- Physiological reasons
- Dental reasons
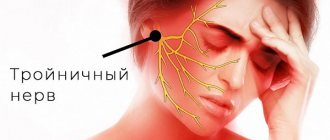
- Paresthesia of the lips due to damage or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
- Numbness due to migraine with aura
- Numb lips due to stroke
- Numb lips due to diabetes
- Numb lips due to allergies
- Shingles
- Neuroses and multiple sclerosis
- Anemia
- Diagnosis and treatment
Lip paresthesia (numbness) is a condition in which tissue sensitivity decreases or disappears.
This process may be accompanied by tingling or other sensations. Numbness of the lips occurs for physiological reasons and is one of the symptoms of a certain pathology. First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the frequency of occurrence and duration of this condition, its spread to other parts of the face and body. Lips may go numb in people who suffer from neurological and dental diseases, diabetes, anemia, allergies and a number of other diseases. If the symptom occurs frequently, an examination by a dentist and neurologist is recommended to determine the exact cause of the numbness.
Physiological reasons
Tissue sensitivity may decrease upon contact with very hot or cold food or drinks. This happens when a person eats ice cream, drinks tea or coffee that is too hot, or eats too spicy food. A similar phenomenon is observed outside in cold weather. The skin of the lips becomes chapped, cracks appear, and sensitivity decreases. Physiological numbness in most cases does not cause harm to health. As soon as contact with the irritant ceases, tissue sensitivity is restored.
To avoid the negative consequences of low-temperature exposure, you should use lipsticks and balms that will protect the skin from chapping and painful cracks.
Another possible cause of tissue numbness is cosmetic and cosmetic procedures. For example, lip products with red pepper extract may cause a slight burning sensation or numbness of the tissues. Some women experience a decrease in lip sensitivity after tattooing if the procedure was performed incorrectly or the wrong lip care was chosen after it.
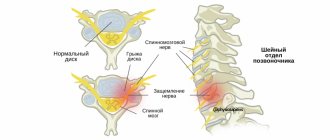
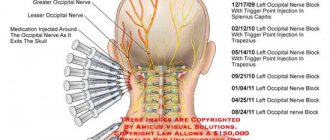
Treatment of numbness of the left hand with folk remedies
Traditional methods for treating numbness of the left hand can be used exclusively as an addition to the main tactics. Before you start using them, you should first consult a doctor and only then resort to them. The main ones are as follows:
- Baths with rosemary - involve the use of an infusion of three liters of water and flowers, which is added to a bath of water and taken before bed for 15 minutes;
- Applying a solution of one liter of water, 10 ml of camphor and 50 mil of ammonia to problem areas, as well as 1 tbsp. l. table salt;
- Apply a fabric bag containing pre-cooked wheat porridge to the affected area for 30 minutes.
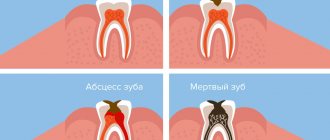
Dental reasons
When treating teeth and performing some types of cosmetic procedures, local anesthesia is used, which reduces the sensitivity of tissues. During the period of action of the drug, lips, cheeks, and other areas of the face become numb. After completion of the therapeutic manipulations, sensitivity is restored on its own.
Numbness of the lips and tongue is accompanied by inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. This happens with gingivitis, periodontal disease, and purulent lesions. Soft tissues are involved in the pathological process, which causes swelling and impaired receptor sensitivity.
Numbness of the face
Stroke
Diabetes
29823 March 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness of the face: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Numbness of the face occurs when the sensitivity of skin and muscle receptors to various impulses is impaired. This symptom may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Loss of facial sensitivity is described as burning, tingling, sometimes pain, and in some cases as a complete absence of sensation. When the face is numb, the color of the skin over the affected area may change in the form of pallor or redness.
In severe cases, sensory impairment is accompanied by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles.
Types of facial numbness
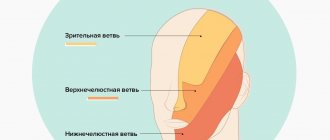
Any external influence, be it heat or cold, light touch or strong pressure, leads to activation of skin receptors and muscle structures. Each receptor is associated with a specific type of nerve fiber that transmits a specific type of sensitivity (sensation of pressure on the skin, vibration, stretching of the skin, and temperature sensitivity). An impulse is generated in the receptor, which is sent through nerve fibers at high speed to the nerve ganglia, which are a collection of sensory neurons. This is where primary information processing occurs to activate vital reflexes. Subsequently, the impulse goes to the brain, where it is processed in special nerve centers, and the person feels pain, pressure, vibration, etc. Thus, we can talk about the following types of sensitivity disorders:
- Violation of surface sensitivity
occurs when receptors (temperature, tactile, pain, etc.) and nerve fibers of the facial skin are damaged. - Violation of deep sensitivity
occurs when the receptors and nerve fibers of the facial muscles are damaged. - Violation of complex types of sensitivity
. A similar type of disorder occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. There is no recognition of two different stimuli that simultaneously affect the skin, or the person cannot determine the location of the touch.
