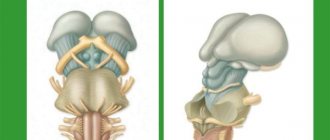
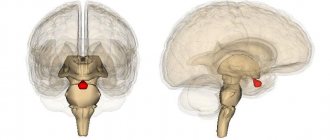
All parts of the brain, including the cerebellum, need good blood supply. Their performance depends on this. For example, the “small brain” is responsible for maintaining a stable body position in space, balance, the ability to perform targeted movements and regulates muscle tone.
Dysfunction of this part of the brain is expressed in hand tremors, unsteady gait, and poor orientation in the room. If these pathological symptoms were not a consequence of a congenital disease, then their appearance can provoke a cerebellar infarction.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on many factors: timeliness of assistance provided, general health, quality of treatment. In addition, the consequences of a stroke depend on the type of stroke, namely the area of the brain affected.
Let's look at the main types of stroke by area and their health consequences.
Major stroke
The outcome for the elderly is unfavorable, since the patient does not fully recover. The result is disability.
Unilateral stroke
The prognosis is influenced by the extent of the lesion and the timeliness of medical care. Often the outcome is death or paralysis. Only in isolated cases does the patient recover completely.
Brainstem stroke
The most dangerous species, often leading to death. The survivors remain disabled.
Cerebellar stroke
The prognosis depends on the extent of the lesion. If treatment is started in a timely manner and the patient is properly cared for during the rehabilitation period, he can fully or partially recover. However, most stroke survivors suffer from impaired mobility, which causes them to walk with support.
Spinal stroke
The prognosis is generally favorable and the mortality rate is low. If treatment is not started in time, the patient can be paralyzed. Problems in the functioning of the pelvic organs cannot be ruled out.
If you are over 80 years old
For people over 80 years of age, the prognosis is rarely good, regardless of the type of stroke. The fact is that at such a respectable age the condition is complicated by existing chronic diseases and weakened immunity, which reduces the chances of recovery.
Elderly people at this age most often fall into a coma, during which they do not breathe on their own. Their blood pressure decreases, which leads to impaired blood circulation. Fever may occur. Lives in a coma for an average of 7 days, after which he dies.
In less severe cases (with a unilateral stroke), the patient remains disabled due to paralysis of the side of the body opposite to the lesion and other disorders.
Symptoms of cerebellar infarction
Signs of pathology depend on the location of the area of insufficient blood supply. If one of the cerebellar hemispheres has been affected, this manifests itself in a complex of vestibular disorders, including dizziness. In addition, the patient has a headache in the back of the head, nausea, gait disturbance and speech disorders.
If the blood supply to the anterior inferior cerebellar artery is disrupted, this is also reflected in disturbances in gait, fine motor skills, speech, and hearing problems also appear. With damage to the right hemisphere of the cerebellum, the receptivity of sounds is impaired on the right, with left-sided localization - on the left.
When the blood flow in the superior cerebellar artery is blocked, movement coordination disorder predominates, and it becomes difficult to perform targeted actions. It is difficult for the sick person to maintain a position in space, the gait changes, and difficulties arise in pronouncing sounds and words.
The first symptoms of cerebellar infarction include:
- Headache in the back of the head;
- Nausea, vomiting, independent of food intake;
- Dizziness;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Increased heart rate;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Loss of balance, unsteady gait;
- Disorientation.
After 3-4 days, if the patient was not provided with first aid, the first signs of cerebellar infarction are accompanied by more serious symptoms of destruction of nervous tissue: depression of consciousness; loss of consciousness; increased headache, deterioration of hearing and vision, possibly coma. Every day the patient's condition becomes worse.
Consequences of a stroke
Unfortunately, as a result of brain damage, important functions are impaired, which are not always amenable to recovery. Let's look at the main ones.
Paralysis
It involves damage to the nerve endings that control muscle function, resulting in loss of motor function. Paralysis can be of the whole body or part of it. The most common form is one-sided. May affect facial muscles.
Speech dysfunction
A common consequence of a stroke that occurs due to damage to the areas of the brain responsible for speech. Expressed in complete/partial loss of the ability to speak and perceive the words of others. With a partial form, the conversation is unclear; with a complete form, there is an inability to utter at least a word.
