What to do in case of inflammation of the temporal artery?
1. Severe, throbbing pain that appears suddenly and is localized mainly in the temples and back of the head.
2. Pain occurs when chewing, moving the jaw and head, for example, when combing; Along with general painful sensations, there is severe pain and pressure in the temples.
3. Redness, a clearly noticeable hard stripe on the temples in the ear area.
4. Pain in the eyes, double vision and blindness (sometimes temporary, sometimes long-term) in one or both eyes.
5. High fever, weight loss, and general weakness may appear.
6. Sometimes I feel dizzy.
If you feel a lot of pain and/or dizziness, or there is tightness and pressure in your temples, cold compresses on your forehead can help. Be careful when combing and brushing your teeth, as... these actions can cause pain.
The nature of the pain and its localization
To more accurately determine the causes of pain and the degree of possible threat to health, you need to understand your own feelings. An accurate description of discomfort, its location and nature can greatly facilitate the correct diagnosis.
The pain felt in the ear and temple can be sharp, wave-like, pressing or low-intensity. In case of minor but prolonged discomfort, a disruption of the vascular system can be assumed. Also, such manifestations are often associated with overwork, especially after prolonged mental work or stress.
Sharp pain should cause concern, since such a phenomenon is definitely outside the norm. If the sensations seem to come in waves, it is quite possible that the situation is due to a change in the weather.
You also need to take into account the localization of discomfort: in case of ear inflammation, this fact indicates the affected area. Please note whether the pain is present in both ears or only on the right or left. If the pain radiates to the jaw and there are problems with the teeth, it is possible that caries has worsened and the sensations radiate throughout the bone tissue.
Acute otitis media
According to statistics, acute forms of otitis media account for 30% of the total number of ENT diseases. Most often it occurs in preschool children.
Symptoms of acute otitis media
The disease is characterized by an acute onset with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- earache;
- ear congestion or hearing loss;
- increased body temperature;
- anxiety;
- disturbance of appetite, sleep;
- headache and toothache.
Causes of development of acute otitis media
In most cases, the disease can be caused by various pathogenic microorganisms - viruses, microbes, fungi, etc. In exudate obtained from the middle ear, respiratory viruses are found in 30-50% of cases. The most common causes of otitis are parainfluenza viruses , influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, etc.
In 50-70% of patients with acute otitis media, bacteria are detected in the exudate from the middle ear (most often Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis).
Often the cause of otitis is a mixed (viral-bacterial) infection.
When making a diagnosis, a differential diagnosis is made with myringitis (inflammation of the eardrum) and exudative otitis media.
The occurrence of otitis media is directly related to the condition of the nose and nasopharynx: rhinitis and tonsillitis often provoke inflammation of the middle ear.
Otitis often occurs against the background of decreased immunity and immunodeficiency states.
1 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
Routes of infection
The most common route of infection into the middle ear is through the auditory tube during rhinitis and sinusitis.
It is possible that infection can penetrate through the blood during influenza, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases.
In rare cases, the infection enters the middle ear through the ear canal due to injury (rupture) of the eardrum.
Stages of acute otitis
There are 5 stages of the disease:
- stage of acute eustachitis: feeling of congestion, noise in the ear, normal body temperature (if there is an infection, it may increase);
- stage of acute catarrhal inflammation in the middle ear: sharp pain in the ear, low-grade fever, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, increasing noise and congestion in the ear;
- pre-perforative stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: sharp unbearable pain in the ear, which radiates to the eye, teeth, neck, pharynx, increased noise in the ear and decreased hearing, increased body temperature to 38-39 degrees, the blood picture becomes inflammatory in nature;
- post-perforation stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: pain in the ear becomes weaker, suppuration appears from the ear, noise in the ear and hearing loss do not go away, body temperature becomes normal;
- reparative stage : inflammation is stopped, perforation is closed with a scar.
Otitis and other ear diseases
In most cases, the ear hurts and radiates to the temple with the development of one or another disease of the hearing organ. The main reason is inflammation, that is, otitis media of the middle and inner ear. In the external form, such sensations are observed only in the event of complications.
When an infection gets behind the eardrum, an environment filled with pathogenic microflora is created. As a result of its vital activity, partial destruction of tissue occurs and the accumulation of viscous secretion in the ear. Putting pressure on parts of the organ causes discomfort, and suppuration is the main factor causing pain.
The most dangerous is inflammation of the inner ear, since this particular part of the organ is closely connected with the cranial bone tissue. When the corresponding nerve endings are irritated, contact occurs and unpleasant sensations spread to neighboring tissues.
If you have pain in your ear and left or right temple, and it has been happening for quite some time and the intensity of the sensations is only increasing, a suspicion arises of a complex disease that has spread beyond the hearing organs.
