Polyneuropathy is a disease that affects many peripheral nerves. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital determine the cause of the development of the pathological process, the localization and severity of damage to nerve fibers using modern diagnostic methods. Professors and doctors of the highest category take an individual approach to the treatment of each patient. Complex therapy of polyneuropathies is carried out with effective drugs registered in the Russian Federation. They have a minimal range of side effects.
The following types of neuropathies are registered in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), depending on the cause and course of the disease:
- inflammatory polyneuropathy (ICD code 10 - G61) is an autoimmune process that is associated with a constant inflammatory reaction to various stimuli of a predominantly non-infectious nature (includes serum neuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, a disease of an unspecified nature);
- ischemic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities (ICD code also G61) is diagnosed in patients with impaired blood supply to nerve fibers;
- drug-induced polyneuropathy (ICD code G.62.0) – the disease develops after long-term use of certain drugs or against the background of incorrectly selected doses of drugs;
- alcoholic polyneuropathy (ICD code G.62.1) – the pathological process is provoked by chronic alcohol intoxication;
- toxic polyneuropathy (ICD10 code – G62.2) is formed under the influence of other toxic substances, and is an occupational disease of workers in the chemical industry or those in contact with toxins in the laboratory.
Polyneuropathy, which develops after the spread of infection and parasites, has the code G0. The disease with the growth of benign and malignant neoplasms is encrypted in ICD 10 with code G63.1. Diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities has an ICD 10 code G63.2. Complications of endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders in ICD-10 are assigned code G63.3. Dysmetabolic polyneuropathy (ICD 10 code - G63.3) is classified as polyneuropathies in other endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders.
Forms of neuropathy depending on the prevalence of symptoms
The classification of polyneuropathy according to ICD 10 is officially recognized, but it does not take into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and does not determine treatment tactics. Depending on the predominance of clinical manifestations of diseases, the following forms of polyneuropathies are distinguished:
- sensory – signs of involvement of sensory nerves in the process (numbness, burning, pain) predominate;
- motor – signs of damage to motor fibers prevail (muscle weakness, decrease in muscle volume);
- sensorimotor – symptoms of damage to motor and sensory fibers are simultaneously present;
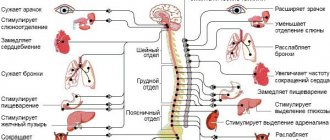
- autonomic – there are signs of involvement of the autonomic nerves in the process: dry skin, rapid heartbeat, tendency to constipation;
- mixed - neurologists determine signs of damage to all types of nerves.
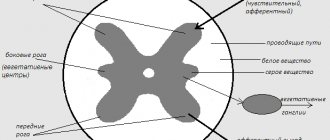
With primary damage to the axon or neuron body, axonal or neuronal polyneuropathy develops. If Schwann cells are affected first, demyelinating polyneuropathy occurs. In the case of damage to the connective tissue sheaths of the nerves, they speak of infiltrative polyneuropathy, and if the blood supply to the nerves is impaired, ischemic polyneuropathy is diagnosed.
Polyneuropathies have various clinical manifestations. The factors that cause polyneuropathy most often first irritate the nerve fibers, causing symptoms of irritation, and then lead to disruption of the function of these nerves, causing “prolapse symptoms.”
DISEASES OF THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYNAPSE AND MUSCLES (G70-G73)
G70 Myasthenia gravis and other disorders of the neuromuscular synapse
Excluded: botulism ( A05.1 ) transient neonatal Myasthenia gravis ( P94.0 )
G 70.0 Myasthenia gravis If the disease is caused by a drug, an additional external cause code (class XX) is used to identify it. G70.1 Toxic disorders of the neuromuscular junction When necessary to identify a toxic substance, use an additional external cause code (Class XX). G70.2 Congenital or acquired myasthenia G70.8 Other disorders of the neuromuscular junction G70.9 Disorder of the neuromuscular junction, unspecified
G71 Primary muscle lesions
Excluded: multiple congenital arthrogryposis ( Q74.3 ) metabolic disorders ( E70 - E90 ) myositis ( M60 . -)