Deterioration of the visual organs
A stroke can damage the parts of the brain responsible for visual function. As a result, there is deterioration in vision, loss of individual parts from the field of view (up to ½), and strabismus (difficult to treat).
Impaired motor coordination
Most often occurs with a brainstem stroke. Manifests itself in the form of dizziness and staggering when moving. Depending on the form of the pathology and severity, it may manifest itself during the first days after the attack or over a longer period.
Swallowing dysfunction
It occurs due to a disruption of the reflex process or paralysis of facial muscles. It is also a consequence of brainstem infarction.
May manifest:
- Difficulty chewing food.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Pain while eating.
- The entry of food particles from the oral cavity into the respiratory organs, in particular the nose.
Formation of bedsores
It is observed in paralyzed patients due to prolonged stay in one position. In this case, less nutrients reach the tissues. The result is their starvation and further death. The areas most affected are areas closely pressed to the bed.
Pneumonia
As a result of paralysis, the patient cannot cough up the mucus that accumulates in the bronchi and enters the lungs. Next, inflammation begins.
Depressive state
The most common consequence that minimizes the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation. You need the help of a qualified psychologist and a course of antidepressants.
Coma
One of the dangerous consequences, considered a transitional state to death. During this period it is noted:
- slowing down metabolism;
- decrease in body temperature;
- change in breathing pattern;
- falling into unconsciousness;
- lack of response to external stimuli.
The prognosis for coma is predominantly unfavorable.
What it is
The main blood flow to the cerebellum is delivered by 3 paired cerebellar arteries, which are branches of the vertebral and basilar arteries. If thrombosis or embolism occurs due to any disease, this leads to disruption of the blood supply to the “small brain”.
Because of this, the corresponding areas of the nervous tissue begin to break down and soften. The process of death of any part of the brain is called the term “infarction”, in this case it will be “cerebellar infarction”.
The main cause of impaired blood flow in the cerebellar arteries is blockage of blood flow by emboli or thrombus. Both are clots of blood particles, only the embolus is able to move inside the blood vessel, and the thrombus “sits in place.”
The building material of a blood clot is platelets, the cells responsible for blood clotting, and the embolus is formed by particles of adipose tissue, an overgrown colony of microorganisms that has entered an air vessel.
Diagnostics
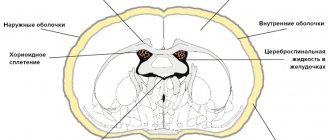
To confirm the diagnosis of cerebellar stroke, an ultrasound is performed. The study allows you to determine the displacement, see the area of edema, and detect a damaged artery.
An informative diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. Both methods provide an accurate picture of the changes, the size of the damage, the depth, and detect the cause of the disease.
A blood test is taken for general formula and biochemistry. The data will allow you to identify the level of sugar, cholesterol, and other substances that are signs of the diseases that provoked the attack.
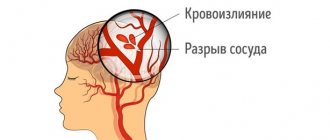
Why do blood vessels rupture?
The main cause is arterial hypertension, especially if untreated or during breaks in taking antihypertensive drugs. The vessels physically cannot withstand the pressure that blood exerts on their walls. A vessel breaks through at the site of thinning or damage, this happens in the presence of an atherosclerotic plaque, congenital aneurysms, head injuries, the use of certain medications that prevent blood clotting, tumors and encephalitis. Another important cause of rupture is arteriovenous malformations, when small arterial and venous vessels do not end in capillaries, but are intertwined into one large ball. Such congenital pathology can be detected during a preventive examination. If a person knows about it, he behaves more carefully and avoids unnecessary risks.