Most often, such phenomena are caused by advanced ear inflammatory diseases that affect bone tissue. For example, with tympanitis, the infection can spread to the auditory ossicles, and pain radiates from them. Also with tubotympanitis, pain spreads to neighboring areas.
Due to the fact that the ears share common walls with the skull, inflammation can cause complications in the form of carious lesions of bone tissue. In this case, there is a risk of not only hearing loss without the possibility of recovery, but also more serious consequences. In rare advanced cases, destruction of the bone partitions occurs and the infection spreads to the brain. This result leads to disability and even death.
In addition to the above-mentioned situations, ear pain radiating to the temple can be caused by other causes. The most common ones include:
- Migraine. A severe headache spreads to other organs and parts of the body: ears, eyes, neck, etc. There is also aversion to bright light and sound. Such manifestations can cause irritability and greatly exhaust a person.
- Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. This joint is closely related to the mentioned affected area. If its normal functioning is disrupted for one reason or another, the ear may suffer and headaches may occur.
- Stress. Severe overwork, tension, and strong emotional experiences can disrupt the normal functioning of any part of the body. This effect is especially enhanced during muscle and vascular spasms.
- Toothache. Inflammation of the gums, jaw tissue and toothaches have an indirect effect on the ears. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the temporal region and cause excruciating discomfort.
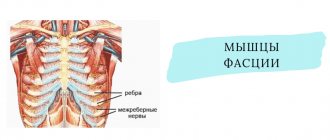
The inflammation affects one or more arteries in the temples, most often the main temporal artery. The reasons why the disease occurs are unknown, but the influence of heredity, viral origin or immune defects is indicated. Often the disease occurs together with polymyalgia rheumatica, a disease characterized by morning sickness and stiffness of muscles and joints.
Symptoms may appear suddenly or develop gradually. Sometimes a small part of the artery in the temples is affected, in other cases the aorta (the largest artery in the body that comes from the heart), heart and carotid arteries are affected. The pain is induced mainly by the illuminated vessel wall, but there is a gradual narrowing of the arteries of pain, ischemia and lack of oxygen.
Sometimes there is spontaneous improvement, but deterioration is also possible: due to the interruption of blood flow to the optic nerve, blindness can occur.
The etymology of pain in the right temple can be harmless or dangerous.
What causes “harmless” right-sided cephalalgia:
- insomnia, sleep disorder, uncomfortable bed or pillow, stuffy room can cause pain when you feel dizzy when getting up and feel sick in the morning;
- stress and overexertion, temporal pain is the scourge of office workers and people who do not know how to rest from everyday work; when pressing on the temple, cephalalgia intensifies;
- uncomfortable workplace, sedentary lifestyle;
- when descending, diving to depths or climbing to heights (mountains), on an airplane, when traveling in transport (especially with large crowds of people), cephalalgia, nausea, dizziness and tachycardia may appear;
- poor nutrition, fasting, long breaks between meals, bad habits, hangover;
- drug abuse, poisoning, intoxication;
- weather dependence.
Such pain can be easily managed with conventional medications. However, if they appear constantly or every day, then anesthetics will gradually begin to have a negative effect on the body or stop helping.
The etymology and symptoms of pain are quite diverse. Why there may be a headache in the right temporal zone - we will consider all the details and the main causes below.
Head injuries
With TBI (traumatic brain injury) or brain dysfunction, tumors or abscesses, swelling, redness and sharp pain may appear in the affected area.
Often such pain does not differ in intensity. Trauma syndrome with dull pain, noise in the ear (depending on the location of the injury), nausea, vomiting and dizziness may appear only after some time.
We invite you to read: Why is it harmful to endure pain?
For any TBI or bruises, it is recommended to immediately go to the emergency room for medical attention.
Perhaps your prolonged pain (even mild) indicates a violation of brain functions, the gradual development of a tumor or an imbalance in the circulatory system.
ENT diseases can be accompanied by acute respiratory manifestations, when the throat is very sore and the cough is suffocating. Inflammatory processes developing in the reflex organs and in the jaw - colds, flu, sore throat, frontal sinusitis, conjunctivitis, an inflamed tooth, sinusitis or otitis media can cause severe pain. The pain can pound and radiate to the ear, forehead or back of the head. If, with right-sided cephalgia, it radiates into the eye, then the organ or skin around it may swell.
Sometimes a cold causes pain that radiates to the tooth. This happens with caries and other untreated dental problems.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to relieve pain only after consultation with your doctor, so as not to harm the baby.
Migraine
Another name is hemicrania, which means "half head". The attack may begin suddenly or with an aura - the threshold of pain, which is expressed in sensitivity to light, smells or sounds.
If the attack is not stopped in time, it can last 2-3 hours, go away on the second day or last several days. The pain is stabbing, varies in intensity, ache most often in the right temple, radiates to the eye (or inside the orbit) and to the jaw.
