Osteochondrosis on x-ray.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative-dystrophic pathology of the skeletal system, caused by metabolic disorders under the influence of provocative factors and characterized by a number of symptoms from many organs and systems. With osteochondrosis, the cartilage of the vertebrae is destroyed, and their bodies and processes are deformed.
Cervical osteochondrosis: symptoms and treatment
It’s rare that anyone today does not encounter manifestations of this widespread disease: according to statistics, about 60% of the population in developed countries suffer from manifestations of osteochondrosis to varying degrees.
The main reasons for such widespread prevalence are sedentary work and the lack of movement of modern people. Previously, cervical osteochondrosis in men usually manifested itself starting from 45-50 years, in women - a little later - 50-55 years.
But now there is rapid rejuvenation: the typical picture is noticeable signs of the disease in 30-year-olds, and it is not uncommon for the first symptoms to appear at 20 years of age.
Symptoms
With prolonged injury to the vertebral artery, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. Due to hypoxia (lack of oxygen), the risk of ischemia (local decrease in blood supply), dyscirculatory encephalopathy (vascular damage to the brain), and stroke increases.
Dizziness is one of the symptoms of cerebrovascular accident with cervical osteochondrosis
Cerebrovascular accident with cervical osteochondrosis has the following symptoms:
- Visual disturbances, oculomotor disorders. In patients, visual acuity decreases, “fog” appears before the eyes, and diplopia (double vision) occurs. These signs appear in the initial stages of pathology.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus. Then coordination of movements is impaired, the patient staggers when walking, and the tone of the muscles of the upper extremities decreases. Other symptoms of impaired cerebral circulation include vertigo (dizziness), hearing disorders (noise, ringing, weakening), disturbances in the perception of objects, etc.
- Changing sleep and wakefulness patterns. Due to impaired blood circulation in the brain, the patient feels weakness, increased fatigue, becomes sleepy during the day, and cannot sleep for a long time at night.
- A vegetative-vascular syndrome occurs. Weakness suddenly appears, the heartbeat changes (increases or slows down), surges in blood pressure, and increased intraocular pressure are observed.
- Paroxysmal disorders. People with cervical osteochondrosis may faint after suddenly turning or throwing their head back. This occurs due to severe compression of the vertebral artery and a sudden slowdown in blood flow.
- Mental disorders. The patient becomes suspicious, overly irritable, and takes offense for no apparent reason. His memory and attention are deteriorating.
In addition to the symptoms described above, cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by severe cephalgia (headache). As a rule, painful sensations begin in the back of the head, but they can spread to the arms. In some patients, throbbing pain appears in the temples, which may be accompanied by the eruption of vomit. The pain reaction intensifies when turning or tilting the head.
With prolonged compression of the vertebral artery, the symptoms intensify and the pathology progresses. In the absence of competent therapy, the risk of disability increases. To avoid dangerous complications, long-term complex treatment is necessary.
No ads 2
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: symptoms
In the early stages, the disease practically does not manifest itself with painful symptoms: you may feel discomfort in the neck after heavy physical activity or prolonged sitting in a tense position, after a sudden movement or tilting of the head.
The main symptoms are headache, dizziness and lack of coordination, a slight crunch when moving the head, general weakness; Less commonly observed are weakness of the arms, numbness of the tongue and speech impairment, problems with breathing, vision, hearing, increased sweating, and abnormally high blood pressure. The main areas are the back of the head, neck, collar area. In most cases, only a few of the listed signs of the disease are observed at the same time.
In general, the symptoms of osteochondrosis are not obvious; they are often masked by the use of painkillers. This is one of its dangers: most of the symptoms are also possible with other pathologies, which makes it difficult to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis.
What diseases can have similar manifestations?
Very often, manifestations of “osteochondrosis” are actually associated with a completely different disease. For example, the cause may be hidden in the muscles - there is a condition called myofascial pain syndrome . Pain occurs due to constant tension in the same muscles.
Sometimes dizziness associated with otolithiasis, a condition in which crystals of calcium salts accumulate in the inner ear, is taken to be a manifestation of “cervical osteochondrosis.”
