Reasons for development
Factors contributing to the development of atheroma on the head are:
- metabolic disorders leading to changes in the properties of the secretion of the sebaceous glands;
- hair dyeing, head shaving with damage to hair follicles;
- hyperhidrosis (especially in combination with seborrheic dermatitis);
- inflammatory diseases of the scalp;
- low-quality hygiene products for hair care;
- Irregular hair washing with the accumulation of viscous oil on the scalp.
Atheromas often form not only on the scalp, but also around the ears and on the chin.
Examples of soft tissue sarcomas of the head and neck
Kaposi's sarcoma
Osteogenic sarcoma of the alveolar process of the maxilla
Osteogenic sarcoma of the mandible
Pleomorphic sarcoma of the soft tissues of the neck on the right
Clinical picture
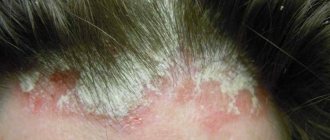
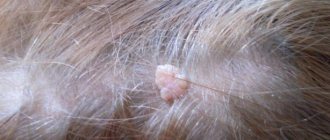
The cyst is a soft lump with rounded contours, located subcutaneously. Even small atheromas are clearly visible if you part your hair and carefully examine the changed skin.
Non-inflammatory atheromas are painless and do not cause discomfort, but if an infection occurs (which almost always happens with an accidental injury), the symptoms become more obvious. Suppuration of the cyst leads to its increase in size, intense pain, redness of the skin, and local swelling. The skin in the area of the inflamed atheroma is hot, and pus may be released from the outlet of the sebaceous duct.
Precancerous neoplasms (precancrosis)
Precancerous neoplasms are those that, under the influence of congenital or current causes, have acquired a tendency to malignant degeneration. As a rule, these are chronic conditions that are observed in a person for a long time.
Thus, precancerous tumors are dangerous neoplasms on the skin that can lead to the development of oncological processes. These include:
- Actinic keratoma is a keratosis in which dry crusts and scales appear on the skin of older people. When they peel off, slight bleeding may occur.
- Xeroderma pigmentosum is a hereditary tumor that develops due to increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation. Rarely encountered, these are pigmented spots that become warty growths.
- The cutaneous horn is a cone-shaped tumor that looks like a horn. Has a yellow or brown color. occurs in exposed areas of the body that are regularly subjected to friction or pressure. Typical for older people
- Bowen's disease is an intraepidermal cancer. Without treatment, it can transform into invasive skin cancer. In the early stage, Bowen's disease appears as a small reddish-brown spot measuring 2-50 mm. has a flaky surface and raised, uneven edges. After removing the scales, a weeping but not bleeding surface remains.
Treatment
The most effective way to remove atheromas with minimal risk of recurrence is radio wave excision using the Surgitron device (USA). The procedure does not require shaving the hair; removal takes place under local anesthesia in 30 minutes. Bleeding does not occur due to instant coagulation of blood vessels. The scalp and hair are not damaged. Removal of the formation is non-contact; after the procedure, the doctor carries out an antiseptic treatment and a follow-up examination of the patient. The procedure is outpatient and does not require hospitalization.
Removal of papillomas on the head in dermatology
Any formations, even large ones, can be removed quickly, painlessly and safely.
Benefits of physical removal:
- instant and guaranteed effect
- formations can be removed in any quantity, of any size
- there is no risk of damage to surrounding tissues if the procedure is carried out correctly
- no pain thanks to anesthesia
- good aesthetic effect
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is a classic way to remove papillomas.
It has a number of advantages:
- simplicity
- rapidity
- no anesthesia needed
- efficiency
- formations of any localization can be removed
- low price
But there are a number of disadvantages.
After liquid nitrogen, an inflammatory reaction often occurs in the affected area, which is fraught with pain.
Only small formations can be removed.
When trying to remove large papillomas, it is necessary to increase the exposure time to liquid nitrogen, which can result in the appearance of scars.
In addition, there is no material left for histological examination.
Laser
Laser removal of papilloma on the head is becoming increasingly popular.
The method has many advantages:
- no bleeding due to vascular coagulation
- there are no infectious complications, since the laser destroys bacteria
- accelerated tissue healing
But there are also disadvantages.
Only small papillomas can be removed (although larger than when using liquid nitrogen).
They do not separate from the body, but are destroyed.
Laser vaporization involves evaporation of the formation.
They usually do not work in laser cutting mode.
Because after it the tissues do not grow well together (a dense scab forms on the surface).
As with removal with liquid nitrogen, there is no material left that could be sent for histological examination to exclude malignant degeneration.
Electrocoagulation
The method uses electricity to heat tissue.
Electrocoagulation works in both cutting and coagulation (resolution) modes.
Advantages of the method:
- even a large papilloma on the head can be removed
- instant sealing of blood vessels and elimination of bleeding
Flaws:
- Wounds take longer to heal than after laser
- sometimes scars appear
Electrocoagulation is more suitable for removing formations that rise above the skin level.
