To make an appointment with a doctor
Calling a pediatrician to your home
Our doctors
Our prices
March 12, 2021
Each of us, more than once in our lives, has experienced the sensation of imaginary rotation of space around ourselves or ourselves in space, that is, we have experienced dizziness. It is not a separate disease, but can be a sign of a number of quite serious diagnoses. Medical statistics claim that in terms of prevalence, this symptom ranks second in neurology after headache.
Dizziness can be systemic, when the sensation of rotating space seems very realistic and intense, and non-systemic, when there is a feeling of uncertainty, unsteadiness, loss of balance during movement, fear of loss of consciousness.
The main cause of dizziness is a failure in the coordinated functioning of the visual, proprioceptive systems and vestibular apparatus. It can be caused by various factors. Both adults and children suffer from dizziness, and they occur much more often than is commonly believed. Diagnosing dizziness due to the subjective nature of the sensations is not easy. This is even more difficult to do with children, because it is difficult for them to explain what is happening to them. And a very young child is not able to complain of dizziness at all. But it is extremely important for parents to notice this phenomenon in time in order to exclude a serious illness.
How can you tell if your child is dizzy?
You can assume that a small child is dizzy based on his behavior:
- suddenly he is distracted from his favorite activity, he looks confused and incomprehensible, he tries to focus his gaze on some point, but he fails;
- closes eyes and/or lies face down; intuitively presses against the wall, headboard, chair, trying to stay on his feet, afraid to make a movement;
- does not want to get out of bed, especially after illness;
- Sometimes nystagmus is observed - rapid movement of the eyeballs, which is involuntary.
Causes of dizziness in children
Dizziness in children can be one of the symptoms of an incipient illness. However, it is also caused by reasons not related to the painful condition. Among them:
- staying in a stuffy room, lack of oxygen;
- excitement and stress, hormonal processes in adolescence;
- high ambient temperature;
- motion sickness in transport;
- feeling of hunger, decreased blood pressure.
Isolated cases, after which the child quickly returns to normal, do not require a visit to the doctor. But frequent dizziness in a child for no apparent reason may indicate serious health problems. Among them:
- neuroses and other mental pathologies;
- lesions of the central nervous system, epilepsy and other neurotic diseases;
- various inflammatory processes;
- disturbances in the activity of the vestibular apparatus;
- infectious diseases;
- migraine;
- decreased hemoglobin level, anemia;
- diseases of the inner and middle ear;
- head injuries, concussion;
- brain tumors;
- helminthiasis, poisoning, allergies.
It is very important to determine in time why a child is experiencing dizziness in order to prevent the progression of serious illnesses.
Causes of headaches in teenagers
In adolescence, headaches may appear due to insufficient cerebral circulation, hormonal changes, as well as daily routine. During this period, migraine attacks may occur, especially after physical and mental stress. It is important not to ignore them, because during headaches, nerve cells do not receive oxygen in the required quantity. This can lead to long-term consequences and manifest as migraine attacks in adulthood.
Tension headaches
Main article: Tension headaches
Tension headaches are the most common type. They may begin to appear during adolescence and occur in attacks. Patients note that the sensation is reminiscent of squeezing the head with a hoop from all sides. This is due to muscle tension, vascular spasms and increasing ischemia of brain tissue. After the spasm is relieved, the pain goes away, and the attacks are usually short-lived. Tension headaches are often caused by:
- stressful situations;
- prolonged mental stress, including during exams;
- violation of the daily routine, lack of rest.
Tension headaches are usually not particularly intense or lasting. They can be episodic or chronic. In the first case, they occur no more often than 15 days out of 30, and the duration of the attack ranges from 30 minutes to 7 days. If they appear more often, they are chronic. Treatment consists of adjusting the diet and diet, as well as taking painkillers.
Migraine
Migraine is another condition that can appear during adolescence. It is a primary headache, that is, it is not associated with any pathologies of internal organs. Its causes are not fully understood, but there are theories of its relationship with vascular and nervous disorders. The disease occurs more often in women, but can occur in anyone.
Migraine occurs in a chronic form. The duration of an attack can range from 4 hours to 3 days, and their frequency differs for each patient. Headaches can occur several times throughout your life or recur almost daily. It is believed that the characteristic signs of migraine are pain in only one side of the head, increased sensitivity to light and loud sounds, and the appearance of an “aura.” It appears several hours before the onset of pain and may include the following symptoms:
- lacrimation, pain and pain in the eyes in bright light;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness, weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- rapid heartbeat, possible fainting.
