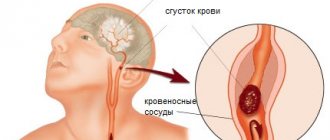
Spinal stroke is a type of myelopathy (diseases of the spinal cord of a neurological nature). Among all strokes it accounts for 1-1.5% of cases. Also, as in the case of the brain, it has two forms:
- Ischemic stroke (infarction) of the spinal cord - cessation of blood supply to a certain area of the brain and hypoxia.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of a blood vessel and bleeding into the spinal cord.
Transient disorders of the spinal circulation and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes) can also be observed.
A distinctive feature of a spinal stroke is that it usually occurs at a younger age than a cerebral stroke, at 30-50 years. Without adequate treatment, it is extremely rarely fatal, but often leads to disability.
| Treatment in a hospital setting | |
| Complex treatment in the rehabilitation department of the 3rd category of complexity (1 day)* | 6600,00 |
| Complex treatment in a rehabilitation center of category 2 (1 day)* | 7900,00 |
| Complex treatment in a rehabilitation center of 1st category of complexity (1 day)* | 12300,00 |
| Accommodation of an accompanying person in the ward (1 day) | 1750,00 |
| Stay in the department (1 hour) | 110,00 |
| Individual care from a nanny at home (1 day) | 2300 |
| Additional care by a junior nurse (1 day) | 600,00 |
| Individual post of a junior nurse (1 day) | 1100,00 |
| Mechanotherapy | |
| Stander BALANS (duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| Motomed (duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| KRD (cardio training, duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| Rehabilitation therapy | |
| Locomotor therapy (duration 60 min.) | 750,00 |
| Locomotor therapy (duration 30 min.) | 580,00 |
| Kinesiotherapy (duration 60 min.) | 750,00 |
| Kinesiotherapy (duration 30 min.) | 630,00 |
| Occupational therapy (duration 60 min.) | 630,00 |
| Occupational therapy (duration 30 min.) | 520,00 |
| Speech therapy (duration 60 min.) | 550,00 |
| Speech therapy (duration 30 min.) | 450,00 |
| Speech therapy in the department | 450,00 |
| Psychological correction | 550,00 |
*Comprehensive treatment in the department includes:
- comfortable stay in the ward;
- balanced individual nutrition;
- constant medical and advisory assistance from the attending physician;
- classes in kinesiotherapy and ergotherapy halls using special equipment (balance trainer, bobat tables, motomed, wheelchair).
The Center also provides services:
- consultations with narrow specialists;
- laboratory diagnostic examinations;
- injections, manipulations and procedures.
Causes of spinal stroke
The causes of a spinal cord stroke do not lie in the spinal cord itself, but in problems with the blood vessels that supply it. Provoke the development of the disease:
- atherosclerosis and blockage of arteries,
- rupture of a blood vessel due to injury or due to blockage,
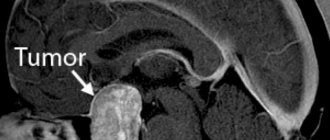
- physical compression of the arteries (osteochondrosis, vertebral listhesis, herniated discs, tumors in the spine,
- congenital anomalies of vascular development, vascular malformations,
- aneurysms (often of the aorta),
- phlebeurysm,
- myocardial infarction and a sharp drop in blood pressure,
- bleeding disorders (hemophilia, thrombocytopenia)
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Symptoms of a spinal stroke
Signs of a spinal cord stroke can vary depending on the location and extent of the injury. The most characteristic neurological symptoms are:
- back pain (region of the spinal column),
- if the upper spine is affected - paresis or paralysis of the arms,
- leg pain, instability, transient lameness,
- paresis and paralysis of the legs are possible,
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (random urination or defecation),
- sensory disturbances in the back and limbs.
Difficulties in diagnosis arise due to the fact that pain can radiate to different parts of the body. Also, due to the connection of the spinal cord with the internal organs, many non-specific (non-neurological) symptoms are observed, and therefore a stroke can be mistaken for multiple sclerosis, spinal hernia, radiculitis, nephritis, inflammation of the bladder, gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, duodenitis , colitis), “women’s” diseases and so on.
Precursor stage
The first stage, the precursor stage, can last from a few minutes to several months. A short stage is inherent in the case of unexpected and rapid blockage of blood vessels by blood clots or in the case of a pinched artery, which is often observed with spinal injuries.
