the achievement of our cherished goals! Make an appointment, together we will definitely make your life better and more comfortable!
Treatment of occipital neuralgia at SL Clinic
At SL Clinic you can receive qualified treatment for occipital neuralgia. Our vertebrologists will be able to thoroughly understand the causes of pain and purposefully influence them. This approach ensures maximum effectiveness of the therapy and increases the chances of a full recovery.
The cost of radiofrequency treatment of neuralgia of the greater occipital nerve is 68,000 rubles and depends on: - The cost of needles for radiofrequency ablation; — Clinics and class wards. The price includes: — Stay at the clinic before and after surgery; — Operation; — Cost of needles for radiofrequency ablation; — Observation and consultation during the rehabilitation period. All clinic services and costs are listed in the price list.
In most cases, conservative therapy, correctly constructed by our doctors, in combination with radiofrequency treatment, gives good results and eliminates the manifestations of neuralgia. Help from vertebrologists can be provided at the SL Clinic at the highest level. Modern operating rooms, the best equipment and highly qualified neurosurgeons who master advanced techniques are the key to the success of surgical treatment and its safety. All this can be provided to you by SL Clinic.
With us you can quickly complete all the necessary research at a time convenient for you. If necessary, our specialists will carry out a blockade or radiofrequency treatment to stop a severe attack and normalize the patient’s condition. Our prices make advanced European-level surgery affordable.
Don’t tolerate pain, sign up for a consultation at SL Clinic.
Ultrasound allows you to see!
When using ultrasound guidance, the doctor sees the position of the needle and knows exactly where the drug is injected! At the same time, we ourselves will show you on the monitor the entire process of performing the procedure so that there is no doubt about the correctness of the manipulation and, if necessary, we will print out a picture of the correctly administered drug.
Ultrasound control greatly increases the effectiveness of the blockade and minimizes dangerous errors. The pain syndrome goes away or is significantly reduced immediately “on the needle” during the manipulation process, and correctly administered and correctly selected drugs provide a long-term therapeutic effect!