Aura is not a necessary precursor to migraine headache. This set of symptoms occurs in only 20−25% of patients and not before every attack. Migraine usually differs from other types of headaches in its high intensity - it is not relieved by conventional painkillers. If it is confirmed, the doctor will select specific medications that affect the sensitivity of nerve endings and relieve acute pain. It is also important to avoid triggers - factors that provoke the development of migraines. These include sudden changes in weather conditions and climate, lack of sleep, disruption of the daily routine and stressful situations.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Adolescents may develop cardiovascular diseases that cause chronic headaches. They can be suspected by the following symptoms: high or low blood pressure, shortness of breath with minimal physical exertion, coughing and wheezing, frequent bouts of dizziness, chest pain, numbness in the arms and legs. If these symptoms appear, you should urgently undergo a cardiac examination and determine the exact cause of your deterioration. During diagnosis, various disorders may be detected:
- Hypertension (Main article: Headache due to hypertension) - previously considered a disease of the elderly, but in reality it also occurs in children and adolescents. It is characterized by an increase in blood pressure even at rest. This condition puts stress on the vascular walls; over time, they expand and lose elasticity. It is important to control hypertension with medications that lower blood pressure, and your doctor may also prescribe sedatives. If left untreated, the disease can significantly weaken blood vessels and cause hemorrhagic stroke.
- Hypotension (Main article: Headache with low pressure) - decreased blood pressure. This condition is accompanied by weakness, nausea, fainting, as well as pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, numbness of the extremities. With hypotension, it is important to control physical activity, consume enough vitamins and follow a daily routine. Low blood pressure is no less dangerous than high blood pressure - the brain experiences a lack of oxygen (ischemia), which is a predisposing factor to the development of ischemic stroke.
- Atherosclerosis (Main article: Headache as a symptom of atherosclerosis) is a chronic vascular disease that occurs when fat metabolism is disrupted. Cholesterol and lipoproteins are not completely eliminated from the body, but are deposited on the walls of the arteries. Subsequently, the vessels become weak and inelastic, and can be damaged during physical activity and changes in blood pressure. In addition, cholesterol can form blood clots that block the lumen of blood vessels. With atherosclerosis, it is important to follow a low-cholesterol diet and take medications that stimulate its elimination.
In addition to acquired diseases, examination may reveal congenital defects. These include heart defects and anomalies in the development of large vessels. These pathologies lead to impaired blood circulation and nutrition to the brain, causing frequent headaches. They require timely treatment according to a regimen selected by a doctor.
Diseases of the ENT organs
One of the causes of chronic headaches in adolescents is sinusitis. The disease is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses:
- sinusitis – maxillary (maxillary) sinus;
- frontal sinusitis - frontal sinus;
- ethmoiditis – cells of the ethmoid bone;
- sphenoiditis – sphenoid sinus.
Normally, the paranasal sinuses are hollow and filled with air. Their walls are lined with single-layer epithelium. A viral infection or bacteria can lead to inflammation of the walls of the sinuses, increased exudation and filling with various types of contents. Serous or purulent exudate may be found in the sinuses, which must be removed. The disease leads to breathing problems and headaches. Its danger is that sinusitis (usually sinusitis) occurs in a chronic form and can worsen annually.
Another reason why a teenager may have a headache is inflammation of the middle ear. This organ is located in the tympanic cavity and includes several small bones. Inflammation requires urgent treatment, as it can spread to the inner ear, and then to the membranes of the brain. Otitis media is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, including intense headaches and hearing loss. There may also be discharge from the ear canal and impaired coordination of movements.
Other reasons
Headaches in a teenager are not a separate disease, but a symptom of various disorders. They can occur against the background of disruption of the heart and blood vessels, nervous system, and endocrine glands. Often its causes are changes in hormonal levels. Headaches occur in the following cases:
- lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet - these substances are necessary for the proper functioning of cells and tissues;
- stress and unstable emotional state are one of the causes of vascular spasms and ischemia of brain cells;
- diseases of the cervical spine and incorrect posture - cause compression of the nerves and blood vessels that pass to the head;
- head injuries and their consequences may appear after a long time;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia - increased reactivity of the nervous system, which is manifested by various somatic symptoms, often headaches;
- intense physical activity leads to a deficiency of microelements, weakness and headaches.
