Human speech belongs to the highest cortical functions; in order to pronounce the simplest sentence, the integrative activity of many parts of the brain and the vocal apparatus is required. This is the most important condition for communication, without which it is impossible to communicate with your own kind. Features of speech directly depend on education and horizons. Speech impairment in an adult always indicates a serious illness. Speech disorders can be congenital or acquired.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,500
Make an appointment
Congenital disorders begin in early childhood and accompany a person throughout his life, practically impossible to correct. Acquired speech disorders always have a pathological cause, organic or functional. Organic causes include damage to the structures of the brain and speech apparatus. Functional include various environmental factors that temporarily disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These are stress, infections, trauma, mental illness.
The following types of speech disorders are distinguished:
- change in tempo - acceleration (tachylalia) or deceleration (bradylalia);
- nasality;
- stuttering;
- dyslalia or tongue-tiedness - “swallowing” of syllables or letters, slurred and unclear speech;
- aphasia or the inability to speak, which in turn is divided into several types - motor, sensory, -
- conductive or conductive, acoustic-mnestic, optical-mnestic, total;
- dysarthria - impaired articulation;
- oligophasia (“few words”) - a condition after an epileptic seizure, when a person is deafened by the convulsions he has experienced and speaks little and in monosyllables;
- mutism (silence);
- dysphonia (hoarseness) or aphonia (lack of voice).
Only a doctor can accurately determine the type of speech disorder; a complete diagnosis sometimes requires a neurolinguistic examination performed by a psychologist and speech therapist. Almost always it is necessary to study the characteristics of blood flow, the affected area, the site of injury, or to identify an infectious or toxic agent.
Change of pace
A normal speech rate is 10 or 14 words per minute. The most common reason for a change in pace is emotions or mental disorders. Stressful influences - an unfamiliar environment, communication with an authoritarian person, an argument - can cause both acceleration and deceleration. Long-term acceleration of speech is observed in affective psychoses (the old name is manic-depressive) and other conditions when thinking is accelerated. Speech also accelerates in Parkinson's disease, accompanied by shaking paralysis. The rhythm and fluency of pronunciation suffers.
Slow speech with a small vocabulary is typical for persons with mental retardation or dementia that has developed as a result of various diseases of the nervous system. Words and sounds are drawn out, pronunciation is unclear, wording is primitive or incorrect.
Nasality can be a consequence of both a displacement of the nasal septum and paralysis of the muscles of the palate. A transient nasal sound is familiar to everyone; it happens with a severe runny nose. If there is no respiratory infection, then nasality is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Tips for parents
It is important for the child to create a positive speech environment.
Repeatedly talk through ordinary, daily activities:
dressing, washing, eating, bathing, walking, getting ready for bed, going to bed, cleaning the room and toys, cooking. All these processes must necessarily be accompanied by the speech of adults.
Say nursery rhymes, tongue twisters, proverbs, proverbs, sing songs
.
Talk to your child as often as possible
, listen carefully to his answers to questions. This will not only improve your baby’s speech, but will also establish a trusting relationship between you.
Read together
, discuss what you read, illustrate the plot together, discuss the drawings.
Stuttering or logoneurosis
Develops in adults after severe fright or unbearable stress against the background of congenital insufficiency of the speech apparatus. The reasons may be outwardly harmless, but affect concepts that are important to a person - love, affection, family feelings, career aspirations.
The basis is a neurotic disorder. Logoneurosis often intensifies in situations of tension - at crucial moments, when speaking in public, during an exam, during a conflict. Several unsuccessful attempts or tactless behavior of others can lead to a fear of speech, when a person literally “freezes” and cannot utter a word.
Logoneurosis manifests itself as long pauses in speech, repetitions of sounds, syllables or entire words, as well as spasms of the lips and tongue. Trying to “skip” a difficult place dramatically increases stuttering. At the same time, there are no specific words or sounds on which a person stumbles; speech may stop on any word.
Stuttering is always accompanied by respiratory neurosis, when respiratory spasms occur. Almost always, along with the fear of speech, a person is worried about anxiety, decreased self-esteem, internal tension, sweating, and sleep disorders. Additional movements in the form of tics of the facial muscles, movements of the arms and shoulder girdle are common. Successful treatment of stuttering is possible at any stage; it is important to consult a doctor in time.
How to maintain a healthy voice and normal speech
Here are some simple tips to help keep your voice healthy and strong for years to come.
- Reading aloud keeps your voice active. Do you like to start your day with a newspaper? Read aloud for 10-15 minutes every morning. It doesn’t matter to whom - your spouse, neighbor, pet or just yourself. This is a great way to train your voice daily.
- The voice is a reflection of our health. He will be fine when the whole body is in good shape. So be sure to stay physically active. Even something as simple as walking will improve your fitness and maintain your voice.
- The larynx should remain moist and elastic, so drink six to eight glasses of clean water a day. Limit caffeine and alcohol, which dry out your throat. Include grapes, melons, cucumbers and other vegetables and fruits that contain a lot of water in your diet. Use a humidifier, especially during the heating season, the recommended humidity is 30%. And, of course, don't smoke!
- The more you use your voice, the stronger it becomes. Be sociable and participate in the conversation. The worst thing you can do is isolate yourself and remain silent. But avoid shouting and loud singing.
Age-related voice problems can begin as early as 50 years of age. But even if there are no changes yet, use these tips. Just as physical training programs help keep your body strong, working on your voice will help keep it healthy.
Aphasia
This is a violation of the structure of speech or understanding of its meaning.
Motor aphasia is a sign of damage to Broca's area or the lower parts of the frontal lobe. The person understands the spoken speech, but cannot say anything. Sometimes individual words or sounds break through, often obscene. This speech disorder is almost always accompanied by motor disorders in the form of paralysis of the right limbs. The cause is blockage of the superior branch of the middle cerebral artery.
Sensory aphasia is the inability to understand the meaning of speech, develops when the temporal gyrus of the hemispheres or Wernicke's area is damaged. The person does not understand the spoken speech, but fluently pronounces a set of words devoid of any meaning. The handwriting remains the same, but there is no essence in what is written. Often combined with visual impairments, the person is not aware of his defect. The cause is blockage of the lower branch of the middle cerebral artery by an embolus or thrombus. Conductive or conductive aphasia - a person understands speech, but cannot repeat anything or write from dictation. Speech consists of many mistakes that a person persistently tries to correct, but cannot. The white matter of the brain in the supramarginal gyrus is affected.
Acoustic-mnestic - a person cannot pronounce long complex phrases, making do with a minimal primitive set of words. It is extremely difficult to find a word. Develops with damage to the left temporal region, characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.
Optical-mnestic - a person recognizes objects, but cannot name or describe them. The loss of simple concepts from everyday life impoverishes both speech and thinking. Develops in toxic and dyscirculatory encephalopathies, as well as brain tumors.
Total aphasia - there is no ability to understand speech, nor to say or write anything. Characteristic of cerebral infarctions in the middle cerebral artery basin, often accompanied by paralysis, visual impairment and sensitivity. When blood flow through the middle cerebral artery is restored, speech may be partially restored.
Diagnostics
The tactics of diagnostic examination depend on the suspected cause of slurred speech. The algorithm consists of medical and pedagogical aspects: the first allows for nosological diagnosis, the second - to establish the leading mechanism and degree of speech dysfunction:
- Neurological diagnostics.
Indicated for patients with dysarthric disorders. Cerebral MRI is performed to visualize focal brain lesions. To assess the severity of paralysis and paresis of articulatory muscles, electrophysiological studies are used: ENG, EMG. - Dental examination.
Required for persons with edentia, jaw dislocation, or poor-quality prosthetics. Diagnostics may include X-ray of the TMJ, orthopantomography, CT scan of the jaws. To make prosthetics, impressions are made and diagnostic models are cast. - Audiological examination.
If slurred speech is due to hearing loss, an audiogram, otoacoustic emissions, and auditory recordings are performed. An audiologist consults the patient with the test results. - Examination of the pharynx.
During pharyngoscopy, the peritonsillar abscess is visualized as a spherical, fluctuating formation. The mucous membrane is hyperemic, and pus can be seen through it in the place of greatest bulging. Sometimes a test puncture of the abscess is performed for differential purposes. - Speech therapy examination.
Assessment of the state of oral speech is necessary for dysarthria and rhinolalia. The speech therapist identifies articulatory difficulties, defects in sound pronunciation (substitutions, distortions, omissions), agrammatisms, and determines the coherence and intelligibility of speech.
Speech therapy classes
Our doctors
Pankov Alexander Rostislavovich
Neurologist
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Novikova Larisa Vaganovna
Neuropathologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Dysarthria
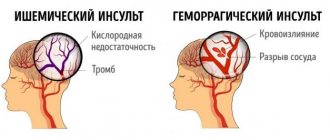
Dysarthria is a violation of pronunciation or articulation due to paralysis of the bulbar muscles, dysfunction of the facial muscles. The motor skills of speech, the pronunciation of sounds, the rhythm of breathing, and intonation coloring are impaired. It becomes difficult to understand what the person wants to say. People around you notice dysarthria. The person slurs his speech, speaks unclearly, and slurs simple words. The meaning and tempo most often do not change, and the strength of the voice is impaired. This disorder is always caused by an organic cause - impaired blood flow, infection or intoxication. In case of such a disorder in an adult, an urgent need to contact a neurologist to find out the cause. There may be a tumor of the nervous system, trauma, hemorrhage or ischemia (oxygen starvation). Dysarthria manifests itself in multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, myotonia, cerebral atherosclerosis, syringobulbia and many other nervous diseases. In healthy people, dysarthria is observed in a state of deep intoxication.
Dysarthria resulting from diseases has several forms:
- bulbar, caused by damage to the nuclei of the cranial nerves, occurs with cerebrovascular accidents, manifests itself as a single slit sound;
- pseudobulbar (damage to one side of the speech muscles), which occurs when the pathways from the cerebral cortex to the nuclei in the brain stem are damaged, manifests itself as slurred, slurred speech with the inability to pronounce hissing and whistling sounds;
- extrapyramidal, when the nerve nuclei located in the subcortex are affected, manifested by involuntary guttural cries;
- cerebellar - “chanted” speech;
- hemispheric or cortical, when lesions occur in the cortex, the use of all linguistic means becomes difficult.
Neurologists and speech therapists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diarthria.
Treatment
Medical stage
The content of medical care depends on the underlying pathology that led to slurred speech. Both therapeutic and surgical approaches, rehabilitation and recovery measures are used:
- Neurological treatment.
Neurosurgical interventions are required for patients with cerebral tumors, hematomas, and skull fractures. For vascular and neurodegenerative pathologies, long-term (often lifelong) drug therapy is carried out. Neuropsychological correction is carried out according to indications. - Dental treatment.
Indicated for maxillofacial defects and orthopedic problems. Primary dentures or adjustment of previously installed dentures, dental implantation are performed. In case of traumatic displacement of the articular surfaces, the TMJ dislocation is reduced. Children with facial clefts undergo surgical treatment - cheiloplasty, uranoplasty. - Audiological treatment.
After establishing the type and degree of hearing loss, the optimal hearing aid method is selected. In case of sensorineural hearing loss, the child needs to select a hearing aid; in case of significant hearing loss (IV degree hearing loss, deafness) - cochlear implantation. - Treatment of ENT pathology.
For phlegmonous sore throat, antibiotic therapy, gargling with antiseptics, and physiotherapy for the submandibular area are prescribed. When the peritonsillar abscess matures, it is surgically opened. - Medical rehabilitation.
It is an essential component of complex therapy. Includes physical therapy classes, mechanotherapy, kinesitherapy, massage. In some cases, patients require sensory psychostimulation, selection of individual orthopedic devices, and medical and social support.