G71.0 Muscular dystrophy Muscular dystrophy: • autosomal recessive childhood type, resembling Duchenne or Becker dystrophy • benign [Becker] • benign scapuloperoneal with early contractures [Emery-Dreyfus] • distal • scapulohumeral-facial • limb-girdle • ocular muscles • oculopharyngeal [oculopharyngeal] • scapulofibular • malignant [Duchenne] Excluded: congenital muscular dystrophy: • NOS ( G71.2 ) • with specified morphological lesions of muscle fiber ( G71.2 ) G71.1 Myotonic disorders. Myotonic dystrophy [Steiner] Myotonia: • chondrodystrophic • medicinal • symptomatic Myotonia congenital: • NOS • dominant inheritance [Thomsen] • recessive inheritance [Becker] Neuromyotonia [Isaacs]. Paramyotonia congenital. Pseudomyotonia If it is necessary to identify the drug causing the lesion, use an additional code for external causes (class XX). G71.2 Congenital myopathies Congenital muscular dystrophy: • NOS • with specific morphological lesions of the muscle fiber Disease: • central nucleus • mininuclear • multinuclear Disproportion of fiber types Myopathy: • myotubular (centronuclear) • nemaline [disease of the nemaline body] G71.3 Mitochondrial myopathy, not elsewhere classified G71.8 Other primary muscle lesions G71.9 Primary muscle lesion, unspecified. Hereditary myopathy NOS
G72 Other myopathies
Excludes: congenital arthrogryposis multiplex ( Q74.3 ) dermatopolymyositis ( M33.- ) ischemic muscle infarction ( M62.2 ) myositis ( M60.- ) polymyositis ( M33.2 )
G72.0 Drug-induced myopathy If it is necessary to identify the drug, use an additional code for external causes (class XX). G72.1 Alcoholic myopathy G72.2 Myopathy caused by another toxic substance If necessary, identify the toxic substance, use an additional code for external causes (Class XX). G72.3 Periodic paralysis Periodic paralysis (familial): • hyperkalemic • hypokalemic • myotonic • normokalemic G72.4 Inflammatory myopathy, not elsewhere classified G72.8 Other specified myopathies G72.9 Unspecified myopathy
G73* Lesions of the neuromuscular junction and muscles in diseases classified elsewhere
G73.0 * Myasthenic syndromes in endocrine diseases Myasthenic syndromes in: • diabetic amyotrophy ( E10 - E14 + with a common fourth sign .4) • thyrotoxicosis [hyperthyroidism] ( E05 . -+) G73.1 * Eaton-Lambert syndrome ( C80 + ) G73.2 * Other myasthenic syndromes in tumor lesions ( C00 - D48 +) G73.3 * Myasthenic syndromes in other diseases classified in other headings G73.4 * Myopathy in infectious and parasitic diseases classified in other headings G73.5 * Myopathy in endocrine diseases Myopathy in: • hyperparathyroidism ( E21.0 - E21.3 +) • hypoparathyroidism ( E20 . -+) Thyrotoxic myopathy ( E05 . -+) G73.6 * Myopathy in metabolic disorders Myopathy in: • disorders glycogen accumulation ( E74.0 +) • lipid accumulation disorders ( E75 . -+) G73.7 * Myopathy in other diseases classified in other headings Myopathy in: • rheumatoid arthritis ( M05 - M06 +) • scleroderma ( M34.8 + ) • Sjogren's syndrome ( M35.0 +) • systemic lupus erythematosus ( M32.1 +)
For somatic diseases
Diabetic polyneuropathy (ICD10 code G63.2.) is one of the most common and studied forms of somatic polyneuropathies. One of the manifestations of the disease is autonomic dysfunction, which has the following symptoms:
- orthostatic arterial hypotension (decrease in blood pressure when changing body position from horizontal to vertical);
- physiological fluctuations in heart rate;
- disorders of gastric and intestinal motility;
- bladder dysfunction;
- changes in sodium transport in the kidneys, diabetic edema, arrhythmias;
- erectile disfunction;
- skin changes, impaired sweating.
With alcoholic polyneuropathy, paresthesia in the distal limbs and pain in the calf muscles are noted. One of the early characteristic symptoms of the disease is pain, which intensifies with pressure on the nerve trunks and compression of the muscles. Later, weakness and paralysis of all extremities develop, which are more pronounced in the legs, with predominant damage to the extensors of the foot. Atrophy of paretic muscles develops rapidly, periosteal and tendon reflexes are strengthened.
In the later stages of development of the pathological process, muscle tone and muscle-joint sensation decrease, and the following symptoms develop:
- surface sensitivity disorder of the “gloves and socks” type;
- ataxia (instability) in combination with vasomotor, trophic, secretory disorders;
- hyperhidrosis (increased skin moisture);
- swelling and pallor of the distal extremities, decreased local temperature.