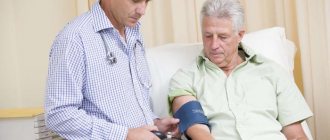
Nature has protected the brain as much as possible from damage, providing it with a mass of protective and backup systems. At a young age they work, but in the second half of life they don’t always work. Therefore, it is advisable that people at risk undergo an annual examination by a neurologist.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,500
Make an appointment
The following people are at high risk of developing hemorrhagic stroke:
- hypertensive patients, they need to take medications daily;
- overweight people - the body grows approximately 1 kilometer of blood vessels per 1 kg of excess weight;
- people with high levels of cholesterol, namely low-density lipoproteins, which form atherosclerotic plaques on the vascular wall;
- people who eat insufficient amounts of protein and do not have the “building material” for complete tissue repair;
- those under chronic stress, often suffering from physical or emotional stress;
- alcohol abusers and smokers;
- those suffering from diabetes or heart disease;
- suffering from chronic infections that destroy the vascular wall - lupus erythematosus, vasculitis;
- people who constantly take medications to reduce blood viscosity;
- having direct relatives who died from cerebral hemorrhage.
First aid
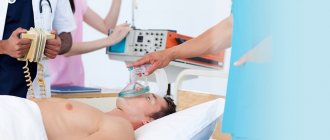
If there is a suspicion that a stroke is developing, then the most important thing is to immediately call an ambulance .
Then you need to check whether the person can breathe, help him by emptying the oral cavity in a position lying on his side. If possible, record blood pressure and pulse readings. If the patient is on the floor, then lay him on his back, placing a towel folded in several layers under his head. It is very important to establish when the attack occurred, this will help in the correct prescription of therapy. You cannot independently lower blood pressure, give water, and especially feed the patient.
First aid for stroke
First aid and treatment
How to recognize a stroke: characteristic symptoms
When a patient shows the first signs of a stroke, immediately call an ambulance. Doctors have only 3.5 hours from the onset of the disease to have time to hospitalize the patient, conduct differential diagnostics, and begin treatment. Before the doctors arrive, try to position the victim so that the body is slightly lower than the level of the head. Do not give water, food, or any pills.
Arriving specialists will quickly assess the general condition of the patient and, if your concerns are confirmed, they will suggest hospitalization. Inpatient treatment for stroke is the only effective one. Therefore, it is very unwise to refuse it.
Medications
Drug treatment for cerebellar stroke consists of two main components:
- basic therapy aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition, eliminating symptoms, and preventing cerebral edema, regardless of the nature of the stroke. Includes breathing restoration (airway clearance, intubation), administration of a number of drugs;
- specific therapy specific to a particular type, localization of a brain stroke.
Main components of basic therapy.
- Ischemic cerebral stroke - consequences and rehabilitation treatment
| Type of procedures or drugs / Mechanism of action | Examples of drugs |
| Antihypertensive drugs / Normalize blood pressure | Captopril, enalapril |
| Antiarrhythmics / Eliminate various types of heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias) | Metoprolol, bisoprolol |
| Nitrates / Relieves symptoms of angina pectoris | Nitroglycerine |
| Cardiac Glycosides / Help the heart pump blood | Digoxin, digitoxin |
| Neuroprotectors, antioxidants / Improves brain microcirculation, metabolism, protects neurons from adverse effects | Vitamins C, E, glycine, magnesium sulfate, mildronate |
| Diuretics / Prevention, treatment of cerebral edema | Diacarb, mannitol |
| Opioid Analgesics/Painkillers | Morphine |
Ischemic stroke requires additional administration of drugs:
- preventing recurrent thrombus formation (aspirin, clopidogrel);
- dissolving existing blood clots (thrombolytics).
How to help a stroke victim?
Recovery largely depends on how the people around the patient behave. First of all, you need to call an ambulance, and until it arrives, try not to move the person. You need to place a cushion or pillow under the shoulders and head, carefully turn the person on the right side, and place a basin or bag in case of vomiting. It is advisable to measure blood pressure. Anti-pressure pills should not be given before the ambulance arrives: there is a possibility of a sharp drop in blood pressure. Only specially trained medical personnel know the rules for lowering blood pressure when it rises above 150/100 mmHg. If respiratory depression occurs, you need to start resuscitation - chest compressions, mouth-to-mouth breathing.
The best prevention is timely treatment of hypertension, atherosclerosis, identification of malformations and aneurysms before they rupture.
Our neurologists see patients every day, and every patient at the clinic can find out their risk for developing a hemorrhagic stroke. Visit your doctor while you still have time.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions