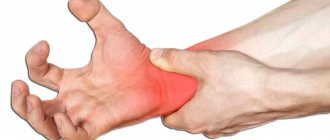
Neuritis is an inflammatory process that occurs in peripheral nerves. The reasons for it can be very diverse.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Depending on the function performed, nerve fibers can be sensory or motor. There are those that are responsible for autonomic functions: regulation of body temperature, blood pressure, functioning of internal organs, frequency and strength of heart contractions, secretion of sweat, saliva, etc. Many nerves in the human body are mixed, that is, they contain fibers of different types. During the inflammatory process, their functions are disrupted.
Types of neuritis
There are different classifications of this condition.
Depending on the number of nerves damaged:
- Mononeuritis is an inflammatory process in a single nerve.
- Polyneuritis is an inflammatory process in many peripheral nerves.
- Plexitis is inflammation of the nerve plexus.
- Radiculitis is a lesion of the nerve roots.
Depending on which nerve is involved in the inflammatory process, there are such varieties as neuritis of the femoral, facial, radial, median, ulnar, peroneal, optic, brachial nerve, etc.
If left untreated, neuritis can lead to serious neurological problems over time, such as impairment (paresis) and complete loss (paralysis) of movement. We advise you not to delay and contact a neurology clinic.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
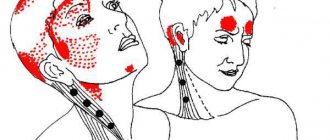
Facial neuritis: symptoms and treatment
In a multifactorial disease of the peripheral nervous system, 7 pairs of cranial nerves are affected. Often the provoking factor is hypothermia of the face. The patient has weakness of the facial muscles.
Signs of asymmetry:
- lack of ability to wrinkle forehead;
- the corner of the mouth is lowered;
- failure to close the eyelids on the affected part;
- failures when trying to smile or whistle;
- speech ceases to be intelligible.
Depending on the level of damage, other symptoms are observed in the treatment of facial neuritis: dry eyes or tearfulness when eating, increased sensitivity to sounds, a pronounced nasolabial fold on the affected side.
To relieve inflammation, medications are used, physiotherapy and therapeutic massage, and acupuncture are performed. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed from the 7th to 10th day of treatment to improve blood circulation and prevent the development of muscle contractures. Therapeutic massage for the treatment of facial neuritis is indicated from 2–6 weeks of the disease, depending on the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Drug treatment of facial neuritis involves taking several groups of medications. The list may include:
- anti-inflammatory drugs: glucocorticosteroids;
- diuretics - to relieve swelling during an additionally prescribed diet;
- B vitamins;
- antispasmodics and analgesics;
- means for symptomatic treatment: for dry eyes, antibacterial drugs, for herpes, acute respiratory viral infections - antiviral drugs.
If the treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out incorrectly or at the wrong time, a complication may occur in the form of contracture of the facial muscles. Spontaneous twitching of the facial muscles is observed; when eating, the palpebral fissure narrows. The cheek on the affected side is thicker. In this case, only plastic surgeons can eliminate the deformity.
Certain types of neuritis:
- Axial (parenchymal). First of all, damage occurs to the axial cylinders - the processes of nerve cells that form the basis of nerve fibers, as well as their myelin sheaths.
- Vegetative. First of all, the nerve fibers that provide autonomic functions are damaged.
- Hypertrophic (Dejerine-Sotta). An inherited disease that usually progresses over time. The nerve fiber sheath grows and compresses the neuron process. It gradually collapses and ceases to perform its functions. Gradually, the patient develops movement and sensitivity disorders.
- Gombo. The nerve sheath disintegrates in certain areas, but the neuron processes are not damaged.
- Interstitial. Inflammation mainly affects the connective tissue within the nerve fiber. Typically, this form of the disease develops as a result of autoimmune processes.
- False optic neuritis. A congenital malformation that may resemble an inflammatory process with its symptoms.
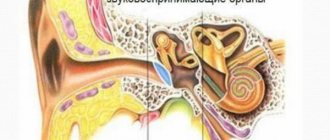
- Cochlear. The inflammatory process occurs in the auditory nerve. At the same time, hearing decreases, the patient complains of tinnitus.
- Rossolimo neuritis. A type of hypertrophic form of the disease. Occurs in children and has a recurrent course.