Possible causes of facial numbness
In many cases, numbness in different parts of the face is short-term, passing within a few minutes.
Such episodes can occur when the head is positioned in an awkward position, for example during sleep.
This occurs due to compression of the nerve fibers and a temporary disruption of impulse conduction. There is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Partial loss of sensitivity is observed with prolonged exposure to the cold due to vasospasm. After gradual warming of the skin, sensitivity is restored.
However, facial numbness can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Acute cerebrovascular accident, or stroke
– a common cause of sudden numbness of the face in combination with a violation of facial activity. Hemorrhage or blockage of brain vessels by a thrombus (blood clot) occurs, acute oxygen deficiency and damage to neurons with disruption of their functions develops. Symptoms develop unexpectedly, sometimes accompanied by headache.
The main signs of a stroke are: numbness of the face and limbs on one or both sides, sudden weakness, speech impairment (inability to clearly pronounce words), drooping of the corner / corners of the mouth, uncoordination of movements.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. A cerebral aneurysm
can cause numbness in the face due to compression of nerve fibers and sensitive centers of the brain. It usually develops gradually; at the onset of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Numbness first affects one area of the face (for example, perioral), and with further growth of the aneurysm, the affected area gradually expands. Sensations may also change: from tingling, burning at first - to a complete absence of sensations later.
There is a danger of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm; in this case, the symptoms are similar to those of a stroke and appear quickly.
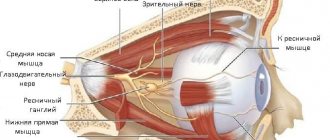
Trigeminal neuritis
often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis), ear (otitis), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis), parotid glands (mumps). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated, which can lead to numbness in the corresponding areas of the face.
Impaired sensitivity with increased tone of the masticatory muscles
occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by muscle fibers. Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is characteristic of damage to the temporomandibular joint due to arthritis and arthrosis, incorrectly selected braces, and certain diseases of the pharynx, for example, peritonsillar abscess.
Diabetes
– with this disease, the process of utilization of glucose from the blood is disrupted, which leads to damage to the vascular wall and disruption of the nutrition of nerve bundles. In the absence of maintenance therapy, tingling and partial loss of sensitivity in areas where the blood supply is impaired may occur.
Numbness of the face in multiple sclerosis
occurs due to demyelination (disappearance of the outer sheath) of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve. Numbness is often preceded by severe pain not only in the face, but also in the limbs.
Tumors of the brain and its membranes
lead to impaired sensitivity in the facial area due to compression of the neurovascular bundles or tumor growth in them.
Which doctors should I contact if I have facial numbness?
If your face becomes numb, you should consult a neurologist or therapist. In some cases, consultation with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, or dentist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for facial numbness
Depending on the suspected cause of facial numbness, the following laboratory and instrumental studies may be required:
- clinical blood test;
Numbness due to migraine with aura
Migraines with aura are attacks of severe headaches, which are preceded by impaired tissue sensitivity, visual disturbances (spots and “floaters” before the eyes), and speech impairment.
Patients with the neurological disease experience temporary numbness of the lips and sometimes half of the face. In some cases, the sensitivity of the upper limb may decrease. In addition to these symptoms, migraine with aura is accompanied by severe headache, which is pressing or throbbing in nature, dizziness and nausea.
Associated symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the reasons why the jaw becomes numb. This may be a slight discomfort, slight tingling, burning, or a feeling of goosebumps. Additionally, the following symptoms may occur:
- excessive salivation;
- severe spasms (trismus) of the masticatory muscles;
- difficulty pronouncing some sounds, smiling, speaking, swallowing;
- impaired sensitivity of the lips and tongue.
Symptoms manifest in different ways. Numbness of the teeth of the lower jaw and chin, tongue, lips can be permanent or have a paroxysmal nature, cover the entire jaw or a small part of it, and manifest itself with greater or lesser intensity.
Numb lips due to diabetes
For patients with diabetes, it is important to control blood glucose levels and avoid sudden increases or decreases in sugar. Lips may become numb due to hypoglycemia - a decrease in glucose levels below 2.8 mmol/l. This happens when you take too high a dose of insulin or violate your diet or skip meals.
