The appearance of a lump on the back of the head is a direct indication for a visit to the doctor. The formation is often the result of injury and the formation of a hematoma in the soft tissues. It may also be a tumor, a manifestation of an inflammatory process, or a skin reaction to an irritant. In some cases, the problem not only causes discomfort, but also poses a health hazard. If the lump appears for no apparent reason, gradually increases in size or is very painful, it is better not to hesitate, but to urgently seek help. It is best to avoid taking medications, topical medications, or physical therapy until a diagnosis is made.
Causes of lumps
Bumps appear on the head not only after blows. Experts identify dozens of reasons for the formation of conglomerates of various sizes, consistency, and appearance. Their occipital localization deserves special attention due to the abundance of blood vessels and nerve endings in the area and the increased risk of injury to the area.
The main reasons for the appearance of bumps on the back of the head:
- a skin reaction is the result of an insect bite or the use of inappropriate hair cosmetics. It can be a small bump or a large swelling, which depends on the cause and the reactivity of the body;
- trauma – a consequence of rupture of blood vessels in a small area and the formation of a hematoma;
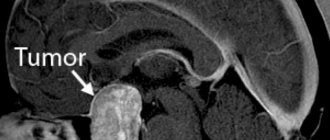
- tumor - a benign or malignant formation of subcutaneous or intradermal localization. Such cones can have different appearance, character, shape, and consistency. Each has its own specifics and requires specific treatment;
- enlarged lymph nodes – when an infection enters the body or inflammation develops, the lymph nodes begin to work more actively, which is why they increase in size. Sometimes they become so swollen that they rise above the surface of the skin;
- inflammatory diseases - boils on the head are not uncommon for people who do not care about their health and neglect the rules of personal hygiene. Purulent-necrotic lesions of the soft tissues around the hair follicle can take on the appearance of a large and painful swelling.
Even a hard lump that appears on the back of the head after a blow deserves a specialist’s assessment. You should not wait for the formation to resolve on its own. It is better to immediately visit a doctor, make sure there is no danger to health, and begin therapy.
How are atheromas removed?
No amount of burdock, plantain or compresses with alcohol help with atheroma. It needs to be treated surgically. You should visit a doctor as early as possible. If the atheroma has festered, you need to run to the surgeon.
The most senseless way to remove scalp atheroma is puncture, when a needle is inserted into the cyst and its contents are pumped out with a syringe. No normal doctor does this (except perhaps to obtain the contents of the cyst and send it for a biopsy). As long as the walls of the atheroma are preserved, it will fill up again and again. In order to rid the patient of a cyst, its walls must be completely removed. The classic operation looks like this:
- Two bordering incisions are made on the skin in the area of atheroma.
- A blunt instrument (most often closed scissors) is placed under the atheroma.
- The atheroma is peeled off, and stitches are placed on the wound.
The intervention is performed under local anesthesia. Usually the operation is performed on an outpatient basis, but if the atheroma is large, hospitalization in a hospital may be required. However, scalpels are becoming a thing of the past. Surgeons now have more efficient tools. For example, lasers. With their help, atheroma on the head less than 5 mm in size can be evaporated without a trace; for larger ones, additional small incisions will have to be made.
An even more advanced way to remove atheromas of the scalp is radio wave and laser surgery. These are the methods that doctors at the ProfMedLab clinic use. Laser or high frequency radio waves work instead of a scalpel. They cause little tissue damage, healing occurs faster, and the cosmetic effect is better.
Types of tumors on the head and their signs
A lump on the back of the head may be small in size and not cause discomfort, but at the same time pose a danger to human health. On the Internet you can find a lot of information about what kinds of soft tissue tumors there are, how to deal with them at home with the help of medications or traditional medicine. The use of such approaches poses serious dangers. Even if the problem can be resolved, there is no guarantee that it will not return. Also, health care workers often send tumors for additional study to rule out the possibility of cancer.
