Intervertebral disc herniation is characterized by a violation of the strength of the fibers of the fibrous ring of the disc, resulting in protrusion of the pulpous fragment. Every year, for every 100 thousand inhabitants, approximately 150 patients are diagnosed with a herniated disc. And in 80% of cases, this disease is a complication of long-standing osteochondrosis. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 40-55 years, however, vertebral hernias at 25-40 years are by no means uncommon. Of the total number of patients, approximately 20% of people require surgery.
The lumbosacral region is most often affected; it has the highest mobility and is the supporting region for the upper and central segments of the spinal column. The discs at the neck level are much less damaged, and in very isolated cases the thoracic intervertebral elements are affected.
Men are more likely than women to face a similar problem, since the connective tissues of the male body have a slightly lower degree of firmness and elasticity. Another explanation is that the male sex is more involved in heavy physical labor. Regular physical activity, incommensurate with the physiological capabilities of the musculoskeletal system, is the leading cause that stimulates degenerative changes in the spine and, as a consequence, leads to the development of unfavorable pathology.
The disease begins with protrusion - a slight deformation of the intervertebral layer, while the internal fibers of the fibrous ring are damaged, but the integrity of its external structures is preserved. In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathogenesis progresses to the stage of a true hernia - prolapse. In the later stages of the disease, the ring ruptures and part of the nucleus falls out beyond the boundaries of the vertebrae, putting compression on the spinal canal and neurovascular structures. In the most severe case, sequestration occurs - separation of the nucleus from the disc and its entry into the spinal canal. Complicated options pose a huge danger to the patient, as they are fraught with complete or partial paralysis of the limbs.
basic information
Between the vertebral bodies there are layers of cartilage - these are intervertebral discs. They consist of a ring-shaped element (annulus fibrosus), inside of which there is a jelly-like substance (nucleus pulposus), which has good elasticity. Intervertebral discs are the main shock absorbers of the spine. When walking, running, and even while standing, they help soften the vertical pressure (axial load) on the spinal column and dampen vibrations when the body moves.
Under unfavorable factors that worsen metabolism in the osteochondral components of the spinal system, degenerative and dystrophic processes in the structure-forming units of the shock-absorbing layer are activated, due to which the fibrous ring is destroyed and torn. The gelatinous substance, in turn, begins to put pressure on the damaged area, which leads to protrusion of the disc from a certain side. Since the protruding part is usually located in close proximity to the spinal nerve formations, irritation occurs of these nerves with which the pathological protrusion comes into contact. Thus, a person begins to experience painful symptoms in the affected area of the back or neck, often radiating to the leg or arm.
Stages of disc herniation formation
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the disc . Micro-tears appear in the fibers of the nucleus pulposus, the fibers of the fibrous ring weaken, and in the end plates there is a decrease in the intensity of blood flow and a decrease in the quality of nutrition of the disc. This leads to a deterioration in the shock-absorbing functions of the disc.
- Partial disc prolapse. The fibers lose their ability to withstand loads, the magnitude of which can reach 150–300 kg per disc. As a result, the nucleus pulposus is displaced and then protrudes into the spinal canal, i.e., protrusion occurs. Often in this condition no special problems arise, but asymmetrical protrusion can pinch the nerve, which leads to pain.
- Disc herniation. Against the background of progressive degenerative changes, the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the fibrous ring and touches the nerve root. The outer shell, which can be called a kind of disc case, can infringe on part of the nucleus pulposus and prevent it from coming out completely. The result is radicular pain that radiates to the leg.
- Sequestration. In severe cases, the prolapsed portion of the disc's internal contents becomes detached and can move up or down the spinal canal, causing serious neurological complications.
Interesting Facts:
In a person weighing about 65 kg, bending the torso forward 30° and lifting a load weighing 14 kg creates a load on the L3-L4 and L4-L5 discs of about 150–200 kg each. If you increase the angle of inclination of the body to 70°, the load increases to 300 kg, which can lead to a crack in the fibrous ring, especially with a weakened muscular system and a worn-out disc.
An intervertebral disc can withstand a load of about 5 atmospheres, while for comparison in a car wheel the optimal pressure level is considered to be 2.2 atmospheres.
Symptoms
Symptoms of herniated intervertebral discs depend on the location, size of the developed protrusion, and the degree of involvement of spinal structures in the pathological process. Below we present the main symptoms that are observed with this disease:
- local pain syndrome (aching, pulling, deep or shooting) in a specific spinal segment, which, as a rule, increases when performing any movements;
- radiating pain that radiates to any part of the upper or lower limb, buttocks, foot, shoulder area or chest;
- impaired sensitivity (hyperesthesia or hypoesthesia) of the limb;
- muscle weakness of the leg or arm (depending on the location of the lesion);
- stiffness in a certain part of the spine;
- frequent headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, blood pressure surges, insomnia, unsteadiness of gait and other neurological disorders;
- dysfunction of the intestines and genitourinary system (spontaneous defecation, urinary incontinence, failure of reproductive functions).
This is how pain zones are distributed depending on the location of the hernia.
Attention! The first sign that should alert you and motivate you to immediately visit a doctor is pain in the back or neck of any intensity in a certain area.
Postoperative management of patients
The duration of strict bed rest is one day from the moment of surgery. As a rule, on the 2nd day we allow patients to get out of bed and sit without using lumbar spine orthoses (lumbar corsets) or any additional means of support. The therapeutic and protective regime lasts 6 weeks from the moment of surgery, during which patients are allowed to walk fully. Upon completion, patients begin active rehabilitation - breaststroke swimming in the pool is recommended at least 2 times a week, and physical therapy aimed at strengthening the back muscles. Patients return to normal physically active life without any restrictions, incl. Sports such as alpine skiing, snowboarding, football, and volleyball are allowed.
Reasons for development
The fundamental factor provoking the pathology is osteochondrosis. A complex of degenerative-dystrophic disorders observed in the cartilaginous tissues of the spine. If it is not treated, which for some reason is considered quite normal for many people, a seemingly harmless diagnosis can develop into a serious problem - a hernia between the vertebrae. Pay attention to the photos; from them you can better understand what the intervertebral layer looks like in a healthy and pathologically altered state. The following reasons contribute to the occurrence of such degenerations in the discs:
- traumatic lesions of the musculoskeletal system;
- excess body weight;
- deficit of motor activity;
- excessive physical activity (playing strenuous sports, lifting weights, etc.);
- congenital and acquired weakness of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus;
- impaired metabolism in the body;
- autoimmune diseases, hormonal imbalances;
- various curvatures of the spine;
- prolonged sitting (often occurs among drivers and office workers);
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unfavorable heredity and age-related aging of the body.
