Doctor of Medical Sciences, professor, oncologist, hematologist, radiologist (radiation therapist) of the highest category, Alexander Pavlovich Seryakov, in an interview with the portal of the Komsomolskaya Pravda publication, spoke about the causes and symptoms of the development of cancer, diagnostic and treatment methods.
Doctor of Medical Sciences, professor, oncologist, hematologist, radiologist (radiation therapist) of the highest category, Alexander Pavlovich Seryakov, in an interview with the portal of the Komsomolskaya Pravda publication, spoke about the causes and symptoms of the development of cancer, diagnostic and treatment methods.
Among all tumors in the central nervous system, spinal cord lesions account for approximately 12% in adults and about 5% in children. What is the cause of these pathologies and how are they treated?
Most often, tumors localized in the spinal cord are detected in people aged 30 to 50 years. Mostly, in about 85% of cases, they affect the membranes of the brain and surrounding structures.
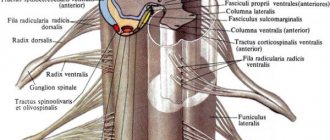
What is a spinal cord tumor
“Spinal cord tumors,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “are pathological neoplasms of a malignant and benign nature that are localized in the spinal cord. They are rare. By location there are:
- intramedullary (18 - 20% of cases) - grow inside the spinal cord;
- extramedullary (80 - 82% of cases) - located near the spinal cord, developing from nearby tissues.
Among benign lesions, the most common are ependymoma (63%) and astrocytoma (30%). Much less common are non-malignant hemangioblastoma and malignant oligodendroglioma.
Causes of spinal cord tumors in adults
The true causes of tumor growth that occurs in the spinal cord have not been determined to date. Scientists have identified a number of risk factors that may increase the likelihood of tumor growth in children or adults, but definitely do not lead to the formation of pathology. These include:
- hereditary predisposition (features of genes passed on from parents to children);
- exposure to substances with carcinogenic effects (chemical dyes, petroleum products);
- development of lymphoma (this is a malignant lesion in the lymphatic system);
- the presence of Hippel-Landau disease (a tendency to grow tumors, both benign and cancerous, is inherited);
- development of neurofibromatosis type 2 (this is a disease associated with gene breakdowns in which multiple tumors are formed - schwannomas or meningiomas in the area of nerves and the nervous system);
- exposure to harmful environmental factors (chemical pollution, radiation exposure);
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle - smoking, drinking alcohol, poor nutrition;
- constant stress;
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- Excessive tanning (in a solarium, on the beach).
Often several factors influence at once and special conditions must be created for the tumor to begin to grow.
Cause and mechanism of development (etiology and pathogenesis) of the disease
The cause of gouty arthritis is a disorder of purine metabolism. Purines are chemical compounds that form the basis of nucleic acids necessary for the formation of DNA and RNA molecules. As cells break down, purines are broken down into uric acid (UA). The latter enters the intercellular space and into the blood plasma, where it combines with sodium, forming a salt - monosodium urate (MUN).
An increased level of urate in the blood (hyperuricemia - GU) may be a consequence of a genetic predisposition (the kidneys do not eliminate MUN completely), high blood pressure (BP), consumption of large amounts of animal food, and alcohol.
With an excess of urates, when they can no longer dissolve in the surrounding fluid (EOR concentration more than 0.4 mmol/l), the salts crystallize, deposit in the articular and periarticular tissues and are surrounded by protein rings. This formation is called tophi. The release of MUN from the tophi causes an immunological reaction: a large number of neutrophils (one of the types of leukocytes responsible for cellular immunity) appear in the synovial membrane and joint fluid.
Neutrophils ingest MUN crystals, which causes the release of proinflammatory (inflammation-causing and maintaining inflammation) cytokines and the development of an acute inflammatory response in the synovium. Acute attacks in the form of synovitis are very painful, but do not leave any consequences. The long-term chronic course of the disease with frequent repeated attacks leads to the destruction of articular cartilage, proliferation of bone tissue, deformation and dysfunction of the joint. Deposition of MUN in the kidneys causes a decrease in their function.