Hemangioma
One of the most dangerous types of neoplasms. It can occur on any part of the head, including the back of the head. Appears against the background of a malfunction of the blood vessels. It looks like a bright crimson or purple bulge with clear edges; on its surface you can see the vascular network. The conglomerate can cause disruption of the trophism of the tissues surrounding it. It also tends to grow to impressive sizes and degenerate into a malignant form. Treatment is carried out strictly under the supervision of a surgeon or oncologist. Most often, surgical removal of the hemangioma is required, after which the biomaterial is sent for histology.
Allergic reaction
Swelling on the skin of the back of the head can occur as a result of the influence of an allergen on the body.
The danger is posed by aggressive cosmetics, household chemicals, hats and synthetic bedding. In this case, the formations are usually small in size, numerous, do not hurt, but itch. Therapy consists of eliminating exposure to the allergen on the body, using antihistamines, and strengthening the patient’s immunity. A special place in this group of causes is occupied by an insect bite. Bees, flies, and mosquitoes can provoke a violent reaction of the body in the form of severe swelling of soft tissues. Typically, these bumps are painful, hot to the touch, and itchy. When pressing on the bite site, a clear liquid or exudate may be released. It is better not to self-medicate, especially if it is not known who bit. We cannot exclude the possibility of the presence of a tick that has crawled under the skin, and only a doctor can get rid of it.
Fibroma and sarcofibroma
Fibroma is a benign tumor, the basis of which is connective tissue. Its danger lies in its ability to grow to impressive volumes and turn into a malignant analogue - sarcofibroma. Initially, formations appear against the background of endocrine disorders, metabolic disruptions, and hormonal changes in the body. The lump itself is hard to the touch and does not cause any discomfort. It only hurts when there is mechanical damage. Treatment of fibroids involves monitoring its growth by an oncologist. If the tumor grows quickly or is in the way due to its location, it is removed.
Lipoma (fat) on the head
A benign tumor often appears in women after 30 years of age. This is facilitated by frequent changes or disturbances in hormonal levels and problems with fat metabolism. The formation is soft, mobile, round in shape, does not hurt when pressed and rarely bothers you. When located at the back of the head, it can cause discomfort due to frequent use of a comb, wearing a headdress, or simply the presence of an aesthetic defect. The treatment method is selected by the doctor depending on the size of the lump and its growth rate. This can be excision of the mass, its removal with a laser, or the introduction of a conglomerate of special anti-lipid drugs into the body.
Pimples and bites
Such bumps are rarely isolated. Most often, they appear unexpectedly, do not reach significant volumes, and go away on their own within 4-7 days. Usually the formations are itchy - scratching leads to infection and inflammation. In this case, the discomfort increases, and the local temperature may rise. In the absence of care or weak immunity, an abscess forms. You can try to deal with such bumps yourself by regularly treating the affected area with an antiseptic. If the condition worsens or there is no effect within 2-3 days, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Bruise or injury
A blow to the head is the most common cause of a bump. Typically, such consequences of injury do not cause serious problems and do not require special treatment. It is enough to apply cold to the sore spot as soon as possible and leave the compress for a quarter of an hour.
A doctor's help is necessary if:
- nausea and vomiting occurred;
- the child has a problem;
- after the blow there was loss of consciousness;
- there is dizziness or signs of incoordination;
- the temperature has risen.
You will learn about methods for eliminating headaches after a blow from this article.
A small hematoma will go away on its own in 3-5 days. To speed up the process, you can use “Troxevasin”, “Rescuer”, “Troxerutin”, and heparin ointment. All these products are good at relieving swelling, stimulating the resorption of bruises, restoring blood vessels, and eliminating pain.
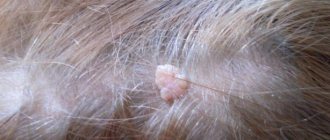
Wart on the head
The most common benign tumor, which is equally often diagnosed in people of different ages, gender, and social status. Most often it occurs in people with impaired metabolism, against a background of stress, when tissues are damaged by an inflammatory process or their frequent mechanical irritation. A wart on the head is rarely dangerous, but is an aesthetic defect. The bumps can take on different appearances, reach significant sizes, and spread over the surface, occupying a large area of the skin. Treatment must be coordinated with a dermatologist.
