One of the types of ischemic stroke is lacunar, localized in the pontomesencephalic region or cerebral hemispheres. This is the most common form of pathology diagnosed at the Yusupov Hospital in many patients with ischemic stroke. Early diagnosis will avoid complications and can be performed in a modern hospital clinic equipped with high-precision medical equipment. Yusupov Hospital, rightfully considered a leading clinic for the treatment of strokes.
Overview of Lacunar Ischemic Stroke
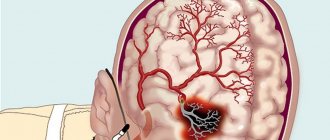
Lacunar ischemic stroke leads to pathological disorders in the deep layers of the brain and the formation of so-called lacunae (cavities), the diameter of which ranges from one to fifteen millimeters. Sometimes the lacunae merge, resulting in the formation of large cavities filled with blood or plasma and fibrin.
With this pathology, the patient’s consciousness, vision, speech, and other functions of the cerebral cortex are practically not impaired. In addition, symptoms of brain stem damage are also completely absent. Thanks to these distinctive features, lacunar stroke can be differentiated from other types of this pathology.
In the absence of qualified neurological assistance, this type of brain catastrophe threatens the development of severe complications, including death. According to statistics, after patients have suffered a lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain, the survival prognosis is: in the first month - 70-80%, within a year - about 50%. Therefore, early diagnosis of pathology plays a vital role.
Set of measures
If the lacunar cyst is a small cyst and the patient is not bothered by the clinical manifestations of brain dysfunction, then treatment, as a rule, is not prescribed, but it is recommended to carry out regular monitoring of the growth of the formation.
There is an opinion that asymptomatic cysts should not be considered diseases, but rather anomalies. Other experts, on the contrary, are convinced that even small formations accelerate the onset of senile dementia and contribute to the development of neurological diseases.
It is necessary to treat the pathologies that caused the cyst. For this, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and antihypertensive drugs can be used, depending on the etiology of the disease.
In cases where formations arise as a result of hemorrhage in the brain or symptoms develop that reduce the patient’s quality of life, surgical intervention is indicated. Today this is the only way to get rid of lacunar cysts.
Methods used to remove formation:
- Bypass surgery - the patient is given a drainage tube through which the fluid filling the cavity drains out. The walls of the cyst fall and grow together. The disadvantage of this method is the high risk of infection when using the shunt for a long time.
- Endoscopy – removal of a cyst through a puncture in the skull using an endoscope equipped with a video camera. The safest and non-traumatic method. However, there are contraindications for its use.
- Craniotomy is a highly effective operation that allows you to remove cysts of any location, but with a high risk of brain damage.
At the moment, shunting and trepanation are used extremely rarely.
Causes of lacunar ischemic stroke
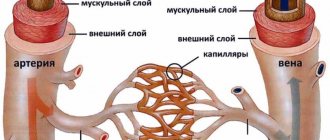
The main cause of lacunar stroke is considered to be arterial hypertension, which leads to brain damage and depends on blood pressure, the degree of damage to the arterial walls and their condition. In order to prevent the development of a cerebral catastrophe, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital monitor surges that occur during the day, since lacunar stroke occurs against the background of sharp changes in arterial pressure.
The risk group consists of persons suffering from the following pathologies:
- hyaline dystrophy AG;
- atherosclerosis;
- infectious inflammation of arterioles localized in the brain (previously suffered);
- diabetes mellitus
Along with the above, lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain can be caused by vasculitis, the form of which can be either specific or nonspecific.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of the development of such a formation may not appear for years. In such patients, cysts are detected during routine head examinations.
As the tumor grows, it compresses nearby parts of the brain. Symptoms that indicate a lacunar cyst depend on the location of the affected areas:
- For example, if a cyst has formed in the basal ganglia area , the patient will complain of problems performing complex movements.
- When the parietal lobe is damaged, coordination of movements, a sense of balance and body position in space are impaired, and oral and written speech skills regress.
- If the formation is located in the temporal region , auditory, olfactory, and taste hallucinations may occur.
- The formation in the frontal part causes involuntary facial movements and epileptic attacks.
- Impaired functioning of the occipital region leads to vision problems.