They can be separated from the body and sent for histological examination.
Radio wave method
The radio wave method is the same as electrocoagulation, only electromagnetic waves have a high frequency.
This is a more advanced removal method.
Papillomas of any size can be eliminated.
Wounds after radio waves are sterile and heal quickly.
If necessary, they can be sutured, as after dissection with a scalpel.
This improves aesthetic results when removing large papillomas.
Seborrheic warts - causes of formation
The causes of seborrheic warts are unknown. But it is reliably clear that they are not related to the HPV papillomavirus, although their name indicates this. Thus, a seborrheic wart has nothing in common with such epidermal lesions as true condylomas, papillomas and warts.
However, there are some factors that predispose you to developing seborrheic warts:
- Age
. Warts most often appear in people over 35 years of age. Many people have more than a dozen of them; - Genetic predisposition
. The presence of seborrheic warts or other epidermal nevi in immediate family members; - Conditions associated with actinic keratosis
or impaired sebum production.
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis of cylindroma, a tumor biopsy is necessary, since clinically (visually) the tumor is very easily confused with other types of pathology. Moreover, a biopsy with excision of a tumor site is the diagnostic method of choice, since puncture of a tumor with a needle can give false results.
On biopsy, cylindroma is described as a benign tumor with eccrine and apocrine differentiation. Usually making a diagnosis is not difficult.
In case of ulceration of the neoplasm or the presence of an inflammatory focus directly on the cylindroma or on adjacent areas of the skin, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological examination. Such diagnostics allows you to identify the infectious pathogen and select the necessary antibacterial treatment if necessary.
Other diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound or dermatoscopy, may be prescribed by a doctor to determine the extent of tumor growth, but they are optional. The results obtained are of an auxiliary nature and are not used to confirm the diagnosis of cylindroma.
Seborrheic wart and IPL laser
Another method for removing seborrheic warts is the use of an IPL laser, which completely burns away the skin lesions, leaving a small concave socket.
IPL laser treatment
Within a few days after the procedure, a scab will form, which will fall off after 2-3 weeks. After treatment, a scar may also remain, but, unlike the previous option, it is almost invisible. Therefore, warts on the face are removed with a laser. A similar effect is also achieved by the radio knife, another modern tool designed to remove moles and warts of almost any type.
Features of skin cylindroma
The tumor grows slowly and continuously. The diameter of a cylindroma can reach 7-8 centimeters after 10-15 years of stable growth. Ulceration of the tumor indicates its transformation into a malignant process. Cylindroma has no tendency to metastasize. The general condition of the patients remains unchanged, the neoplasm causes exclusively aesthetic discomfort.
Symptoms
Cylinders are more often found in women in the form of isolated single nodes. A rarer form is multiple cylindromatosis (Brook-Spiegler syndrome). Initially, cylindromas appear as uniform reddish subcutaneous nodules with a smooth surface.
Soreness is not a characteristic symptom and can occur in the event of mechanical impact on the adjacent nerve trunk. Palpation does not cause significant discomfort, the tumor is homogeneous and mobile. The color of the tumor usually matches the color of the skin or has a slight reddish tint.
If a tumor occurs in the area of hair growth, the hair follicle moves away from the center of the tumor towards the edge of the tumor.
Types of skin cancer
There are 3 types of common malignant skin tumors. They differ both in incidence (i.e., the chance of getting sick) and in the degree of danger to life - basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Melanoma is one of the rare and dangerous skin tumors. It accounts for only 4% of the total number of malignant skin tumors, but is the cause of almost 80% of deaths in this localization. You can read more about melanoma here.
Sign up for the webinar “Carcinogens in cosmetics: truth, lies and... marketing”
What does a seborrheic wart look like?
Seborrheic papillomas are characteristic skin rashes that look like mushrooms. However, such a wart can be confused with other skin lesions, such as actinic keratosis or some malignancies, mainly cutaneous melanoma. It also happens the other way around, when skin cancer is mistaken for a harmless seborrheic formation.
Keratinized pigmented lesion
Multiple seborrheic keratomas
Development of seborrheic papilloma
Therefore, diagnosis and treatment of any neoplasms should be carried out strictly by an experienced dermatologist. It is strictly prohibited to independently diagnose yourself, much less remove tumors at home.
Here are the features that distinguish a seborrheic wart from other skin lesions:
- Seborrheic papilloma is well demarcated from healthy skin. It gives the impression of being superimposed on the surface.
- The size of the formation ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- On the surface of the nipple there are numerous depressions containing an accumulated mass of callus epidermal cells and sebum.
- Depending on the stage of development, the color of the nipple varies from a color similar to healthy skin to dark black, which is not a sign of melanoma.
Seborrheic warts are not accompanied by symptoms such as pain, itching, burning. The exception is mechanical irritation, for example, when changing clothes.