Various types of tumors in the brain account for approximately 6% of all tumor formations in the human body. They occur in approximately 10 - 15 cases per 100 thousand population.
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ALEXANDER SERYAKOV MD, professor, oncologist, hematologist, radiologist (radiation therapist) of the highest category, leading oncologist of the SM-Clinic holding »
What is a brain tumor
“Brain tumors,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “are intracranial neoplasms, including both tumor lesions of the brain tissue itself, as well as nerves, membranes, blood vessels, and endocrine structures of the brain.
Such formations can be benign or malignant in nature. Benign tumors put pressure on certain areas of the brain directly adjacent to the tumor and can lead to disruption of the functioning of individual structures in the brain itself.
A malignant tumor is distinguished by very rapid growth and the ability to grow into the surrounding tissues. Glioma is one of the most common types of malignant brain tumor. Its most aggressive type is glioblastoma. It grows quickly and has no clear edges. It is difficult to treat, with a high relapse rate.
Other malignant brain tumors include:
- meningiomas – tumors of the meninges;
- neuroepithelial tumors (gangliomas and astrocytomas);
- Neuromas are special tumors from the membranes of nerve cells.
Causes of brain tumors in adults
Scientists have not yet determined the exact cause of tumors, but there are assumptions about the connection of their growth with the effects of radioactive radiation, toxins penetrating the body, and environmental pollution.
Children may develop congenital neoplasms - one of the reasons is considered to be intrauterine development disorders. A possible factor may be traumatic brain injury, which can also intensify an already existing process.
There is evidence that some brain tumors can develop after radiation therapy prescribed for the treatment of other pathologies, immunosuppressive treatment, and HIV infection. There is a hereditary predisposition to certain types of brain cancer. But for many people the cause remains unknown.
About 10 - 30% of brain tumors are of metastatic origin - these are cells that are carried by the blood flow (less often lymph) into the brain vessels, tissues, and membranes. About 60% of such tumors are multiple.
Most often it metastasizes to the brain:
- in men – lung damage, colorectal cancer, kidney damage;
- in women - breast cancer, melanoma, colorectal and lung cancer.
Intracerebral metastases occur with cancer of the uterus, digestive tract or prostate.
REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS
THE RUSSIAN - JAPANESE ONCOLOGICAL CENTER HAS DEVELOPED REHABILITATION PROGRAMS FOR PATIENTS AFTER TREATMENT, CHEMOTHERAPY AND RADIATION THERAPY.
Rehabilitation is aimed at areas of the brain that are responsible for important body functions: speech, movement, sensory organs, thinking, memory.
With rehabilitation treatment, the risk of complications after chemotherapy is reduced to a minimum. The patient does not experience severe symptoms after the procedures and does not lose quality of life.
Feel the quality of life after rehabilitation!
The patient should never forget that brain cancer is an aggressive type of cancer and develops quite quickly. Relapses are possible, so we make sure to monitor our patients at least 2 times a year and repeat the supporting set of rehabilitation measures after a year or a year and a half.
Our experience shows that treatment of brain cancer is always possible, even regardless of its stage and location.
The developed and tested methods of our Oncology Center are aimed at curing this disease, reducing its symptoms, preventing the progression of the disease and improving the quality of life!
Signs of a brain tumor in adults
Focal symptoms are often among the first to appear.
They arise due to the pressure of the tumor on the surrounding tissues and chemical reactions to foreign cells, hemorrhages, blockage of blood vessels with a tumor embolus, compression of tissues and nerves. As the tumor grows, symptoms from neighboring areas appear, then general brain symptoms. If the tumor is large, a so-called mass effect may occur (the main structures of the brain are displaced, causing the cerebellar region to become wedged into the opening of the skull). One of the early signs is headache. It is usually local and occurs due to irritation of blood vessels, nerves, and meninges. There may be diffuse pain throughout the head, which is typical of meningeal lesions. The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, deep, intense or bursting.
Another sign is vomiting, which is not associated with food intake. It may or may not be at the peak of the headache.
Dizziness occurs in the form of dips, rotation of the body or objects around.
Possible muscle weakness, muscle hypertonicity, uneven on one and the other side of the body, changes in tendon reflexes. Muscle-joint sensations may also suffer - sensations during movement, pressure, vibration.
For many tumors, convulsive syndrome is typical - sometimes it becomes the first sign of brain damage. There may be absence seizures or tonic-clonic seizures, Jacksonian epilepsy. Some people also experience an aura before attacks. As the tumor grows, there may be partial seizures or decreased activity of the lesions.
Some people may have mental disorders. Sloppiness, lack of initiative, aggression, euphoria or causeless gaiety, apathy, complacency can also be signs of brain damage. Tumor growth increases the severity of symptoms. Visual hallucinations, severe memory disturbances, attention problems and thinking problems may occur.
Possible problems with vision, congestion in the area of the optic nerve - these are floaters before the eyes, blurred vision, fog, blurred vision. Fields of vision may be lost.
Additionally possible:
- hearing loss;
- aphasia;
- ataxia;
- eye movement disorders;
- hallucinations (auditory, gustatory);
- autonomic dysfunctions.
If the hypothalamic-pituitary region is affected, hormonal metabolism suffers.
PDT is the best alternative and auxiliary option for complex restoration
Long-term studies in the Russian Federation and abroad have proven the high effectiveness of photodynamic therapy (PDT) at the time of surgery and after it. Natural or artificial concentrates are used as a photosensitizer (PS). The patented method of Dr. Borisov Selective chronophototherapy (2341307) (ICP), which is based on photodynamic therapy, is capable of activating a cascade of biochemical and cellular reactions to regulate the level of immune status indicators. A special substance is introduced into the body - chlorin E6 (a natural photosensitizer of the latest generation), which accumulates in cancer cells. A laser beam is sent to the site of accumulation, capable of synchronizing with the patient’s rhythms, which makes it possible to reduce or increase the intensity of the effect. Penetrating to the required depth, it concentrates on pathological cells, destroying them, without touching healthy ones. Over the course of several months, the tumor disintegrates.
In our clinical practice, we use highly purified E6 chlorine, chlorophyll, processed using a unique technology and having a wide spectrum of action:
- diagnostic and antitumor;
- antiviral and antibacterial;
- normalizing hormonal status;
- improving metabolism, circulation and blood properties;
- increasing immunity.
It is capable of localizing in pathological areas and being activated under the influence of the red spectrum of hardware radiation, after which it begins to release high-energy molecular oxygen. Which, in turn, is considered a powerful oxidizing agent that destroys tumors and cleanses the body of them.
Carrying out ICHFT0, which is based on PDT, when removing meningiomas of the brain and spinal cord increases the inter-relapse period and human life expectancy.
Stages of brain tumor in adults
A typical stage for a cancerous lesion determines treatment options, prognosis, and typical signs and symptoms.
There are 4 stages in total - from the mildest to the extremely severe. The first stage is when one of the parts of the brain is affected by a small neoplasm, a nodule, there is no penetration into neighboring tissues, there is no pressure on the surrounding areas of the brain.
The second stage - the tumor grows slowly, but there is penetration into neighboring areas;
The third stage - the tumor changes its structure, cells divide faster, neighboring sections and tissues grow;
Stage four – the tumor is large, grows into neighboring brain structures, and distant metastases are possible.
Diagnostics
The first examination is carried out by a neurologist.
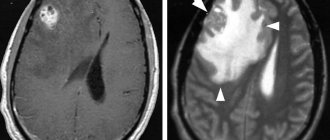
The doctor evaluates general complaints, conducts an examination, examines muscle tone, reflexes, communication, emotions and cognitive functions. EEG and echo-encephalography are also performed. A visit to an ophthalmologist is indicated to assess the condition of the fundus, acuity, and visual fields. Suspicion of a tumor formation is an indication for a CT or MRI of the brain. Angiography of cerebral vessels, PET scan and other complementary examinations may be prescribed. In some cases, a biopsy can help determine the type of cancer, but it is not possible in all cases.