Prognosis and prevention
Despite timely and correctly prescribed treatment, the prognosis is most often unfavorable. Often there remains a strong decrease in visual function and persistent defects in the periphery of vision caused by atrophy of the optic nerves. An increase in visual acuity of only 0.1-0.2 can be achieved only in 50% of cases. If both eyes are affected at once, there is a high probability of developing low vision or complete blindness.
Prevention of ischemic optic neuropathy is important and involves the treatment of vascular and systemic diseases. A patient who has suffered ischemic optic neuropathy in only one eye urgently needs follow-up with an ophthalmologist with appropriate preventive therapy.
Treatment of neuritis
Despite the large number of different types of neuritis, they are treated in approximately the same way. Usually the doctor prescribes:
- B vitamins , which improve the functioning of the nervous system.
- Drugs that improve blood flow in small vessels.
- Nootropics are drugs that improve metabolic processes and neuronal function.
- Adaptogens are drugs that tone the body and increase defenses.
- Painkillers .
- Calming agents.
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis, pulsed currents, UHF therapy.
- If necessary , if the inflammatory process is caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and antiviral agents.
You should not self-medicate. Without an examination by a neurologist and proper diagnosis, you cannot know exactly what is causing the symptoms that bother you. This means that measures taken independently will most likely be ineffective and may even cause harm. Consult a specialist. Make an appointment with a neurologist at our clinic
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Neuritis is manifested by two main symptoms: pain and dysfunction of the affected nerve: deterioration or complete loss of sensitivity, movements, autonomic functions (sweating and salivation, vascular reactions, etc.).
Some nerves in the human body perform specific functions. For example, the visual one provides vision, the auditory one provides hearing. With the development of inflammation, these functions also deteriorate.
Sensitivity disorder:
- decrease (in severe cases - complete loss) of skin sensitivity;
- numbness;
- paresthesia (unusual, unpleasant sensations): tingling, sensation as if “goosebumps are crawling” on the skin.
Movement disorder:
- partial loss of movement (in severe cases - paralysis of the corresponding muscle group);
- decrease (in severe cases - complete loss) of reflexes;
- muscle atrophy: they become weaker and decrease in size.
Disorders of vegetative functions and symptoms of tissue trophism (nutrition) disorders:
- hair loss on areas of the body;
- brittle nails;
- the skin becomes sweaty, or, on the contrary, excessively dry due to impaired sweating;
- thinning of the skin;
- swelling of the skin; cyanosis, pale skin;
- in severe cases, trophic ulcers appear on the skin.
These symptoms can occur not only with neuritis, but also with other neurological diseases. Only a neurologist can correctly determine the true cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Causes
The main causes of neuritis:
- infectious (viruses, bacteria, their toxins);
- exposure to toxic factors
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, deficiency of vitamins B1 and B6);
- allergic reactions;
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- hereditary diseases;
- diseases of the spine leading to mechanical compression of the nerve trunk (intervertebral hernia, tunnel syndromes, etc.).
The mechanism of nerve damage when exposed to various unfavorable factors is associated with the launch of a cascade of inflammatory reactions. Swelling of the nerve trunk occurs, damage to the myelin sheath and subsequently to the axial cylinder, which in turn leads to the death of the nerve cell.
Make an appointment
Symptoms of certain types of neuritis
Neuritis of the nerves in the forearm. There are three main nerves in the forearm: the radial, ulnar and median. When they are affected, pain occurs, flexion or extension of the hand and fingers is impaired. There is a feeling of numbness and tingling in the hand.
Damage to the brachial nerve. The main symptom is pain. The affected hand becomes less active, the patient uses it worse and less often. Sensitivity is impaired. There is increased sweating of the skin.
Neuritis of the peroneal nerve. The patient limps, often stumbles, and shuffles his feet while walking. Due to impaired movement, he cannot stand on his heels. When taking a step, a person forcefully throws his foot up and forward.
Damage to the femoral nerve. It is difficult for the patient to bend the leg at the hip and knee joint. The muscles on the front of the thigh become weaker and decrease in size. The sensitivity of the skin in the lower half of the thigh and on the inside of the lower leg decreases.
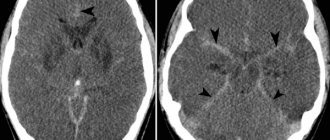
Optic neuritis. There is a sharp decrease in vision. The patient complains of constant or periodic presence of spots and flashes before the eyes. There is severe pain behind the eye, which intensifies when turning the eyeball, and headache.
Cochlear neuritis. The inflammatory process develops in the auditory nerve. As a result, hearing decreases and the patient is bothered by tinnitus.
Clinical picture of some individual nerves
- Trigeminal nerve – pain is sharp, piercing, in series, along one or several branches of the nerve.
- Facial nerve – muscle weakness on one side of the face. It is difficult to close the eye, the corner of the mouth on the affected side is drooping. When liquid food or drink is taken, everything comes out of the mouth.
- Diaphragmatic – feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, hiccups.
- Median – impaired flexion of the hand, fingers I, II and III and decreased sensitivity on the palmar surface.
- Ulnar – weakness of the flexors of the IV, V and partly III fingers, decreased sensitivity on the palmar surface of the above fingers.
- Radial – impaired extension of the hand and fingers, decreased sensitivity in half of the back of the hand (I and II fingers). It is difficult to move the thumb away.
- External cutaneous nerve of the thigh (Roth-Bernhardt disease) – pain, numbness and burning along the outer surface of the thigh.
- Femoral – impairment of leg extension at the knee joint and hip flexion. Pain and sensory disturbances on the lower 2/3 of the anterior surface of the thigh, the anterior inner surface of the lower leg.
- Sciatic – pain along the back of the thigh and lower leg, weakness of the flexors and extensors of the foot.
- Olfactory – anosmia on one side (lack of sense of smell). When a nerve is irritated, foreign odors may appear.
- Visual – decreased acuity and loss of visual fields. The phenomena of nerve irritation manifest themselves in the form of photopsia (sensation of light, flames, sparks, etc.).
- Oculomotor – drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis), limited mobility of the eyeball, dilated pupil, diplopia (double vision).
- Block - restriction of the mobility of the eyeball downwards and outwards.
- Auditory – hearing loss, often accompanied by a feeling of noise or ringing in the ear.
- Glossopharyngeal - twitching pain in the tonsils, root of the tongue, pharynx and taste disturbances in the back third of the tongue, impaired salivation and swallowing.
- Wandering – manifested by disturbances in swallowing and speech. On the affected side, the soft palate is lowered, the uvula is deviated to the healthy side. There are also disturbances in the functioning of internal organs - bradycardia, shortness of breath, motility disorders of the esophagus, stomach and intestines (spasms), etc.
- Additional – difficulty turning the head in the healthy direction, the head is tilted towards the affected nerve, the shoulder is lowered.
- Tibial – the foot is extended, but the patient cannot bend it. Cannot stand on toes. Sensitivity is reduced along the back of the lower leg and on the sole.
- Peroneal – the impossibility of standing on the heels and straightening the foot, it hangs down. Sensitivity is reduced on the outer surface of the lower leg and the back of the foot.
- Intercostal nerves – pain in the intercostal space, often radiating into the chest, simulating pain in the heart, chest, lungs, and stomach. Often, pain in the paravertebral muscles is detected at the level of the thoracic spine.
Symptoms of polyneuritis
Polyneuritis (multiple damage to small nerves) most often leads to “socks” and “gloves” type disorders - sensitivity and movement are impaired in the hands and feet. Typical symptoms of neuritis occur: deterioration of sensitivity, decreased muscle strength, vegetative manifestations (increased sweating or dryness, chilliness, thinning of the skin, increased brittleness of nails). Over time, ulcers appear on the skin as a result of tissue malnutrition.
If you consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms of neuritis appear, especially in young people, there is a high chance that the treatment will be successful and a complete recovery will occur. The prognosis is worse when the disease has not been treated for a long time, it manifests itself with severe symptoms, especially in older people. If you become concerned about the symptoms described in this article, try to immediately contact a neurologist. You can make an appointment with the doctors of our neurological clinic by calling
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Neuritis is a general term that refers to an inflammatory process in the nerves. Its symptoms depend on which nerve is affected and what functions it performs. The reasons can be very diverse. In this article we will talk about the main ones.
Blog
Neuritis is a common nerve disease. It is characterized by pain, as well as a number of other complications, including loss of sensitivity, paralysis, etc. Depending on the affected nerve, several types of neuritis are distinguished.
Optic neuritis
This disease is associated with inflammation of the optic nerve. The main causes of the development of optic neuritis are various infections: influenza, dental diseases, sore throat. Other causes include: eye injuries and inflammatory processes in the brain; liver problems and diabetes; blood diseases and various types of allergies; smoking and alcohol abuse.
Modern treatment of optic neuritis involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. To achieve an effect in treatment, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible, who will prescribe diagnostic procedures, after which he will make a diagnosis and determine the course of treatment.
Among all types of pathology, one of the most common is optic neuritis, treatment of which, depending on the diagnostic results, may include therapy: vitamin therapy, using antispasmodics, detoxification, etc. If you start the course of treatment on time, the result will not be long in coming, in in particular, normal eye functions can be restored.
If it is too late to see a doctor, neuritis will cause serious harm to visual functions and destroy cells, and this can lead to such a serious complication as optic nerve atrophy. Therefore, it is very important to contact a specialist in a timely manner who will prescribe effective treatment.
Facial neuritis
Another common disease is facial neuritis. Treatment of pathology should begin as early as possible to prevent the development of complications. The disease affects the nerve responsible for the facial muscles, which leads to their weakness and decreased (or absent) movements.
There are several characteristic signs by which facial neuritis can be recognized. Symptoms: pain behind the ear and smoothing of the nasolabial fold; violation of facial asymmetry; dysfunction of facial muscles (difficulty smiling, raising eyebrows, etc.).
Other symptoms characteristic of a disease such as facial neuritis include difficulty closing the eyelids or moving the lips (for example, it is difficult to stretch the lips with a tube). One of the features of the pathology is a clear clinical picture, so usually the doctor quickly makes a diagnosis (but if necessary, an MRI, computed tomography, etc. is performed to exclude other diseases).
Various diseases and injuries lead to the development of this type of pathology, including diseases associated with metabolic disorders. Neuritis can be triggered by a genetic predisposition.
A doctor can easily identify neuritis of the facial nerve. Treatment begins immediately to prevent the development of complications. The course of prescription depends on the general condition of the patient. In addition, the specialist looks at the main symptoms of facial neuritis, after which he prescribes special medications (including corticosteroids), and also gives other recommendations.
Brachial neuritis
When the spinal and cervical nerves are damaged, brachial neuritis occurs. Treatment of the disease is based on complete rest of the patient (especially regarding the limb affected by the pathology). For this purpose, the limb is fixed with a splint and bent. To keep the hand in this state, a special bandage is used. Then the neurologist prescribes medications and physical therapy.
The disease is characterized by severe pain and decreased mobility of the arm. In some cases, neuritis can cause partial loss of sensation in the limb: the inability to move the fingers or perform simple flexion movements of the hand. All this can lead to muscle atrophy.
Surgical treatment of brachial neuritis allows achieving effective results. The main drugs prescribed to the patient are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; they are applied to the areas of the shoulder where pain occurs (orally or subcutaneously).
The main symptoms of the pathology: loss of sensation in the shoulder and forearm; weakening of the shoulder muscles and difficulty bending the elbow; impaired fine motor skills and loss of sensation in the fingers.
There are two main types of brachial neuritis: lower and upper; depending on the pathology, symptoms may differ. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis by conducting an examination and prescribing a diagnosis for the patient (ultrasound, X-ray, MRI and other procedures may be prescribed at the discretion of the specialist).
Trigeminal neuritis
Thanks to modern techniques, treatment of trigeminal neuritis allows you to quickly overcome the disease. This pathology is characterized by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which causes severe pain in the facial area. The disease is quite common; in total, about 1 million people suffer from this type of neuritis in the world. Women over the age of forty are at risk.
What causes the development of the trigeminal nerve? Let's highlight the main reasons:
- meningitis and various injuries;
- consequences of concussions;
- viral infections and herpes;
- colds, etc.
Bacterial infections, multiple sclerosis, long exposure to cold - all this also leads to a pathology such as trigeminal neuritis. treatment is prescribed by a doctor who focuses on the general condition of the patient and diagnostic results.
The main symptoms of trigeminal neuritis are severe pain in the face (sometimes so painful that the patient cannot find a place to rest and suffers from insomnia). The pain may be cyclical, affecting the lower face or areas around the eyes and nose. In different cases, pain occurs at different frequencies - hourly or once a day.
To stop the attacks, you need to urgently start treatment by contacting a specialist. Our medical center uses various techniques, including conservative treatment, which helps eliminate symptoms and completely cope with the disease.
Auditory neuritis
Many patients are diagnosed with a type of pathology such as auditory neuritis. Treatment of the disease begins after the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. The pathology develops due to inflammation of the auditory nerve, which leads to hearing problems. Most often, this type of neuritis affects older people. Let us highlight the most common symptoms of auditory neuritis:
- hearing problems are a key symptom; if treatment is not started in time, neuritis will continue to progress, which can lead to complete hearing loss;
- noise and ringing in the ears - patients often complain of such symptoms characteristic of advanced neuritis, so if you see a doctor right away, these symptoms can be avoided;
- dizziness, gait disturbance (unsteadiness), frequent headaches, etc.
Among the patients, most of them are men (over the age of 55-60 years). One of the reasons for the development of the disease and the deterioration of the patient’s condition is a late visit to the doctor, since at this age many older people attribute deteriorating hearing to years, considering this a completely typical phenomenon.
If you start treating acoustic neuritis on time, you can relieve symptoms and stop the progression of the disease. Neuritis is diagnosed by audiometry (the doctor checks the quality of the patient's hearing by playing sounds at different frequencies). Patients are prescribed analgesics, diuretics, and special medications that help improve blood circulation.
Main causes of neuritis
Infections. Neuritis can be caused by diseases such as herpes simplex, shingles, diphtheria, influenza, mumps (mumps).
Inflammatory processes in neighboring organs. For example, with otitis media (inflammation of the tympanic cavity), neuritis of the facial nerve may develop.
Injuries. Mechanical factors (trauma, constant vibration), chemicals, and ionizing radiation can lead to damage to nerve fibers with subsequent development of inflammation. Often, an inflammatory process in a nerve occurs after it is bruised.
Long-term nerve compression. Probably, any person is familiar with the state when he “rested” his leg or arm in a dream. Numbness, tingling, and other unpleasant sensations occur. They usually go away quickly. But sometimes neuritis can develop. People who constantly use crutches may develop brachial neuritis.
Herniated intervertebral discs. Prolonged compression of the nerve root can lead to inflammation.
In order to eliminate the cause of the disease, it must be reliably diagnosed. In addition, you need to understand the degree of impairment of motor, sensory, and autonomic functions. This can only be done by a qualified neurologist. Self-medication will be ineffective at best, and can be harmful at worst.
Polyneuritis usually occurs as a result of a systemic effect on the body, when many small nerves are damaged. Reasons that can lead to this condition:
- Hypovitaminosis and avitaminosis. Some vitamins are necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system, for example, B1, B12.
- Diabetes. Diabetic polyneuritis is one of the most common complications in diabetics. Sometimes symptoms appear before a person even knows that he has diabetes.
- Various infections. Unlike mononeuritis (damage to one nerve), in this case pathogens or their toxins affect the entire body, resulting in damage to many small nerves.
- Poisoning with certain substances. For example, salts of heavy metals.
- Chronic alcoholism. Ethyl alcohol and its metabolic products have a toxic effect on nervous tissue.
- Autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune inflammation develops in the nerve fibers, which leads to their death.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant tumors release toxic metabolic products that travel through the bloodstream and have a negative effect on various organs and systems.
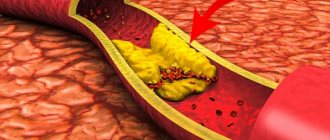
- Vascular disorders. For example, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis. As a result, the nerve fibers cease to receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients, and an inflammatory process occurs in them.
Causes of inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve
Factors contributing to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve are:
- surgical interventions on the jaw bones;
- fractures of the base of the skull, lower and upper jaws;
- tumors;
- complex tooth extraction;
- hypothermia;
- surgery on the maxillary sinus;
- improperly administered anesthesia;
- incorrectly performed dental prosthetics;
- metabolic disorders;
- the presence of foreign bodies that irritate the nerve trunk or injure nerve endings;
- bacterial or viral infection;
- various types of intoxication of the body;
- hypovitaminosis;
- weakening of the immune system.
How does a neurologist determine the cause of a disease?
In order for the doctor to understand why you have neuritis, he needs to get detailed information from you. You may be asked questions:
- When did your symptoms start bothering you?
- After what did they arise? Have you had any illness or injury before?
- Do you have arterial hypertension, diabetes, or other chronic diseases?
- Where do you work? Does your profession involve exposure to harmful substances or vibration?