Speech therapy stage
The content of speech therapy sessions and the methods used vary depending on the structure of the speech defect. However, in all cases, to overcome slurred speech, it is necessary to develop articulatory motor skills and improve pronunciation skills. For this purpose, the following methods are used in speech therapy practice:
- breathing and articulation exercises;
- speech therapy massage;
- myofunctional correction;
- speech therapy taping;
- neuromuscular stimulation using the VocaStim device.
As part of speech rehabilitation after hearing loss, classes with a teacher of the deaf are recommended. During the adaptation period, people with dentures are advised to talk more, read slowly and count out loud, and practice the pronunciation of “difficult” sounds and sound combinations. With systematic practice, slurred speech gradually decreases, and in many cases clear, intelligible pronunciation is achieved.
Mutism
The etiology of mutism is complex - silence develops both in people with intact brain and speech apparatus, and in many brain lesions.
Sometimes mutism is caused by atrophy of Broca's area or other brain lesions that are not immediately detected. Akinetic mutism develops with the loss of all voluntary movements, including speech. Such mutism has been described in coma, AIDS, and neuroleptic syndrome. This is a condition in which a person looks intently into the eyes of his interlocutor, but cannot move or utter at least one sound. A similar condition is observed in the acute period of severe traumatic brain injury, when not only speech is impaired, but also consciousness, along with other voluntary functions.
Often the cause of mutism is mental illness, especially hysteria, deep depression, catatonia (special movement disorders when a person looks like a wax doll) with endogenous major psychoses. Hysterical mutism occurs more often in women and is accompanied by demonstrative behavior aimed at achieving one’s goals.
Speech Disorder Specialists
Speech therapist.
Most speech disorders are a speech therapy problem, which is why speech therapists should be contacted first.
Neurologist
provides medication support to children with cerebral palsy, alalia, dysarthria, etc.
A defectologist is able to significantly “pump up” a child’s brain, develop intelligence and thinking.
An otorhinolaryngologist determines pathologies of the peripheral speech apparatus of a medical nature: hearing loss, cleft palate, adenoid growths, sore throat, etc.
A teacher of the deaf is involved in the development of speech in deaf and hard of hearing children and adults.
Psychologist. Due to shyness or aggressive behavior, the child’s speech is distorted and impoverished. Problems in the family and with peers can cause delayed speech development.
Neuropsychologist (clinical psychologist) - in case of speech disorders (caused by impaired brain function), teaches the child’s brain to function correctly through motor and play exercises.
| Defectology and speech therapy, as well as Neurology services are available in our center. |
Dysphonia
A disorder in which the voice loses its sonority. It happens with respiratory infections, diseases of the vocal cords, tumors. This is an occupational disease of singers, teachers, and public figures.
CELT doctors understand in detail what exactly happened to a person’s speech. High-class diagnostics and timely treatment help to save patients with cerebrovascular accidents, growing tumors, and aggressive infections.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Causes and risk factors
Classification of a pathological condition involves division into organic and functional. The disorder may be a consequence of central nervous system dysfunction and hearing impairment. Also, its occurrence is caused by injuries and bruises of the head, damage to the speech organs. This could be a brain tumor, stroke, thrombosis. In older people, there is a connection with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In this case, pathological memory disorders and mental disorders occur in parallel. Less commonly, epilepsy, alcohol abuse, cerebral palsy, and infectious diseases of the brain contribute to dysfunction.
The functional causes of speech disorder are considered to be external factors, for example, stress, fear, hysteria, untreated pathology from childhood. Under the influence of taking certain medications (antidepressants, tranquilizers), auditory perception may decrease, which aggravates speech disorders. An important role is played by the hereditary factor. If there is a predisposition, it is necessary to monitor the person’s condition over time.
The simultaneous influence of external and internal causes is possible, in which case the picture of disorders becomes multi-layered and manifests itself in a large number of symptoms.
A person’s communication functions also suffer when dentures are installed incorrectly. A deep state of stress and overexertion can lead to spastic dysphonia. In this case, tension in the voice or its disappearance is noted.