Also characteristic symptoms indicating damage to the membranes of the brain are nausea, vomiting, headaches, photophobia, and loss of elasticity of the neck muscles.
Diagnosis of lacunar ischemic stroke
In order to determine lacunar ischemic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, which are the most informative in this situation. Using these studies, the location, number and volume of formed lacunae are revealed. With lacunae of small diameter, fixation of lesions is difficult. To make a final diagnosis, along with the results of the studies, the neurologist takes into account the patient’s medical history, especially if he is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension or alcoholism.
Consequences and forecasts
In the absence of adequate therapy, the development of a lacunar cyst can have a number of adverse consequences, such as impaired coordination of movements, damage to vision and hearing, inflammatory processes in brain tissue, and death.
Children may develop hydrocephalus - accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, leading to compression of brain structures.
However, with the correct diagnosis and timely treatment, it is possible to completely get rid of the signs of the disease and prevent the formation of new cysts.
To prevent the disease, you should undergo a preventive examination at least once every 2 years and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Treatment of lacunar ischemic stroke
Treatment of lacunar stroke at the Neurology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is based, first of all, on the use of drugs whose action is aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as having a neuroprotective effect. The development of collateral blood flow is promoted by drugs such as cinnarizine and Cavinton.
The Yusupov Hospital attaches great importance to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused vascular damage. Blood pressure is constantly monitored. If its levels are high, the patient is prescribed antihypertensive drugs. High cholesterol levels, determined by laboratory tests, are corrected by taking lipid-lowering drugs - statins, the action of which is aimed at blocking enzymes that help the synthesis of cholesterol compounds in the liver.
Specialists at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital constantly monitor the function of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If necessary, the patient is prescribed medications that correct the water-electrolyte balance in the body and reduce swelling of brain tissue.
To prevent relapse, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet agents. For arterial thromboembolism, warfarin is used. In some cases, a course of anticonvulsant drugs is recommended.
To prevent dementia, patients are prescribed a course of drugs Neuromidin or Gliatilin. In the presence of pseudobulbar syndrome, fluoxetine is used.
For patients with lacunar ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use an individual approach, resulting in high treatment results.
Types of lacunar cysts
Cysts are divided into primary and secondary:
Primary - formed in the prenatal period. Their appearance is due to the incorrect behavior of future matter: smoking, drinking alcohol. Other factors may affect the development of the fetus in the early period: taking medications or previous infections. The appearance of a lacuna can occur at any stage of embryogenesis, but experts believe that it is more often a consequence of negative influences in the first trimester of pregnancy. This may be radiation, insufficient tissue nutrition due to hypoxia. The secondary form of pathology is associated with previous diseases that affected the state of the nervous system, TBI.
Experts' prognosis for lacunar ischemic stroke
If a patient is diagnosed with a single lacunar stroke of the brain, the prognosis is favorable. As a rule, after rehabilitation, the patient experiences restoration of all functions, although the presence of sensory residual and motor symptoms may sometimes be observed.
During a relapse, a lacunar state of the brain may develop, and the risk of this complication is very high: according to statistics, after a repeated lesion, this occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Despite the restoration of all impaired functions, lacunar ischemic stroke negatively affects the mental state of the patient, in which gradual changes occur. There is the appearance of memory loss, disorientation and difficulty communicating, tearfulness, frequent hysterics, a feeling of helplessness and a state of passion.
Prevention
A lacunar cyst of the brain is an asymptomatic formation and is difficult to detect. This tumor is found in only 25% of patients, and not from the beginning of its formation. A person may not be aware of the problem all his life. And when cyst symptoms begin to appear, it will be too late.
People who have already been diagnosed are advised to maintain their condition in several ways. This includes medications that improve a person’s overall health, controlling blood pressure, blood clotting, and cholesterol levels. Sanatoriums and other health institutions also help.
If you suspect a disease, you should quickly go to the doctor and get examined. Don't panic - stress will harm your health even more. It is necessary to monitor the functioning of the body, blood pressure readings, and overall well-being. It is advisable not to get sick, beware of viruses and hypothermia.
It is important for expectant mothers to take care of their health. As a matter of urgency, a pregnant woman must get rid of bad habits, eliminate alcoholic beverages, cigarettes and psychotropic substances from her life. You also need to boost your immunity and beware of viruses. A woman should remember that any change or deterioration in health has a negative impact on the fetus.
Rehabilitation after lacunar ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital involves a whole range of measures: medical, social and psychological. They are aimed at restoring functions lost after a stroke. The hospital’s highly qualified doctors: neurologists, physiotherapists, psychotherapists have extensive practical experience in the field of rehabilitation medicine; they have in their arsenal the world’s leading techniques, modern medical equipment and the latest drugs for treating the consequences of brain accidents, thanks to which they can achieve high results. The clinic provides services for transporting patients to the hospital. Call and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Clinical syndromes of lacunar disease
Clinical manifestations observed during the development of lacunae are referred to as lacunar syndromes. Lacunar cerebral infarction is often accompanied by lacunar transient ischemic attacks (TIA, micro-strokes). Transient ischemic attacks (TIA, micro-strokes) can occur in the patient several times a day and last only a few minutes.
The development of cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) may be accompanied by a sudden onset or increasing neurological deficit over several days. A few hours or days after the development of a cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke), the patient's condition improves, although some patients become disabled. The patient's recovery may be complete over a period of several weeks to months, or there may be minimal residual neurological deficit.
Neurological manifestations of many lacunar syndromes are known. Some of these neurological syndromes require confirmation. The most common neurological syndromes with lacunar disease are:
- Pure motor hemiparesis with an infarction in the area of the posterior thigh of the internal capsule or the base of the bridge. The face, arm, leg, foot and fingers are almost always involved. Muscle weakness can be intermittent during a transient ischemic attack (TIA, microstroke), gradually increasing or sudden. Muscle weakness can progress to paralysis (plegia) and then often regress. In many cases of such syndromes, recovery is complete;
- Syndromes with purely sensory disorders of the hemitype in thalamic infarctions;
- True ataxic hemiparesis due to infarction at the base of the pons and dysarthria with awkwardness in the hand or arm due to infarction at the base of the pons or knee of the internal capsule;
- Pure motor hemiparesis with “motor aphasia”, caused by thrombotic blockage of the lenticulostriate branch of the artery of the lentiform nucleus and striatum, supplying blood to the knee and anterior thigh of the internal capsule with the adjacent white matter of the corona radiata.
Before treatment for arterial hypertension, multiple lacunae often cause patients to develop pseudobulbar palsy with emotional lability, a state of lethargy, abulia and bilateral pyramidal symptoms. Currently, this syndrome is rare.
There are other lacunar syndromes that have been associated with observed arterial pathology:
- Pseudobulbar syndrome with loss of the ability to form speech sounds (anarthria), caused by bilateral infarctions in the area of the internal capsule, can develop with damage to the lenticular nucleus and striatum.
- Syndromes caused by narrowing of the lumen (occlusion) of the penetrating branches of the underlying portion of the posterior cerebral artery (listed above).
- Syndromes observed with possible narrowing of the lumen (occlusion) of penetrating arteries emanating from the main artery. These lacunar syndromes include ipsilateral ataxia and paresis of the lower extremity, pure motor hemiparesis with horizontal gaze palsy, and hemiparesis with crossed abducens (VI cranial) nerve palsy.
- Downstream basilar artery syndromes include sudden nuclear ophthalmoplegia, horizontal gaze palsy, and appendicular cerebellar ataxia.
- Syndromes that develop with possible narrowing of the lumen (occlusion) of the branches of the vertebral artery include pure motor hemiparesis (while the facial muscles remain intact) due to the involvement of the pyramid of the medulla oblongata, as well as the syndrome of damage to the lateral parts of the pons and medulla oblongata, accompanied by dizziness, vomiting, weakness facial muscles, Horner's syndrome, ipsilateral numbness in the area of innervation of the trigeminal nerve and contralateral loss of sensitivity due to damage to the spinothalamic tract (partial lateral medulla oblongata syndrome).
Brief information
Lacunar infarction is a type of serious malfunction in the functioning of the circulatory system of the brain, as a result of which small cavities begin to form in the human body in places where atrophied cerebral tissue is localized after suffering ischemia. The designations for such depressions were invented back in the 19th century, thanks to the medical scientist Fendal. It was he who was the first to name the identified pathological processes in patients suffering from arterial hypertension.
A detailed description of the presented disease was given later in the mid-60s of the last century. Professor Fisher revealed its direct dependence on encephalopathy of hypertensive nature. According to average statistics, a similar disease is diagnosed in approximately a third of patients diagnosed with stroke. Due to the small volume of lesions and minimal consequences, lacunar abnormalities have long been considered benign. But after carrying out certain studies in the field of neurology in a clinical setting, it became clear that such a disorder causes the development of cognitive deficits, the secondary stage of Parkinson's disease and some mental instability.
Types of cerebellar cysts.
The classification is based on the causes of disorders and tumor location.
The most commonly diagnosed types are:
- Changes in the right half of the cerebellum - manifested by dizziness, migraines, chronic fatigue. They develop as a result of an injury.
- Retrocerebellar cyst of the cerebellum is localized in areas of necrotization after head injury, surgery, inflammation and infectious lesions. Diagnosis requires examination of the cerebrospinal fluid to detect infection. When localized behind the cerebellum, severe migraines occur that are not relieved by analgesics, hallucinations, and mental disorders.
- Cyst-like expansion of the arachnoid space can be primary or acquired. Hydrocephalus often occurs as a result. In the case of a secondary nature, the most common cause is neuroinfection.
- An arachnoid cyst in the cerebellum forms in the area of adhesions, scars due to improper movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Cystic-atrophic formations are caused by prolonged disruption of the blood supply. Develop after injury or ischemic disease. It is difficult to treat.
- Lacunar cyst of the left hemisphere is an acquired neoplasm that arose against the background of a stroke. Characterized by the appearance of small single cysts.
- Cystic-glial formations of the left half appear after a stroke. Manifested by motor impairments, paralysis is possible. Speech disturbances are possible.
In cases where the appearance of a neoplasm is not accompanied by dangerous symptoms and does not impair the quality of life, experts consider it an anomaly. This is characteristic of primary cysts in the cerebellum of the brain.
Symptoms of a brain cyst
Symptoms are determined by the underlying disease that caused the cyst to appear. Therefore, they are diverse and nonspecific.
One or more of the following symptoms may occur:
- Headache;
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the head;
- Sensation of pulsation in the head;
- Noise in the ear with intact hearing;
- Hearing impairment (sensorineural hearing loss);
- Visual disturbances (double vision, spots before the eyes, etc.);
- Symptomatic epilepsy;
- Paresis (partial paralysis) of an arm and/or leg, permanent or transient;
- Episodes of loss of consciousness;
- Balance imbalance;
- Numbness of any part of the body, permanent or transient.
If the brain cyst is a trace of a long-term illness, there may be a complete absence of any symptoms.
Manifestations
Typically, the pathology manifests itself with a rapid onset of focal manifestations within a couple of hours. But there are cases when the violation occurs in stages with a gradual increase in the number of problems (this period can last from 72 hours to 6 days). At certain moments, transistor attacks of an ischemic nature are distinguished. In addition, with a lacunar infarction, cerebral symptoms, disturbances in the cortical regions and meningeal phenomena are not noticed. Consciousness remains clear and distinct. Also, the patient has the following symptoms:
- Hemiparesis.
- Sensory problems.
- Loss of the ability to independently perform physical activity.
- Problems with the speech apparatus.
- Pelvic dysfunction.
- Pseudobulbar anomaly.
- Neurological abnormalities.
- Depressive state.
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering received information.
- Decreased level of intellectual abilities.
- Slow thinking.
If such phenomena are neglected, a person begins a rapid progression of the disease, as a result of which the degree of cognitive imbalance begins to increase. The patient ceases to perceive any information, and there is a loss of motor reflexes.
Treatment Options
The main goal of ridding patients of the disease is to stabilize and maintain normal blood pressure levels, as well as prevent the formation of cardioembolism and conduct and changes in lipid metabolism. In some situations, regular appointments with a cardiologist are prescribed to monitor the correctness of therapy. It is he who prescribes additional antihypertensive measures and the use of antithrombotic drugs. To correct lipid metabolism, doctors prescribe statins. Also, therapeutic treatment is carried out using neurotropic components. Positive effects were noticed by experts after performing special exercises aimed at developing attentiveness, improving memory and level of thinking. If the patient suffers from depression, mild antidepressants are prescribed.