Factors contributing to increased urate levels in the blood:
- the presence in the diet of a large number of meat dishes, offal, eggs, alcoholic beverages,
- overweight;
- taking certain medications - diuretics, aspirin, nicotinic acid, medications to lower blood pressure (Concor), etc.;
- lead poisoning;
- increased breakdown of purines in blood diseases, psoriasis, etc.;
- increased formation of purines;
- impaired renal function and uric acid excretion.
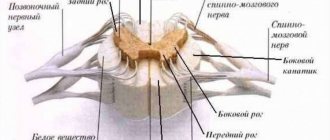
Symptoms of a spinal cord tumor in adults
There are no typical or characteristic symptoms only for a tumor; all signs can mimic other diseases, especially in the early stages. Therefore, you should consult a doctor to determine or rule out the problem with the following complaints.
- Pain syndrome. The most common manifestation of a tumor is pain that occurs in the area of the spine where the tumor began to grow. In the early stage, the pain may be mild or more severe, but there are no significant neurological symptoms. As the tumor progresses, disturbances in sensitivity and movement occur, the pain becomes stronger against the background of coughing or sudden movements, sneezing, physical activity, at night and when moving, tilting the head.
- Movement disorders. Muscle weakness is also possible, which occurs in combination with sensitivity disorders, the phenomenon of muscle atrophy, sharp and sudden contractions, twitching of muscle groups that are relaxed.
- Sensitivity disorders. Sometimes there is no pain, but superficial sensitivity may suffer, while maintaining a deep tactile sense. The patient may not feel pain, temperature, or touch, but perceives pressure and vibration.
- Problems with the functioning of the sphincters. Possible disturbances in urinary functions and, less commonly, bowel movements. This leads to retention of urine or stool.
Also, as the process progresses, scoliosis of the spine may occur, which is formed due to pain, motor dysfunction or destruction of the vertebral bodies.
It is impossible to identify spinal cord tumors externally; they are located quite deep in the spinal canal.
Spondylodiscitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
The most common disease of the spine - osteochondrosis - destroys intervertebral discs, starting from the edges, from the outside. But there is a disease that attacks cartilage tissue. Spondylodiscitis is an inflammatory disease of an infectious nature. One of the manifestations of nonspecific spondylitis leads to destruction of the colloid structure and disruption of the supporting function of the spine.
Causes
Infectious diseases of the spine occur for two reasons:
- penetration of bacteria through the circulatory system (hematogenous infection);
- post-traumatic infection (this method can include complications after spinal surgery).
- Intervertebral discs rarely suffer from inflammation caused by infection, since the cartilage tissue does not contain blood vessels. The growth of the fibrous ring is carried out by the division of unspecialized “chondroblast” cells on the surface of the hyaline layer of the endplates (thin layers between the bone tissues of the vertebrae and the cartilaginous tissues of the disc). The chondroblasts then mature and differentiate into chondrocytes. Through these same plates, fluid, glycoproteins, proteoglycans and minerals enter the fibrous ring. The dense cells of the ring tissues (chondrocytes) are laid out in the intercellular substance “matrix”, rich in fibrous collagen molecules and amorphous colloidal substance. But the nucleus pulposus consists of a colloidal solution with a high water content, which provides a nutrient medium for pathogenic bacteria, isolated from the circulatory system, through which immune cells enter the site of infiltration.
- In many cases, the reason for the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the central part of the MP disc is injury to the fibrous ring. Osteochondrosis of the second and higher stages (the occurrence of protrusions and intervertebral hernias) provides bacteria with a path for penetration through radial microcracks - ruptures of a thinned disc.
- The consequences of surgical removal of an intervertebral hernia can be as dangerous to health as an unsuccessful operation: in 34% of cases of spondylodiscitis, infection occurs with the blood flow through the tissues surrounding the site of excision of the protruding portion of the nucleus pulposus.
The causative agents of infection of the MP disc in most cases are the same pyogenic bacteria that cause the most dangerous lesions of bone tissue (osteomyelitis, tuberculosis):
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- coli;
- Staphylococcus epidermidis;
- proteas;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc.
Hematogenous infection of spinal tissue is secondary in nature, because First, the internal organs of the chest and abdominal cavities and pelvis are exposed to bacterial attack.
For information: according to statistics, the inflammatory process in the center of the MP disc occurs for an unexplained reason in every third case.
Spondylodiscitis most often affects children and adolescents (from 7-8 years to 18-20 years) during the period of active growth of the spine, as well as adults after 45-50 years of age. Like most infectious diseases of the spine, spondylodiscitis is more often detected in men (60-70%). Infectious inflammation of the MP disc can (and does) be multiple: in the case of hematogenous infection, neighboring vertebrae are affected. Most often, such lesions occur in children 8-10 years old.
Mechanism of development and symptoms
Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the central part of the intervertebral disc through the slightest damage to the fibrous ring or blood capillaries in the hyaline layer of the endplate, which closely touches the liquid “core”. Any violation of the integrity of the matrix can become an “open gate” for pyogenic bacteria attacking chondroblasts and chondrocytes. Proteolytic enzymes secreted by bacteria destroy the protein membrane of cells, which allows “aggressor” microorganisms to feed on decomposition products or penetrate the cytoplasm.
The inflammatory-destructive process begins with the endplates. Then the purulent melt, containing living bacteria, lymphocytes, bacteriophages, antigens, antibodies and a mixture of enzymes secreted by dead bacteria and immune cells, spreads in the denser tissues of the fibrous ring and in the thinnest place (in the center of the disc) breaks into the nucleus pulposus.
An abscess in the intervertebral space creates an embolus (bubble) with thinned walls, inside which the increased pressure of the liquid contents causes pain in the spine: the roots of the spinal nerves signal irritation created by the protruding edges of the fibrous ring (as with osteochondrosis protrusion).
A purulent mass can cause infection of the external soft tissues of the periosteum and ligaments located in the paravertebral (paravertebral) space.
Breakthrough of exudates into the spinal canal causes the formation of an epidural abscess, infection of the spinal membranes and compression of the spinal cord. Possible consequences: muscle paresis, dysfunction of internal organs, impaired motor function.
The melting of the cartilage tissue of the MP disc does not remain only within the intervertebral space: an active bactericidal attack of the immune system can damage the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies. Osteolytic enzymes secreted by certain types of pyogenic bacteria and bacteriophages destroy the surface layers of osteocytes. Erosion and demineralization of the bone tissue adjacent to the endplates begins. This may become a prerequisite for deeper infection of the vertebral bodies.
Resorption of the abscess after the cessation of the immune reaction becomes the first phase of the recovery process. Connective tissue cells replace the damaged cartilage layer, which does not restore the intervertebral disc. On the contrary, the less durable connective tissue wears out and the bone bodies of the vertebrae come into contact.
Superficially located osteoblasts (immature bone tissue cells) begin to actively divide along the edges of the vertebral body, differentiate into full-fledged osteocytes, and fill with calcium compounds. The outgrowths (“osteophytes”) grow until they adhere to the outgrowths of the adjacent vertebra and form a strong connection. The process of vertebral fusion is accompanied by blocking of the spinal nerves, which leads to paralysis and severe pain in the back and limbs.
Symptoms of secondary infectious diseases, which include spondylodiscitis, are similar in terms of the immune response:
- increase in temperature (mostly to the level of subfebrile, 37.5-38.2o);
- lack of appetite, weight loss;
- physical weakness, lethargy;
- headache.
Pain in the back and parts of the body depends on the location in the spine. As a result of pinching of the upper roots, nerve impulses from sensory receptors are blocked (the acuity of sensations is weakened to the point of numbness). Blocking of the lower roots, which transmit command impulses from the spinal cord and brain, entails a weakening of the motor functions of the limbs and disruption of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive, excretory and reproductive systems.
Most often, the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae suffer from infectious lesions. Hematogenous infection from infected organs of the genitourinary system and lungs (tuberculosis infection) is the cause of up to 50% of all known cases of spondylodiscitis.
Inflammation of soft tissues in the paravertebral region is determined by swelling and increased blood supply to the affected area. The pain syndrome is expressed in dull nagging pain with attacks when turning and bending. Spasms of the deep muscles connecting the transverse processes distort posture and constrain the movements of the affected part of the spine. Prolonged spasms and dorsomyalgia (pain in the back muscles) lead to poor circulation, which is where muscle fiber degeneration begins.
Spondylodiscitis can occur secretly, “masquerading” as attacks of pain characteristic of osteochondrosis, nonspecific spondylitis, spondyloarthritis. All of them are characterized by radicular syndrome, severe attacks of sciatica, and thoracoalgia. In addition, infectious inflammation does not always cause an active immune response in the body: an increase in temperature of 0.5 degrees will not be considered a full-fledged symptom. The doctor will make a conclusion about the presence of infection in the spine based on tests and visiscopic studies.
Diagnostics
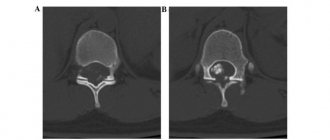
Examination of the soft tissues of the spine using radiography gives ambiguous results: it is not possible to clearly distinguish violations of the integrity of the disc discs. Purulent melting and the formation of abscesses can only be determined by blurring the contours of the endplates and distortion of the outlines of the vertebral bodies.
Computed tomography makes the image more visual, presenting it on the monitor screen as a three-dimensional figure, and allows you to more accurately assess the size of the abscess.
Survey spondylograms of the affected area, performed using an X-ray unit, provide visual information about the erosion of the surface layers and sclerotization of bone tissue along the edges of the vertebrae.
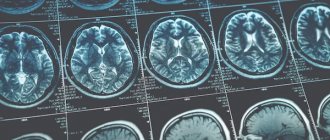
In the diagnosis of spinal diseases, magnetic resonance imaging (or more precisely, “nuclear magnetic resonance imaging”), which is safer and more sensitive than hard x-rays, is more popular. In the photographs, bone structures appear black, but soft tissues filled with water convey all shades of gray and white. This allows you to detect the smallest objects (nodules, infiltrations) and monitor the dynamics of abscess development.
The primary task in case of infectious inflammation is to correctly determine the type of microorganism that causes the disease. The presence of infection is determined by general and clinical blood tests:
- an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in the sedimentation time of erythrocytes - standard tests for the presence of an immune reaction;
- an increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein indicates an active inflammatory process;
- “Pirquet reaction”: the analysis is carried out to exclude secondary tuberculosis from the list of possible diseases (a 15% reaction gives distorted results);
A biopsy or puncture with sampling of exudate from the site of inflammation is the most effective way to obtain reliable results. Microbiological studies reveal abnormally multiplied bacteria and determine the concentration. The sown cultures are also tested for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for infectious diseases of the spine are based on conservative methods: drug therapy, gentle motor regimen (in extreme cases, immobilization, i.e. bed rest). Spondylodiscitis is treated according to the same scheme.
Initially, antibiotics are used to destroy aggressive microfauna (targeted, if the pathogen is known; broad-spectrum, if several types of pathogenic microorganisms are detected in the tests and the conclusion is controversial). During the first 2-4 weeks, medications are administered intravenously. Then, if blood tests (ESR) show positive dynamics, the patient receives less active forms of medications.
When doctors believe that the infectious attack has been suppressed, the patient is prescribed regenerative drugs (chondroprotectors) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Additionally, vitamins and immunostimulants are prescribed.
Immobilization is recommended for patients who have undergone spinal surgery or for those whose inflammation has reached a significant stage of disc destruction. The rigid cradle helps maintain immobility.
Surgical operations to remove the abscess and reconstruct the MP disc are prescribed for 25% of patients. Pumping out exudate (drainage) from the central region of the intervertebral space is the simplest operation for spondylodiscitis. Drainage of internal multi-chamber abscesses (inside the spinal canal) takes longer because it is necessary to create access through soft or bone tissue.
Laminectomies (removal of bone plates) are also performed to release the roots from under the sagging articular processes. Decompression of spinal nerves is the most important reason for performing surgery.
Discectomy (removal of a destroyed disc) and corpectomy (removal of a fragment of the vertebral body) allow you to completely clear the affected tissue. The introduction of spacer grafts (cut from bone structures taken from the ribs or iliac crest) allows the cartilage tissue to begin to recover, and titanium structures that fix the spinal column will temporarily relieve the load on the affected vertebrae. Rehabilitation takes from 3 months to six months. The prognosis for curing spondylodiscitis is always positive.