Atheroma on the head
The formation looks like a lipoma, but has a yellowish tint. It appears due to disruption of the sebaceous glands and blockage of their ducts. A dense lump with a smooth surface begins to cause pain and significant discomfort as it grows. The tumor must be removed surgically or using a laser. The resulting material is sent for histology, but it rarely contains cancer cells.
Not all bumps on the back of the head are abnormal.
It is very common to find swelling and bulges at the back. Masses form on the skin, under the skin or in the bones. There is a wide range of reasons for these strokes. From trauma to congenital diseases such as craniosynostosis. But in addition to these cases, the human skull also has natural bumps on the back. This bump, called an inion, is located at the bottom of the skull and where it connects to the neck muscle.
But if you feel any unusual lumps on your back that are growing and you feel pain and fever, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Features of bumps on children's heads
In childhood, bumps on the back of the head in most cases are the result of injury. Even newborn babies are not immune from them - the soft tissues of the head are damaged during the process of passing through the birth canal. Typically, such bumps do not require special treatment, but it is better to consult a doctor.
Also, the appearance of swelling on the back of a child’s head may indicate inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes. Children are not immune from wen. They occur in childhood due to disruption of the sebaceous glands or ignorance of basic rules of personal hygiene. The likelihood of a malignant tumor or precancerous condition forming in a child is small, but it cannot be excluded.
Why does atheroma occur on the head?
Atheromas can be congenital or acquired. In the second case, their development is facilitated by:
- metabolic disorders,
- hormonal changes (high testosterone levels),
- poor hygiene,
- abrasions,
- increased skin oiliness.
Atheromas can be single or multiple, their sizes range from a pea to a chicken egg and larger. Since atheromas develop from the sebaceous glands, they occur more often on those parts of the body where there are many of these glands: on the head, face, neck, and armpits.
Which doctor should I contact?
If bumps appear on your head, it is recommended to first visit a therapist. The doctor will conduct an initial examination, collect anamnesis and refer you to a specialist. If a formation on the head appears after a blow, then you can initially go to a traumatologist.
Surgeons treat boils and most tumors that need to be removed. When there is a suspicion that a tumor is malignant, oncologists are involved in the work. If the lymph nodes are enlarged, ENT intervention is required. Bumps that occur after contact with an allergen or an insect bite are monitored by an allergist. In the latter case, an infectious disease specialist can be involved in the diagnosis. A dermatologist works with warts and pimples.
How to treat
Conservative treatment of atheroma without surgery is mostly a myth
. Traditional medicine cannot make a tumor disappear without a trace. So even an atheroma that has gone inside under the influence of Vishnevsky ointment will still appear again. In order to avoid a relapse of the unpleasant disease, the atheroma must be removed completely - along with the capsule around it. And only a surgeon can do this.
Therefore, at the first signs of the disease, you need to contact a plastic surgeon. Only this specialist will be able to not only remove atheroma on the head, but also make sure that the consequences in the form of scars and cicatrices do not overshadow your life in the future.
“Before” and on the 12th day after removal of myofibrolipoma of the forehead area. Tips&tricks on the forehead for faster resolution of swelling. Surgeon Vladislav Gladysheva.
Diagnosis of the disease
Often, the clinical picture alone is sufficient to make a diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, the use of additional diagnostic techniques is still required. In particular, they are necessary to clarify the nature of the tumor and exclude its malignant nature.
To determine the nature of the lump, you may need to undergo the following procedures:
- general blood and urine tests - aimed at identifying an infectious or inflammatory process;
- blood biochemistry - allows you to identify problems with metabolism and suspect oncology;
- the use of tumor markers is an informative method for detecting cancer;
- X-ray or CT scan of the skull - help assess the condition of the bones of the skull, exclude their fractures, the presence of cracks;
- Ultrasound – aimed at studying the structure of the lump, its composition and the depth of penetration into the tissue;
- histology – studies the cellular structure of the biomaterial, which allows you to quickly make a diagnosis;
- A biopsy is another way to examine tissue for cancer.
