One of the types of ischemic stroke is lacunar, localized in the pontomesencephalic region or cerebral hemispheres. This is the most common form of pathology diagnosed at the Yusupov Hospital in many patients with ischemic stroke. Early diagnosis will avoid complications and can be performed in a modern hospital clinic equipped with high-precision medical equipment. Yusupov Hospital, rightfully considered a leading clinic for the treatment of strokes.
Overview of Lacunar Ischemic Stroke
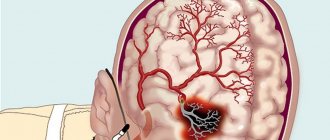
Lacunar ischemic stroke leads to pathological disorders in the deep layers of the brain and the formation of so-called lacunae (cavities), the diameter of which ranges from one to fifteen millimeters. Sometimes the lacunae merge, resulting in the formation of large cavities filled with blood or plasma and fibrin.
With this pathology, the patient’s consciousness, vision, speech, and other functions of the cerebral cortex are practically not impaired. In addition, symptoms of brain stem damage are also completely absent. Thanks to these distinctive features, lacunar stroke can be differentiated from other types of this pathology.
In the absence of qualified neurological assistance, this type of brain catastrophe threatens the development of severe complications, including death. According to statistics, after patients have suffered a lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain, the survival prognosis is: in the first month - 70-80%, within a year - about 50%. Therefore, early diagnosis of pathology plays a vital role.
Classification
Clinical classification is based on clinical symptoms and is discussed in the section on symptoms of lacunar infarction.
In the development of the disease there are:
- the most acute period is the first 3 days;
- acute – 28 days;
- early recovery – the next 6 months after suffering a circulatory disorder;
- late recovery – for 2 years.
Due to mild symptoms and the absence of pronounced motor, speech and sensory disorders, it is very difficult to describe the features of each interval. Therefore, this division is of secondary importance.
Causes of lacunar ischemic stroke
The main cause of lacunar stroke is considered to be arterial hypertension, which leads to brain damage and depends on blood pressure, the degree of damage to the arterial walls and their condition. In order to prevent the development of a cerebral catastrophe, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital monitor surges that occur during the day, since lacunar stroke occurs against the background of sharp changes in arterial pressure.
The risk group consists of persons suffering from the following pathologies:
- hyaline dystrophy AG;
- atherosclerosis;
- infectious inflammation of arterioles localized in the brain (previously suffered);
- diabetes mellitus
Along with the above, lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain can be caused by vasculitis, the form of which can be either specific or nonspecific.
Preventive measures
In a person, even if the pathology suffered did not cause serious harm to health, life after a lacunar stroke changes. This is necessary to prevent the re-formation of lacunae that disrupt brain function.
Tips for preventing lacunar stroke are useful not only for people who have suffered a small focal ischemic attack, but also for those who have a predisposition to developing the disease (hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.). Doctors recommend:
- monitor blood composition (cholesterol levels and viscosity);
- stabilize blood pressure;
- regularly spend time in the fresh air;
- provide regular physical activity (gymnastics, swimming, cycling);
- stop eating at fast food outlets and add a large amount of vegetables and fruits to the menu;
- limit salt intake;
- give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
These simple methods will help you avoid the bitter experience of learning what it is, the formation of lacunae in the brain tissue. And for those who have already suffered an attack, preventive measures are necessary to prevent a relapse.
Diagnosis of lacunar ischemic stroke
In order to determine lacunar ischemic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, which are the most informative in this situation. Using these studies, the location, number and volume of formed lacunae are revealed. With lacunae of small diameter, fixation of lesions is difficult. To make a final diagnosis, along with the results of the studies, the neurologist takes into account the patient’s medical history, especially if he is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension or alcoholism.
Treatment of lacunar ischemic stroke
Treatment of lacunar stroke at the Neurology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is based, first of all, on the use of drugs whose action is aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as having a neuroprotective effect. The development of collateral blood flow is promoted by drugs such as cinnarizine and Cavinton.
The Yusupov Hospital attaches great importance to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused vascular damage. Blood pressure is constantly monitored. If its levels are high, the patient is prescribed antihypertensive drugs. High cholesterol levels, determined by laboratory tests, are corrected by taking lipid-lowering drugs - statins, the action of which is aimed at blocking enzymes that help the synthesis of cholesterol compounds in the liver.
Specialists at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital constantly monitor the function of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If necessary, the patient is prescribed medications that correct the water-electrolyte balance in the body and reduce swelling of brain tissue.
To prevent relapse, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet agents. For arterial thromboembolism, warfarin is used. In some cases, a course of anticonvulsant drugs is recommended.
To prevent dementia, patients are prescribed a course of drugs Neuromidin or Gliatilin. In the presence of pseudobulbar syndrome, fluoxetine is used.
For patients with lacunar ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use an individual approach, resulting in high treatment results.