Each situation needs to be analyzed individually. A neurologist at the International Clinic Medica24 center will correctly assess your symptoms, prescribe the necessary examination, establish a reliable diagnosis and recommend effective treatment. Appointments can be made 24 hours a day by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Pain and crunch in the neck, headaches - when these symptoms occur, many people “diagnose” themselves with osteochondrosis. Everything is clear - when it hurts, you need to take painkillers or get an injection, apply heat, and everything will go away. Why go to the doctor if you can handle it yourself?
However, self-medication often does not lead to anything good. Painful attacks may become more frequent, severe, and prolonged over time. If you uncontrollably take painkillers almost every day, you can get stomach or kidney problems. After all, any medicine has side effects.
And the cause of pain is not always due to osteochondrosis. In order to find out the real reason and understand how to effectively deal with it, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
In the development of cervical osteochondrosis, it is customary to distinguish 4 stages. But this is a rather arbitrary division, since most of the symptoms of the disease can also manifest themselves in other pathologies. In addition, the actual degree of tissue degradation of the cervical spine may not correspond to the externally manifested symptoms.
First stage (preclinical)
At the initial stage, symptoms are mild and are often attributed to stress or other diseases. You feel unpleasant stiffness in the neck, pain with sudden movements or bending. At this stage, it is quite possible to get rid of incipient osteochondrosis with the help of therapeutic exercises or simply move more and adjust your diet.
Second stage
The pain intensifies, becomes constant, and becomes severe with sharp turns or bends. Severe headaches appear, the patient begins to get tired quickly, becomes absent-minded, and areas of the face periodically become numb.
Third stage
The formation of disc herniation often causes dizziness, weakness of the arms, pain radiates to the back of the head and arms, and is constantly felt in the shoulders.
Fourth stage
Eventually, the intervertebral discs are destroyed and replaced by connective tissue. The nerves are pinched, which leads to difficulties in movement, acute pain, increased dizziness, and tinnitus.
Causes of cerebrovascular accident in cervical osteochondrosis
To understand why blood circulation to the brain is impaired during osteochondrosis, you need to study the anatomy of the cervical spine. The transverse processes of the cervical segment have openings that form a canal, and veins, nerves and vertebral arteries pass through it. The latter arise from the subclavian arteries, pass through the transverse foramen of C6 (sixth cervical vertebra) and rise higher. At the level of the hindbrain, the left vertebral arteries on the left and right join, forming an artery from which the posterior cerebral, internal auditory, and cerebellar arteries (anterior and posterior) depart.
Based on what is described above, arteries pass through the cervical spine, which are necessary for normal blood supply to the brain. In addition, veins and sympathetic nerves are located in the spinal canal.
The transverse foramina are considered narrow, but there is enough space for the neurovascular bundle. Blood vessels and nerves are not pinched even when moving the head (turning, bending).
The cervical vertebrae are connected by elastic intervertebral discs. These are a kind of cartilage pads that soften shocks during running and jumping. These structures also protect nerves and blood vessels from damage.
With cervical osteochondrosis, the discs lose a lot of fluid and become fragile. Increased load provokes flattening of the cartilage pads and the appearance of cracks on their outer shell. As a result, protrusions (protrusions, disc herniations), osteophytes (bone growths) appear, which injure nerves and blood vessels.
Reference. According to medical statistics, about 30% of cases of circulatory failure in the vessels of the brain are associated with damage to the vertebral artery. In most cases, the disorder occurs against the background of cervical osteochondrosis and atheromatosis (overgrowth of connective tissue on the vessel wall).
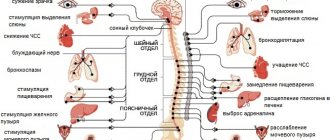
Cerebral circulation in cervical osteochondrosis occurs for the following reasons:
- The nerve that supplies the vertebral artery is compressed. It provokes a spasm of the artery, then the blood flow to the brain is disrupted.
- Long-term compression of the vertebral artery. Due to constant compression, the lumen of the vessel narrows or is completely blocked (occlusion). The risk of vertebral artery syndrome then increases.
- Rough compression of the vertebral artery, which prevents the outflow of blood. This can happen when turning the head, then the person experiences a severe headache and may lose consciousness.
