Diseases that start with the letter “M”: Lesser chorea, Slow infections of the central nervous system, Medulloblastoma, Herniated disc, Thoracic disc herniation, Lumbar disc herniation, Cervical disc herniation, Intercostal neuralgia, Meningeal syndrome, Meningioma, Meningitis, Meningococcal meningitis, Meningomyelitis , Meningoencephalitis, Metabolic myopathy, Metastatic brain tumors, Metachromatic leukodystrophy, Weather sensitivity, Myasthenia gravis, Migraine stroke.
Meningoencephalitis is a disease of a neuroinfectious nature, occurring with simultaneous damage to the substance of the brain and its membranes. It is expressed by variable focal, membrane, infectious symptoms. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a neurological examination, assessment of cerebrospinal fluid, MRI and CT results of the brain, and examinations designed to identify the pathogen. Complex treatment consists of prescribing antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal drugs in combination with symptomatic and pathogenetic drugs.
Meningoencephalitis viral, bacterial, parasitic
The term “meningoencephalitis” includes two nosological forms: “encephalitis” and “meningitis”.
The definition describes the morphological changes that occur against the background of pathology - damage to the white matter and meninges. The pathology is characterized by high mortality, disability, and a large number of disorders. Diagnosis of the symptoms of the disease at the beginning of its development, prevent dangerous consequences, eliminate damage to functional centers. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the cause, pathogen, and extent of the inflammatory focus.
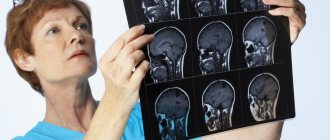
The initial signs of pathology are neurological disorders. Neurologists conduct differential diagnostics that allow one to suspect meningoencephalitis and timely prescribe neuroimaging methods (brain MRI and CT).
Development of the disease
Inflammation is a response to the introduction of a pathogen into brain tissue. Its purulent or serous nature is associated with the type of infectious factor. An inflammatory focus forms around blood vessels, which causes cerebrovascular accident. As a result, secondary tissue ischemia and a compensatory increase in the production of cerebrospinal fluid occur, which affects the development of intracranial hypertension.
The membranes of the brain damaged by infection become irritated and cause meningeal syndrome. Inflammatory foci can have varying degrees of distribution in the cerebral substance. Focal manifestations are formed due to neurological insufficiency of brain functions. Persistent neurodeficiency is the result of massive death of brain neurons.
Meningoencephalitis - what is it?
There are congenital and acquired forms. Meningoencephalitis in children occurs due to intrauterine infection (cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, meningococcal). Immediately after birth, it is difficult to identify the nosology, since the child cannot talk about sensations.
In the first month of life, the first signs appear. Only the acute variety is accompanied by multiple changes, which often lead to death. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid helps to suspect inflammation of the brain and membranes at the beginning of development.
The procedure is invasive and is prescribed according to strict indications. The harmlessness of MRI for meningoencephalitis makes it possible to prescribe examinations for newborns and infants. The high cost of equipment excludes the possibility of installing devices everywhere.
The main causes of mortality from inflammatory processes of the soft membrane and brain parenchyma:
- Intracerebral edema;
- Infectious shock;
- Cerebral hypertension;
- Kidney failure.
The consequences of the disease in subacute and chronic forms develop over several years.
MRI meningoencephalitis
Treatment
An integrated approach to treatment includes a combination of pathogenetic, etiotropic and symptomatic therapy in the intensive care unit:
- Antibacterial treatment includes cephalosporins with ampicillin. The adjustment occurs after isolating the pathogen and determining sensitivity.
- Antiviral drugs are included in treatment when determining the viral etiology. Ganciclovir is prescribed for herpes, ribavirin for arbovirus. Additionally, interferon is prescribed.
- Among antifungal drugs, fluconazole B and amphotericin B have a powerful effect. Sometimes they are combined in especially severe cases.
- Antiparasitic drugs are combined with antibiotics and antifungal agents.
- Diuretics and glucocorticosteroids reduce cerebral edema. The integrity and viability of neurons is ensured by neuroprotectors and neurometabolites.
Symptomatic treatment relieves the main signs of the disease. It includes cardiovascular drugs, oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, anticonvulsants and psychotropic drugs. Rehabilitation measures are aimed at restoring nervous functions (massage, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, acupuncture).
ICD 10 code for meningoencephalitis
The international classification of the tenth revision identifies the following types of brain inflammation with code “G04”:
- Meningomyelitis;
- Meningoencephalitis;
- Acute ascending myelitis.
The category excludes multiple sclerosis (“G95”), toxic, alcoholic encephalopathy “G31.2”, “G92”.
Classification of meningoecephalitis by course:
- Chronic – long-term development with a slow increase in symptoms;
- Subacute - erased signs of nosology increase over two to three years;
- Acute – rapid progression of symptoms helps early diagnosis;
- Fulminant – rapid cerebral damage causes death.
The difficulties of verifying pathology are complicated by the variety of etiological factors.
Diet
High protein diet
- Efficiency: 5-6 kg in 2 weeks
- Terms: 7-14 days
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
If you have meningoencephalitis, you need to eat a nutritious and varied diet. Doctors recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- Reduce the amount of salt.
- Introduce a sufficient amount of easily digestible protein products into the diet - milk, fish, meat, eggs.
- You need to consume about 100 g of fat per day.
- It is important to include a sufficient amount of vitamin-rich foods in your diet to prevent deficiency of substances important for the body. Foods high in vitamin B (vegetables, bran, meat, yeast) are especially important.
- You can't practice low-calorie eating.
Causes of meningoencephalitis
Viral forms provoke chronic and subacute varieties. An acute course can be observed in people with immunodeficiencies. Pathogenic bacteria quickly destroy the arachnoid, subarachnoid membranes, and brain parenchyma. Parasitic (amebic) species progress slowly.
Features of influenza hemorrhagic meningoencephalitis
Nosology is a consequence of influenza. An acute respiratory viral infection provokes a rise in temperature and enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsils. Long-term persistence of infection causes epileptic convulsions.
Fever increases brain destruction, but no antiviral treatment has been developed. Vaccination and strengthening the immune system are the main measures to counter the spread of influenza hemorrhagic infection.
Principles for diagnosing viral meningoencephalitis:
- Absence of bacteria in brain preparations when stained by Gram;
- Cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis;
- Detection of enteroviruses, arboviruses, herpesviruses using polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Severe and fatal cases are caused by enteroviruses. Over serotypes of pathogens have been identified, causing a variety of clinical manifestations of the disease. Enteroviral neuroinfection often leads to death and disability.
After a bite from ticks, insects, or mosquitoes, the inflammatory process of cerebral tissues is caused by arboviruses if the carrier was infected with microbes. In addition to humans, these pathogens infect horses and dogs, which can also be a source of infection for humans.
Common encephalitis caused by arboviruses:
- West Nile fever;
- Encephalitis St. Louis;
- California uniform.
The prevalence of diseases has been increasing in recent years.
Symptoms of herpetic encephalitis
Activation of herpetic neuroinfection is the cause of death in approximately seventy percent of adults and children. The lack of antiherpetic therapy excludes the possibility of effective treatment. Only a strong immune system can cope with the herpes virus. The weak body of a pregnant woman in the presence of infection becomes a source of infection of the fetus in utero.
Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) becomes the source of a mild transient type of neuroinfection. Meningoencephalitis is activated in adolescents with an active sexual life.
In newborns, herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2 is part of the associated infections. A generalized disease affecting many organs is caused by HSV in patients with immunodeficiencies, including AIDS. The lack of pharmaceuticals causes the death of 2/3 of infants.
The first signs of herpesvirus neuroinfection:
- High fever;
- Strong headache;
- Behavioral disorders;
- General cerebral symptoms.
The drug virolex (acyclovir) increases your chances of survival. In severe cases, the drug is ineffective.
Rare forms of viral encephalitis
Damage to the central nervous system is caused by the varicella zoster virus, which occurs after an illness. Nosology has symptoms:
- Cerebellar ataxia – incoordination of muscle activity, unsteady gait;
- Acute encephalitis.
Acute manifestations are rare. The chickenpox virus is characterized by a chronic course with cycles of remissions and exacerbations, since the pathogen persists in the nerve ganglia. Reactivation of chickenpox is possible with a decrease in immunity.
Rare types of viral meningoencephalitis:
- Cytomegalovirus - destroys cerebral tissue only in immunodeficiencies;
- Mumps – caused by the mumps virus. It is characterized by a mild course, but causes inflammation of the auditory nerve.
The lack of a complete diagnosis excludes the possibility of early detection of neuroinfection.
Clinic of bacterial meningoencephalitis
Pathogenic bacteria enter the brain through the blood and lymphatic fluid. The penetration of microorganisms from the primary focus of internal organs is dangerous due to the resistance of the agents to the antibiotics used to eliminate the disease.
Types of bacterial meningoencephalitis:
- Brucellosis;
- Toxoplasmosis;
- Syphilitic;
- Tuberculous;
- Meningococcal.
Signs are determined by the type of etiological factor. Damage to cerebral tissue appears against the background of a primary infection of internal organs. Congenital types arise due to the entry of microorganisms into the fetus during childbirth.
Tuberculous encephalitis develops in people with primary tuberculosis of different localization. The peak of infection occurs in the spring-autumn period, when immune activity is reduced. The nosology has no specific manifestations. Diagnosed by laboratory, clinical and instrumental methods.
Mycobacterial infection is difficult to treat. Of the bacterial species, nosology is the most dangerous. Main clinical signs of pathology:
- Poor concentration;
- Strong headache;
- General cerebral disorders;
- Photophobia;
- Vegetative manifestations;
- Neurological disorders;
- Hydrocephalus.
Acute manifestations of the disease are characterized by an increase in temperature to thirty-nine degrees. Clinical manifestations of the disease are accompanied by fever, joint pain, sleep disturbance, abnormal meningeal signs, and fever. The average duration of the disease is about ten days. Associated signs of nosology are lack of appetite, excessive sweating, cerebellar disorders, mobility impairment, positive Rehberg test. (a person cannot touch the tip of his nose with his index finger).
The temperature curve against the background of inflammatory changes in the cerebral parenchyma and meninges has a specific course. Initially, the fever increases to 39 degrees. After 5-7 days, the fever subsides to low-grade levels (38.5 degrees). A second wave is observed on the tenth day. Focal neurological symptoms appear with neuritis, radiculitis, changes in the activity of the heart, pulmonary system, dizziness, convulsions, paresthesia (lack of sensitivity).
The brucellosis species provokes pyramidal symptoms with paresis, paralysis, and muscle cramps.
Characteristics of parasitic meningoencephalitis
Amoebas are found in young children and newborns. The parasites cause inflammation of the brain with a high mortality rate.
Pathogens enter through the upper respiratory tract. The source of infection is reservoirs, tap water, contaminated vegetables and fruits.
Clinical manifestations of amoebic encephalitis, meningitis:
- Granulomatous inflammation of the white matter takes several months to form. Damage to the membranes clinically resembles a volumetric intracerebral formation with the formation of several centers of activity - convulsions, personality disorders, paralysis, paresis;
- Acute variety - lasts two weeks. It begins with lightning speed, accompanied by nausea, headaches, and a significant increase in temperature. Multiple foci cause death in infants and children.
Early detection and proper drug therapy eliminate the risk of serious complications.
First aid
If there is a suspicion that the patient is showing symptoms of meningoencephalitis, he should be hospitalized immediately. In case of seizures, it is important to support the person's head to avoid injury. Before emergency help arrives, if you have severe headaches, you can give a pain reliever ( Tramadol , Metamizole sodium ). If you have a fever or high temperature, apply cold to your forehead.
Emergency care that doctors provide before hospitalization is aimed at preventing the development of infectious-toxic shock. To this end, the following actions are practiced:
- A lytic mixture is injected intramuscularly - solutions of Metamizole sodium , antispasmodics and Promethazine .
- An antiemetic drug ( Metoclopramide ) is administered.
- For convulsions, a sedative ( Diazepam ) is administered.
- Prednisolone are administered . If the pressure remains low, a Dopamine .
- If infectious-toxic shock develops, infusion therapy is performed ( Reopoliglyukin ).
- If indicated, a breathing tube is inserted into the trachea for artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Characteristics of autoimmune encephalitis
The formation of antibodies to brain tissue causes demyelination. The process is long but progressive. Rasmussen's encephalomyelitis is a typical manifestation of an autoimmune lesion of the cerebral parenchyma. Depending on the characteristics of the development of the process, the duration is from five to fifteen years. In most cases, the clinical peak occurs at six years of age.
Nosology has been thoroughly studied by scientists. The causes of the occurrence could not be established, but the link to which immunoglobulins are formed was identified. The presence of NMDA receptors is a weak point that is susceptible to destruction by the immune system.
There are case studies showing the nonspecificity of glutamate receptor antibodies for Rasmussen's encephalomyelitis. Other anti-inflammatory cytokines formed during the nosology have been identified.
Meningoencephalitis of newborns
The most common pathogen is viruses. Intrauterine infection of a baby occurs from a mother suffering from glandular fever, measles, rubella, herpetic infection, and mumps.
The most common symptoms are focal disorders, hyperkinesis, hydrocephalus. Nonspecific manifestations of meningoencephalitis in newborns:
- Eye twitching;
- Difficulty feeding from the breast;
- High fever;
- Intoxication syndrome;
- Vomiting reflex;
- Diarrhea;
- Strabismus;
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- Muscle twitching.
Neurologists define neurological disorders in the form of Kernig's sign (the inability to bring the head to the chest due to stiff neck muscles). Cerebrospinal fluid contains an increased amount of lymphocytes and protein.
Manifestations of meningoencephalitis in adults
Various symptoms of the disease in an adult are caused by different pathogens and characteristics of the course. The incubation period of the disease lasts several weeks.
Symptoms of the clinical stage:
- Muscle stagnation;
- Decreased appetite;
- Constant fatigue;
- Headaches without the effectiveness of painkillers.
Inflammatory changes in the meninges lead to meningeal syndrome with special manifestations:
- Nausea;
- Speech disorders;
- Interruptions of heart activity;
- Respiratory disorders.
The occurrence of the described manifestations leads to death. The progression of individual symptoms becomes a cause of disability.
Consequences of meningoencephalitis
In addition to high mortality, the disease is characterized by dangerous conditions leading to disability. Severe consequences of inflammation of the white matter and meninges:
- Paralysis of limbs;
- Epileptic seizures;
- Mental retardation in children;
- Hydrocephalus;
- Psychoses;
- Hallucinosis.
The conditions are irreversible. Early verification and competent therapy prevent negative consequences in bacterial types of encephalitis and meningitis. For other forms of nosology, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the brain and soft membranes
The most accurate laboratory method for verifying nosology at the beginning of development is cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Turbidity in the cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord indicates the presence of infection. Determination of additional impurities, accumulations of leukocytes and lymphocytes indicates a bacterial infection. With pathology, an increase in the content of glucose and protein occurs.
Clinical and instrumental methods for examining the cerebral parenchyma - radiography, CT, MRI, electroencephalography (EEG). Neuroimaging determines the spread of inflammation, the depth of the lesion, and concomitant pathology.
Prevention
- The most important method of prevention is timely vaccination. Vaccinations are given in childhood in accordance with the existing vaccination calendar. Vaccination against meningococcal and pneumococcal infections and Haemophilus influenzae is carried out.
- People in contact with patients are given prophylaxis with antibacterial drugs.
- During epidemics of influenza and ARVI, you should have less contact with patients and avoid large crowds of people.
- It is important to exercise, practice adequate hardening and eat right.