OTHER NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS (G90-G99)
G90 Disorders of the autonomic nervous system
Excludes: alcohol-induced autonomic nervous system disorder ( G31.2 )
G90.0 Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy. Syncope associated with irritation of the carotid sinus G90.1 Familial dysautonomia [Riley-Day] G90.2 Horner's syndrome. Bernard(-Horner) syndrome G90.3 Multisystem degeneration. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension [Shay-Drager] Excludes: orthostatic hypotension NOS ( I95.1 ) G90.8 Other disorders of the autonomic nervous system G90.9 Disorder of the autonomic nervous system, unspecified
G91 Hydrocephalus
Included: acquired hydrocephalus Excluded: hydrocephalus: • congenital ( Q03.- ) • caused by congenital toxoplasmosis ( P37.1 )
G91.0 Communicating hydrocephalus G91.1 Obstructive hydrocephalus G91.2 Normal pressure hydrocephalus G91.3 Post-traumatic hydrocephalus, unspecified G91.8 Other types of hydrocephalus G91.9 Hydrocephalus, unspecified
G92 Toxic encephalopathy
If it is necessary to identify a toxic substance, use an additional external cause code (Class XX).
G93 Other brain lesions
G93.0 Cerebral cyst. Arachnoid cyst. Porencephalic cyst, acquired Excludes: periventricular acquired cyst of the newborn ( P91.1 ) congenital cerebral cyst ( Q04.6 ) G93.1 Anoxic brain lesion, not elsewhere classified Excludes: complicating: • abortion, ectopic or molar pregnancy ( O 00 - O 07 , O 08.8 ) • pregnancy, labor or delivery ( O29.2 , O74.3 , O89.2 ) • surgical and medical care ( T80 - T88 ) neonatal anoxia ( P21.9 ) G93.2 Benign intracranial hypertension Excludes: hypertensive encephalopathy ( I67.4 ) G93.3 Fatigue syndrome after a viral illness. Benign myalgic encephalomyelitis G93.4 Encephalopathy, unspecified Excluded: encephalopathy: • alcoholic ( G31.2 ) • toxic ( G92 ) G93.5 Compression of the brain Compression } Incarceration } of the brain (trunk) Excluded: traumatic compression of the brain ( S 06.2 ) • focal ( S 06.3 ) G93.6 Cerebral edema Excludes: cerebral edema: • due to birth trauma ( P11.0 ) • traumatic ( S06.1 ) G93.7 Reye's syndrome If necessary, identify an external factor, use an additional code for external causes (class XX ). G93.8 Other specified brain lesions. Radiation-induced encephalopathy If it is necessary to identify an external factor, use an additional code for external causes (class XX). G93.9 Brain damage, unspecified
G94* Other brain lesions in diseases classified elsewhere
G94.0 * Hydrocephalus in infectious and parasitic diseases classified in other headings ( A00 - B99 +) G94.1 * Hydrocephalus in tumor diseases ( C00 - D48 +) G94.2 * Hydrocephalus in other diseases classified in other headings G94. 8 * Other specified brain lesions in diseases classified in other headings
G95 Other diseases of the spinal cord
Excludes: myelitis ( G04.- )
G95.0 Syringomyelia and syringobulbia G95.1 Vascular myelopathies. Acute spinal cord infarction (embolic) (non-embolic). Thrombosis of the spinal cord arteries. Hepatomyelia. Non-pyogenic spinal phlebitis and thrombophlebitis. Edema of the spinal cord Subacute necrotizing myelopathy Excludes: spinal phlebitis and thrombophlebitis, except non-pyogenic ( G08 ) G95.2 Spinal cord compression, unspecified G95.8 Other specified diseases of the spinal cord. “Spinal” bladder NOS Myelopathy: • drug • radiation If necessary, identify an external factor, use an additional code for external causes (class XX). Excludes: neurogenic bladder: • NOS ( N31.9 ) • associated with cauda equina syndrome ( G83.4 ) neuromuscular bladder dysfunction without mention of spinal cord involvement ( N31.- ) G95.9 Disease of the spinal cord, unspecified. Myelopathy NOS
G96 Other disorders of the central nervous system
G96.0 Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid [cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea] Excluded: during spinal puncture ( G97.0 ) G96.1 Lesions of the meninges, not elsewhere classified Meningeal adhesions (cerebral) (spinal) G96.8 Other specified lesions of the central nervous system G96 .9 Damage to the central nervous system, unspecified
G97 Nervous system disorders following medical procedures, not elsewhere classified
G97.0 Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid during lumbar puncture G97.1 Other reaction to lumbar puncture G97.2 Intracranial hypertension after ventricular bypass G97.8 Other nervous system disorders after medical procedures G97.9 Nervous system disorder after medical procedures, unspecified
G98 Other disorders of the nervous system, not elsewhere classified
Nervous system damage NOS
G99* Other disorders of the nervous system in diseases classified elsewhere
G99.0 * Autonomic neuropathy in endocrine and metabolic diseases Amyloid autonomic neuropathy ( E85 . -+) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy ( E10 - E14 + with a common fourth sign .4) G99.1 * Other disorders of the autonomic nervous system in others diseases classified in other headings G99.2 * Myelopathy in diseases classified in other headings Compression syndromes of the anterior spinal and vertebral artery ( M47.0 *) Myelopathy in: • lesions of the intervertebral discs ( M50.0 +, M51.0 +) • tumor lesion ( C00 - D48 +) • spondylosis ( M47 . -+) G99.8 * Other specified disorders of the nervous system in diseases classified in other headings
Hereditary and idiopathic polyneuropathy (code G60)
Hereditary polyneuropathy is an autosomal dominant disease with systemic damage to the nervous system and varied symptoms. At the onset of the disease, patients experience fasciculations (visible contractions of one or more muscles) and spasms in the muscles of the legs. Next, atrophy and weakness develop in the muscles of the feet and legs, a “hollow” foot and peroneal muscular atrophy are formed, the legs resemble the limbs of a stork.”