Compression and stretching of the vertebral arteries can occur even in healthy people. With cervical osteochondrosis, an important vessel is damaged regularly, and then dangerous complications arise.
No ads 1
Causes and risk factors
Oddly enough, the possibility of developing osteochondrosis in humans is due to one of its evolutionary advantages - upright posture: the vertebrae press on each other, and with age, the connective tissue degrades. As a result, in older people this is an almost inevitable process. But there are many factors that contribute to the earlier and more intense development of cervical osteochondrosis:
- First of all, this is a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, often observed in modern life (office workers, drivers and other “sedentary” professions, TV, long hours at the computer), lack of physical activity
- Tense, unnatural postures while working: for example, at a computer, a person often leans forward, taking a tense posture
- The opposite reason is that the load is too high and unusual for a given person; but even trained athletes, for example, weightlifters, are at risk;
- Any reasons that disrupt a person’s natural posture: uncomfortable shoes, especially high heels, poor sleeping position, flat feet, rheumatism, scoliosis;
- Excess weight, which is often caused by poor diet
- Frequent stress, severe nervous tension, constant overwork
- Local hypothermia
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous?
Many vital vessels, arteries, and capillaries are concentrated in the neck area, so any disturbance there can have unpleasant consequences, including oxygen starvation, hypertension, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Cervical osteochondrosis affects the segments of the spine that control the functioning of the shoulder and elbow joints, the thyroid gland, hands and other organs. With osteochondrosis, if left untreated, there is a high probability of pinched nerves and compression of blood vessels, which inevitably affects the functioning of other organs.
Key signs of stroke
With cervical osteochondrosis, doctors identify a number of signs that may indicate the development of a stroke:
- dizziness;
- constant headaches with increasing intensity;
- profuse sweating;
- chills;
- facial asymmetry;
- the appearance of dark spots before the eyes;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- loss of consciousness;
- feeling of lack of air;
- speech disorder;
- numbness of the limbs.
As the disease progresses, the signs of the disease become more pronounced.
Which doctor should I contact?
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are usually mild, especially at the initial stage, in addition, almost all of them are characteristic of other pathologies: in such conditions, it is best to consult a therapist who will analyze your complaints, conduct an examination and refer you for diagnosis and to a more highly specialized specialist - neurologist, orthopedist.
Who will carry out further treatment depends on the stage of the disease and the disorders detected during diagnosis.
For example, the formation of a hernia or displacement of discs may require the help of a traumatologist. Massage and exercise therapy, physiotherapy are non-surgical methods of treatment; in severe cases, the patient is referred to a surgeon.
How to determine that noise in the head is from osteochondrosis:
You cannot engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, since noise in the head against the background of osteochondrosis can be confused with another disease: hypertension, cerebral aneurysm, auditory neuritis, atherosclerosis, brain tumor.
Let's look at the specific signs of the disease.
Neck pain and headache
One of the first manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis is pain in the neck, back of the head, and collar area. Its nature and intensity depend on the stage of the pathology.
At the initial stages, it is mild, periodic, similar to muscle strain, and can spread from the neck to the entire head. The pain is aching, intensifies after sleep, prolonged stay in one position. It can go away on its own after warming up the neck, without taking painkillers.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
In the later stages, the pain becomes constant, it is so strong that the person cannot move his head. Without treatment, “lumbago” occurs - attacks of sharp pain that immobilize.
The noise in the head increases as blood circulation worsens. At first it appears only under the influence of irritants:
- sudden movements;
- stress;
- temperature changes;
- physical and emotional fatigue;
- staying in one position for a long time, working at the computer.
Without treatment, it bothers a person even at rest, which disrupts psycho-emotional balance and can cause nervous breakdown and depression.
Pain in the back of the head
Pain in the neck gradually moves to the occipital region, and then to the temples. It is associated with the destruction of cervical vertebral discs and pinched nerve endings. But it is always accompanied by other neurological symptoms. The most common include noise in the head and headache.
Noise in the head when turning the head
With osteochondrosis, any change in head position provokes noise or ringing. As the intervertebral discs become deformed, the functions of the spine are impaired. It is difficult for a person to turn his head and move the upper shoulder girdle. Such movements are accompanied by pain, crunching, numbness and other neurological signs.
Headaches and head pressure
Cervical osteochondrosis is almost always accompanied by headaches of various localizations, depending on the damaged spinal segment. It is often accompanied by dizziness, noise in the head, blurred vision and impaired coordination of movements.
Characteristics of headache:
- has a “cervical” character, that is, it appears when moving the neck, being in one position;
- Tension headaches can occur in the morning due to the head remaining in one position for a long time or at the end of the working day;
- localized in the area of the back of the head and crown, in the temples, less often in the frontal part, in the area of the orbit;
- can spread to the entire head or cover only half;
- often has a sharp, pulsating or vascular character, that is, there is one painful pulsating point;
- not relieved by analgesics for headaches.
Often the pain syndrome has the character of pressure on the skull and eyeballs. Sometimes there is not a throbbing or squeezing pain, but a strong bursting pain.
If the pain syndrome is of the migraine type, then the pain sensations going from the back of the head to the temples intensify when changing position, nausea, vomiting occurs, and darkening in the eyes. In severe cases, the condition is close to fainting.
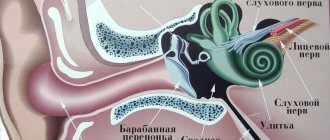
Congestion in the ears and noise in the head
When the pain in the neck intensifies, that is, osteochondrosis progresses, noise in the head appears, a feeling of stuffy ears, ringing in the ears. These signs are most pronounced when there is a sudden change in body position or when sudden movements are made. Often accompanied by dizziness.
Congestion and ringing in the ears may indicate high blood pressure, which is a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis. Hypertension occurs due to compression of blood vessels, its symptoms:
- ear ringing;
- congestion in one or both ears;
- headache, dizziness;
- chest tightness that leads to difficulty breathing;
- nausea;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of heat in the face.
Pressure surges often occur against the background of physical or psycho-emotional stress, after overheating in the sun, or sudden movements. They can cause a hypertensive crisis, stroke or heart attack, so ringing and other sounds in the ears and head cannot be ignored.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of osteochondrosis are mild and often overlap with other pathologies, it is better to conduct an initial examination with a therapist or other specialist - a neurologist, orthopedist. He will ask you about pain and other symptoms, check neck mobility, skin condition, balance, and reflexes.
If a primary diagnosis of “cervical osteochondrosis” is made, the doctor will then refer you for additional studies. The most effective of them is MRI, followed by computed tomography. X-ray studies are much less effective than the first two, especially with advanced disease. The condition of soft tissues is checked using ultrasound. If your doctor suspects blood vessel damage, you may be referred for a vascular duplex scan.
Since some symptoms overlap with signs of angina and coronary heart disease, you may need to consult a cardiologist who will refer you for an ECG and echocardiography.
Features of treatment
Insufficient blood supply to the brain due to osteochondrosis of the cervical segment must be treated comprehensively. The basis of therapy is medications; in addition, other conservative methods are used (physical therapy, physiotherapy, etc.). And in advanced cases, surgery may be necessary.
Doctors have identified the main goals of therapy:
Osteochondrosis and panic attacks
- Restoring the functionality of the brain, improving its blood supply, due to which the organ is saturated with a large amount of oxygen and nutrients.
- Relief of the inflammatory reaction, activation of regeneration processes of damaged tissues.
- Some medications help normalize the composition of the blood, making it more fluid, which improves its quality and speed of movement.
- Expand the lumen of blood vessels, make the damaged areas thicker.
- Stabilize blood pressure.
- Restore the normal structure of the spine, saturate the cartilage tissue with useful substances, and strengthen it.
It is important to understand that complex therapy will help eliminate circulatory problems in the brain, but it will not be possible to completely cure osteochondrosis. But with proper treatment, it is possible to slow down the development of pathology for a long time.
Carefully. You can take any medications for cerebral circulatory disorders due to cervical osteochondrosis only for medical reasons. Otherwise, the symptoms of the disease may worsen or be supplemented with new ones, for example, drug-dependent headaches. When drugs are abused, blood circulation in the brain deteriorates.
Groups of drugs to improve cerebral blood flow
The following groups of medications will help improve cerebral circulation in cervical osteochondrosis:
- Vasodilators accelerate blood flow and transport of nutrients to the brain by increasing the lumen of blood vessels. Tanakan, Vazobral, Cavinton are used for this purpose.
- Medicines that prevent blood clots, for example, Dipyridamole, as well as aspirin-based medications. They improve the permeability of blood vessels and prevent red blood cells and platelets from sticking to their walls. As a result, the blood thins out and flows faster to the brain.
- Diuretics: Mannitol or Furosemide. These medications prevent stagnation and swelling. The first drug is used for excess fluid accumulation in brain cells, the second is suitable for eliminating swelling of any localization.
- Osmodiuretics are the only drugs that do not block urine formation. These include Britomar, Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron. Used to stimulate diuresis in cervical osteochondrosis.
- Antioxidants, for example, vitamin E, Mexidol, Neurox. These tablets improve the condition of nerve endings and reduce harmful oxidative processes in the body's cells.
- Antipsychotics: Glycine, Novo-Passit. These medications slow down the transmission of nerve impulses, relieving pain for a long time. They help cope with stress, prolonged pain, and improve the condition of the spinal nerves.
Tanakan dilates blood vessels and normalizes cerebral circulation
However, it should be remembered that all medications have contraindications, so taking them without the knowledge of a doctor is prohibited.
Drugs to improve cerebral circulation
Doctors have identified drugs that improve blood circulation in intracranial vessels for osteochondrosis of the neck:
- Eufillin is a bronchodilator that eliminates spasm and normalizes blood flow. It is often used during electrophoresis, a physiotherapeutic procedure during which drugs penetrate the body through the skin under the influence of current.
- Trental, based on theophylline and nicotinic acid, saturates the blood with oxygen and improves its quality. When used, microcirculation accelerates, blood vessels dilate, and blood circulation normalizes. The medication can quickly lower blood pressure.
- Berlition contains thioctic acid, which helps expand the lumen of blood vessels. It improves metabolic processes and eliminates vascular spasm.
- Actovegin is based on cattle blood. It helps normalize the condition of intracranial vessels, enriches neurons with oxygen and glucose.
- Pentoxifylline and its substitutes relax the walls of spasmodic blood vessels and thin the blood. As a result, microcirculation improves.
- Nicotinic acid helps dilate small blood vessels, reduces the concentration of bad cholesterol, and restores blood supply to the brain.
- Cinnarizine dilates blood vessels, makes blood less viscous, normalizes microcirculation, and helps get rid of dizziness.
Reference. In case of cerebrovascular accident associated with osteochondrosis, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are used. These medications help relieve pain that occurs in the later stages of the pathology. For this purpose, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, etc. are used. However, taking them for a long time without the knowledge of a doctor is prohibited, as they have many contraindications.
As a rule, several drugs are used during therapy according to a specific regimen.
[node:field_similarlink]
Other groups of medications
If cervical osteochondrosis occurs over a long period of time, then during complex therapy the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antidepressants, for example, Afobazol, Fenozepam. They do not affect the blood circulation of the brain, but they stabilize the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
- Medicines for hypertension: Cardura, Reseprin. These medications are used for prolonged compression of the artery, poor circulation and high blood pressure. They help prevent brain swelling.
- Drugs from the group of low molecular weight dextrans: Reopoliglucin, Reogluman. They thin the blood.
- Calcium antagonists: Phezam, Cinnarizine, Stugeron. They relax the walls of spasmodic vessels, normalize the functionality of neurons, and prevent ischemic reactions.
- Venotonic drugs: Phlebodia, Detralex. Restores blood flow from the brain.
- Nootropic drugs: Piracetam, Ceraxon. They are used when speech, memory, and thinking disorders occur.
- Vitamins: Cytoflavin, Milgamma. They improve the condition of nerve cells, prevent oxygen starvation, and normalize the condition of the body.
- Chondroprotectors: Chondroitin, Dona, Teraflex. Restore cartilage tissue.
- Histaminergic drugs: Betaserc, Vestibo, Betahistine. Eliminate vertigo, improve the functionality of the vestibular apparatus.
Phlebodia normalizes blood flow from the brain
Depending on the symptoms, this list may be supplemented with other medications. But in any case, the decision on the choice of appropriate drugs is made by the attending physician.
No ads 3
Additional Treatments
Combined treatment is complemented by physical therapy, which affects the cause of the disease. With the help of exercise therapy, you can improve blood circulation, metabolic processes, and improve trophism of the spine. With regular exercise, the muscles around the damaged vertebrae are strengthened, which allows them to be slightly relieved. However, to get good results, classes must be carried out regularly.
In case of cerebral circulation disorders associated with cervical osteochondrosis, special gymnastics is indicated
The patient must follow these training rules:
- Start with simple movements at a slow pace and minimal amplitude, gradually increasing the pace.
- Before exercising, massage your neck or take a warm shower to warm up your muscles.
- During training, be attentive to your feelings. At first there may be some discomfort, but after 3-4 days the body will adapt and your health will improve. If this does not happen or acute pain occurs, then visit a doctor.
The complex for each patient is compiled by a doctor, taking into account symptoms, severity of pathology, age and general health.
Reference. It is recommended to supplement exercise therapy in case of cerebral circulation disorders with walking or cycling, swimming, yoga, breathing exercises, and cardio exercises (elliptical, exercise bike).
An auxiliary treatment method is physiotherapy. To improve cerebral circulation, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, medicinal baths, and acupuncture are prescribed.
In order for the spine and blood vessels to function normally, the patient must eat properly. The diet needs to be supplemented with foods rich in fiber, fatty acids, group B elements, tocopherol, and ascorbic acid. To do this, you need to eat more vegetables, fruits, berries, and herbs. In addition, it is useful for patients to eat fatty sea fish, lean meat, nuts, vegetable oils, etc. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of filtered water per day.
With a poor diet, the lack of nutrients can be compensated with the help of vitamin and mineral complexes. Your doctor will help you choose the right drug.
Surgery for poor circulation in the brain due to cervical osteochondrosis is performed only in extreme cases. The need for surgical intervention may arise if there is a large bone growth that compresses the vessel. During the procedure, the osteophyte is removed; if this cannot be done for some reason, then a stent is inserted into the blood vessel.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
Real, sustainable success in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can be achieved only with an integrated approach, which includes medications, massage of the collar area, therapeutic exercises, and physiotherapy.
In particularly advanced cases, surgical intervention may be required. Naturally, the patient must eliminate or minimize factors contributing to the development of the disease: move more, eat better, etc. We strongly advise against resorting to self-medication, primarily because the symptoms of osteochondrosis can mean a completely different disease: not only will the drugs you choose not help in treatment, they can also cause harm. Even during painful exacerbations, do not rush to the pharmacy for painkillers - it is better to make an appointment with a doctor, and even better - do it in advance, at the first symptoms.
Relieving acute pain
Osteochondrosis, especially in the later stages, is accompanied by severe pain, so the first task of the attending physician is to alleviate your suffering. He will prescribe you painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, chondroprotectors to restore cartilage tissue, medications to improve blood circulation and reduce muscle spasms.
In this article, we deliberately do not give the names of specific drugs - it is better to leave their choice to doctors who will take into account all possible consequences and evaluate contraindications.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis
The simplest and most accessible method, including at home, is therapeutic exercises. At the same time, it is also quite effective, as it strengthens the neck muscles, restores blood circulation in damaged areas, and compensates for the lack of movement in everyday life. Physical therapy can be supplemented with swimming and aqua gymnastics.
There are many methods, including the use of simulators: most of them do not require special equipment or any special conditions, but we advise you to contact the exercise therapy office, where they will select the most effective sets of exercises for you and conduct classes under the guidance of an experienced specialist.
Physiotherapy
Correct and constant use of physiotherapeutic methods improves blood circulation in damaged areas, reduces inflammation and pain, and slows down the ossification process.
For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, shock wave therapy, therapeutic baths and showers, mud therapy and other methods are used.
Neck massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
For osteochondrosis, massage can be very effective: it improves blood circulation, reduces the likelihood of spasms by reducing muscle tone, relieves pain symptoms and improves the general well-being of the patient.
But massage and manual therapy must be used extremely carefully, since inept and rough influence on diseased areas of the body can only cause harm. We strongly advise you to consult your doctor first.