Attacks can be accompanied by vomiting, nausea, disorientation, and even provoke a migraine stroke.
What causes migraine:
- the disease often affects those suffering from lack of sleep or overwork;
- with surges in blood pressure, hypo- and hypertonicity of blood vessels;
- when choosing the wrong products;
- Abuse of caffeine or tyramine can be a symptom of an attack.
The nature of origin of hemicrania has not been studied. The disease is considered hereditary and usually occurs in women. However, studies in recent years have shown a large increase in migraine syndrome among men.
Painful sensations caused by hormonal disorders are varied - the head aches or throbs in the temple, when you press on the temporal area, the pain usually intensifies.
- The right temple hurts very badly in women (up to 75%) during menopause, as well as with severe PMS (premenstrual syndrome);
- It is believed that the first attacks against the background of hormonal changes appear during puberty in boys and girls, sometimes during pregnancy;
- vegetative-vascular problems or intracranial hypertension can trigger migraines in adolescents or young people due to hormonal instability.
Intracranial hypertension or ICP is characterized by the presence of an increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). With cerebrospinal fluid pressure on different parts of the brain, cephalgia can occur in any location.
Often accompanied by pressing, throbbing pain in the right temple, general malaise, weakness, tachycardia, shortness of breath, heart pain and tinnitus.
- psycho-emotional character;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- magnetic storms.
Such disturbances must be taken seriously, as visual disturbances, loss of consciousness and convulsions are possible.
Cerebral angiodystonia is accompanied by pain in the right temporal zone, which radiates to the eye. Formed due to a violation of the elasticity of blood vessels or arteries.
- sleep disturbance, dizziness;
- sudden changes in pressure;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- numbness of fingers;
- decreased brain activity and memory.
Stress, depression, anxiety are overstrains of a psychogenic nature, leading to a surge or release of adrenaline. As a result, blood pressure increases.
If you stay in such an environment for a long time, you can end up not only with a serious nervous disorder, but also with loss of physical health.
Right-sided pain, when there is a knocking and shooting in the temple, is one of the first symptoms of the development of a serious illness.
Atherosclerosis
Often, pain in the right or left temporal region appears after the diagnosis of atherosclerosis. The disease is characterized by narrowing or blockage of the lumen of blood vessels due to the formation of cholesterol plaques.
Gradually, pain in the right temporal zone becomes constant, and analgesics cease to help. The pain intensifies when you press on the temple on one side of the head.
Patients experience unmotivated irritation, anxiety, decreased brain activity, memory and intelligence.
Types of otitis
Depending on the direction of the pain, it is customary to distinguish 3 types of otitis: external, middle and internal otitis.
Otitis externa most often appears as a result of mechanical damage to the auricle or external auditory canal. The following symptoms are characteristic of external otitis of the ear: aching, dull pain, swelling of the ear, and a slight increase in temperature.
Otitis of the middle ear is an inflammatory disease of the air cavities of the middle ear: the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and the mastoid process.
Internal otitis is untreated otitis media of the middle ear. With internal otitis, inflammation of the inner ear occurs and the entire vestibular apparatus is damaged.
Blood flow disturbance
An increasingly common problem among the population is poor circulation, which can be expressed as a symptom of pain in the temples, back of the head and ears. Such manifestations most often indicate cervical osteochondrosis. This disease can occur due to a sedentary lifestyle, heavy loads on the spine, poor nutrition and crooked posture.
The consequence of this process is pinching of blood vessels and nerve endings. Unpleasant sensations in approximately half of the cases are concentrated in the temple. For treatment and prevention, it is imperative to develop the cervical area and improve your diet.
Also, problems with blood vessels can be associated with congenital pathologies and age-related changes. Twisted vessels lead to many problems. Plaques and stenosis of the artery walls are also a threat. Thinning of the walls leads to ruptures and hemorrhages. All this can lead to stroke and death. If you suspect such problems, you should undergo a full examination.
Injury
An accidental minor injury to the ear can have enormous consequences. An even more dangerous situation is a head injury. In some cases, the pain is constant and is explained by a disruption of the nervous system.
Serious injury does not go away without leaving a trace in the vast majority of cases. Against this background, the ear may become inflamed. The risk of developing tumors in the ear and cranial cavities also increases. Severe pain can signal cancer.
If the cause of the pain lies precisely in injury to the head and ears, the damaged area will be marked by the presence of hematoma and swelling. In case of serious damage, bleeding, disruption of brain function, dizziness and loss of orientation in space are observed. If nerve endings and blood vessels are damaged, a person may behave inappropriately, lose consciousness, succumb to attacks of aggression, epileptic seizures, etc.
Under no circumstances should a head or ear injury be ignored. Consultation with a doctor is required. If a child is injured, immediately call an ambulance or go to the emergency room immediately, even if you think there is no reason to worry.
Drug treatment
In order not to trigger the possible development of the disease, treatment must be timely.
What is a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- interview and examination by a therapist or neurologist to identify medical history, referral to related specialists as necessary: otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, vertebrologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon and others;
- prescription of REG (radiography) or EEG (electroencephalogram);
- undergoing CT or MRI (computed or magnetic resonance imaging);
- taking a complete blood test.
All procedures are painless and do not cause harm to health.
First aid, what pills to take to relieve pain
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Paracetamol | No more than 4 g per day (1-2 tons per dose) | No more than 10 days |
| Spasmalgon | Up to 6 tables in a day | Maximum 5 days |
| Solpadeine | Powerful pain reliever, 1-2 tablets. 4 times a day | No more than 3 days |
| Ibuprofen | For pain relief up to 2 capsules per dose | No more than 14 days |
| Tempalgin | 1 dose up to 3 times a day | Maximum 10 days |
We suggest you read: How to soothe a toothache
A headache cannot be tolerated; you need to start fighting it immediately after it appears. First, you should limit yourself to ventilating the room, walking, lightly massaging the problem area, or taking a short rest. If there is no effect, you can take the Citramon or Analgin tablet. If you suspect a muscle or vascular spasm, it is better to take No-Shpu or Spazmolgon. If this does not help, you should contact a specialist who will select the best option for help.
Depending on the causes and severity of the symptom, the following groups of drugs can help the patient:
- analgesics – relieve discomfort and can help with cluster and migraine headaches;
- NSAIDs – relieve discomfort and fight inflammation;
- antispasmodics – relax muscles, dilate blood vessels, improve blood flow to the brain;
- hypotensive - lower high blood pressure to normal or acceptable levels;
- triptans are specialized medications that can quickly help with migraines;
- narcotic drugs - you have to resort to them in the presence of tumors, cluster cephalgia;
- sedatives – relieve psycho-emotional stress, help to relax and improve sleep;
- nootropics – stimulate cerebral circulation, improve organ function.
Inadequate treatment without taking into account the provoking factor creates additional risks to human health. It threatens to increase the severity of the symptom, provoke complications, and cause an abusive headache. If a drug taken once does not bring relief, repeating the manipulation is prohibited!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rg5tPHftkSI
In some cases, alternative medicine can help as well as medicine. It is better to resort to them after finding out the causes of the disease and with the permission of the attending physician. For organic problems, such approaches should not replace traditional therapy; they can only act as a supplement. If the headache is due to stress or overexertion, these approaches may be sufficient.
If you have pain in the temple on the right, you should try the following emergency methods:
- cabbage compress - you can apply a cloth soaked in cabbage juice or the cabbage leaf itself, slightly mashed, to your temple;
- massage of the temples using ethers - dilute a couple of drops of menthol or mint ether in a teaspoon of vegetable oil. Massage the problem area with the resulting mixture;
- vinegar compress – dilute a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water. Soak a bandage or piece of gauze in the solution and apply to the sore spot;
- lemon rub – take a fresh lemon peel, press its light inner side to the sore temple and massage with light pressure;
- tea with mint, lemon balm, chamomile - a drink made from individual components or a mixture of them relieves nervous tension. The main thing is that it is fresh, not very strong and without added sweeteners.
The listed approaches are safe, accessible and effective. However, it is not recommended to resort to them systematically. Abuse of manipulations reduces their effectiveness and increases the risk of developing allergies.
The main treatment is corticosteroids. The doctor usually starts therapy with 40-60 mg daily dose of Prednisolone, which is divided into 2-4 doses. If the symptoms (severe headache, pressure in the temples) subside (usually within a few weeks), you can take the medicine only in the morning.
As the condition stabilizes, the dose is gradually reduced. The goal of therapy is to free the patient from taking corticosteroids so that the disease does not relapse.
Treatment usually lasts about 1-2 years, sometimes much longer. Prednisone and other corticosteroids cause a number of side effects, such as weight gain, bone loss, high blood pressure, bruising, cataracts, and mood swings.
Headache treatment
The treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account individual characteristics, diagnostic results, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases. This will include both symptomatic pain relievers and specific medications to address the underlying cause of the pain. The doctor may prescribe the following methods:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the presence of inflammatory processes;
- specific treatment of spinal diseases, including muscle relaxants, massage, physiotherapy;
- means for improving blood circulation in the vessels of the brain;
- sedatives;
- surgical treatment – recommended in the presence of neoplasms, intervertebral hernias, aneurysms.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the timeliness of the necessary measures, so it is important to consult a doctor when the first signs of discomfort appear. You should not self-medicate if the headache occurs in the form of attacks, occurs frequently and is accompanied by additional symptoms.
Prevention
For frequent right-sided temporal pain, self-medication is highly not recommended. It is better to relieve periodic attacks not with medications, but with homeopathy or proven folk remedies or prevention. For example: Cabbage recipe Take fresh cabbage leaves, crush until the juice releases and apply to the sore spot.
CompressTake 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar, dilute in a liter of warm water. Apply a napkin soaked in liquid to your temple for half an hour.
For migraine pain, herbal decoctions or tea made from lemon balm, chamomile, mint, oregano, and elderberry help well.
Measures to prevent right-sided temporal pain:
- Consult a specialist who will choose the right diet for you, rich in saturated vitamins.
- Give up bad habits.
- Avoid drafts and external irritants.
- Learn to react correctly to stressful situations.
- Provide yourself with good sleep, relax, and give yourself a good rest.
- Therapeutic gymnastics or yoga classes help well.
Often people do not pay attention when they have a headache in their temples. If the symptom occurs only from time to time after emotional stress or at the end of the working day, there is no need to panic. True, it’s still worth making adjustments to your usual routine. It’s another matter if discomfort bothers you regularly or even constantly.
Attempts to eliminate pain in the temporal part of the head by systematically taking analgesics threaten to aggravate the problem and develop complications. It is better to visit a doctor as soon as possible, find out the cause of the sensations and carry out adequate therapy. Often, when the right temple hurts or is pulled, it is enough to change your lifestyle. Sometimes the manifestation indicates serious health problems and requires immediate professional intervention.
Prevention of organic pain in the right temple means combating the pathologies listed above. In most situations, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle, adjust your work and rest schedule, and systematically visit a therapist to identify hidden diseases.
Universal symptom prevention requires compliance with the following rules:
- refusal of junk food, processed foods, fast food, too spicy dishes;
- introduction to a regime of gentle physical exercise and walks in the fresh air;
- body weight control;
- maintaining a drinking regime - sometimes a headache signals dehydration;
- timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases;
- visiting the pool, yoga classes and massage sessions during sedentary work, which negatively affects the condition of the spine;
- prevention of stress, physical and emotional overload;
- getting a full night's sleep and avoiding daytime rest.
Almost every person has experienced pain in the right temple at least once in their life. In half of them, the symptom occurs regularly. Only in 10% of cases do people go to doctors and receive adequate medical care in a timely manner. Others risk their health and well-being by trying to cope with the problem on their own. In half of the situations this leads to the development of emergency or chronic conditions.
Until now, preventive measures are unknown.
Attention!
With every unusual condition in which there is a headache, pressure on the temple/temples and visual disturbances occur, something needs to be done! That is why it is advisable to contact a specialist as soon as possible. In particular, with inflammation of the temporal artery, attention should be paid to ophthalmological symptoms. If you experience double or blurred vision, see your doctor immediately. Delay in treatment can lead to permanent blindness.
What to do: general recommendations
In order to somehow get rid of the discomfort, most people decide to take a painkiller. Analgesics temporarily relieve discomfort and normalize the patient’s condition, but this is not a solution to the problem. To completely get rid of symptoms and their consequences, it is necessary to eliminate the causes that provoke them.
Diagnostics will reveal the cause of discomfort and pain. Standard procedures in the form of anamnesis collection, examination by a therapist and otolaryngologist can be supplemented by more narrowly focused procedures. To identify the condition of the ear, skull, spine and brain, as well as blood vessels and other elements, the doctor may prescribe:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- radiography;
- tympanometry;
- Dopplerography, etc.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with What is herpetic and aphthous stomatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
To eliminate the problem, appropriate treatment is prescribed. There are a number of general recommendations to reduce pain:
- relax and avoid stressful situations;
- establish a rest and sleep schedule;
- take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- prevent the development of otitis media;
- Avoid getting water and foreign objects into the ear;
- visit the dentist and have your teeth treated in a timely manner;
- eat right;
- eliminate smoking and do not abuse alcohol;
- play sports, lead an active lifestyle.
After suffering injuries, it is necessary to reduce the load on the body. In the case of vascular problems, surgery may be necessary, especially for congenital pathologies. When an infection in the ear spreads to the bone tissue, surgical treatment is also used.
Timely measures taken to identify the problem and eliminate it reduce the risk of serious complications. Some conditions cannot be completely cured, but if you maintain a healthy lifestyle and good rest, the frequency of discomfort is significantly reduced.
Treatment of otitis media
If you have otitis media, treatment can only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist. Treatment of otitis media depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition.
In acute eustachitis, treatment of otitis media is aimed at restoring the functions of the auditory tube. Sanitation of the paranasal sinuses, nose and nasopharynx is carried out in order to eliminate infection - rhinitis, sinuitis, etc.).