In addition to numbness of the lips, the patient experiences severe weakness, tremors in the limbs, rapid heartbeat, and excessive sweating. In severe cases, hypoglycemia leads to loss of consciousness and coma. To eliminate this dangerous condition, you need to eat something sweet with quickly doubling carbohydrates. If the patient is unconscious, intravenous glucose and glucagon injection are required.
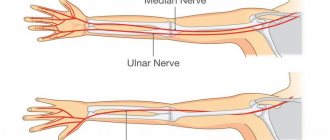
Preventing numbness in the left hand
Numbness of the upper extremities is the cause of discomfort, limited movement and decreased quality of life. A range of preventive measures will help prevent its occurrence:
- Regular moderate physical activity and exercises to keep arm muscles toned;
- Minimizing the amount of salt in food consumed;
- Proper nutrition, ensuring the body receives all the necessary vitamins and microelements;
- Elimination of smoking and consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Prevention of cold hands, as it has an adverse effect on the condition of the joints. They need to be kept warm and be sure to wear mittens or gloves in the cold season;
- Systematic warm-up for the arms, alternating with the load.
Do not forget: numbness in the left hand can be a symptom of serious illnesses. Trust its diagnosis and treatment to professionals - contact CELT!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Diagnosis and treatment
Numbness of the lips itself occurs only for physiological reasons and does not require treatment. In other cases, patients note other signs of pathology: pain, weakness, dizziness, etc. Based on these, the cause of the sensitivity disorder can be determined and a treatment regimen can be selected. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a therapist, dentist or neurologist.
If inflammatory processes or tumors in the oral cavity are suspected, an x-ray is prescribed.
For neurological pathologies, CT and MRI are used to make a diagnosis. Laboratory tests help confirm or exclude the presence of diabetes and anemia. To get rid of numb lips, you need to eliminate the underlying cause. To do this, patients are prescribed drug therapy that effectively combats the symptoms of the disease. For tumors, fractures or injuries of the jaw, pulpitis, abscesses, and strokes, surgical treatment is required.
Where to go if your left hand goes numb?
If you encounter a similar problem in Moscow, contact CELT. Our clinic is multidisciplinary, which means that we have doctors from different specialties. You can get professional advice from a therapist, cardiologist or neurologist and, based on the results of the research, contact an orthopedist, surgeon or rehabilitation specialist.
The diagnostic department of our clinic is equipped with the latest technology. Our specialists have the greatest capabilities in terms of accurate diagnosis and detection of diseases in the early stages of their development. We employ leading domestic specialists, doctors of the highest category, candidates and doctors of science, conducting scientific activities and having many years of practical experience.
You can find out the cost of our services by going to the “Services and Prices” tab in this section. We recommend that you check the numbers with our operators by contacting them by phone. This way you can avoid any misunderstandings.
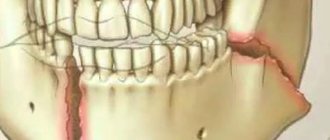
Sinusitis, maxillary sinus cyst, loss of sense of smell after visiting the dentist
The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw can normally be adjacent to the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses of the nose and even survive in them . Sinusitis, maxillary sinus cyst and loss of smell are possible when infection or filling material penetrates from the teeth into the paranasal sinuses. Unfortunately, this is not uncommon. Moreover, some cases of persistently recurrent sinusitis are associated with infection penetrating from the roots of the teeth . In this case, a possible symptom is a strong unpleasant odor from the nose and mouth.
Odontogenic sinusitis after treatment by a dentist
Odontogenic sinusitis (scheme). Teeth and maxillary sinus. On the left is the norm. On the right – the root of the “seven” (tooth 2_7) is destroyed, inflammation around the destroyed root, pus in the maxillary sinus.
Filling material in the maxillary sinus and sinusitis after filling the “six” canals (tooth 2_6). Pain in the left side of the face after visiting the dentist.
1 – roots of teeth, 2 – normal, air in the right maxillary sinus (front view, the air looks black in the picture), 3 – in the left maxillary sinus there is a fragment of filling material surrounded by an inflammatory shaft. The patient had been mistakenly receiving treatment for trigeminal neuralgia for a long time.
Cysts of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses in diseases of the roots of the teeth.
1 – roots of the teeth, 2 – cysts of the maxillary sinuses, growing from the roots of the teeth (cysts are round “bubbles”, they look gray in the picture).
How can we help you:
- Let's find the source of pain after dental treatment;
- We will treat inflammatory processes, sinusitis, sinusitis and neurological complications; if necessary, your health will be taken care of jointly by a neurologist and an ENT doctor. Treatment of sinusitis without puncture