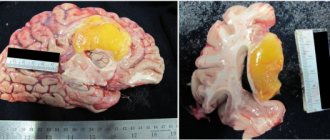
A malignant brain tumor, often called brain cancer, is a neoplasm of modified cells that is characterized by relatively rapid growth and the ability to grow into neighboring tissues and other organs. This is an extremely dangerous pathology, since at an early stage, when it is quite easy to cope with, it is discovered only as a result of special studies. The disease can develop in a person of any age and gender; even cases of congenital neoplasms have been reported. As the tumor grows, it takes up more and more space in the skull, which leads to compression of other tissues and a gradual increase in intracranial pressure. Therefore, even a benign cell formation over time acquires a malignant course and can lead to death.
Kinds
Based on the method of tumor formation, oncologists distinguish between brain cancer:
- primary – formed directly from cells belonging to the organ;
- secondary, or metastatic - occurs when metastases from other organs of the body penetrate into the skull.
Primary neoplasms occur 3-4 times less frequently than secondary ones and account for approximately 1.5% of all cases of cancer. The overall incidence of cerebral tumors is 5-6%, and the risk of their development increases with age. In children, this disease is extremely rare - statistics record no more than 2.4 cases per 100 thousand population under the age of 18 years.
Depending on what tissue became the source for the neoplasm, the following types are distinguished.
- Astrocytomas (gangliomas), which develop directly in brain cells and account for up to 80% of all clinical cases.
- Meningiomas, the source tissue for which is the membranes of the brain, and their cells rarely acquire malignant characteristics, although the growth of tumors in any case negatively affects the functioning of the brain.
- Neuromas that grow from the myelin sheath of nerve fibers inside the skull.
- Pituitary adenomas form in the tissue of the pituitary gland and exhibit malignant features in rare cases.
Symptoms
Signs of brain cancer are divided into general cerebral, i.e. manifested in all types of disease without exception, and focal ones, from the totality of which one can form a primary idea of the localization of the neoplasm.
Common symptoms of a brain tumor that appear as a result of increased intracranial pressure include:
- the appearance of constant headaches, which intensify with sudden movements of the head and are not relieved by medications;
- sudden dizziness, nausea and vomiting, fainting;
- feeling of constant fatigue, drowsiness;
- the appearance of problems with visual perception – blurred pictures, “sights”, hallucinations;
- violation of spatial orientation and coordination.
In turn, focal symptoms of brain cancer depend on the location of the tumor and allow localization of the pathology:
- in the forehead area - due to weakening of one half of the body, loss of smell, change in the patient’s character;
- in the temple area - for convulsions, speech disorders, developing forgetfulness;
- in the crown area - for speech impairment, loss of sensitivity of half the body;
- in the occipital lobe - due to loss of vision in one of the eyes;
- in the cerebellum - by vibration of the eyeball, lack of coordination of movements, spasm of the neck muscles;
- in the brain stem - due to unsteadiness of gait, disturbances in swallowing and difficulty speaking, weakness of the facial muscles.
In order not to miss the onset of the disease, if even one or two of the first signs of brain cancer appear, you must consult a neurologist and undergo an examination.
Head and Neck Cancer: Symptoms and Signs
Patients with head and neck cancer often experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes patients with head and neck cancer do not experience any of the following changes. Or the cause of the symptom may be a non-cancer disease.
- Non-healing inflammation or wound
- Red or white spot in the mouth
- Lump, lump, or mass in the head or neck area, painful or painless
- Long-lasting sore throat
- Putrid odor from the mouth that cannot be explained by hygiene
- Hoarseness or hoarseness of voice
- Frequent nosebleeds and/or unusual nasal discharge
- Difficulty breathing (including nasal breathing)
- Double vision
- Numbness in the neck or weakness in the occipital region
- Pain or difficulty chewing or swallowing even small pieces of food
- Jaw pain
- Bloody discharge in saliva or phlegm, mucus that is secreted into the mouth from the respiratory tract
- Loose teeth
- Dentures that no longer fit
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Ear pain or infection
If you are concerned about any of the above, you should contact a specialist. Your doctor will ask, among other things, how long and how often you have been experiencing the symptom(s). This conversation will help in making the correct diagnosis.
Once cancer is diagnosed, symptom relief remains an important part of cancer care. This may be called palliative or supportive care. It often begins soon after diagnosis and continues throughout treatment.
Causes and risk factors
As medical practice shows, the main cause of brain cancer is metastasis from other organs affected by the disease. For primary neoplasms, risk factors have been identified that increase the incidence of pathology:
- old age – 50 years and above;
- having a close relative with a brain tumor;
- negative impact of radioactive exposure;
- genetic pathologies;
- prolonged contact with certain chemicals;
- brain injury or concussion.
Having one or more of these symptoms does not mean that you will definitely get sick. However, in this case it is necessary to be especially careful and undergo examination if warning symptoms appear.
Where to go if you have brain cancer?
The diagnosis and treatment of brain cancer and astrocytoma are the most successful in Germany and other developed countries, which is confirmed by patient survival statistics. If you want to use the services of German doctors, please contact ]Booking Health[/anchor]. We organize treatment abroad.
Our advantages:
- A team of doctors who understand modern methods of treating various diseases will select the best clinic for the treatment of brain cancer for you.
- Thanks to direct contracts with the best medical institutions in Germany, you can save up to 70% of the cost of the treatment program. In addition, the waiting time for a doctor’s appointment will be reduced.
- The initially agreed cost of treatment is guaranteed not to change. Even if complications arise and additional therapeutic measures are required, all unforeseen expenses will be covered by insurance.
- A full package of services: we will completely organize the entire treatment process in Germany, provide an interpreter, and provide transfer from the airport to the clinic.
- Absolute transparency of financial relationships: you can always find out what services you paid for and in what volume. Unused funds after treatment will be returned.
To take advantage of all the benefits of German medicine, leave a request on our website. After processing it, we will contact you and you will be able to receive comprehensive advice on the treatment of brain cancer abroad.
Stages
Cancer specialists distinguish four main stages characteristic of brain cancer.
- A small number of cells are affected, the size of the neoplasm is small, but it is already beginning to have an effect, expressed by a feeling of weakness, drowsiness, and periodic headaches without clear localization. If you do not neglect these symptoms of early stage brain cancer and undergo examination, then the detected tumor is cured in almost one hundred percent of cases.
- The tumor grows and spreads to neighboring tissues that are located next to it. Symptoms intensify, become more pronounced and noticeable. Some patients already at this stage develop convulsions and seizures similar to epileptic ones. The chances of successful surgical treatment remain, although not to the full extent.
- The growth of the tumor accelerates, it grows into healthy tissue, and there is a threat of death. A characteristic sign of the third stage is nystagmus - constantly moving pupils. There is a high probability that the tumor will be recognized as inoperable, in which case the patient receives only symptomatic treatment.
- The tumor affects all brain tissue located near it and rapidly increases in size. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply, possibly falling into a coma. At this stage, surgery to remove the pathological formation is impossible, and the prognosis is unfavorable. Therapy is aimed only at alleviating the patient's suffering.
In primary brain tumors, there are no metastases to other organs. A secondary disease most often develops due to the patient’s existing melanoma, kidney cancer, sarcoma, or colon tumor that metastasizes to the brain.
How to detect a brain tumor?
A multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of brain tumors abroad involves high-quality diagnostics, correctly selected therapeutic procedures, a rehabilitation course, social adaptation of the patient, and qualified psychotherapeutic assistance.
The main methods for detecting tumor formations in the brain today are:
- CT scan . This study is carried out for suspicious pathology in the early stages of the disease.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance . The procedure allows you to obtain an image of the tumor and determine its characteristics.
- Whole body PET . The examination helps diagnose the primary tumor, as well as assess the spread of abnormal cells if there are metastases. This method is often used in the diagnosis and treatment of brain cancer abroad.
In addition to these methods, to clarify the diagnosis after a consultation of specialists, other additional diagnostic procedures may be required, including ventriculoscopy and stereotactic biopsy, which are related to complex procedures.
Diagnostics
As a rule, diagnostic examinations for brain oncology are carried out as follows. You come for a consultation with a neurologist, who listens to complaints, conducts an examination and prescribes instrumental studies.
- CT scan of the head, which detects the presence of neoplasms already at the first stage.
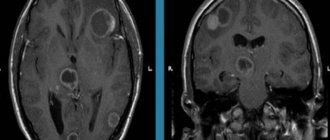
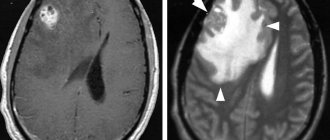
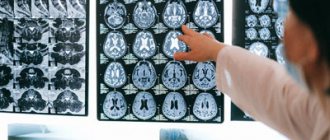
- MRI of the brain with contrast, which is performed for early detection and localization of cancer.
- Angiography, which reveals abnormalities in the structure of the blood vessels of the brain.
- Scintigraphy, or radioisotope contrast study, is effective for the early detection of tumors.
- Lumbar puncture, through which a sample of tumor tissue is obtained for subsequent analysis.
The types of studies are selected by the doctor depending on the symptoms. The totality of the data obtained allows not only to identify a tumor, but also to accurately localize it, determine the size and stage of development of the disease, which is important for determining subsequent actions.
Advantages of the MRI method
Magnetic resonance imaging has a number of advantages over other methods of diagnosing diseases:
- The effectiveness of this research technique is due to the fact that the resulting images are of high quality. The studied areas are viewed with the most contrast and clarity. During a detailed examination, it is possible to obtain photographs from different angles and 360-degree positions. It is possible to display 3D images on the computer screen.
- With MRI diagnostics, specialists have the opportunity to clearly distinguish the type of deviation from the norm, detect the disease at an early stage, determine the location and degree of growth, find out the exact size and level of “pressure” that the tumor exerts on adjacent tissues. The accuracy of the examination results directly affects the speed of subsequent care. The earlier the problem is detected, the greater the patient's chances of recovery.
- The safety and harmlessness of the procedure, proven by thirty years of experience in using this method. The absence of harmful radiation in no way affects the deterioration of the patient’s condition.
- If constant observation and monitoring of the course of the disease is required, MR diagnostics can be performed repeatedly and with high frequency, in contrast to CT of the brain. It is harmful for cancer patients to be exposed to additional irradiation effects on the body.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics allows you to “get” to hard-to-reach places where tumors are localized, for example, near the bone shell or deep in the brain body.- The high accuracy of the examination results allows diagnosticians to determine what methods to use for treatment, whether surgical intervention is possible and how effective and risky it will be. MRI does not have any contraindications for frequency of use, so it can be used in preoperative preparation and postoperative monitoring.
Treatment
Since the brain is an extremely specialized organ, treatment of tumors is the prerogative of a neurologist or neurosurgeon if it is decided that surgery is necessary. The choice of method depends on the location of the pathological formation and the stage of its development.
- Surgical intervention allows you to completely get rid of the disease only in some cases, when the tumor is located in a place convenient for penetration and affects a minimum of tissue. More often, surgery is performed to reduce the severity of symptoms.
- Chemotherapy can be administered not only to adults, but also to children; drugs are administered orally or by injection.
- Radiation therapy is usually needed to remove any remaining tumor that cannot be removed during surgery.
- Corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce tissue swelling and inflammation. They have no effect on malignant cells.
- Symptomatic medications, which include painkillers, anticonvulsants and antidepressants, are prescribed to make the patient feel better and reduce symptoms.
Rehabilitation
To return the patient to a normal lifestyle after treatment, the doctor may prescribe rehabilitation procedures depending on the nature and extent of brain damage.
- Physical therapy is necessary to restore motor coordination and muscle strength.
- Classes with a speech therapist are useful for speech disorders.
- Treatment by a psychologist or psychotherapist is required for patients with developed depression, memory and thinking disorders.
- Taking anticonvulsant medications to prevent epileptic seizures.
After completing treatment, you must remember that brain tumors can recur, and you need to undergo regular preventive examinations.