The human spinal cord is a complex mechanism that consists of many different “parts”. And each of them is important for our full life. It is thanks to the fact that we have a spine that we move. The reflex function of the spinal cord is one of the main ones it performs. In addition to it, there is also a conductor. It is worth considering these functions in more detail and finding out what each of them is responsible for.
The formation of the spinal cord in the fetus occurs in the mother's womb, and at a time when she is not yet aware of her pregnancy. By the end of the first month, the first foundation of the spinal column is laid. However, it will take some more time for its complete formation after the birth of the child. Some parts of the brain are fully formed when the baby is 2 years old.
What does the spinal cord look like?
Not everyone knows what the spinal cord looks like. Moreover, not all people have an idea of what its role is in the life of every person. It is therefore worthwhile to fill this knowledge gap. In addition, many people mistakenly believe that the brain and spinal cord are separate parts.
To find out what the reflex function of the spinal cord is for, let's try to determine what it looks like. It is impossible to clearly understand where the spinal cord begins and ends. It starts from the first vertebra just below the skull, smoothly connecting to the brain in this area. The division into the spinal cord and the brain is formal, but in reality the spinal cord smoothly passes into the brain. Thus, we can conclude that these two parts are a single whole.
Location of the spinal cord and its membrane
The brain is protected by the cranium, and the spinal cord is hidden in the spine and surrounded by three membranes. The first of them is the most delicate, thin and soft. It contains blood vessels that deliver nutrients to the brain. In other words, the spinal cord is a kind of “courier” for delivering food.
Continuing to talk about how the reflex function of the spinal cord works, we cannot ignore the analysis of the structure of the second arachnoid membrane. There is a special space here called the subarachnoid space. Along the entire length of the spine it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is this that is taken during puncturing for analysis in order to determine the health status of the spinal cord.
The last shell is located on the outside and has a harder surface, which allows it to provide protective functions against various types of external damage.
Major diseases
Spinal pathologies can develop due to trauma, infectious or inflammatory processes. The most common diseases are the following:
- Devic's disease is a pathology characterized by the development of inflammation in the spinal structures and accompanied by the destruction of myelin in them. As a result, transverse myelitis and damage to the optic nerves develop (up to their complete atrophy).
- Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation in the spinal cord. The causes of spinal stroke are often atherosclerotic disease of the aorta or blood vessels supplying the organ.
- A cyst is the formation of cavities in the spinal structures, which are subsequently filled with pathological contents.
- Meningitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the membranes of the spinal cord. Has a viral or bacterial etiology.
- Myelopathy is a collective name that implies the development of inflammatory processes in the spinal cord in different parts of the ridge.
- A tumor is a neoplasm localized in the area of the spinal structures and has a benign or malignant nature. Read more about spinal cord tumors →
- Edema is a pathological condition in which excessive accumulation of fluid occurs in the spinal tissues. Often the anomaly becomes a consequence of a violation of metabolic processes in the organ.
- Brown-Séquard syndrome is a pathological condition that accompanies damage to half of the spinal diameter.
- Tabernacle is the last stage of syphilis, characterized by “shrinkage” of the spinal cord.
- Funicular myelosis is a pathological process that affects the posterior and lateral cords of the joint. Often the disease occurs in combination with perincisional anemia.
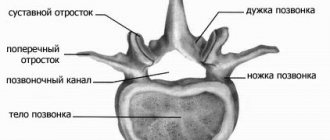
Characteristics of the spinal cord
In adults, the spinal cord reaches 45 cm in length and 1.5 cm in thickness. Its weight, by the most conservative standards, is no more than 35 grams. The entire brain is divided into several sections, from which various roots extend:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar;
- cross;
- coccygeal
Since the reflex function of the spinal cord is carried out, the cervical and lumbosacral regions are the most important parts of the spine. In this regard, they are best protected - nature itself took care of this, making them significantly thicker and denser. It is in these places that important nerve endings are located, the defeat of which can lead to serious consequences. In the cervical region there is a cluster of roots responsible for the movement of the arms. The roots of the lower section are responsible for the movement of the lower extremities.
The human spinal cord controls the activity of all internal organs. Each of them is associated with a specific department. In addition, the entire spinal canal is divided into segments and each of the listed sections has its own number. There are 8 of them in the cervical, 12 in the thoracic, 5 in the lumbar and sacral, and one or two in the coccygeal.
Is it possible to restore conductivity?
Therapy for non-conduction is aimed at stopping the death of nerves and eliminating the causes that provoked the pathology.
Medication therapy
This type of treatment involves prescribing medications that counteract the death of brain cells and also provide blood flow to the damaged area of the brain in the back. In the process of such therapy, the specificity of the conductive function of the brain is taken into account, which is associated with the patient’s age, as well as the severity of the disease or injury. In order to stimulate nerve cells, therapy is prescribed using electrical impulses to help maintain muscle tone.
Surgery
The operation performed to restore conductivity has 2 goals:
- eliminate factors that provoke paralysis of neural connections;
- This is brain stimulation to restore lost functions.
As a rule, before performing an intervention, doctors conduct an examination of the body to identify the location of the degeneration process. Since the list of paths is very large, the neurosurgeon tries to narrow the search area using diagnostics. In case of severe injuries, it is very important to quickly remove the causes of spinal compression.
ethnoscience
The means of such medicine for pathology of impulse conduction should be used with caution so as not to provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition. Often when this problem occurs:
- apitherapy;
- herbal medicine;
- hirudotherapy.
Apitherapy is a treatment with bee stings, which helps restore efferent pathways, in particular when the pathology is caused by a growing hernia, radiculitis or other similar ailments. Bee venom has another useful feature - it provides blood flow to the problem area. In the case of herbal medicine, medicinal plant herbs that improve metabolism and help normalize blood flow are suitable. Hirudotherapy, which involves the use of leeches, helps eliminate congestion, which is inevitable with problems in the structure of the spine.
Complete restoration of neural connections after serious injury is not an easy task. A lot depends on immediate medical attention and timely assistance from a qualified neurosurgeon. But it is important not to forget: the more time has passed since the onset of degenerative changes, the less chance there is of restoring the functional capabilities of the spinal cord.
Gray matter
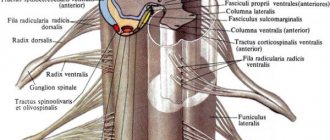
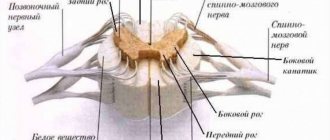
Gray matter or substantia grisea is represented by several columns connected to each other by two plates (anterior and inferior), called commissures. On a cross-section of one of these pillars, you can see that the gray matter in its shape resembles a butterfly with spread wings or the Latin letter H.
In addition, you can also notice that there are projections extending from the substance, which are otherwise called horns. They can be either front, located on the front wall, or rear, running along the back wall. Both the first and second pairs, and have a narrow and wide shape. But in addition to the rear and anterior ones, there are also lateral horns, which contain the centers of the autonomic nervous system.
What is the reflex function of the spinal cord? The fact is that in the anterior horns there is a special type of motor neurons, the processes of which form nerve roots.
In the middle of the gray matter there is a central canal, which is also filled with cerebrospinal fluid. In the upper part, the canal is connected to the ventricles of the brain. In this case, all sections: the ventricles, the central canal and the subarachnoid space take an active part in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Average
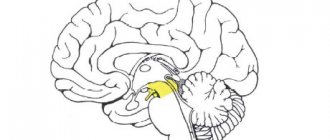
This department is small in size and simple in structure, consisting of parts:
- roofs – visual and auditory centers are included;
- legs - includes pathways.
The midbrain is 2 cm long and is a narrow canal that circulates cerebrospinal fluid. The rate of renewal of cerebrospinal fluid is approximately 5 times a day.
The main functionality of the midbrain:
- Sensory. The contained subcortical centers are responsible for the auditory and visual departments.
- Motor. Along with the oblongata, it ensures the functioning of the reflex actions of the body, helps to navigate in space, and is also responsible for the reaction to surrounding stimuli: the volume of sound or the brightness of light. Responsible for controlling automatic actions: swallowing, chewing, walking, breathing.
- Ensures the functioning of the body's motor system, coordination and muscle tone.
- Conductor. Provides conscious work of body movements.
The midbrain provides control over the work of muscles, giving instructions for straightening or bending, i.e. allows a person to move.
Midbrain nuclei
The nuclei play a special role in the functioning of the body:
- The colliculus nuclei in the upper part belong to the visual centers of the brain. Signals are sent from the retina to the brain, and an orientation reflex occurs - turning the head towards the light. The pupils dilate, the lens changes curvature - this ensures clarity and clarity of vision.
- The colliculus nuclei in the lower part are auditory centers. They are responsible for reflex work - the head turns in the direction of the outgoing sound.
- When the sound is too loud and the light is too bright, the brain reacts to such stimuli - irritation, which pushes the human body to a sharp and quick reaction.
White matter
White matter - substantia alba, envelops the gray matter, is formed by a collection of nerve fibers, which also come in three types:
- front;
- rear;
- lateral.
Moreover, all the roots have a different direction, and some of them are connected directly to the brain and central nervous system (hereinafter simply the CNS). And if the reflex function of the spinal cord is to transmit signals from the motor neurons of the gray matter, then the task of the white matter neurons is the prompt delivery of impulses from the muscles and joints to the medulla oblongata. Thus, the transmission of all commands along the entire spinal cord is realized.
Here are the paths through which all information regarding sensitivity and pain is transmitted. Only before entering the cerebral cortex, the information first reaches the diencephalon, and only then rushes further to its destination.
central nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
- the main part of the nervous system of animals and humans, consisting of a collection of nerve cells (neurons) and their processes.
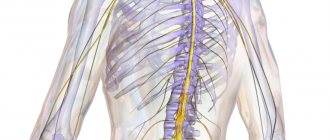
The central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord and their protective membranes.
The outermost layer is the dura mater.
, under it is the arachnoid (arachnoid
), and then
the pia mater
, fused with the surface of the brain.
Between the pia mater and the arachnoid membrane is the subarachnoid space
, which contains cerebrospinal fluid, in which both the brain and spinal cord literally float. The action of the buoyant force of the fluid leads to the fact that, for example, the adult brain, which has an average mass of 1500 g, actually weighs 50–100 g inside the skull. The meninges and cerebrospinal fluid also play the role of shock absorbers, softening all kinds of shocks and shocks that tests the body and which could lead to damage to the nervous system.
The central nervous system is made up of gray and white matter
Gray matter
consist of cell bodies, dendrites and unmyelinated axons, organized into complexes that include countless synapses and serve as information processing centers, providing many functions of the nervous system.
White matter
consists of myelinated and unmyelinated axons that act as conductors transmitting impulses from one center to another. The gray and white matter also contains glial cells.
CNS neurons form many circuits that perform two main functions
: provide reflex activity, as well as complex information processing in higher brain centers. These higher centers, such as the visual cortex (visual cortex), receive incoming information, process it, and transmit a response signal along the axons.
The result of the activity of the nervous system
- this or that activity, which is based on the contraction or relaxation of muscles or the secretion or cessation of secretion of glands. It is with the work of muscles and glands that any way of our self-expression is connected. Incoming sensory information is processed through a sequence of centers connected by long axons that form specific pathways, for example pain, visual, auditory. Sensitive (ascending
) the pathways go in an ascending direction to the centers of the brain.
Motor (descending
) tracts connect the brain with motor neurons of the cranial and spinal nerves. The pathways are usually organized in such a way that information (for example, pain or tactile) from the right side of the body enters the left side of the brain and vice versa. This rule also applies to the descending motor pathways: the right half of the brain controls the movements of the left half of the body, and the left half controls the right. There are, however, a few exceptions to this general rule.
How our brain works
Ascending and descending pathways are responsible for the fast and correct functioning of our body. The latter flows are formed using the red nuclear and lateral pathways. It is thanks to these pathways that the reflex and conduction functions of the spinal cord are carried out. Thanks to the red nuclear spinal tract, involuntary motor impulses are produced. While the lateral corticospinal tracts are responsible for voluntary impulses.
All roots are supplied by personal veins and arteries, which as a result form neurovascular bundles. Each such beam is responsible only for its own segment and works autonomously, analyzing incoming information and transmitting the necessary impulses.
Damage to these bundles leads to serious pathological and sometimes irreversible changes in the human body. And so that specialists can determine which particular bundle is damaged and localize the pain, it is necessary to conduct a whole range of studies.
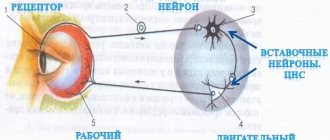
Reflex function
Everything in our body is thought out to the smallest detail, and our body reacts differently to every external stimulus. The defense mechanism is based on reflexes. We sneeze, cough, get burns, flinch from a sharp sound, or react in our own way to gusts of wind. These are all examples of the reflex function of the spinal cord and such actions occur outside of our control.
So that we can respond in a timely manner to any irritant, including critical situations, pain receptors are located throughout the surface of our skin. As a striking example: after touching a hot kettle or any surface, we almost instantly withdraw our hand. The reaction speed is so fast that it is impossible to understand the time frame. In a split second, a reflex ring is formed, which causes the muscles to contract.
Another common case can be cited. If you accidentally swallow a portion of smoke or sniff dust particles with your nose, you will start sneezing or coughing. Thus, it became clear that in such a short time the information was received, processed, and our “defenders” received instructions to free the body from the presence of foreign bodies.
Conductor function
So, it is now clear what the reflex function of the spinal cord is expressed in, we can move on to another, also significant task - conduction. It involves transmitting signals along ascending pathways to the main brain. From it, depending on the situation, the impulse is directed along descending pathways to some organ.
The conductor function allows us to perform meaningful actions:
- take or throw;
- stand up or sit down;
- walk slowly or run;
- draw;
- cut off.
We perform all these actions in everyday life: at home or at work, and usually we simply do not notice.
This whole connection of the brain, spinal cord, the entire central nervous system, internal organs and all limbs makes the human body unique in nature. Even the most modern robot cannot boast of the number of movements that any biological organism can perform.