Pathogens
The described disease can manifest itself as a result of a failure in the blood supply in one of the perforating vessels of the arteries. In almost 80% of lesions, the area of change is the white matter of the cerebral region, located in the subcortical zone and the inner shell, in the remaining 20% - in the base and bridge. Typically, the main cause of progression of deformities is chronic arterial hypertension. Due to this, anomalies begin to appear in the walls of the vascular canals. In the case of such a process, the patient experiences a decrease in the lumen of the artery, which entails problems in the circulatory system, which supplies a certain area of cerebrotissue. After this, signs of ischemia and death appear in the affected lobe; subsequently, a hole is formed in place of the removed cells.
The main etiological sources of the disease are:
- Chronic disease of the arteries of the elastic and muscular-elastic type, renal failure with an increased number of creatinine in the blood cells.
- Diabetes.
- Alcohol abuse.
- The chronic stage of obstructive disorders occurring in the pulmonary apparatus.
- Infectious agents that have entered the body.
- Autoimmune diseases, etc.
Experts' prognosis for lacunar ischemic stroke
If a patient is diagnosed with a single lacunar stroke of the brain, the prognosis is favorable. As a rule, after rehabilitation, the patient experiences restoration of all functions, although the presence of sensory residual and motor symptoms may sometimes be observed.
During a relapse, a lacunar state of the brain may develop, and the risk of this complication is very high: according to statistics, after a repeated lesion, this occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Despite the restoration of all impaired functions, lacunar ischemic stroke negatively affects the mental state of the patient, in which gradual changes occur. There is the appearance of memory loss, disorientation and difficulty communicating, tearfulness, frequent hysterics, a feeling of helplessness and a state of passion.
Clinical picture of the disease
So, a lacunar infarction (stroke) is a small-diameter (about 10-20 mm) brain injury associated with a disruption of the normal process of delivery of nutrients, minerals, and oxygen to this area. This occurs as a consequence of vascular damage, the entry of blood clots, emboli, or bacterial clots into the capillaries, which is why partial blockage of the supplying vessels occurs.
From the editor: Treatment and symptoms of mixed type dystonia
It is believed that among all strokes, 30% are lacunar infarctions, that is, those that are directly related to blockage of blood vessels. At the same time, doctors themselves claim that it occurs more often in men, but in 90% of cases it is discovered by chance (during an MRI examination). The final diagnosis is made only after an autopsy.
The main danger of lacunar infarction is the absence of primary symptoms and pathogenesis. In only 0.5% of cases, the disease can be detected in advance, focusing on a visual examination of the patient, monitoring the functioning of the nervous system (reaction to light, coordination in space). Once symptoms become apparent, the disease may no longer respond to treatment.
Very often, patients with a similar problem come to a medical facility in a rather advanced form, because often it is not accompanied by any symptoms. The disease can occur in the form of a mini-stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Features of the course of the disease are expressed by the following factors:
- history of arterial hypertension;
- absence of meningeal and general cerebral signs, that is, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and others;
- loss of consciousness also does not occur;
- the disease manifests itself at night, forming all the signs of a lacunar stroke by morning;
- after a relapse, all impaired brain functions are restored with partial neurological deficit;
- MRI and CT scans reveal only small foci of low density; if the infarction is small, then they may be completely absent.
In medicine, there are several syndromes that can accompany the disease. The most common are:
- Isolated motor type (55 – 60% of cases). The location of the pathology is the posterior thigh of the internal capsule. In this case, there is paralysis of half the body and plegia on the opposite side of the one where the foci of the disease are localized. Apart from this, no signs are observed.
- Isolated sensitive type (21% of cases). Its cause is damage to the ventral thalamic ganglion. In this case, all types of sensitivity of the patient are disrupted, that is, pain, muscle-articular, temperature, tactile and proprioceptive are affected. The location of symptoms is the limbs, torso and head. Over time, sensory disturbances may disappear partially or completely.
- Atactic hemiparesis (12% of cases) develops when cavities form in the dorsal femur of the internal capsule and inside the pons. In this case, muscle weakness, ataxia on the side of the localization of the disease and pyramidal disorders are noted.
- Clumsy upper limb and dysarthria (6% of cases). The pathology affects as follows: lacunae form in the layers of the nervous tissue of the bridge. In this case, previously absent problems with speech, awkwardness when moving, paralysis of the head, arms and legs appear.
In addition, regardless of the type of syndrome, lacunar stroke has the following symptoms:
- involuntary movement;
- walking is carried out in small steps;
- the urge to urinate is imperative, and from time to time it is simply impossible to hold urine;
- sensory and motor types of stroke may be combined;
- in some cases Parkinson's syndrome is noted.
Rehabilitation after lacunar ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital involves a whole range of measures: medical, social and psychological. They are aimed at restoring functions lost after a stroke. The hospital’s highly qualified doctors: neurologists, physiotherapists, psychotherapists have extensive practical experience in the field of rehabilitation medicine; they have in their arsenal the world’s leading techniques, modern medical equipment and the latest drugs for treating the consequences of brain accidents, thanks to which they can achieve high results. The clinic provides services for transporting patients to the hospital. Call and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.