Based on the diagnostic results, the optimal treatment method is selected. If necessary, the procedures are repeated several times, which makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Causes of lipoma
The causes of lipomas on the head and body, as well as in internal organs and muscles, are not precisely known. There are several theories, each of which cannot definitively explain why this tumor occurs.
Genetic predisposition is the main theory. The gene responsible for the development of this benign neoplasm has not yet been identified, but it has been proven that children of parents suffering from lipoma very often inherit this feature. If one of the identical twins has it, then in almost 100% of cases it develops in the second one.
In case of lipid metabolism disorders (second theory), lipoproteins, clogging microscopic blood vessels, begin to accumulate, forming a clot of fat. Subsequently, it can grow capillaries and connective tissue, which will divide it into lobules, creating a lobular lipoma structure.
The theory of the appearance of a lipoma from clogged sebaceous glands is the third in a row. According to it, the fat secreted by the sebaceous gland cannot reach the surface of the skin due to blockage of the duct and begins to accumulate. The further process is similar to how it is described in the previous theory. Unfortunately, it is impossible to explain the appearance of a lipoma in the abdominal cavity by such a mechanism (there are no sebaceous glands in the abdomen).
Treatment of cones
Methods for dealing with bumps on the back of the head are selected individually and depend on the causes of the problem. Treatment options can be very different, and for different diagnoses they give different results. It is extremely important not to self-medicate. Applying heat to a boil will aggravate its course, and combating the consequences of the injury with cold a day after receiving it will slow down the healing process. You should not be afraid of surgical treatment if a specialist insists on it. Sometimes this is the fastest, safest and most effective option for eliminating a lump. Today, laser and cryotherapy are increasingly used to remove tumors. They are able to destroy the formation without compromising the integrity of the skin.
A hard lump on the back of the head does not always pose a danger to human health and life, but it can cause significant discomfort. You should not delay treatment even in cases where the formation does not bother you. Accidentally touching it can damage the integrity of the skin and introduce an infection into the wound. The close location of the abscess to the brain threatens damage to the membranes and substance of the organ. This can lead to serious complications, including death.
Is scalp atheroma dangerous?
If there are no complications, then the biggest trouble that atheroma of the scalp causes is the lack of hair in the place where it is located. But the situation may change:
- If an infection gets inside the atheroma, it will turn into an abscess. An abscess of the soft tissues of the head will occur.
- Ulcers are dangerous on any part of the body, but especially on the head. The infection may spread deeper to form an intracranial abscess.
- Sometimes (although very rarely, there is such a possibility) atheromas transform into malignant tumors.
If an incomprehensible lump appears on the scalp, you should not wait for complications. Contact our doctors, they will remove it quickly and carefully!
Cephalohematoma in newborns on the head - symptoms, treatment
Cephalohematoma is a birth injury characterized by the formation of a hematoma.
Pathology is diagnosed in 3% of children, regardless of gender. Cephalohematoma in newborns on the head can be accompanied by various kinds of complications: deformation of the skull bones, suppuration, anemia and jaundice. The formations come in different sizes and depend primarily on the volume of accumulated blood. Due to the failure of the hemostatic system in the baby's body, blood can accumulate for several days after birth, contributing to an increase in the size of the hematoma. Causes of cephalohematoma during childbirth:
- large fruit;
- rapid labor;
- malposition;
- premature or prolonged labor;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- discrepancy between the sizes of the mother's pelvis and the fetal head;
- pathologies of intrauterine development;
- use of forceps during childbirth.
Classification of cephalohematoma
As noted above, external cephalohematoma is a hemorrhage between the periosteum and the surface of the skull bones, which disappears by the end of the second month of the baby’s life.
Depending on the location, hemorrhage can be frontal, occipital, parietal and temporal. Based on the severity, cephalohematoma is divided into grade I (hematoma volume 3-4 cm), II (4-9 cm) and III (hemorrhage more than 9 cm). The consequences of a birth cephalohematoma in the future depend on the size of the formation and the general condition of the newborn. Considering the location of the hemorrhage, cephalohematoma can be left-sided, right-sided or bilateral. In some cases, the pathology is accompanied by concomitant injuries in the form of a fracture (crack) of the skull bones.
Treatment methods
Methods for eliminating soft or hard bumps on the head depend on their origin, the severity of symptoms, and the age of the patient. If it does not increase in size and does not interfere with a person’s normal lifestyle, then doctors adhere to a wait-and-see approach. Only with its sudden growth will conservative or surgical treatment be carried out.
Ointments, gels, creams, balms
Immediately after a head injury, it is advisable to use a cold compress. A plastic bag should be filled with ice cubes and then wrapped in a thick cloth. Apply the compress every hour for 10 minutes. If a lump does form, external remedies will help. What to do to eliminate pain, what medications to use:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketorol, Nise, Voltaren. Ointments and gels relieve pain, relieve inflammation, and prevent the formation of edema;
- angioprotectors, venoprotectors - Troxevasin, Troxerutin, Lyoton, heparin ointment. They restore the integrity of damaged capillaries and eliminate bleeding.
Time-tested remedies have proven themselves well in resolving bumps on the head - balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky, Naftaderm, balms with comfrey or cinquefoil. They are characterized by complex effects. The components remove excess fluid so that it does not compress sensitive nerve endings and reduce the severity of pain.
Tablets, capsules, dragees
The formation of bumps on the head, large and painful, often signals infection of the tissues. A similar situation usually arises when a doctor’s prohibition is violated - do not touch the lump, be careful when washing your hair. Staphylococcus aureus and epidermal staphylococci and opportunistic fungi penetrate into microcracks. An infectious-inflammatory process starts, which can only be stopped by taking antibiotics or antimycotics:
- macrolides Clarithromycin or Azithromycin;
- semisynthetic penicillins Amoxiclav, Augmentin;
- cephalosporins Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin;
- antimycotic agents Flucostat, Nystatin.
When the allergic nature of the neoplasm is identified, antihistamines are included in the treatment regimen - Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadine. A persistent headache may indicate compression of the nerve endings by the lump. Ketorol, Maksigan, Spazgan are used as analgesics.
Surgery
Surgical removal of cones is the most commonly used treatment method with many advantages. Within 30-60 minutes, the patient gets rid of the tumor, which causes both physical and psychological discomfort. The likelihood of compression of blood vessels and nerves, the formation of ulcers and malignant degeneration of the tumor is completely eliminated. Surgical therapy is performed by doctors in government institutions and private medical centers.
How the operation is performed:
- the neoplasm is completely excised with a scalpel or a certain part of it is removed;
- the surgeon makes a puncture at the appointed point and removes the contents of the formed cavity;
- Laser excision is practiced for small tumors, localized mainly in the occipital zone, on the top of the head.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia in a hospital setting. The patient's condition is monitored by medical staff for several days, and then he is discharged home.
Folk remedies
Doctors allow traditional medicine to be used only to eliminate hard or soft lumps formed as a result of a bruise. Their use is also possible at the final stage of allergy therapy. In all other cases, folk remedies will not help, but will only harm. As long as a person uses ointments and infusions with mild analgesic properties and does not consult a doctor, the pathology rapidly progresses. If the tumor is malignant, then both health and life are at risk. The earlier cancer is diagnosed, the significantly greater the chances of a complete cure.
For injuries that lead to bruises, swelling and bumps, the following homemade ointments help well:
- Grind a tablespoon of aloe juice and full-fat sour cream. Without ceasing to stir, add 150 g of Vaseline, 2 drops of juniper essential oil;
- In a mortar, mix a teaspoon of tar and honey. Add a drop of essential oils of thyme, spruce and fir, 100 baby cream.
Folk remedies for oral administration are recommended for use in case of insect bites. They will speed up the removal of allergens from the body, relieve pain, and relieve swelling. To prepare the infusion, pour a glass of boiling water over a teaspoon of dry plant material, cool and filter after 20 minutes. Drink 1/2 glass 2 times a day. Sage, birch leaves, linden blossom, and nettle are used as raw materials.