Speaking about a longer period of this stage, a gradual and slow cessation of blood circulation is assumed (for example, in the case of tumor growth or an increase in the size of an atherosclerotic plaque).
Preceding symptoms of this disease may be:
- occasional lameness;
- pain in the spine area;
- numbness of the limbs;
- feeling of crawling “goosebumps”;
- discomfort in the direction of branching of the spinal roots.
Intermittent claudication in neurology is a condition in which the patient feels a characteristic numbness of the lower extremities, weakness when standing for a long time or walking for a long time. The latter is explained by the resulting oxygen starvation in the spinal region, which is responsible for the mobility of the legs. In addition, the cause of such lameness may be poor blood circulation in the vessels.
Diagnosis of spinal cord stroke
As already mentioned, a spinal stroke can masquerade as many other conditions, but the common symptom that is always present is back pain. Of course, there are a huge number of causes of back pain, but the presence of such a symptom should always be alarming. Therefore, if there is such a complaint, an experienced neurologist will immediately prescribe:
- x-ray of the spine
- computed tomography of the spinal cord
- revazography or vascular Doppler
- electroneuromyography
- spinal tap
- laboratory blood tests
Based on the results of the studies, a repeated consultation with a neurologist is carried out and treatment is prescribed.
Acute stage of the disease
Rehabilitation in the acute period takes place in a medical institution under the guidance of doctors. It is advisable to begin rehabilitation treatment as soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes, optimally 3-4 days after the stroke. The main tasks at this stage are: restoration of simple motor and speech functions, prevention of complications and relapses, assessment of the degree of damage to the body and development of a rehabilitation program.
To restore the motor system, passive gymnastics, massage and treatment by changing body position are used, when the patient’s limbs are placed in various positions to prevent the development of muscle hypertonicity. The return of lost speech skills begins with simple articulation exercises, gymnastics of the tongue, cheeks, and lips. Speech is more actively restored 3-6 months after a stroke, but full recovery requires 2-3 years of work with the patient.
An important condition that accelerates rehabilitation in the acute period is the use of medications and physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures - magnetic, electro- and laser therapy.
Treatment of spinal stroke
As in the case of a stroke of the brain, in case of a spinal stroke the main actions in the acute period are aimed at maintaining the vital functions of the body, eliminating the cause of the stroke, restoring the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and normalizing blood pressure. Blood thinners are prescribed (if the cause was a blood clot), myelorelaxants, and neuroprotectors. In some cases, surgical restoration of damaged vessels may be required. If the patient is paralyzed, bedsores and congestive pneumonia are prevented.
Mechanism of pathogenesis
Spinal stroke accounts for approximately 1–1.5% of all CNS pathologies associated with acute hemodynamic disorders. The greatest prevalence occurs in the age category from 30 to 70 years, regardless of gender. The bulk of spinal strokes are of the ischemic type, and the overwhelming majority of lesions occur in the lower thoracic and/or lumbar region.
Impaired blood flow in the vessels causes oxygen deficiency (hypoxia), neural metabolic failures and hemorrhages in the pathological area. The sudden development of such conditions does not give the body time to react adequately, launch compensatory processes and rebuild the metabolism of neurons. A hemorrhagic zone is formed, the consequence of which is neurological necrosis. This condition is called “spinal stroke.”
Rehabilitation after spinal stroke
Depending on the complexity of the disease, the consequences of a spinal cord stroke may be completely unnoticeable or minimal (mild tremor of the fingers, transient loss of sensation in the skin of the back). However, a stroke is often accompanied by impaired motor functions of the limbs and even paralysis. To return the patient to normal life, physical rehabilitation cannot be neglected. The Aximed Neurology Clinic offers the services of its rehabilitation center.
- The neurologist will assess the patient’s condition and determine whether it is possible to begin rehabilitation measures (the optimal start of rehabilitation is 1-3 weeks after the patient’s condition has stabilized).
- The rehabilitator will draw up an individual program of physical exercises and physiotherapeutic procedures, and will adjust it as the course progresses.
- The rehabilitation room is equipped with the latest simulators, orthoses and robotic rehabilitation complexes.
- You can visit the hall while staying in a “full” hospital setting or as a day hospital.