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (otrivin, nazivin, etc.) are prescribed; in case of excessive mucous discharge from the nose, drugs with an astringent effect (collargol, protargol) are prescribed. Catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out using aqueous solutions of corticosteroids, and pneumomassage of the eardrums.
In the stage of acute catarrhal otitis media, catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out with the introduction of aqueous solutions of corticosteroids and antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) into the cavity of the middle ear. Local anesthesia is prescribed (otipax drops, Anauran, Otinum). An intra-ear endaural microcompress according to Tsytovich is carried out: a cotton or gauze turunda soaked in a drug with an analgesic and dehydrating effect is inserted into the external auditory canal. Painkillers with an antipyretic effect (nurofen, solpadeine, etc.) are also prescribed. If there is no effect from symptomatic therapy, antibiotic therapy is prescribed within 48-72 hours.
Purulent otitis in the pre-perforated acute stage requires the same set of procedures as in the second stage, but supplemented with the following measures:
- prescription of penicillin antibiotics (amoxicillin, etc.), cephalosporins or macrolides;
- paracentesis (incision of the eardrum) when the eardrum appears to bulge.
It is important to prevent complications of the disease at this stage. After spontaneous opening of the eardrum or paracentesis, the disease progresses to the next stage.
The post-perforation stage of acute purulent otitis media involves the following treatment regimen:
- started antibacterial therapy continues;
- catheterization of the auditory tube is performed with the introduction of corticosteroids and antibiotics;
- a thorough toilet of the external auditory canal is carried out daily - cleaning it from purulent contents;
- transtympanic infusion of drops with an antibacterial and anti-edematous effect is prescribed (alcohol-based drops (otipax, 3% boric acid solution) are not used in this case).
In the scarring stage of AOM, spontaneous restoration of the integrity of the membrane occurs, and all functions of the ear are completely restored. However, this period requires mandatory observation by an otolaryngologist: there is a danger of chronic inflammation in the middle ear, its transition to a purulent form, or the development of an adhesive scar process in the tympanic cavity. It is also possible to develop mastoiditis.
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Audiometry in MedicCity
3 Audiometry in MedicCity
In case of acute otitis media, timely contact with an otorhinolaryngologist is very important. The only measure to prevent complications is correct and timely diagnostic and treatment measures for otitis media. Sometimes the consequences of acute otitis media are adhesions in the tympanic cavity (adhesive otitis media), dry perforation in the eardrum (dry perforated otitis media), purulent perforation (chronic suppurative otitis media), etc. In addition, AOM can lead to such complications as such as mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, petrositis, meningitis, sepsis, venous sinus thrombosis, brain abscess and other life-threatening diseases of the patient.
Why does tinnitus occur with headaches in the temples, and what to do about it?
1. Spondylitis, osteochondrosis, dislocation of small joints between the vertebrae, sprains that were received as a result of injury to this department. In this situation, the unpleasant sensation is localized directly in the back of the head and neck. When moving, the pain intensifies, it can radiate to the ears, nausea, noise, ringing, and congestion occur.
2. Nervous tension. Why does this happen? This deviation occurs in the patient due to stressful situations. To a greater extent, cephalalgia in the back of the head with this disorder appears in the female half of the population, after 25 years. In this state, the following symptoms are noted: noise, ringing in the ears, dizziness, noise, it seems that something is pressing on it, and nausea occurs.
3. Overwork. In most cases, it happens when a person is very tired due to prolonged stress of a different nature, or being in an uncomfortable position. The result is unpleasant sensations in the back of the head, nausea, dizziness, and stuffy ears.
4. Cervical spondylosis. Diagnosed in elderly patients, as well as in mental workers. It manifests itself as pain in the back of the head, shoulders, eyes, especially when stationary for a long time. Poor neck mobility is also noted. Insomnia, noise, ringing in the ears may occur, sometimes they become blocked, the head is dizzy, and when blowing the nose, pain radiates to the back of the head.
5. Myogelosis is a disease associated with stiffening of the neck muscles. Can be triggered by many factors. Symptoms of the pathology: pain in the back of the head, near the shoulders, increased stiffness in movements, dizziness, in rare cases, patients may also complain of ringing and noise.
6. Neuralgia of the occipital nerve. In this situation, the pain is periodic and spreads to many parts of the body. It also rings, makes noise in the head, and stuffs up the ears. Ringing and noise occurs when the patient twists his neck.
7. Arterial hypertension. Provokes pain in the back of the head, especially in the morning.
8. Cervical migraine. The patient in such a situation complains of tinnitus and hearing loss, dizziness.
9. Prolonged muscle tension. Why does this happen? This condition is diagnosed when physical exercises are performed incorrectly, which causes tinnitus and a nagging, unpleasant pain in the back of the head, which can radiate to the forehead.
