One of the first places in the world is occupied by mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Vascular diseases, blockage of arteries and veins negatively affect the functioning of all organs of the body.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood throughout the body. With the bloodstream, the necessary vitamins, hormones, and nutrients are carried to every part of the human body. Healthy blood vessels have smooth inner walls, and blood flows smoothly through them.
What is vascular blockage?
Blockage of blood vessels occurs due to various factors:
- thrombosis;
- injuries;
- the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls.
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms as a result of damage to the inner wall of an artery. The plaque is formed from substances circulating in the blood: calcium, cholesterol, fibrin. The body evaluates this formation as a defect and the process of thrombus formation begins. Unlike arterial thrombosis, venous thrombosis is not characterized by cholesterol deposition.
As deposits build up in the arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis occurs. This condition leads to narrowing and hardening of blood vessels.
Risk factors contributing to vascular blockage:
- increased cholesterol levels;
- high blood pressure;
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of vascular blockage
Often, poor arterial patency does not cause any pain until a serious complication such as a stroke develops.
In other cases, especially when more than half of the artery is blocked, symptoms such as:
- discomfort, chest pain;
- severe shortness of breath;
- rapid heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- sweating
Due to a decrease in blood flow to the heart, chest pain (angina) appears, then coronary heart disease develops.
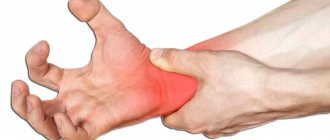
Peripheral artery blockage can cause:
- Leg pain.
- Poor healing of foot injuries.
- Gangrene.
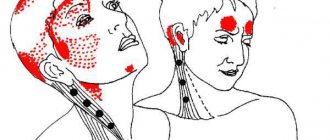
If there is obstruction of the cerebral vessels, a person experiences headaches, constant or periodic, increased blood pressure, dizziness, vomiting, and unclear consciousness.
Consequences of the disease
Depending on the location of the damaged vessel, various complications arise. With obstruction in the extremities, nagging pain in the legs first appears, then trophic ulcers and tissue necrosis. Amputation is indicated, otherwise gangrene may develop. With prolonged ischemia of the heart vessels, myocardial infarction occurs. Long-term obstruction of blood vessels in the brain causes a stroke.
Symptoms of OASNK
- Pain in the leg at rest, depriving the patient of sleep;
- Pain or a feeling of fatigue in the leg muscles when walking (usually in the calf muscles) - this symptom is one of the early signs of atherosclerosis of the leg vessels;
- Unusual feeling of chilliness and numbness in the foot, aggravated by physical activity (walking, climbing stairs;
- The presence of a non-healing wound or trophic ulcer, usually located in the foot or lower third of the leg;
- Darkening of the skin, often in the form of dark brown or black necrosis of the toes (gangrene);
- Difference in skin temperature between extremities (the affected leg is cooler than the healthy leg).
Stages of development of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
The manifestation of one or another symptom depends on the stage of atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities. In this connection, the following stages are distinguished (in our country, classification according to A.V. Pokrovsky, 1976):
- Stage I – pain in the lower extremities manifests itself during heavy physical activity, walking over a distance of more than 1 km.
- Stage II A – pain in the limb occurs when walking at a normal pace for more than 200 m.
- Stage II B - pain in the limb occurs when walking at a normal pace of less than 100-200 m,
- Stage III – pain in the limb occurs at rest or when walking less than 25 m.
- Stage IV – the pain is constant, there are ulcerative-necrotic changes in the tissue.
Most often, the level of damage is accompanied by complaints of characteristic localization.
With atherosclerosis of the aorta and iliac arteries, the so-called Leriche syndrome, in which pain is localized in the gluteal muscles, thigh muscles, there is no pulsation in the femoral arteries, or it is sharply weakened. Men also experience impotence.
With obliterating atherosclerosis of the femoral and popliteal arteries, pain is localized in the muscles of the legs and feet.
Diagnostics
If poor patency of arteries and veins is suspected, the following studies are performed:
- Cholesterol analysis.
- Chest X-ray.
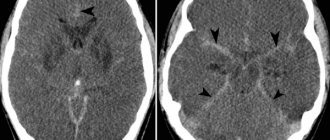
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound.
- Echocardiogram.
- ECG.
- MRI scan.
- Angiogram.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses magnets and radio waves to produce images inside the body without a surgical incision. Unlike CT scans, MRIs do not use ionizing radiation. This is considered a safer alternative.
"They won't go away"
— Is the process of atherosclerosis already begun irreversible?
“Unfortunately, the atherosclerotic plaques that have already formed will not “resolve.” And conversations about miracle drugs, IVs that dissolve plaques, have nothing to do with reality. We can only slow down the process of plaque increase in size and prevent complications of atherosclerosis that are dangerous to health and life.
Article on the topic
We ran away from a heart attack and caught up with him. How sports can lead to atherosclerosis
“Nevertheless, the Internet is full of advice on how to clean vessels.
— This formulation is incorrect and is used to promote artisanal treatment methods. There is no cleaning, only surgical techniques.
— For atherosclerosis, statins are usually prescribed. However, information has emerged that they can lead to the development of cancer.
— The effectiveness of statins in the treatment of atherosclerosis has been absolutely proven by multicenter studies. Their use can reduce the number of dangerous complications in patients suffering from atherosclerosis and lipid metabolism disorders, and slow down the further development of atherosclerotic plaques.