Modern methods of treatment
“The volume of treatment is selected depending on the course of the brain tumor,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov.
– The most effective is surgical removal of the tumor. The use of surgical microscopy and navigation allows for radical removal of the tumor and minimizes injury to healthy tissue. If the tumor cannot be completely removed, after its partial removal, the patient is prescribed radiation, as well as chemotherapy, targeted (“targeted”) or immunotherapy. For small malignant tumors (up to 3 cm), stereotactic radiosurgery is possible (using Cyber-Knife linear accelerators or Gamma-Knife gamma machines). To remove tumor tissue, many beams of radiation are used at once, which are directed at one point or collected into one beam. Its direction will constantly change during the irradiation session, but the beam necessarily passes through the tumor tissue.
For large tumors, and especially in cases where it is impossible to surgically remove the tumor, classical external beam radiation therapy is used. In some cases, it is used after surgery to reduce the risk of relapse (regrowth).
Chemotherapy is carried out with cytostatic drugs, taking into account the type of tumor. The effectiveness of chemotherapy increases significantly if it is combined with radiation therapy.
Targeted therapy in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy improves survival of patients with aggressive brain tumors. Most often used in the treatment of glioblastomas.
Currently, methods of using immunotherapy for malignant tumors (antitumor vaccines, immunotherapy drugs) and its integration into existing standards of treatment are being considered.
Activities carried out for rapid recovery
Immediately after the operation, medications are prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure, reduce swelling, and eliminate inflammatory processes. Physiotherapy is used with devices to relieve pain, stimulate cognitive abilities, and activate regenerative and metabolic processes.
After discharge, you will have to refrain from physical activity for some time. Strict adherence to the daily routine, diet, and mental peace are required. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, iodine, magnesium, and calcium is recommended. Limit intake of salty, spicy and meat dishes, foods that cause increased gas formation.
We recommend taking VIALIFE capsules or VIALIFE solution, because they contain the highest possible concentration of chlorophyll, which:
- strengthens the immune system;
- enhances cell regeneration;
- saturates tissues with oxygen;
- has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, detoxifying effects.
Upon completion of the rehabilitation period, after 2 months, it is advisable to begin physical exercise to restore strength, health, and performance:
- morning exercises;
- swimming in the pool;
- daily walking;
- occupational therapy in case of loss of some skills in performing everyday tasks. Such as using household appliances, dressing independently, taking a hygienic shower, etc.
It is imperative that you regularly visit your doctor for examination and undergo examination.
Prevention of brain tumors in adults at home
Prevention of brain tumors, according to oncologist Alexander Seryakov, generally includes:
- healthy lifestyle;
- optimal physical activity (preferably in the fresh air);
- complete rest;
- giving up bad habits (for smokers and alcohol abusers, the likelihood of developing brain tumors increases by almost 30%);
- a diet rich in fruits and vegetables;
- limiting stressful situations (or changing your attitude towards negative circumstances).
How long do they live after glioblastoma removal?
When faced with glioblastoma, many patients immediately give up, looking for a complete answer to the question “what is the life expectancy with this diagnosis”? At the same time, realizing that even their attending physician will not be able to give them an exact answer.
The answer to this question depends on:
- patient's age group;
- localization of the tumor;
- presence of metastases.
In order to improve your condition and maintain your body, doctors recommend adjusting your sleep and rest patterns, minimizing stressful situations, eating a balanced diet and giving up all bad habits. Timely detection and seeking qualified medical help can extend the life of a cancer patient by more than 10 years. Such an outcome is possible only with a positive course of the disease and with proper compliance with all the recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician.