Head injuries include damage to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, skull bones and brain matter. These are particularly dangerous injuries for the human body, since soft tissue injuries are often accompanied by heavy bleeding, and bone fractures are complicated by brain damage, which in injury statistics accounts for half of all injuries. A quarter of the victims die from cardiac arrest due to untimely or ill-provided medical care.
Causes of head injuries
Head injuries occur as a result of such events:
- • injuries in everyday life, fights;
- • injuries at work;
- • use of firearms;
- • injuries during an accident.
Classification of head injuries
The following types of head injuries are distinguished:
- injury to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles,
- fractures of the skull bones.
All injuries can be closed (bruise) or open (wounds). There are also fractures of the skull (vault and base) and facial skull (the most common are fractures of the upper and lower jaw, the temporal bone).
Consequences of a head injury
In most cases, mild bruises of the soft tissues of the head in the form of bumps and bruises disappear on their own within 7-14 days, without causing negative consequences.
Consequences of a head injury can include headaches and dizziness.
If the injury is serious enough and there is no treatment, the following complications may develop:
- deterioration in performance;
- memory impairment;
- sleep problems (drowsiness during the day or insomnia at night);
- difficulty concentrating;
- frequent dizziness;
- headache;
- weather dependence;
- irritability.
To prevent a bruise of the soft tissues of the head from causing complications, the patient must follow all the doctor’s recommendations during the treatment period. It is important to avoid heavy physical activity and spend less time at the computer.
It is necessary to follow a routine, sleep at least 7 hours a day and walk in the fresh air for a long time. If, despite treatment, the general condition does not improve, you should consult a doctor again.
Signs of head injuries
All types of head injuries have their own symptoms and mechanisms, knowledge of which will allow you to provide competent assistance to the victim at the scene of the incident. A bruise occurs when struck by a hard object. It can manifest as subcutaneous limited or diffuse hemorrhage, characterized by the presence of fluctuation (softening).
Head wounds can be penetrating (in which the dura mater is damaged) and non-penetrating (without damaging it). Depending on the wounding object, they are divided into cut, chopped, stabbed, bruised, and gunshot wounds.
Cut wounds are inflicted with a knife, blade and other sharp objects. They are accompanied by pain, heavy bleeding; their edges are even, smooth, and gape widely. Chopped wounds occur when struck by a sharp heavy weapon, deep; As a rule, the substance of the brain is damaged. Puncture wounds have a deep channel and are dangerous for the development of anaerobic infection. Bruised wounds are less dangerous, however, they are accompanied by severe damage to surrounding tissues with their further necrosis. Scalped wounds are characterized by damage to surrounding tissue and heavy bleeding. Gunshot wounds are superficial (without damage to the bone) and deep (non-penetrating and penetrating - with damage to the bone, meninges and brain substance).
Fractures of the facial bones reach 4% of skeletal fractures, but the most common are fractures of the lower jaw. With such a fracture, the following signs are determined:
- the patient has difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- the jaw is tilted to the side,
- speech is impaired,
- pain and pathological mobility of fragments are noted.
A calvarial fracture occurs after strong impacts with depression and rupture of the skull bones. It is characterized by:
- the presence of deformation, depression or protrusions,
- mobility of bone fragments and crepitus (a sound reminiscent of that heard when walking on snow in cold weather).
- with an open fracture, brain matter can be seen in the wound.
Fracture of the base of the skull appears:
- leakage of blood and cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) from the nose and ear,
- symptom of “spectacles” - hemorrhage into the tissue around both eyes,
- exophthalmos (displacement of the eyeball forward).
It must be remembered that the severity of the victim’s condition will be determined not by a bone fracture, but by a traumatic brain injury.
Symptoms
Signs of a soft tissue injury to the head:
| Symptoms | Description |
| Painful sensations | They arise as a result of a blow, as well as a subsequent sharp spasm of blood vessels. In severe cases, headache may accompany the patient during the recovery period |
| Hematoma | Formed at the site of impact. A hematoma (often called a lump) occurs due to hemorrhage due to rupture of large and small capillaries. Blood accumulates in the resulting cavity, and swelling and bruising appear on the skin |
| Other Possible Signs | When the skin is cut, abrasions and wounds occur. If the bruise occurs in the nasal area, bleeding may develop. When the lips are damaged, severe swelling is often observed in this area. Damage to soft tissue in the forehead, eyes and bridge of the nose leads to bruising |
The following symptoms may indicate a concussion:
- short-term loss of consciousness and memory (up to 3–5 minutes);
- moderate headache;
- single vomiting without nausea;
- involuntary eye movement (nystagmus).
First aid for head injury
In case of a soft tissue bruise, you need to put a bag of snow, ice or water on the victim's head. You can also moisten several layers of gauze with cold water, squeeze well and apply to the bruised area. The edges of the wound should be treated with a 1% alcohol solution of iodine or a 5% alcohol solution of brilliant green and cover it with a sterile gauze bandage; bleeding is stopped with a pressure bandage. If there are signs of fractures of the cranial vault, then the bandage is applied very carefully. Pieces of bones, metal, and fragments protruding from the wound are not removed to avoid bleeding. If brain matter is visible in the wound, do not press it down; several sterile napkins are placed on the wound, and a roller is placed around them, which is rolled up from cotton wool and gauze like a donut. A bandage should be applied on top. If the base of the skull is fractured, the victim is laid horizontally, with the head turned to the side. In case of a fracture of the lower jaw, stop the bleeding using tampons and a sterile bandage; bleeding can also be stopped by pressing the artery with a finger to the angle of the lower jaw. You can also bandage the lower jaw to the head with a sling bandage. The victim's mouth must be cleared of knocked out teeth, vomit and blood clots. If there are no wounds, apply cold to the damaged area. If necessary, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
The life of a victim with a head injury depends on who is nearby at the time of the incident: a person can be saved only when the injury is recognized in a timely manner and qualified first aid is provided. After providing first aid, be sure to call an ambulance.
Treatment at home
Treatment of hematomas
In order to quickly get rid of a hematoma at home, external agents are used, which include heparin, troxerutin, horse chestnut or medicinal leech extract (Lioton, Lyogel, Troxevasin, Sinyak-OFF, Venitan). They are applied to the damaged area up to three times a day.
Heparin-based agents are used to treat hematomas
Drugs from this group improve blood circulation, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, and resolve blood clots. Their use speeds up recovery and shortens the treatment period.
Such ointments and gels are not recommended for use in cases of hypersensitivity to the components, as well as in diseases accompanied by blood clotting disorders. The products should not be applied to damaged skin; they should be used with caution during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Painkillers and decongestants
If a head injury is accompanied by severe pain, the doctor may recommend taking analgesics: Paracetamol, Analgin, Tempalgin. Drugs based on ibuprofen (Imet, Nurofen, Ibuprom) or nimesulide (Nimid, Nimesil) help cope with pain.
If a bruise is accompanied not only by pain, but also by severe swelling of soft tissues (in case of injuries in the nose or eyes), then the patient’s condition can be alleviated with the help of drugs such as Flamidez or Maxigesic. The composition of the products includes diclofenac potassium, paracetamol and serratiopeptidase.
Drugs in this group have pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-edematous and fibrinolytic effects. The medicine is taken twice a day after meals with a glass of water. Treatment is continued for 5 days. During this period, the patient's condition improves significantly.
Folk remedies
A bump or bruise due to a contusion of the soft tissues of the head can be dealt with using folk remedies:
- recipe No. 1: peel the potatoes and grate them on a fine grater. The pulp is wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected area for half an hour. The procedure is repeated 3–4 times a day;
- Recipe No. 2: starch helps to quickly remove a bruise. The powder is diluted with warm water to the consistency of thick sour cream and applied to a bruise or bump. After the product dries, it is washed off with warm water. The procedure is repeated twice a day until the condition improves;
- recipe No. 3 : to quickly remove a lump, beat off a cabbage leaf and apply it to the hematoma, securing it with a bandage on top. The sheets are changed as necessary. Use this remedy until the lump decreases;
- Recipe No. 4: immediately after a bruise, wash the damaged area with laundry soap and leave it until dry, this will make it possible to prevent the appearance of a bruise. This product should not be used if the skin is damaged;
- recipe No. 5: in order to reduce swelling, you can use a compress with apple cider vinegar. For these purposes, only natural products are used. Vinegar is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1, a napkin is moistened in the solution and applied to the damaged area, securing it with a bandage. The compress is left for two hours. The procedure is carried out daily. You should not use apple cider vinegar if your skin is damaged, as it may increase pain.
Prevention
Here are some tips to help prevent or minimize the risk of head injuries:
- Wear protective clothing when playing sports and other recreational activities. Ensure that the equipment is properly installed, in good condition and used correctly. Follow the rules of the game and exercise good sportsmanship. Wear a protective helmet when riding a bicycle, motorcycle, snowboard or any other activity that may cause head injuries.
- Fasten your seat belts. A seat belt can prevent serious injuries, including head injuries, during a car accident.
- Make your home safe. Keep your home well lit and the floor clear of any trip and fall hazards. Falls in the home are one of the leading causes of head injuries.
- Protect your children. To reduce the risk of head injuries to your children, block the stairs and install window guards.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise regularly to strengthen your leg muscles and improve your balance.
- Educate others about concussions. Educating coaches, athletes, parents and others about concussions can help spread awareness. Coaches and parents can also help promote sportsmanship.
Features of treatment in children
You can prepare ice cubes with parsley in advance; they will help relieve swelling in case of a severe forehead bruise. To do this, pour water on the leaves of the plant, freeze and use as needed.
The baby will have a bruise and bump on the forehead even after a small bruise. However, injuries before the age of 3 can be dangerous because the child's skull is not yet strong and cannot protect the brain from shock. After an injury, you need to closely monitor your child.
If he loses consciousness, has incoordination, vomiting and a severe headache, then an ambulance should be called.
If the injury does not cause the child much discomfort, then cold should be applied to the bruised forehead and, if necessary, an anesthetic should be administered (Panadol, Ibufen). Don't worry while your baby is still happy and active.
To treat hematomas in a child, you can use Aibolit ointment. The composition of the drug is safe for children, made on the basis of beeswax. The bruise should be lubricated with ointment every morning and evening.
Types of occipital headache after a blow
Types of pain that occurs after a blow to the back of the head:
- superficial (superficial) – better localizable, localization depends on the number of afferent fibers; there is sensitivity of the lips, tongue, hands;
- deep somatic - pain transmitted from the periosteum, muscles and ligaments, has a dull nature, longer duration; most often occurs in sports (when a person is hit in the back of the head - martial arts);
- visceral – characterized by transmission to various superficial areas; pain is transmitted along the surface of the body innervated by the same spinal segment;
- radicular - occurs when the dorsal roots are irritated, pain can affect the entire area of innervation of the affected segment, the pain is sharp, irregular attacks are typical;
- neuralgia - pain in the area of the brain or spinal nerves, can be caused not only by injury, but also by infection; the pain is caused by the hypersensitivity of neurons, i.e. we are not talking about a morphological lesion;
- causalgia - nerve damage that causes irritation of the dorsal spinal roots; the pain is paroxysmal.
Diagnostics
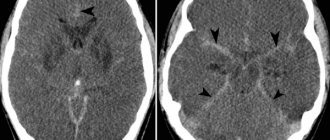
Timely, correct diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis for severe head injuries; the doctor identifies the nature and extent of the damage and determines what to do. Priority methods of instrumental diagnostics are CT and MRI. During neuroimaging, the exact localization of the pathological focus, the presence of intracranial hematomas, and the extent of the pathological process are detected.
To assess the state of consciousness, the criteria of the Glasgow scale are used. In a hospital setting, a blood test is done to determine the concentration of glucose and electrolytes, blood clotting indicators. In some cases, lumbar puncture is indicated (confirmation of the presence of intracranial bleeding, exclusion of infectious lesions of the central nervous system).
Risk factors
Activities and factors that may increase the risk of a concussion include the following:
- Falls, especially in young children and older adults
- Participation in high-risk sports such as football, hockey, football, rugby, boxing or other contact sport
- Participating in high-risk sports without proper protective equipment and supervision
- Get into a car accident
- Have been involved in an accident due to a pedestrian or bicycle
- Be a soldier involved in battle
- Being a victim of physical violence
- Having previous concussions
Treatment of a bump on the forehead
If no complications arise after a bruise on the forehead, the bump can be treated at home. The victim was hospitalized with symptoms of a concussion and intracerebral hemorrhage. To treat the tumor, you can use medicinal ointments and traditional medicine methods. As a rule, the use of medicinal products is not allowed. It is necessary.
A cold compress to relieve swelling is first aid for a bruised forehead
In the first days, treatment of the tumor consists of stopping bleeding and reducing swelling of the soft tissues using cold. Then it is necessary to speed up the resorption process, which allows you to quickly remove the lump.
Large hematomas are removed by a doctor in a hospital by bending them with special needles to collect excess fluid from the soft tissue after bleeding.