Also, examination is of great importance in identifying the causes of the disease.
Sometimes the cause of neuritis is a serious pathology that requires separate treatment. Therefore, as soon as symptoms begin to bother you, it is better to immediately consult a doctor. Get a consultation with a specialist at our neurology clinic in Moscow. Sign up for a time convenient for you by phone
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
As with many other diseases, the effectiveness of treatment for neuritis largely depends on early diagnosis. If the disease is detected when the first symptoms appear, especially in young people, the likelihood that all nerve functions will be restored is highest.
If time is missed, especially in older people who have chronic diseases, paralysis may occur and contracture may form. The muscles decrease in size, joint mobility is limited, and the limb freezes in one position.
Thus, early diagnosis of neuritis plays an important role. It can be divided into three stages: a conversation in the doctor’s office, examination and special tests, instrumental and laboratory tests.
Basic treatment methods
- Tissue neuroadaptation
- Pharmacoacupuncture
- Magnetotherapy
Drug treatment is also carried out, taking into account the specifics of the patient’s condition.
In a particularly severe form of nerve inflammation, the patient may require surgery, especially if something is putting pressure on the nerve.
Some people with neuritis try classical practices that are now used in modern spine and joint clinics. For example, acupuncture.
Conversation in the doctor's office
When questioning the patient, the doctor may suggest the presence of neuritis and its possible causes. The most frequently asked questions are:
- What are your complaints? Are you bothered by pain? Is movement or sensitivity of the skin impaired? Have you noticed that lately your hands or feet have started to sweat more, or your skin has become drier?
- When did the complaints start? What happened before this? Have you suffered from any illness? Was there an injury?
- What illnesses have you had during your life? What chronic diseases do you have?
- What infections have you had recently?
- Where and who do you work for? Do you have to deal with harmful chemicals? Are you affected by vibration in your workplace?
Try to answer as detailed and accurately as possible. After questioning, the doctor proceeds to the examination.
The worst thing you can do when symptoms of neuritis appear is to self-diagnose and self-medicate. Most likely, without examination and prescriptions from a neurologist, without examination, independent treatment will not be beneficial, and in the meantime the disease will progress.
Neuralgia of the sciatic nerve:
characterized by dull or shooting pain along the nerve (buttock, back of the thigh, lower leg).
Decreased sensitivity may occur.
Neuralgia, the symptoms of which include decreased muscle tone in the affected lower extremity, suppressed tendon reflexes in the area of the nerve, increased pain when lifting the leg in a supine position (Lasegue's sign or tension) or during squatting, may have tenderness in the area of the sciatic nerve exit ( middle of the gluteal fold).
Neuralgia of the sciatic nerve is very common in people with osteochondrosis or intervertebral hernia in the lumbar spine.
Sciatic neuralgia is a very painful condition that greatly worsens the patient’s life.
Neuritis, the symptoms of which can be different, are similar in that this inflammation causes quite severe pain that worsens a person’s daily life.
Neurological examination and special tests in the diagnosis of neuritis
First, the doctor conducts a standard neurological examination, during which he checks reflexes, skin sensitivity (by touching it with a brush and a needle), assesses muscle tone and strength, sense of balance, and coordination of movements. Then, depending on the damaged nerve, special tests are performed:
Diagnosis of median nerve neuritis:
- The brushes lie on the table, palms down. The doctor asks you to scratch the table with your index finger. The patient fails to do this.
- The patient cannot clench his hand into a fist because the flexion of his thumb, index and middle fingers is impaired.
- The patient cannot connect the tips of the little finger and thumb.
Diagnosis of ulnar nerve neuritis:
- The brushes lie on the table, palms down. The doctor asks you to scratch the surface of the table with your little finger. The patient fails to do this.
- The patient's hands lie on the table, palms down. The doctor asks him to separate his little finger and ring finger. The patient fails to do this.
- The patient cannot completely clench his hand into a fist due to impaired flexion of the little finger and ring finger.
Diagnosis of radial nerve neuritis:
- The brushes lie on the table, palms down. The doctor asks you to raise your middle finger and place it on the adjacent one. The patient fails to do this.
- The patient's hands lie on the table, palms up. The doctor asks him to move his thumb to the side. The patient is unable to do this.
- They ask you to put your palms together and spread your fingers. As a result, the fingers on the affected hand become bent.
Causes of the inflammatory process
Pathology appears after bacterial and viral infections or under the influence of external factors and internal processes in the body. The most common reasons are:
- consequences of ARVI, sore throat, bronchitis, influenza;
- previous injuries;
- pathological changes in blood vessels;
- poisoning: alcohol, toxic substances;
- diseases of the endocrine glands: thyrotoxic goiter, diabetes mellitus.
The disease also occurs due to compression of the nerve trunk. The reason may be the constant adoption of an uncomfortable posture. Thus, pianists and cellists often suffer from neuritis of the median nerve of the hand. Treatment will help avoid complete loss of sensitivity in the fingers or hand, and atrophy of muscle tissue.
Instrumental and laboratory methods for diagnosing neuritis
In order to identify the location and extent of nerve damage, electroneuromyography is used, a diagnostic method during which electrical impulses in nerve fibers are recorded.
To diagnose the cause of the disease, the doctor may prescribe other studies and tests. In case of optic neuritis, the patient is sent for consultation to an ophthalmologist, in case of cochlear neuritis - to an ENT doctor.
The sooner you visit a doctor and undergo an examination, the more effective the treatment will be, and the higher the likelihood that the functions of the affected nerves will be fully restored. Need a consultation with a neurologist? Call our neurological center in Moscow.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Diagnostics and therapy
When a patient comes in, the doctor performs functional tests. At the Innovative Medical Center, consultations are carried out by high-level specialists, doctors and candidates of medical sciences.
Regardless of the form of the pathology, physiotherapy and medication are prescribed. The latter enhance the effect of drugs during the treatment of neuritis of the femoral nerve and other types of lesions of the nervous system. The procedures do not injure the skin and soft tissues, do not cause complications, and act locally.
To recover from sciatica, a complex of physiotherapeutic methods is often used. In our clinic we carry out:
- Shock wave therapy (SWT). It relieves swelling, improving the effect of medications in the treatment of facial neuritis. When a nerve is pinched in the carpal tunnel, it removes fibrosis and tendon deposits.
- HIVAMAT - massage with a pulsating electrostatic field. Physiotherapy helps eliminate swelling and pain, inflammation, and improves trophism.
- Acupuncture. Usually prescribed for the treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve. Reviews from satisfied patients indicate a rapid recovery after therapy. The procedure reduces swelling along the movement of the nerve trunk, restores sensitivity and nerve patency, and relieves inflammation.
- Massotherapy. Indicated for almost all types of neuralgia, including the treatment of traumatic neuritis. In the first days of illness, professional massage therapists perform it in a gentle manner locally, depending on the area of inflammation. For example, during the treatment of trigeminal neuritis, the collar area, the occipital part and the affected area of the face are rubbed and stroked.
A positive result is possible only with complex treatment of neuritis, eliminating the symptoms and causes of its occurrence. Success depends on many factors, in particular on the stage of the disease, which is diagnosed after examining the patient by a neurologist. To quickly get rid of the problem without surgery, it is important to promptly contact competent specialists for help.
The article was reviewed by Professor, Dr. med. Sciences, neurologist Ronami V.G.
Symptoms of neuritis
Most peripheral nerves consist of nerve fibers of different types: sensory, motor and autonomic.
Damage to each type of fiber gives the following symptoms characteristic of any neuritis:
- Pain and numbness when the nerve is damaged by neuritis;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Impaired motor functions, muscle weakness;
- Autonomic disorders (impaired skin condition, pupils, blood pressure, breathing, etc.);
- Trophic disorders - the appearance of ulcers on the human body.
How to treat neuritis
Treatment of the disease consists of relieving pain and eliminating its cause. The Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics uses the following methods for treating neuritis:
- Manual therapy;
- Osteopathy;
- Medical massage;
- Acupuncture;
- Pharmacopuncture;
- Isometric kinesiotherapy;
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation;
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations;
- Therapeutic droppers.
During treatment, the patient is offered a comprehensive individual program, consisting mainly of gentle, time-tested treatment methods.
Prognosis for neuritis
Neuritis, the symptoms of which have not progressed, as well as in young people whose tissues are easily restored, have a good prognosis in treatment.
In elderly people with chronic concomitant pathology, the prognosis is not so favorable.
In the absence of adequate treatment for this inflammatory process, the listed complications may occur, the main of which will be muscle atrophy and the development of contractures that interfere with movement.