Most of the pains that have been listed are bilateral and localized in different places. Basically, cephalalgia is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Why does this happen? Because due to intense pain, the patient’s body is exhausted. In case of prolonged attacks, as well as those that are often repeated, you should contact a specialist who can accurately determine the cause of the poor condition and prescribe effective treatment.
1. Clinical and general blood test. Helps determine if there is an inflammatory process in the body.
2. Electroencephalography. If the examination is carried out during a migraine, changes will be noted on the EEG.
3. Magnetic resonance imaging. Determines the presence of a tumor in the brain, which provokes cephalgia in various parts of the head.
4. Echo of EG. Helps determine the position of brain structures and their displacement.
5. Dopplerography. Helps to carefully study the blood circulation in the vessels and what changes have occurred.
6. Radiography. Conducted to study the skeletal system and joints of the skull.
7. Audiometry, otoscopy. Helps eliminate hearing diseases.
Factor #1 – stress
Stress is often responsible for conditions where there is ringing in the ears and headaches (mainly in the temporal region). The pain is not so severe as to prevent a person from doing something, but there is little pleasure in it.
High levels of ongoing stress and anxiety in people whose profession involves talking on the phone constantly puts them at risk, and they are the most vulnerable to developing tinnitus.
Medicines and sedatives can relieve symptoms, but on the other hand, they have many side effects.
Some case studies point to lack of sleep as a trigger for the development of tinnitus. Often, due to international business trips, people experience lack of sleep due to time zone changes; they are most at risk of becoming victims of this disease.
True, in case of physical discomfort due to the above reasons, there is no need to do anything or take medications. Relief will come when a person rests for at least 7 hours.
We are talking about bleeding into the space between the brain, which can occur spontaneously due to a burst cerebral aneurysm or severe traumatic brain injury. However, such cases are rare, accounting for about 1 in 15,000 cases of tinnitus today.
A lumbar puncture is a test in which cerebrospinal fluid is collected using a needle. After it, a severe headache may appear, lasting up to 12 hours after the procedure. The painful sensations are very intense, preventing the person from doing practically anything.
Causes of unilateral headaches
If soreness appears on only one side of the head, it may be a sign of various problems. It is important to consult a doctor if the pain is acute, intense, occurs frequently, or is accompanied by additional symptoms: nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, deterioration of hearing and vision. Headaches are not an independent disease, but a manifestation of internal pathologies associated with blood circulation, nervous regulation and other factors.
Migraine
Migraine is the primary headache. It is not associated with any pathologies of internal organs, therefore specific symptomatic remedies are used for its treatment. The causes of migraine have not been precisely established, but doctors determine the relationship with vascular or nervous disorders. It manifests itself in attacks that last from several hours to several days. They can be triggered by any irritants, including disruption of sleep schedules, moving to another climate zone, stress, intense physical activity, or prolonged stay in a noisy room.
A typical symptom of migraine is unilateral pain that covers the left or right side of the head and is concentrated in the temple area. Before the main attack, an “aura” often appears - a set of symptoms that develop several hours before the onset of the headache. There are several types of migraine:
- Simple migraine without aura – occurs in most patients. It is accompanied by nausea, weakness, increased sensitivity to bright light and sound stimuli.
- Migraine with aura - the duration of the attack can be up to several days. An aura often appears before a headache and includes visual disturbances, hearing loss, and a change in the sense of smell. General weakness and psychoemotional disorders are also noted.
- Vestibular migraine is a less common type that causes dizziness. This symptom may develop simultaneously with the headache or precede it by several hours.
- Ocular migraine - acute pain lasts less than with other types (no more than 3 hours). Before this, various visual disturbances are observed, including difficulty focusing on near and distant objects, the appearance of dark circles and spots in front of the eyes, and the loss of individual fragments from the field of vision. Symptoms disappear with the onset of a headache attack or simultaneously with it.
- Ophthalmoplegic – lasts more than 7 days. After a few days, damage to the optic nerves occurs, which causes dangerous symptoms: strabismus, drooping of the upper eyelid, dilation of the pupil.
Migraine is an acute pain that makes you unable to work. It is often accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health, nausea and vomiting, as well as other typical symptoms. During this period, it is recommended to rest, avoid harsh irritants and stress, and take specific anti-migraine medications. Conventional painkillers may not be effective enough.
Hypertension
Main article: Headache due to hypertension
High blood pressure is a common problem for both older and younger people. The diagnosis is made if the readings consistently exceed 140/90 mm. rt. Art. The disease manifests itself in attacks, during which the patient’s health sharply deteriorates. An attack can be triggered by an increase in atmospheric pressure, physical activity, stress and nervous tension, as well as a violation of the diet.
Hypertension can be recognized by the following signs:
- pressing, throbbing headache, which often appears in the morning;
- redness of the skin of the face and mucous membranes;
- rapid heartbeat, arrhythmia;
- nose bleed;
- other symptoms (muscle tremors, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, fainting).
You can measure blood pressure at home, but to understand the full picture, daily monitoring in the hospital is recommended. For treatment, medications are prescribed to reduce blood pressure, thin the blood, and improve blood supply to the brain.
Paroxysmal hemicrania
Main article: Paroxysmal positional vertigo
Paroxysmal hemicrania is a rare disease that occurs in no more than 1–2.5% of the population. Its exact cause is unknown, but Doppler ultrasound of the brain vessels shows areas with insufficient blood circulation. The disease first appears in adulthood, between the ages of 20 and 40.
Paroxysmal hemicrania is characterized by attacks of acute unilateral headache, combined with autonomic disorders. It can be triggered by physical activity, climate change, emotional distress, and alcohol abuse. An attack can be recognized by its characteristic symptoms:
- acute pain of aching, stabbing, cutting nature, concentrated in the temple and eye area;
- an increase in symptoms in the first few minutes;
- fever, increased sensitivity to light;
- blurred vision, lacrimation, drooping eyelid on one side, constriction of the pupil;
- increased sweating.
During an exacerbation of paroxysmal hemicrania, headache attacks occur multiple times throughout the day. On average, their number reaches 5–10 per day, but can increase to 20 per day. The duration of each attack is 13–15 minutes, but can range from 5 to 45 minutes. The main goal of treatment is pain relief with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, calcium channel blockers or steroids.
Cluster pain
Main article: Cluster headache
Cluster headaches are a rare disorder that occurs primarily in adulthood. They are highly intense, so treatment at home will not be effective enough. Headaches arise abruptly, with an increase in symptoms in the first few minutes, and then disappear just as quickly after 30–60 minutes. At this time, the patient experiences increased activity and excitability, anxiety, and abnormal behavior.
A distinctive feature of cluster pain from other types is its very high intensity, short duration of attack (no more than an hour), and periodic repetition over a certain period of time. Often pain occurs at the same time of day during an exacerbation, but is then followed by a period of remission from several months to several years. Treatment consists of taking strong painkillers. Several surgical techniques have also proven effective, including greater occipital nerve block and transcutaneous vagus and supraorbital nerve stimulation.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is a disease in which there is insufficient blood circulation in the vertebral and basilar artery systems. This leads to a decrease in blood flow to certain areas of the brain, ischemia of nervous tissue and gradual necrosis of neurons. Statistically, patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency are more susceptible to strokes and suffer from recurrent headaches.
Causes of vertebrobasilar insufficiency include:
- intervertebral protrusions and hernias;
- displacement of the vertebrae, especially in the cervical region;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- neck injuries and their consequences.
Headache with vertebrobasilar insufficiency is strong, intense, concentrated in one part of the head. It may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, hearing and speech, as well as tinnitus and visual hallucinations. In addition, some patients experience motor coordination disorders and sudden falls without loss of consciousness.
Other reasons
Unilateral headache is a dangerous sign in which it is important to determine the cause. It may be associated with various diseases that first appear in adulthood. Thus, as a result of diagnostics, the following violations can be detected:
- periodic migraine neuralgia of Harris - similar to migraine, but manifests itself without warning;
- tension headaches – occur as a result of stress, physical or emotional stress;
- giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory systemic disease that often affects the temporal artery;
- middle ear diseases;
- meningitis (main article: Headache as a symptom of meningitis) is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
Headaches can also occur in a healthy person due to bad habits, disruption of sleep and nutrition schedules. Thus, complaints often arise against the background of stress or intense physical activity. Drinking cold water leads to vasoconstriction and the development of pain. Also, headaches can be caused by excessive consumption of foods high in nitrates - they have a vasoconstrictor effect.
Tinnitus, headache and temple pressure: secondary factors
Contrary to early claims that explained unpleasant episodes of tinnitus as “all due to stress,” it is now known that a family history or group of conditions known as temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) may be responsible for tinnitus.
It was also found that headaches and tinnitus are symptoms of the disorder, not the disorder itself. That is why treatment of these symptoms will be most effective if you begin therapy with the treatment of VNR.
In addition to the fact that the temporomandibular joint is located very close to the human ear, there are a group of mechanisms that cause the symptoms to appear. For example, the nerve muscles that are directly connected to the ear originate at the intersection of the nerves that serve the muscles of mastication. With this arrangement, it is easy to predict that a slight disorder could lead to changes in the muscles associated with the ear.
It has been observed that certain types of ototoxic drugs that contain antibiotics such as aminoglycosides, vancomycin and erythromycin, quinine, and chemotherapy may be responsible for tinnitus and cause unpleasant temple headaches in older age group. The toxins present in most of these medications cause irritation in the temporal part of the skull and thus stimulate pain and discomfort in this area.