It is important to remember that after a spinal stroke, the spine forever remains the “weak spot” of the body. During the recovery period, it is worth taking care of supporting corsets and orthopedic mattresses/pillows. However, over time, the corset will need to be abandoned, since constant wearing of it can cause dystrophy of the back muscles, can cause curvature of the spine, disc instability and increased stress on the spinal cord.
Also, for patients who have suffered a spinal cord stroke, in order to avoid repeated circulatory disorders (including the brain, because there is only one area of the disease), it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet, monitor your weight, blood pressure and sugar levels / cholesterol in the blood), take a daily walk in the fresh air, give the body light physical activity, and harden up.
Forecast and preventive measures
The consequences of a spinal stroke are not as life-threatening as a cerebral stroke. An unfavorable prognosis occurs in extremely severe general somatic conditions, malignant tumors, and secondary infections.
Competent therapy triggers symptomatic regression, but with extensive damage, aggravated by other pathologies, and delayed therapy, recovery cannot be complete, the patient faces complete disability.
The basis of disease prevention is the timely detection, treatment and prevention of any vascular and vertebral pathologies. Giving up bad habits, physical activity, weight and nutrition control minimize the occurrence of predisposition factors to the disease.
If you notice any warning symptoms, call us at the numbers listed on the website. Our specialists will help make an accurate diagnosis and prevent the disease. At the Consulting and Diagnostic Center we use only modern diagnostic and treatment methods. Click the "SIGN UP" button and come see us.
Possibilities of modern diagnostics
The only method of choice for high-quality and accurate neuroimaging of this pathology is MRI of the spine and spinal cord. Our website will help you choose a clinic and make an appointment. You can find out any information: address of the diagnostic center, opening hours, tomograph capacity, types of studies, cost of MRI of the spine. This will help deliver the patient to the clinic faster and not overpay for the study.
It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with acute myelitis, tumors, epidural hematomas and abscesses, which may cause compression (compression of the spinal canal).
Early diagnosis and quality rehabilitation are two main factors influencing the prognosis. Therefore, if you feel a sharp pain (in the chest, neck, shoulder), then you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a spinal stroke, the doctor first collects an anamnesis to find out whether there were so-called prodromal manifestations (precursors) and how the pathological condition developed over time. The following diagnostic measures are also carried out:
What is vertebral concrescence
- a neurological examination to identify the severity of the condition and the location of the pathological focus;
- MRI or SCT. Thanks to these methods, it is possible to determine the presence or absence of damage to the vertebrae, spinal arteries and intervertebral discs. In addition, modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect spinal cord tumors whose size does not exceed a few millimeters;
- Lumbar puncture. In the case of a hemorrhagic stroke, blood cells will be found in the cerebrospinal fluid. If ischemic stroke is suspected, lumbar function may not be performed;
- angiography. Vascular examination makes it possible to identify aneurysms, ruptures of blood vessels, or the presence of blood clots blocking the lumen of the arteries.
No ads 2
Prognosis for patients
In this case, it all depends on the size of the area that was damaged and the location of the stroke. In half of the cases, taking into account timely seeking help from specialists, competent treatment and rehabilitation, the patient’s almost complete recovery occurs. In other cases, the risk that persistent neurological disorders will remain with the person for life is high.
Death can result from cases with large tumors of the spine that are not amenable to surgical intervention, as well as severe damage to the aorta and the development of complications in the heart and urinary system.
Causes
In total, medicine distinguishes 3 categories of causes that provoke the development of an attack, namely:
Damage to the cardiovascular system is diagnosed in 20% of cases. This is mainly a congenital anomaly of the structure of the heart and blood vessels, as well as vascular diseases acquired throughout life.
External compression of the vessel is diagnosed in 75% of cases. Occurs due to compression by any formations in the thoracic or abdominal region of the aorta and the vessels extending from it. Formations include:
- pregnancy;
- enlarged lymph nodes due to tumor metastases;
- lymphogranulomatosis.
The radicular arteries are compressed due to the presence of:
- vertebral hernia;
- spinal cord tumors;
- spinal injuries (fractures).
The result of medical manipulations is in 5% of cases. During operations, specialists may violate the technique, which leads to the development of ischemic stroke. For example, during surgery on the spine or nearby tissues, in order to prevent bleeding of the artery, it is clamped with a surgical clamp for a long time. Also, circulatory disorders can develop due to spinal anesthesia and blockade of the spinal nerve roots.