Yes, statins have side effects. The most well-known is liver dysfunction. Therefore, these drugs are used under laboratory monitoring of liver function. In case of obvious changes, the dosage is reduced or statins are discontinued.
Article on the topic
Statins and discipline. Reducing blood pressure in Russian
— Tell us about surgical methods for treating atherosclerosis.
— Today, three main methods are used.
Open vascular surgery:
— The artery is opened, the plaque is removed, and the lumen of the vessel is sutured (so-called endarterectomy).
— Bypass surgery. In case of longer vessel blockage (10-15 cm or more), shunts are used. A backup artificial vessel made of synthetic materials or autovenous is sewn to the artery to ensure blood flow bypassing the area of narrowing or blockage.
Endovascular (intravascular) techniques are considered the most progressive today and are increasingly used in the world. In this case, the blockage or narrowing of the vessel is eliminated without cutting the skin, through a puncture in the artery. For example, we can make a puncture in the leg or arm and pass instruments through the lumen of the vessel into the femoral, carotid, and coronary arteries. The access zone and the operation zone are often tens of centimeters apart. In the place of the blocked plaque, we restore the lumen, insert a balloon, push apart the walls of the vessel and install a frame (stent) that will support the created lumen.
— Do such operations cure forever?
“Unfortunately, eliminating the narrowing and restoring blood flow in one place does not stop the development of the process in other vessels. Especially if a person does not change his lifestyle: he continues to eat poorly, moves little, smokes. There are patients whom I operated on the arteries of the legs, brain, and aorta. Although all patients are given recommendations upon discharge after vascular surgery, on nutrition, observation by a cardiologist and surgeon, and ultrasound monitoring of the condition of blood vessels, few follow them. Most, when they are no longer bothered by previous complaints, return to their usual way of life. And then they come with a new problem.
Article on the topic
Neither sigh nor groan. Atherosclerosis of blood vessels threatens to turn into a heart attack
Treatment of vascular blockages
There are many options for preventing and treating blood clots. Depending on the severity of the condition and the patient's medical history, the doctor prescribes various methods.
Disease prevention:
Quitting bad habits, urgent lifestyle changes:
- a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, less sugar and simple carbohydrates, and high in fruits and vegetables;
- body weight loss;
- ban on smoking and alcohol;
- fitness classes;
- minimizing stress;
- lowering blood pressure and cholesterol using folk remedies;
- maintaining low blood sugar levels by avoiding large amounts of sweets, jam, and sweets.
Drug treatment
Some medications help prevent clogged arteries, such as:
- cholesterol-lowering medications;
- drugs that lower blood pressure;
- blood thinners, which reduce the chance of dangerous blood clots.
Surgical intervention.
In the later stages of the disease, drug measures do not help improve the situation and then surgical procedures are used:
Stenting
A small tube called a stent is placed in the artery to maintain good blood flow. A catheter is inserted through an artery in the leg to reach the heart, and a stent is inserted through the catheter into the area of the blockage.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
In this surgery, arteries from other parts of the body are moved to the site of blocked arteries to help the blood reach its target destination.
Balloon angioplasty
A device is used that pushes the plaque towards the side walls of the arteries, resulting in the opening of the vessel lumen.
But in advanced cases, especially when the vessels of the legs are damaged, it is not possible to save the limbs, amputation is indicated.
Hormones, fat and genes
Yulia Borta, AiF: Konstantin Borisovich, what are atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels? And why do they suddenly appear?
Konstantin Frolov : Atherosclerotic plaques are deposits of lipids, that is, fats. There are many theories about the development of atherosclerosis, but why this begins to happen is not completely clear. It has been established that heredity plays a major role in the development of the disease. As a rule, in patients who suffer from atherosclerosis, relatives were ill or died from its complications: stroke, heart attack, etc. No one disputes an excess of animal fats in food as the main provoking factor in the development of atherosclerotic plaques. The negative effects of smoking have also been proven. Among our patients, more than 90% are experienced smokers.
Article on the topic
Don't be afraid of fat. How to eat to get rid of atherosclerosis? However, following a healthy diet does not provide a 100% guarantee that the disease will not appear. There are interesting studies that have shown that through various hormonal manipulations it is possible to induce the development of significant atherosclerosis in herbivores that have not eaten a single gram of animal fat in their lives. So there are many theories on this topic, but none of them gives a comprehensive answer to the question about the causes of atherosclerosis. Therefore, we can fight, alas, only with its consequences.
— With excess fat it’s understandable. How does calcium appear in plaques?
— With pathological changes in the vessel wall, when its nutrition is disrupted, first fibrosis occurs, the formation of connective tissue, and then calcification, that is, the deposition of calcium in this area. This is the final stage of plaque development, when it becomes hard and stable. Before this, the plaque has a softer structure; parts of it can come off, “fly away” with the bloodstream and clog smaller blood vessels.
Prognosis and prevention
The most important prognostic criterion for acute occlusion of the vessels of the extremities is the time factor. Early surgery and intensive therapy can restore blood flow in 90% of cases. If treatment is started late or is absent, disability occurs due to the loss of a limb or death. With the development of reperfusion syndrome, death can occur from sepsis, renal failure, or multiple organ failure.
Prevention of acute vascular occlusion of the extremities involves timely elimination of potential sources of thromboembolism and prophylactic administration of antiplatelet agents.