Surgery
In particularly advanced cases, even surgical intervention cannot be ruled out: narrowing of the lumen of the spinal column, the formation of herniated intervertebral discs, or spondylolisthesis.
The decision on the need and method of surgical intervention is made by the surgeon, who also determines the preparatory operations, the duration of the postoperative period and rehabilitation.
Causes of cerebral circulatory disorders and venous outflow
Impaired venous outflow with cervical osteochondrosis is a common cause of headaches, decreased mental performance, constant weakness and drowsiness. Stagnation of venous blood leads to the effusion of fluid into the intercellular space. This can cause increased intracranial pressure. The structures of the brain are under enormous pressure and are unable to function normally. Blood pressure levels may then begin to rise. In general, this situation is dangerous because there may be a threat of hemorrhagic stroke. It has a very high mortality rate even among young patients.
Therefore, at the first signs of vertebrobasilar insufficiency, effective treatment should begin. But in order to cope with this problem, the patient needs to change his lifestyle so as to eliminate all potential risk factors.
The main reasons why cerebral circulation is impaired in cervical osteochondrosis are:
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle without sufficient regular physical activity;
- predominantly sedentary work, in which the muscles of the neck and collar area are statically tense for a long time;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, which leads to disruption of microcirculation processes, muscle tissue is subject to ischemia due to impaired trophism;
- stoop, scoliosis and other types of postural disorders and curvature of the spinal column, as a result of which the functional ability of the muscles changes;
- cicatricial deformities of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus, which put pressure on the surrounding soft tissues, including arteries;
- improper organization of sleeping and working spaces;
- wearing tight clothing and tight collars;
- injuries in the neck and collar area;
- driving a car without a seat belt fastened.
In order to prevent the risk of developing cerebrovascular accidents and make future treatment more effective, it is necessary to eliminate all potential causes and risk factors. An experienced vertebrologist, already during the initial consultation, provides the patient with comprehensive information on how to eliminate the possibility of further development of the pathology. These recommendations allow you to gradually eliminate all risk factors from your life. This becomes an excellent foundation for effective treatment.
Possible complications and consequences
In the neck area there are many nerve endings and blood vessels that directly affect the functioning of other parts of the body: if cervical osteochondrosis is not treated, it can lead to an increase in many other diseases:
- Migraine – it is in the neck area that the vertebral artery delivers blood to the brain: narrowing also leads to severe headaches.
- Visual impairment - the carotid and vertebral arteries, which are responsible for supplying blood to the visual organs, pass through the neck: compression of the nerve roots and blood vessels leads to decreased vision.
Consequences
The main complications of impaired blood supply to the brain and peripheral circulation include the following acute (emergency) conditions:
- thrombosis: myocardial infarction, acute thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower extremities or pelvis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome;
- ischemia: angina attacks, micro-strokes. Repeated attacks can cause a heart attack or ischemic stroke;
- embolism: pulmonary embolism, infarction-pneumonia;
- bleeding. Hemorrhagic stroke, hematoma, purpura - a consequence of hemorrhage into the internal organs;
- blood stasis - cessation of blood flow. Short-term hemostasis is a reversible process. Prolonged stoppage of blood supply to an organ is dangerous due to necrosis;
- venous and arterial congestion - a change in the volume of circulating blood. Risks the development of acute heart failure.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a disease whose negative impact can be minimized with proper and timely prevention. You need to think about its prevention in childhood: poor posture and flat feet in a child are a reason to consult a doctor for a diagnosis.
The basis for the prevention of osteochondrosis is a correct lifestyle: reasonable physical activity and periodic exercise during sedentary work, a healthy diet, body weight control.
Complications
Chronic oxygen starvation quickly leads to disruption of processes in the human body. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the above symptoms will gradually intensify. Depending on which brain is most affected by the deficiency of the necessary substances, there is a possibility of developing a number of complications.
Consequences of cerebrovascular accident in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- hypertonic disease;
- cerebral ischemia;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- problems with orientation and coordination;
- change in the quality and type of breathing;
- decreased mobility of the upper limbs.
Even if the listed conditions have begun to appear, this is not a reason to panic. In such cases, there is also a chance for cure and complete restoration of impaired functions. The main thing is not to delay any further in visiting a doctor, but to quickly begin therapy.