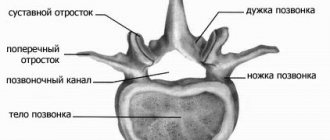
Classification of spinal cord tumors in adults
There are many options for classifying tumors localized in the spinal cord. It is possible to divide into groups according to a number of characteristics - the location of the tumor focus relative to the spinal cord, spine or meninges, features of the histological picture, as well as the specific location of the lesion.
If we divide tumors by origin, they can be classified into two groups:
- primary is tumor tissue that developed from the cells of the spinal cord itself, its roots or membranes;
- secondary are tumors of a different localization that affect the spinal cord (including metastatic ones).
Based on the location of the tumor, they can be divided into several groups:
- extradural tumor - a lesion above the area of the dura mater;
- intradural – tumor under the dura mater;
- intramedullary - grows inside the spinal cord, originating from its cells.
Tumors can be located behind the spinal cord, in front, on the sides, affecting the cervical or thoracic, lumbar or sacral regions.
There is a very wide classification based on the origin and type of cells; tumors are determined based on biopsy data.
Classification
Based on the causes of occurrence, gouty arthritis is divided into forms:
- primary
– associated with hereditary characteristics of purine metabolism and excretion of MUN by the kidneys; - secondary
– the cause of development is some other diseases, nutritional disorders, bad habits, etc.
According to the mechanism of accumulation of MUN, gout is divided into types:
- metabolic
– increased internal production of purines during their normal excretion by the kidneys; - renal
– impaired excretion of uric acid by the kidneys; - mixed
.
By severity:
- mild course
- attacks of gouty arthritis no more than 2 times a year with damage to no more than two joints; single tophi no more than 1 cm in diameter; there are no complications from the kidneys or impaired joint function; - moderate severity
- no more than 5 attacks per year affecting no more than 4 joints with minor changes in cartilage and bone tissue; a large number of small tophi; stones in the kidneys; - severe
– attacks of gouty arthritis more than 5 times a year, multiple large tophi and arthritis; decreased kidney function.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is a step-by-step process that allows you to determine the size and type of tumor and draw up a plan for its treatment. First of all, the doctor is interested in the patient’s complaints, symptoms, and medical history. It is important when symptoms developed and how they changed over time.
A full neurological examination is also carried out - determination of muscle tone, reflexes, muscle strength, spinal mobility, sensitivity.
To refine the pathology you need:
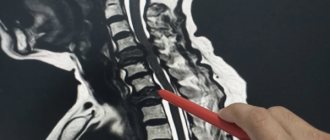
- MRI with contrast - this method helps to determine the condition of the entire spinal cord, its structures and determine the tumor;
- CT myelography is a technique for assessing the tumor border;
- diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor MRI;
- scintigraphy;
- direct angiography.
After clarifying the type, location and size of the tumor, a treatment plan is drawn up.
Spinal biopsy is a reliable tumor diagnosis
Despite the development of modern diagnostic methods, spinal biopsy is still one of the main examination methods. Only with its help can you obtain a “piece of tumor” for further research, obtain information about the histological structure of the tumor, conduct a histochemical study, find out the degree of its malignancy, establish the primary nature of the tumor and, if necessary, select chemotherapy drugs and the dose of gamma therapy.
A tumor biopsy in the vertebra can be performed in 2 ways:
- Puncture biopsy - using a navigation device, a special needle is passed to the desired point of the affected vertebra, from where a part of the tumor is taken for examination.
- Endoscopic biopsy is the most modern type of biopsy, however, in cases of vertebral tumors, its use is not possible in all cases.
The biopsy is carried out under the control of a navigation device, which allows you to take material from any, even inaccessible place.
Modern methods of treatment
“The main type of treatment,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “is a neurosurgical operation in which the tumor is completely removed and decompression (removal of compression) of the spinal cord is performed. Micro-neurosurgical techniques, intraoperative neuroimaging and neuronavigation are often used.
For malignant tumors of the spinal cord, in addition to surgical treatment, the patient may be prescribed chemotherapy and radiation therapy (stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery using linear accelerators of the CyberKnife type).