It is important to understand that headaches occur periodically even in a healthy person. Their causes are unbalanced nutrition, disruption of the daily routine, stress and excessive workload. In most patients, they disappear after rest and normalization of the psycho-emotional state. You should consult a doctor if your headaches occur frequently, 15 days a month or more, the attacks are too intense or prolonged, and are accompanied by additional symptoms.
Types of dizziness
Depending on the duration and frequency of occurrence, such unpleasant conditions in children are:
- one-time, acute;
- regular (periodic);
- permanent.
Sometimes they are accompanied by migraines.
In addition, dizziness of various natures is distinguished:
- psychogenic (occur under strong emotional stress, fatigue, neuroses and mental pathologies);
- associated with brain pathologies (brain tumors, head injuries, cervical spine injuries, concussions and disorders of the blood supply to the brain, autonomic disorders, intoxication with chemicals or drugs);
- ocular in nature (noted in completely healthy children due to visual stimulation, when they have to look at fast moving objects, as well as in pathologies of the eye muscles, when the projection of objects onto the retina is disrupted);
- associated with ear diseases (due to malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus, damage to the nerves and blood vessels of the ear; inflammatory processes).
Features of the cervical spine
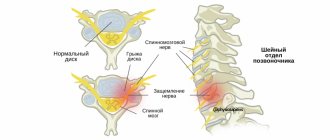
The cervical spine is formed by 7 vertebrae, the upper of which is adjacent to the bones of the skull and is called the atlas. This is the only vertebra that does not have a cartilaginous layer (intervertebral disc) with the next one - the axis. It is also distinguished from all others by its unusual shape.
In general, the cervical spine is more complex than the thoracic or lumbar spine, and at the same time much more vulnerable. Its vertebrae are the smallest, and their structural features ensure high mobility of the neck.
It is thanks to this that a person can change the position of the head in many directions with a fairly large amplitude. But the structural features of the cervical spine also provide a fairly high risk of developing changes in it, which can also occur in children, causing headaches and attacks of dizziness. This:
- Weakness of the neck muscles, as a result of which the spine does not receive proper support, and increased loads, for example, prolonged sitting with a bowed head or prolonged maintenance of another forced position, leads to rapid wear of the intervertebral discs and the development of osteochondrosis.
- The passage of large blood vessels called vertebral arteries through natural openings in the vertebrae of the cervical region. They are responsible for the blood supply to the brain. Therefore, when diseases of the cervical spine occur or there are congenital developmental anomalies, they can become bent or pinched, which leads to a decrease in the amount of blood entering the brain.
- There is a high risk of injury to the nerve roots that extend from the spinal cord in pairs at the level of each vertebra, if even minor deformities occur, including a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs.
Kinetosis
Many children and some adults get motion sickness in transport. This phenomenon is called kinetosis and occurs due to irritation of the receptors of the organs of balance and vision due to acceleration of movement or change in body position. The phenomenon can occur due to strong and prolonged swinging on a swing or being on a merry-go-round, during an airplane takeoff, or in a car while accelerating. Its mechanism is not yet fully understood.
The degree of manifestation of kinetosis varies: from weakness, mild nausea and loss of balance to tinnitus, drooling, vomiting, diarrhea, cold sweat, rapid heartbeat, fainting and severe dizziness. Healthy children quickly recover after eliminating the irritant, but if the cardiovascular system is disrupted, chronic diseases can worsen.
Methods for preventing kinetosis:
- do not overload your stomach with food before the trip;
- on the road, consume candies and drinks with a sour taste (preferably water acidified with lemon);
- use special pharmaceutical products for motion sickness;
- in land transport, choose seats closer to the driver, on a ship or on an airplane - in the middle of the cabin;
- while moving, it is better not to look at sharply changing and swaying objects, and also to read, it is better to direct your gaze into the distance;
- the symptoms of kinetosis disappear during sleep, so it is better when the child sleeps on the road.
Prevention methods
Timely prevention is the key to the health of the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular and nervous systems in adulthood. For teenagers, it is important to follow the following recommendations from doctors:
- monitor your posture throughout the day, especially when working at a monitor, writing or reading;
- carry out light physical activity that will maintain muscle tone;
- include a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the diet;
- undergo regular heart and spine examinations;
- avoid stressful situations;
- establish a daily routine, leaving at least 7-8 hours of time for sleep.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of headaches in adults, children and adolescents. In our center you can undergo a full examination and select an effective treatment regimen. Our main features are high-precision modern equipment, as well as competent, highly specialized specialists with many years of experience in treating headaches of various origins.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
When should you see a doctor?
You should immediately make an appointment with a doctor in cases where dizziness in a child is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe headache and cramps;
- sudden deterioration of vision and hearing;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- rapid movements of the eyeballs (nystagmus);
- tinnitus;
- insomnia.
You cannot do without professional help for headaches and dizziness that occur after head injuries. In this case, the child needs to be put to bed and external stimuli (bright lights, loud music) removed.
Diagnostic methods
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of headaches in adolescents. When visiting a doctor, it is important to accurately identify the location of the pain, the conditions of occurrence and other nuances. To clarify the diagnosis, the following tests may be required:
- electroencephalography – assessment of the activity of brain neurons;
- X-ray of the cervical spine to identify osteochondrosis, curvature and other pathologies;
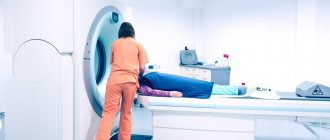
- MRI of the neck and head is an informative technique that allows you to detect neoplasms and cysts, protrusions and hernias of the spine;
- general and biochemical blood tests, study of hormone levels.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a complete examination for headaches of various origins. Examinations are carried out using precise and high-quality equipment using modern technologies. In addition, our center can conduct laboratory tests and complex diagnostic procedures. They allow you to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis in order to begin the stages of treatment.
Which specialist should I contact if my child has dizziness?
In all of the above cases, you should visit a pediatrician. We recommend making an appointment with one of the specialists in the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) by telephone 24 hours a day or calling a doctor at home. JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) is conveniently located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamsky Lane, 10. The medical institution is equipped with modern diagnostic and therapeutic equipment and provides a wide range of services in the field of pediatric medicine. Many problems associated with dizziness are resolved by visiting a pediatrician; sometimes consultation with specialized specialists is required.
If a child experiences short-term loss of consciousness, after an attack of dizziness he does not orient himself in space and time, loses balance and falls with his eyes closed, cannot pick up an object, misses when asked to touch the tip of his nose with a finger, the pediatrician recommends visiting a neurologist. And if you feel dizzy due to tinnitus and impaired coordination of movements, you need the help of an otolaryngologist. Sometimes a consultation with a child psychologist may be required.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the pediatrician should find out the frequency and duration of dizziness attacks, identify provoking factors, connections with changes in body position, as well as taking medications or exposure to chemicals. It is also important to find out if family members have diseases such as migraines, seizures, pathologies of the endocrine system and kidneys, movement disorders, aura syndromes and ataxia, which may be hereditary. After clarifying the details to clarify the preliminary diagnosis, the doctor sends the small patient for laboratory and (or) instrumental research.
At JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) they quickly and thoroughly perform various blood tests, ultrasound, x-rays, electrocardiograms and magnetic resonance imaging. You can invite a specialist to your home to collect material for analysis.
Treatment
Treatment of dizziness in children consists of treating the underlying disease that caused this condition. Often medications are prescribed aimed at strengthening the autonomic nervous system: vitamins, drugs that improve blood supply to the brain and dilate blood vessels. Patients are recommended physical therapy and therapeutic exercises to train the vestibular apparatus. At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), specialists conduct physical therapy classes with children. A properly selected set of exercises can solve many health problems at once. Physiotherapeutic treatment is also carried out using modern professional equipment.
Treatment of headaches in teenagers
Treatment of headaches is complex. The regimen will include techniques to relieve symptoms as well as address the underlying cause. Taking painkillers at home can relieve pain for a short time, but without proper treatment, attacks may recur. The doctor will select medications individually, depending on the exact diagnosis and individual characteristics:
- muscle relaxants - prescribed for problems with the cervical spine;
- painkillers - necessary to relieve migraine attacks, as well as for the symptomatic treatment of headaches;
- means for improving cerebral circulation;
- physiotherapy – a set of techniques to stimulate blood circulation and nerve conduction;
- therapeutic exercises and massage;
- specific treatment for diseases of the ENT organs, which may include antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
For most patients, conservative treatment is sufficient - surgery may be required only in the presence of tumors, hernias, or heart defects. However, for recovery it is important to follow doctors' instructions at home. The medications must be taken in full, and exercise must be performed regularly. In addition, the doctor will recommend getting proper rest, normalizing your daily routine and avoiding activity at night.