Correct technique of body position during physical work.
A disc herniation not only suppresses motor functions at the local level, but also inhibits the transport branch of the nervous system, giving rise to a whole chain of neurological disorders and quite dangerous damage to the central nervous system, ending in immobility of the limbs. In its neglected state, it leads to severe disorders of the pelvic organs, brain, cardiovascular system and other vital functional components of the body that are adjacent to the area of damage to the spinal column.
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, when symptoms of intervertebral hernia occur, people often delay visiting a doctor and undergoing an examination, look for information on dubious sites and relieve pain with self-selected medications. This helps to temporarily relieve the condition, which creates a false feeling of recovery.
Therefore, patients continue to perform their usual work, which further aggravates the situation and increases the risk of developing neurological complications. Such negative consequences can be avoided if a timely examination is carried out and the cause of the discomfort is determined.
The main method for diagnosing a hernia is MRI. The study is safe for humans and at the same time provides comprehensive, accurate data. It allows you to detect the slightest degenerative changes in the disc, as well as protrusion, the actual hernia and displacement of the vertebrae.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be performed using special large-sized closed or open type devices. In the first, the patient lies down on a couch, which slides into a pipe where a magnetic field is created. It is important to remain completely still to get a clear image. The procedure lasts about 20 minutes, but it is not suitable for people who have older generation metal implants (not titanium), fragments and other objects in their bodies, or those who suffer from claustrophobia.
Open machines are designed for MRI in patients who are afraid of closed spaces. But they create a less powerful magnetic field (up to 0.2–1.2 tesla), which negatively affects the quality of the resulting image. Moreover, in closed-type devices, the magnetic induction power can be 1, 1.5 and 3 Tesla.
If it is impossible to conduct an MRI, for example, if there is metal (except titanium structures) in the body, other diagnostic methods are used:
- CT is a highly accurate procedure that allows you to detect deviations in the condition of the bone components of the spine by passing a beam of ionizing radiation through it. With its help, osteoporosis, fractures are diagnosed, and hernias are also detected. The study lasts 5 minutes and has virtually no contraindications.
- X-ray – used to diagnose instability of the spinal motion segment. The study is usually carried out in lateral and direct projection. Additionally, it may be prescribed to take images during flexion and extension in a standing position. This helps to increase the load on the spine and obtain objective information. X-ray images allow you to evaluate the height of the discs, determine the presence of bone growths, vertebral anomalies and their displacement.
Deciphering the results of hardware research requires specific knowledge and experience. Therefore, you should not try to diagnose the pathology yourself; it is better to immediately contact a specialist who will correctly assess the nature of the existing changes and be able to select the optimal treatment regimen.
Which doctor should I contact?
Initially, if you have back pain, you should consult a neurologist, or better yet, a vertebrologist. This specialist will conduct a thorough examination, collect anamnesis,, if necessary, prescribe the necessary list of studies and will be able to correctly decipher their results.
If during the examination a protrusion or hernia is detected, the vertebrologist, based on its size and clinical picture, will develop an effective tactic of conservative treatment or refer the patient to a neurosurgeon, spinal surgeon, or orthopedic traumatologist for consultation and surgical removal of the hernia.
Complications and consequences:
If you ignore the problem, increased pain will not be the only consequence of the progression of the hernia. Since it gradually increases, this is fraught with:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- disruption of the pelvic organs;
- paresis or paralysis of the lower extremities.
Diagnostics
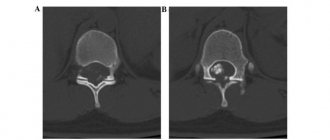
Conventional x-rays have low information content regarding the recognition of vertebral hernias, because they visualize bone structures well, in our case the vertebrae. Based on the X-ray image showing the distorted relative position of the vertebral bodies (angular displacement, narrowing of the space between them, etc.) and the presence of dystrophic signs (osteophytes, etc.), we can only assume that there is a disc protrusion. However, magnetic resonance imaging has the ability to clearly visualize precisely soft tissues (disc structures, spinal cord, nerve endings). Computed tomography is an average method in terms of information content - better than x-rays, but worse than MRI.
Hernia between the 3rd and 4th segments.
However, visit any thematic forum, where you will learn that patients who complain of pain in the back first undergo an x-ray. Hence the question: why not immediately send for highly informative diagnostics? Initially, specialists issue a referral for radiography, and only after receiving primary information about the condition of the ridge, do they decide whether the person needs to further undergo a diagnostic examination using MRI or CT.
Dynamics from the initial to the last stage of the disease.
Many other pathologies that are completely unrelated to damage to this organ manifest themselves with similar signs, for example, true diseases of the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. With multiple sclerosis, numbness of the limbs occurs, which is often observed with an intervertebral hernia. Therefore, it is important to correctly differentiate the problem. Perhaps an x-ray will show the ideal condition of the spine, then further diagnostic measures will be of a completely different plan.
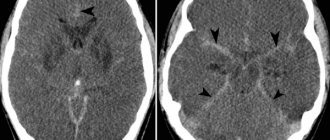
Diagnosis of spina bifida
Diagnosis of spina bifida at the Yusupov Hospital is a comprehensive examination. First of all, the doctor collects anamnesis - finds out the patient’s complaints, studies medical documentation, the results of previous examinations and records of specialists.
Then a neurological examination of the patient is carried out: a specialist visually examines the protrusion in the spinal column, assesses muscle tone and strength in the limbs, and determines the intensity of reflexes in them.
Additionally, the following diagnostic studies are prescribed:
- transillumination - the hernia is illuminated, revealing the nature of the contents of the hernial sac;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging – for layer-by-layer study of the spinal cord in the area of the pathological focus in order to identify concomitant damage to brain tissue;
- myelography - a contrast agent is injected into a peripheral vein and accumulates at the site of pathology, which allows one to assess the degree of damage to the nervous tissue in the hernial sac.
Which doctor treats you?
Which doctor should I contact if I feel painful discomfort in the lower back, thoracic and cervical vertebrae? Initially, you should visit a therapist, he will listen to your complaints, examine you and send you for x-rays, and also issue forms for urine and stool tests. Next, based on the primary diagnostic data received, the general practitioner will refer you to the right specialist.
Neurosurgeon.
There are two main doctors who specialize in the treatment of intervertebral disc herniations: an orthopedist and a neurologist. If we are talking about surgical intervention, the spine is operated by a neurosurgeon. In addition to the main specialists, physiotherapists and exercise therapy instructors will work with you. Conservative therapy takes place on an outpatient basis and partly at home, surgery and rehabilitation after it take place in a hospital setting.
Pregnancy and hernia
If there is a pregnancy, an experienced specialist recommends gentle conservative therapy that does not negatively affect the fetus and the well-being of the expectant mother. Pregnant women will require treatment according to a specific regimen, since its absence can lead to very bad consequences, including disability. The operation is postponed until the postpartum period. Typically, during pregnancy, wearing a bandage, light exercise, swimming, and the use of non-aggressive medications and folk remedies to relieve pain are recommended.
Main principles of treatment
Disc protrusions measuring less than 6 mm are generally treated with symptomatic and supportive therapy. Symptoms in mild forms are most amenable to conservative treatment. Non-surgical tactics make it possible to stop the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life by increasing blood and lymph flow in the paravertebral structures and limbs, normalizing muscle tone, and beneficial load distribution. The standard therapeutic regimen includes:
- creating temporary rest for the affected part and wearing special orthopedic devices (corset, bandage, collar);
- physical therapy exercises (they develop the spine, increase the endurance of the musculoskeletal corset without overloading the problem area);
- visiting physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, electrophoresis, ultrasound with Karipain, etc.;
- conducting massage sessions, manual therapy, kinesitherapy, horizontal or vertical traction (help relieve pressure from the hernia from the nerve roots, improve local blood circulation and tissue nutrition);
- drug treatment, namely the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, vitamin-mineral complexes, etc.;
- following a special diet.
When a conservative approach does not bring relief, and the size of the hernia does not exceed 6-7 mm, then it is advisable to perform a non-traumatic and painless procedure called nucleoplasty. It comes in various types: laser, cold plasma, electric wave. For large sizes (from 8 mm or more), complex surgical intervention is used: discectomy (a traumatic and rarely used tactic) or microdiscectomy (a common technique).
Most often the center is located at the level l5 S1; treatment for the pathogenesis of such localization is important to begin as early as possible, even at the stage of protrusion. A damaged disc element with a prolapsed nucleus pulposus, located between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae, poses a real threat to the performance of the legs, the functioning of the intestines and the urinary system. Immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis, immediately begin responsibly implementing all medical prescriptions. Never self-medicate, a highly qualified doctor will tell you how to treat a l5 S1 hernia in your case, but only after you have undergone a full examination.
If we take into account the frequency of lesions in the cervical region, then in the C5 C6 segment the disease is most often detected. Despite the fact that only 8% of hernias are detected in the cervical intervertebral cartilage, any of them is considered dangerous, as important vessels, nerves, and arteries responsible for the functionality of the brain pass nearby. Large formations can compress the vertebral artery supplying the brain and cause an early stroke, or damage the conductive function of nerve impulses and lead to partial or complete paralysis of the upper limbs.
Any surgery near the head, where the spinal cord connects to the brain, carries the greatest risks. Therefore, in the area C5 C6, treatment (5 mm is already a lot) is tried in every possible way to limit it to intensive conservative methods. However, unfortunately, lesion volumes of even 5-6 mm are considered large, which sometimes forces emergency surgery.
Spina bifida: treatment, patient reviews
To treat this disease, only a radical method is used - the pathological formation in the spinal column is surgically removed; treatment of spina bifida without surgery is ineffective. During surgery, the defect in the spinal column is reconstructed and the unclosed hole in the bone tissue is closed. After a thorough examination of the hernial sac, non-viable tissue is removed from it, and healthy spinal cord structures are placed in the spinal canal.
Patients with spina bifida may develop hydrocephalus, which threatens irreversible changes in the brain. In order to prevent the harmful effects of excessive intracranial pressure, a shunt is installed to divert cerebrospinal fluid into the thoracic lymphatic duct.
To prevent the progression of the disease and improve the general condition of the patient, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe conservative therapy:
- taking medications that normalize the function of nervous tissue (nootropics, neurotrophics);
- taking vitamins A, C, E, B - to improve metabolic processes in the affected area of the spinal cord;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, according to patient reviews, can significantly restore tissue trophism and motor activity (laser, magnet, etc.);
- physical therapy – for patients diagnosed with spina bifida, exercise therapy helps develop neuromuscular connections in the affected area of the body;
- diet – a large number of foods enriched with coarse fiber are introduced into the diet of patients, which helps to normalize intestinal motility.
Operation
Surgical intervention is primarily indicated if conservative therapy for 2-3 months has not produced any results. Surgery can be performed at any stage if significant complications arise. With severe compression of the spinal cord, spinal nerves and blood vessels, which caused the cauda equina syndrome, inability to flex and extend the feet, muscle atrophy and paresis of the arm or leg, serious impairment of blood supply and oxygen starvation of the brain, etc. The stage of sequestration, at the time of which a herniation occurs from the disc, requiring immediate surgical attention.
Position of the patient during surgery.
Microdiscectomy involves performing corrective and anti-compression manipulations through a small surgical incision (maximum up to 3 cm) under the control of an endoscope or microscope, without damage to muscle and ligamentous tissues. Only the prolapsed element of the disc, in fact, what we call a hernia, can be removed. And the disk itself is preserved to the maximum. This minimally invasive technology is easily tolerated, but in the future, despite the minimal invasiveness, high-quality rehabilitation of the patient must follow. With an impeccably performed microdiscectomy and ideally organized restorative therapy, you can confidently count on a favorable prognosis.
In the early stages, if persistent symptoms make it impossible to live a normal life, gentle surgical treatment using one of the methods of nucleoplasty is permissible. Reconstruction of the disc occurs by exposing the displaced central nucleus to cold plasma or laser. Cold plasma or laser energy is supplied to the pulpous element through an electrode placed in a thin conductor probe. The probe is inserted into the nucleus under X-ray control and the specialist begins to expose it to the appropriate type of radiation. Thus, it is compressed and the sagging mass is pulled into place, and at the same time the normal shape of the disc is restored. Rehabilitation is quick and hospitalization is not required.
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine
The main treatment, as we have previously witnessed, is possible in two options: without surgery and with the use of surgical tactics. The choice of which approach is appropriate in a given situation is made by the doctor. Everything is taken into account: symptoms, severity and generalization of pathomorphological signs, direction of protrusion, individual characteristics of the patient (weight, age, professional activity, etc.), concomitant pathologies, etc. The main symptoms in the presence of a lumbar herniated intervertebral disc are as follows:
- the appearance of pain in the lumbar region, gluteal area, thigh and lower leg, foot;
- pain syndrome, usually radiating to one of the legs;
- feeling of numbness, tingling, tingling, coldness or crawling in the lower limb, in the perineum;
- atrophic syndrome (weakness) of the leg muscles;
- feeling of a “hoop” in the lower back;
- a very common phenomenon is when the foot loses its ability to support itself and when walking it drags;
- disturbances in the functioning of organs located in the pelvic cavity (rectum, bladder, ovaries);
- reduced potency in men, infertility in women, problems with the menstrual cycle.
All points relate mainly to moderate and severe degrees. It’s sad, but it is at these stages that a person most often begins to experience severe discomfort, which forces him to visit a doctor. Treatment is always prescribed, regardless of the severity of the manifestations. The forum is not the place to look for remedies to solve your problem; you should urgently seek highly specialized help from a medical institution. Otherwise, irreparable consequences may occur in which surgery will not help. A fatal outcome when hernial fragmentation occurs is also not excluded.
A highly specialized specialist will instruct you on how to treat a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation correctly. Not only is he directly familiar with the real clinical picture of your problem area, he knows all the subtleties and pitfalls of the anatomy of the spine, and measures for its safe and effective treatment.
| Lumbar hernia size | Characteristic | Therapeutic approach |
| from 1 mm to 5 mm | slight protrusion | outpatient therapy and treatment at home (physical therapy, exercise therapy, spinal traction, taking chondroprotectors, etc.) |
| from 6 mm to 8 mm | moderately expressed lesion | conservative methods are still valid if there is no progression of the disease |
| from 9 mm to 1.2 cm | very large protrusion | surgical intervention is generally required |
| more than 1.2 cm | critical stage, dangerous due to sequestration | emergency surgery is performed |
Spina bifida: rehabilitation after surgery
Surgical removal of a hernia is not the only and final stage of treatment. To consolidate the effect of the manipulations performed, the patient needs high-quality postoperative rehabilitation. An individual rehabilitation treatment plan at the rehabilitation center of the Yusupov Hospital is drawn up by highly qualified experienced rehabilitation doctors.
Competent rehabilitation after removal of spina bifida allows you to achieve the following results:
- eliminate pain syndrome as soon as possible;
- prevent possible complications (infections, thrombosis, scars, etc.);
- bring general health indicators back to normal;
- restore muscle strength of the limbs, abdomen, back;
- restore the functionality of the spine;
- master the skills of proper load distribution;
- correct defects in posture and gait;
- return the patient to a full life with a minimum number of restrictions;
- minimize the risk of relapse of the disease.
You can make an appointment with a rehabilitation specialist at the rehabilitation center and find out the cost of medical services by calling the Yusupov Hospital or on the clinic’s website by contacting the coordinating doctor through the feedback form.
Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine
In the cervical region, hernias are the most insidious in terms of danger. Do not delay treatment and do not ignore preventive measures if you have cervical osteochondrosis, because it is this that becomes the provocateur of threatening pathogenesis. You most likely know how its symptoms can manifest themselves. But still, let us remind you:
- crunching, grinding with various movements of the neck;
- burning sensation between the shoulder blades;
- limited mobility of the head in a certain direction (tilting to one side, turning to the side, lowering to the chest);
- neck muscle tension;
- recurrent or constant headaches, sleep disturbances;
- impaired coordination of movements when walking;
- absent-mindedness, memory loss, deterioration of visual acuity and hearing;
- unpleasant sensations in the hands and head (tingling, numbness, goosebumps, etc.).
Cervical region.
The progression of degenerative-dystrophic reactions, if appropriate measures have not been taken for a long time, contributes to the development of a hernia. Depending on where it is concentrated, certain symptoms appear. Let's consider the symptoms of the disease with localization C5-C6, where a bundle of nerve fibers lies, which, by the way, is responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the shoulder and elbow joints, and the thumb:
- tremor of the hands, loss of sensation in the hands;
- weakness in the wrist, biceps brachii;
- difficulty in raising and bending the elbow, the limb hangs like a whip;
- along the back of the forearm, a feeling of numbness, crawling, burning or tingling;
- local painful phenomena, including those that “hit” from the shoulder to the thumb;
- a sharp drop in vision, spots before the eyes.
As for the size, if there is a hernia of 1-5 mm, mandatory outpatient treatment is recommended: therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy and immobilization of the neck for some time using a cervical collar are the basic principles. 6 mm or more is an absolute reason for surgery.
If the diagnosis is disc herniation: information, thoughts, conclusions
Make an appointment
- Home / If the diagnosis is disc herniation: information, thoughts, conclusions
INTERVIEW OF NEUROSURGEON, SPECIALIST IN TREATING THE SPINE WITH MINI-SURGICAL METHODS, SERGEY SARYCHEV (RE-CLINIC, MOSCOW) to a correspondent of the online publication med-news.ru
From the editor: according to statistics, half of the world's population has back problems, and each of us has experienced all the delights of neck or lower back pain at least once in our lives. Back pain has a wide variety of origins. But today we want to talk about one of the most common and insidious causes of spinal pain syndrome - a herniated disc. It is pain that is the first manifestation of a hernia, which makes a person begin to worry about his health. The pain can be constant or occur unexpectedly and inexplicably, for example, when sneezing or simple and habitual movement. Weakness in the legs and difficulty urinating may occur. Since people tend to love self-medication, they often do not turn to specialists, but instead begin taking analgesics on their own and without control. An advanced hernia leads to loss of performance, quickly depriving a person of the ability to walk normally. Modern medicine offers many options for salvation. We asked Candidate of Medical Sciences Sergei Leonidovich Sarychev about how to get rid of a hernia and become a healthy person, how to prevent serious consequences of the disease.
Sarychev Sergey Leonidovich (Re-Clinic, Moscow) - Candidate of Medical Sciences, neurosurgeon of the highest category, vertebrologist, author of more than 30 scientific works on neurosurgery, performed over 10,000 minimally invasive operations on the spine. Since 2011, chief surgeon of the department of vertebropathology of the international Russian-Israeli Center Re-Clinic (Moscow), leading specialist in the field of mini-surgical treatment of back diseases.
— Sergey Leonidovich, the first question: how to notice the signs of a hernia in time? When should a person sound the alarm?
A hernia manifests itself as pain in the spine. Alarming symptoms are increasing or sudden weakness in the legs and difficulty urinating. A hernia interferes with normal life; in order not to feel pain, you have to constantly control your movements and limit physical activity. Previously it was believed that hernias could only occur in old age. Now we see among our patients young people, starting from the age of 20. The nature of the occurrence of a hernia in older patients is associated with metabolic-dystrophic processes characteristic of osteochondrosis. We can say that a hernia in the elderly is a complicated course of osteochondrosis. At a young age, a hernia is provoked by incorrect posture, leading to scoliosis, that is, curvature of the spinal axis, extreme physical activity, heavy lifting and injury. When should you see a doctor? When the first pain occurs in the cervical or lumbar spine, weakness in the limbs, loss of sensitivity. However, there is no need to panic.
The hernia itself is not life threatening. Its danger is not in the pain it causes. The risks associated with a hernia lie in those neurological disorders that will inevitably arise when the nerve root is pressed against the vertebral bone for a sufficiently long time at the place where it leaves the spinal canal. The spinal root, like any tissue in the body, is nourished and lives thanks to the blood supply and discharge vessels, only very small ones. If the vessels are partially compressed and their lumen is reduced, then the nutrition of the root deteriorates and its gradual atrophy and dysfunction of the conduction of nerve impulses occur. If you ignore the first symptoms, start taking painkillers on your own, dampen the pain, or simply endure it, then within six months, sooner or later, the first signs of serious complications will inevitably appear. An underexamined patient may initially be misdiagnosed and given the wrong, inappropriate treatment. You must understand that for back pain you cannot limit yourself to consultation and treatment with a neurologist; a mandatory consultation with a neurosurgeon-vertebrologist is required. The main thing is not to waste time and not rely solely on drug treatment. Otherwise, you may miss the onset of neurological complications. Unfortunately, we see patients being treated endlessly by neurologists and physiotherapists, massage therapists, chiropractors, kinesiotherapists and other specialists. No conservative methods can force a herniated disc back into the disc. There are methods for minimally invasive removal of protrusions and hernias, and delaying the start of such mini-surgical treatment can be costly for health and lead to complications.
— Sergey Leonidovich, tell us about the possible complications of hernias if they were not detected in time or if they were not dealt with...
Complications develop at different rates. Most often, this happens gradually over time, from six months to several years. There are cases of rapid manifestation of signs of complications. First, patients experience pain in a specific part of the spine - cervical, thoracic or lumbosacral. They are associated with the pressure of an incipient hernia, which is called protrusion, on an area with a large number of pain receptors...
...then the outer fibrous ring of the disc ruptures and the protrusion turns into a hernia itself. Part of the disc falls out into the spinal canal, the hernia presses the nerve root against the vertebral bone, and a picture of severe radicular syndrome and radiculitis develops. In fact, at this stage, pain has four sources of origin - mechanical compression of the root, swelling of the root, aseptic, that is, non-microbial, inflammation of the root and reflex spasm of the local back muscles above the site of the lesion. Damage to the root itself begins to increase due to a decrease in the lumen of the vessels feeding it, as we discussed above. Movement disorders and numbness in certain areas of the body appear, most often in the upper or lower extremities, depending on the location of the hernia in the neck or lower back. If adequate treatment is not started in time, the blood supply to the spinal cord is disrupted, and an ischemic spinal stroke (i.e., local necrosis due to lack of blood flow) may occur.
— Did I understand correctly that a herniated disc goes through stages in its development? The first stage is an incipient hernia or protrusion, and what next?
— Indeed, the development of a hernia is a dynamic process that has its own stages or phases. Protrusion of the intervertebral disc is the initial phase of its degeneration and destruction. A protrusion is essentially a protrusion of the disc substance beyond its normal boundaries. Protrusion is associated with the formation of microcracks in the internal fibrous rings while the outer one remains intact. Through these cracks, the disc substance, under the influence of high intradiscal pressure, penetrates to the boundaries of the disc and forces the outer ring to bend outward and press the nerve root against the vertebral bone. Symptoms of protrusion, like hernia, are pain, impaired motor function, forced immobility and pelvic disorders, muscle spasm and numbness. With the progressive course of hernia formation, the next phase begins - the formation of a true hernia. It is marked by a rupture of the outer fibrous ring. The symptoms are still the same, but may be even more pronounced. And finally, a complete separation of the hernia from the main “mother” substance of the disc is possible. This phase is called disc sequestration, and the detached part of the disc itself is called sequestration. At each stage or phase of hernia formation, the neurosurgeon decides on the use of one or another treatment method - from minimally invasive for protrusions, small and medium hernias to open major surgery when removing a large hernia or sequestrum.
— And yet, what should a person do if the diagnosis of “herniated intervertebral disc” is confirmed?
— First of all, if there is a reasonable assumption that back pain is associated with a problem of the spine, and not the internal organs, I would advise you to contact a neurologist and get a referral for an MRI scan of the painful area.
If the radiologist’s report mentions the presence of spinal pathology, such as protrusion, hernia, stenosis, vertebral fracture, spondyloarthrosis or other abnormalities, then you need to go to an appointment with a neurosurgeon-vertebrologist.
You can immediately take an MRI, without a referral from a neurologist, now it’s easy. In conclusion, everything will be written. You should come to a consultation with a vertebrologist with an MRI image or disc.
— And what can a vertebrologist, as a specialist in the treatment of the spine, offer in this case?
“You need to understand that there are many options to alleviate or temporarily remove pain. These are medications, physiotherapy, a course of massage, acupuncture, etc. All these methods, individually or together, can eliminate inflammation of the nerve root, its swelling, and reflex spasm of the spinal muscles over the site of the lesion. But they will never be able to eliminate the pressure of the hernia on the root, the mechanical component of the problem, and this is the cause of suffering. Therefore, a vertebrologist thinks in terms of radically ridding the patient of the cause of the disease. In the clinic where I operate, there is a large arsenal of minimally invasive, gentle treatment methods, which in terms of their sensitivity are close to conservative therapy, and in terms of their effectiveness in achieving the goal - to surgery. Minimally invasive microsurgery occupies an intermediate position between treatment in a clinic and treatment in a hospital, figuratively speaking, between pills and a scalpel.
This is a separate area of spinal surgery, and it includes a whole range of high-tech mini-operations or manipulations. All of them are carried out using sophisticated equipment and consumables from the world's best manufacturers and require the doctor to have special knowledge and skills acquired during training in foreign clinics. I work in a specialized Spinal Center, which is fully equipped to perform the main types of minimally invasive procedures currently used in the world as an alternative to open “scalpel” surgery. In modern foreign clinics, open operations are used only for strict indications, when all possibilities of minimally invasive surgical treatment have been exhausted. There is a goal that the world vertebrosurgery declares - to cure the patient in one day, complete safety of treatment and the absence of complications. So, new technologies of micro-operations really make it possible to do this today.
— What minimally invasive methods are we talking about specifically and what do you use in your Center?
— I probably won’t dive into the world of technology and the biophysical foundations of micro-operations themselves.
If we just list the main or basic methods, then these are DISC-FX Nucleotomy, endoscopic transforamenal discectomy, laser thermodisplasty, cold plasma nucleoplasty, vertebroplasty, radiofrequency denervation, X-ray controlled blockades.
— What can you recommend to our readers? For those who do not want to waste precious time and want to get rid of pain as quickly as possible and return to normal life? What should these people do to avoid the serious consequences that you just talked about?
— Many people think that surgeons are just waiting for the opportunity to cut something off! For a spine surgeon, the main task is to establish the correct diagnosis, clarify the phase of the process, and understand the method of possible treatment. I prescribe and carry out not only minimally invasive or major surgical treatment. At our Center we have an excellent department of physiotherapy and rehabilitation medicine. If there are indications for conservative therapy and radical methods can wait, the patient is sent to this wonderful unit of ours. In 80% of patients who come to us, they receive conservative care in the absence of indications for any surgery, in 17% they receive minimally invasive procedures, and only in 3% they undergo open access treatment and major operations. Therefore, you should not be afraid of coming for a consultation; you must definitely decide on a diagnosis and treatment program for the future.
— Considering your many years of experience, is it possible to get a consultation with you?
— You can make an appointment without any problems. I would especially like to note that the Center hosts outstanding doctors from Israel. We regularly organize international consultations - consultations. Doctors of different specializations participate in them and a comprehensive treatment program is drawn up. We cooperate with:
Professor Ruven Gepstein (Herzliya) -
Doctor of Orthopedics, world-famous spinal surgeon, organizer of our clinic in 2011
and Dr. Alex Kalganov (Assuta) -
expert level specialist in the field of knee and hip replacement.
— Thank you, Sergey Leonidovich, for the interesting interview; it will be very useful for readers of our online resource!
Publications by Dr. Sergey Sarychev, Re-Clinic
- Back pain: you can’t tolerate it, treat it!
- Ask a vertebrologist: answers and advice
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Intervertebral hernia of the thoracic spine
This zone is less likely to suffer from such pathogenesis. However, it is impossible not to inform people what symptoms are characteristic of intervertebral hernias that appear in a certain area of the thoracic region. The most commonly observed signs are:
- sharp, dull, aching, shooting pain in the upper back (the most common complaint);
- pain in the chest (many perceive it as pain in the heart), ribs, upper abdominal area, axillary area, arms (from the armpits to the palm);
- pancreatic enzyme deficiency, dyspepsia, intestinal dyskinesia;
- various kinds of skin paresthesia (numbness, crawling, tingling, etc.), which are felt in the upper extremities along the inner surface, in the epigastric part of the abdomen, on the front side of the chest;
- pain and feeling of weakness in the glenohumeral region;
- difficulty breathing, night snoring, shortness of breath.
If the damage is not limited to the nerve roots and damage to the spinal cord has also occurred, then unpleasant symptoms can spread to the legs, bladder and rectal cavity. A dramatic crisis in the form of paralysis can occur in the entire part of the body located below the damaged segment.
Pain due to lumbar hernia of the spine
Types of pain with a hernia of the lumbar spine:
- Lumbago (lumbago) is the occurrence of acute, sudden pain in the lumbar region associated with some physical movement that causes displacement of the intervertebral disc. At the same time, an instant protective spasm of the back muscles occurs, increasing the pain. Signs of a hernia of the lumbar spine, complicated by lumbago: the patient freezes in the position in which the pain occurred. The attack can last from several minutes to a day and pass as suddenly as it began or decrease under the influence of drug therapy. The cause of lumbago is most often caused by heavy lifting or a sharp turn of the body, so it is more common in men in young and middle age.
- Sciatica (lumbosacral radiculitis) is a sudden infringement of the lumbar roots of the spinal nerves. The continuation of the roots is the sciatic nerve, located in the buttock and posterior surface of the lower limb. The main symptom of a herniated disc in the lumbosacral region, complicated by sciatica, is the appearance of a burning unilateral pain in the leg along the sciatic nerve.
- Constant or recurring pain in the lower back of a very different nature and intensity: aching, twitching, sharp, burning, etc. mainly due to irritation of nerve endings.
How to relieve pain
If the lumbago started suddenly, you need to:
- stop moving or take a position that helps reduce pain;
- ask others to call an ambulance;
- if possible, take any painkiller (analgin, diclofenac, paracetamol, etc.);
- apply anesthetic ointment (Voltaren, Fastum-gel) to the lower back;
- if possible, lie on the floor on your back, bend your knees and place a pillow under your knees.
Emergency medical assistance:
- treatment begins with the intramuscular injection of any pain reliever from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - diclofenac, nimesulide, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, etc.;
- at the same time, a medicine is administered that relieves spasms of the lumbar muscles (muscle relaxant), for example, Mydocalm;
- Neuromultivitis (B vitamins), enhances the analgesic effect of other medications;
- if the pain is not relieved, treatment is continued by performing a paravertebral block: a solution of novocaine or lidocaine is injected subcutaneously into the exit site of the spinal roots;
- if this does not help, treatment is continued in a hospital setting, an epidural block is performed: an anesthetic is injected into the epidural space, located between the hard shell of the spinal cord and the vertebrae.
Dorsal hernia l5 S1
This is one of the most common and dangerous types of protrusion, and mostly occurs in the lumbosacral link l5-S1. This form can also occur in the neck, mainly involving the C5 C6 disc. The word “dorsal” means a hernia in which the displacement is concentrated directly towards the spinal canal (posterior location). That is, if the hernial protrusion is directed into the intervertebral lumen of the spinal canal, it will be called dorsal. Such a hernia, in turn, can be median (central) and paramedian (at an angle). As we said, this is the most typical form of the disease, but central protrusions are more severe because they prolapse into the spinal canal just along the midline.
Education at level I5 S1.
Since it is here that the central nervous system (spinal cord) and the adjacent abundance of nerve plexuses are localized, the appearance of this type of deformation is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms and a more sophisticated set of neurological signs. And in the absence of adequate treatment - blocking the lumen of the canal and paralysis of the limbs. The reasons for its development are the same as for all other hernias.
Why is lumbar hernia dangerous?
The danger of a lumbar hernia is that in the initial stages it occurs with minimal symptoms, and then can instantly manifest itself in severe pain and dysfunction of various organs.
Paying close attention to your health will allow you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and prevent the progression of the disease.
Stages of lumbar hernia
There are several stages during the course of the disease:
- Initial – the lumbar discs change and become thinner. Symptoms: tired and aching lower back, goosebumps.
- Protrusion is cracking of the disc in the lumbar region and displacement towards the nucleus pulposus. At this stage, the pain intensifies, and short-term radicular pain may occur due to disc displacement. Patients tolerate this condition differently: for some, the pain is not too intense and is transient; for others, debilitating local and acute radicular pain due to a herniated spine sharply reduces the quality of life.
- Rupture of the lumbar disc, protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord. All characteristic manifestations of a vertebral hernia appear.
- Sequestration is the separation of individual segments (sequestra) from the nucleus pulposus and their penetration into the spinal canal. Symptoms of irritation and compression of the spinal cord appear: paresis, paralysis, fecal and urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction.
By size, lumbar hernias are divided into small (1 - 6 mm), medium (6 - 8 mm), large (more than 9 mm).
Possible complications
Symptoms of lumbar intervertebral hernia increase rapidly
In the absence of adequate treatment, a lumbar hernia can have serious consequences:
- sudden onset of severe pain in the lumbar region (lumbago) or along the sciatic nerve (sciatica); monstrous pain cannot be relieved using home methods;
- paresis and paralysis – partial or complete immobilization;
- neurological symptoms such as sensory disturbances such as “saddle block” on the inner thighs, perineum and lower buttocks due to compression of sensory nerve fibers; a dangerous symptom, a signal that the disease has progressed;
- dysfunction of the pelvis and genital organs of men and women due to injury to the cauda equina, a bundle of spinal nerves extending from the end of the spinal cord.
Even if one of these symptoms appears briefly, you should immediately seek medical help. If this is not done, the symptoms will quickly increase and the consequences in the form of complications will not keep you waiting. Helping such a patient will not be easy.
What to do during an exacerbation
In some patients, lumbar hernia occurs for a long time without significant symptoms. Periodically, symptoms either disappear completely (remission) or increase (exacerbation). A peculiarity of this course is that with each exacerbation the condition of the fibrous ring worsens. One fine day, instead of a slight exacerbation, paralysis or severe, knocking down pain may suddenly occur.
To prevent this from happening, a lumbar hernia should be treated regularly under the supervision of a doctor, trying to prevent an exacerbation or begin to treat an aggravated disease as early as possible.
Foraminal type and disc protrusion
Foraminal hernia and protrusion are disc bulges facing the aperture where the nerve roots emerge. In other words, the lesion migrates to the narrowest opening in the spine, which in Latin is called “foramen” (intervertebral foramen). This compartment is formed by the posterior arches of two adjacent vertebral bodies. The spinal nerves are freely located in it. When a foreign body appears, especially a larger one, it becomes oppressed, irritated, inflamed, and compressed.
Protrusion.
This is also one of the alarming diagnoses, which differs from others in its rapid progression. It causes the so-called neurocompression syndrome, namely, compression of the roots, which makes itself felt by sharply occurring, pronounced, local attacks of pain, which forces a person to take a forced adaptive posture. When changing position, the pain only intensifies. Analgesics and NSAIDs provide a short-term and insignificant effect.
Surgery relieves persistent excruciating pain that cannot be relieved. Such a fatal stage as sequestration occurs within a fairly short time after the formation of protrusion. Fortunately, this classification of the disease is diagnosed quite rarely; of the total number of all possible variations of protrusion, it accounts for 7%.
Therapeutic drug blockades in the form of hormonal injections, which are given directly to the diseased area, cannot be performed on yourself! This is too complex a manipulation that requires high precision needle insertion and excellent professionalism. Local corticosteroids are indicated in the most extreme situations, if there are debilitating pain symptoms that do not go away after the use of NSAIDs. And remember, hormones do not resolve the hernia, but only relieve local swelling, thereby reducing pressure on the nerve endings.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of a hernia forming or reoccurring, it is important to make lifestyle changes. First of all you should:
- stop smoking and minimize the amount of alcohol consumed;
- do exercise therapy and stretching exercises daily;
- undergo a course of manual therapy twice a year;
- avoid stress and change your attitude towards stressful situations;
- sleep at least 7–8 hours;
- wear high-heeled shoes no more than 2 hours a day;
- visit the pool twice a week;
- balance your diet, give up unhealthy foods and adhere to a normal drinking regime (at least 1.5 liters of water per day);
- take vitamins, especially group B and unsaturated fatty acids (Omega-3).
Localization feature l4 l5
A designation such as l4 l5 means that between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae the integrity of the cartilage lining is broken. This object affects the L4 nerve, which is part of the structure of one large nerve - the sciatic. If we take into account the corresponding part of the spinal column, such damage to the l4 l5 disc (treatment is urgently necessary!) occurs in 46% of cases. In 48% - between the fifth lumbar body and S1 (first sacral), which is not much more common.
Zone l4 l5, the focus is indicated by arrows.
A flat subligamentous hernia l4-l5, known in medicine as hernial sequestration, is the final stage of the disease. With such unfavorable development, the contents of the disc (nucleus pulposus) begin to flow in parts into the cavity of the spinal canal, which is fraught with the complete disappearance of voluntary movements in the limb. When the subligamentous process has begun, even sneezing and coughing cause incredible pain to a person in the form of a terrible lumbago in the lower back, not to mention performing physical tasks. In 80% of cases, the final stage ends in disability. If you undergo emergency surgical treatment, and after it are well rehabilitated, you can hope for 70-80% of the restoration of supporting and locomotor functions as close as possible to normal.
Clinically, the disease in this place manifests itself in a special way, so it is not difficult to distinguish it from a problem, for example, with the cervical area C4 C5. Firstly, there is local hyperalgesia (shooting, aching, pulling in the lower back), and there is also pain radiating to the right or left leg. In addition, the patient complains that the leg is numb, especially in the area of the lower leg and foot, and also that the knee bends insufficiently or muscle-ligamentous weakness is felt in the ankle area. Additionally, increased sweating, marbling of the skin, and curvature of the spine may occur.
Do not sleep on a hard bed or lie down or sit on a cool surface. In case of intervertebral hernia, as orthopedic specialists warn, this is strictly contraindicated.
ICD 10 classification
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, or ICD for short, is a normative document that includes all known human diseases, each of which is assigned its own alphanumeric code. By converting the verbal formulation of the diagnosis into a code value, the convenience of collecting, archiving, retrieving, analyzing, and exchanging data in an international format about a particular disease is ensured. The ICD allows for adherence to uniform standardization in relation to diagnosis and methodological principles in the treatment of a particular pathology. Simply put, it is a referral network that is intended for medical and healthcare professionals.
Patients may encounter an incomprehensible abbreviation, for example, in medical documentation regarding disability. Well, so that you are not puzzled when you see incomprehensible letters and numbers in the statement, we will try to inform you on this issue. So, according to the international classifier, the ICD code for vertebral hernia is assigned strictly taking into account the type and location of the lesion.
- Since the disease belongs to the group “Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue”, to which the Latin letter “M” is assigned, it will begin the code.
- Next comes a certain two-digit number from the “Dorsopathy” category, where 50 are lesions of the cervical spine, 51 are lesions of the thoracic, lumbar and sacral spine.
- Then a dot is placed, and after it another number from the range 0-9 is entered, which will clarify the clinical picture.
For the cervical region, including the cervicothoracic region, for example, 0 is a hernia with myelopathy, 1 is with radiculopathy, etc. For the thoracic/lumbar/sacral zones: 0 and 1 – similar clarifications; 2 – displacement of a different nature (Lumbago); 3 – formation occurring without neurological signs (the same with the neck); 4 – placed for Schmorl’s hernias, known to everyone, and so on. To make it clearer, we give an example of a complete diagnosis in an abbreviated version of a Schmorl’s nodule: M51.4. If the diagnosis is not specified, an additional clarifying examination is required, then M50.9 or M51.9. Although you don’t need ICD codes in principle, a superficial idea of what they are will be enough.
Rehabilitation
The main objectives of rehabilitation are the elimination of postoperative pain, the prevention of complications and the restoration of normal functioning of the spine and muscles. For each patient, a set of measures aimed at solving these problems is selected individually. In some cases, it is enough to stop lifting heavy objects and adjust your lifestyle, but after complex open interventions, serious rehabilitation is required.
The main components of a rehabilitation program can be:
- Exercise therapy is the basis for proper and rapid recovery. Classes begin under the guidance of a specialist and gradually increase the load. It is important to perform all the exercises regularly, not to make sudden movements and monitor your own sensations.
- Wearing a corset - orthopedic structures help to reduce and correctly distribute the load on the spine, which will facilitate rapid recovery.
- Drug therapy – treatment is aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration processes and relieving pain. It may include drugs from the NSAID group, chondroprotectors, vitamin complexes,
- Kinesitherapy is popular because, unlike exercise therapy, it also involves training on orthopedic simulators. Thanks to individual selection of the level of load on the back muscles, it is possible to quickly develop the back muscles without risks.
- Manual therapy is prescribed only by a doctor after the end of the early rehabilitation period. But even after receiving permission, a chiropractor can only use an extremely gentle method of influence - PIR.
- Swimming – regular visits to the pool help to gently and without risks strengthen the muscular corset, which will help maintain the spine in the correct position.
- Therapeutic massage – helps eliminate swelling and avoid muscle atrophy. But you can begin a course of procedures only a few weeks after the operation, and only with the permission of the doctor.
- Physiotherapy – electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, mud baths are used to alleviate the patient’s condition and accelerate reparative processes.
Some patients are additionally recommended to do yoga, stretching exercises, etc. But you can start classes only with the permission of a doctor.
The duration and severity of rehabilitation directly depends not only on the type of surgical intervention performed, but also on the individual characteristics of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, etc. After some operations, patients are not allowed to sit, bend over, or perform certain work. If you ignore medical recommendations, patients run the risk of experiencing postoperative complications or relapse of the disease.
Paramedian hernia T6 T7
The disc, which forms a shock-absorbing “cushion” at the T6-T7 level, which corresponds to the thoracic area, is almost never damaged. This is due to the fact that it is in this part that the spinal structure is very securely fixed by a muscle corset. However, destruction of the T6 T7 disc with all the ensuing consequences cannot be 100% ruled out. It may be a tiny percentage, but it is there. Therefore, if you feel some painful discomfort between the shoulder blades and/or in the hypochondrium, a high-quality differential diagnosis is necessary to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms:
- pneumonia and pleurisy;
- abscess pneumonia;
- heart attack;
- angina pectoris;
- pericarditis, myocarditis;
- inflammation of the esophagus, pancreas, gastric mucosa, etc.
When it is confirmed that the disturbing signs are associated with paramedian protrusion, prolapse of the thoracic intervertebral plate, you need to start fighting it. After all, complications can be terrible - paresis and paralysis of all parts of the body that are located below the focal point.
Surgical treatment of lumbar hernia
Indications for surgical treatment of lumbar spinal hernia:
- severe pain that cannot be relieved by painkillers, blockades and physiotherapeutic methods;
- motor disorders - paresis and paralysis;
- progressive sensory impairment of the “saddle block” type;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
The type of surgical intervention is chosen by the doctor together with the patient. Currently, there are several types of operations when the disc, disc core, and vertebral arches are removed in different ways with the possible subsequent installation of an implant.
Neurologists believe that conservative treatment of lumbar disc herniation is more effective. But there are situations when surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
Army service
We cannot help but touch upon the issue of the army, because the male sex often suffers from this disease. Therefore, we want to immediately inform you about whether they will be recruited into the army if the young man’s medical history includes a herniated disc. In most cases, the conscript is given an exemption.
The pathology we are considering does not allow intense physical training, and is also often accompanied by quite serious complications. A person is shown a special way of life: constant medical supervision, immobilization, proportionate gentle loads and strict adherence to a treatment and prophylactic course.
But it is worth considering that the medical commission considers each case individually, based on the complexity of the specific problem. Uncomplicated, asymptomatic and mild forms of the disease are not an absolute contraindication for enlistment in the military.
To obtain an exemption from the army, you must provide a medical commission with medical information. documentation (together with photographs) from the main place of treatment confirming the diagnosis. Based on the severity of the clinical picture, a verdict will be made: service with restrictions; stock; deferment, when the recruit must recover before the next conscription campaign; complete exemption from conscription (unfit).