Later, movement disorders in the upper extremities develop and increase, and difficulties arise in performing small and routine movements. Achilles reflexes are lost. The preservation of other groups of reflexes varies. Vibration, tactile, pain and muscle-joint sensitivity decreases. In some patients, neurologists determine thickening of individual peripheral nerves.
The following types of hereditary neuropathies are distinguished:
- sensory radiculopathy with disorders of the functions of peripheral nerves and spinal ganglia;
- atactic chronic polyneuropathy - Refsum's disease.
- Bassen-Kornzweig disease is a hereditary acanthocytotic polyneuropathy caused by a genetic defect in lipoprotein metabolism;
- Guillain–Barré syndrome – unites a group of acute autoimmune polyradiculoneuropathies;
- Lhermitte syndrome, or serum polyneuropathy, develops as a complication of serum administration.
Neuropathologists also diagnose other inflammatory polyneuropathies that develop from insect bites, after administration of anti-rabies serum, rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, periarteritis nodosa, as well as neuroallergic and collagenoses.
LESIONS OF INDIVIDUAL NERVES, NERVE ROOTS AND PLEXUSES (G50-G59)
G50 - G59 Lesions of individual nerves, nerve roots and plexuses G60 - G64 Polyneuropathies and other lesions of the peripheral nervous system G70 - G73 Diseases of the neuromuscular junction and muscles G80 - G83 Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes G90 - G99 Other disorders of the nervous system
The following categories are marked with an asterisk: G53 * Lesions of cranial nerves in diseases classified in other headings G55 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in diseases classified in other headings G59 * Mononeuropathy in diseases classified in other headings G63 * Polyneuropathy in diseases classified in other headings G73 * Lesions of the neuromuscular junction and muscles in diseases classified elsewhere G94 * Other brain lesions in diseases classified elsewhere G99 * Other lesions of the nervous system in diseases classified elsewhere
Excluded: current traumatic lesions of nerves, nerve roots and plexuses - see • nerve injuries by body region neuralgia } neuritis } NOS ( M79.2 ) peripheral neuritis during pregnancy ( O26.8 ) radiculitis NOS ( M54.1 )
G50 Trigeminal nerve lesions
Includes: lesions of the 5th cranial nerve
G50.0 Trigeminal neuralgia. Paroxysmal facial pain syndrome, painful tic G50.1 Atypical facial pain G50.8 Other lesions of the trigeminal nerve G50.9 Lesion of the trigeminal nerve, unspecified
G51 Lesions of the facial nerve
Includes: lesions of the 7th cranial nerve
G51.0 Bell's palsy. Facial paralysis G51.1 Inflammation of the knee ganglion Excludes: postherpetic inflammation of the knee ganglion ( B02.2 ) G51.2 Rossolimo-Melkersson syndrome. Rossolimo-Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome G51.3 Clonic hemifacial spasm G51.4 Facial myokymia G51.8 Other lesions of the facial nerve G51.9 Lesions of the facial nerve, unspecified
G52 Lesions of other cranial nerves
Excludes: disorders of: • auditory (8th) nerve ( H93.3 ) • optic (2nd) nerve ( H46 , H47.0 ) • paralytic strabismus due to nerve palsy ( H49.0 - H49.2 )
G52.0 Lesions of the olfactory nerve. Lesions of the 1st cranial nerve G52.1 Lesions of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Damage to the 9th cranial nerve. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia G52.2 Lesions of the vagus nerve. Lesions of the pneumogastric (10th) nerve G52.3 Lesions of the hypoglossal nerve. Lesion of the 12th cranial nerve G52.7 Multiple lesions of the cranial nerves. Polyneuritis of cranial nerves G52.8 Lesions of other specified cranial nerves G52.9 Lesions of the cranial nerve, unspecified
G53* Lesions of cranial nerves in diseases classified elsewhere
G53.0 * Neuralgia after herpes zoster ( B02.2 +) Postherpetic: • inflammation of the genu ganglion • trigeminal neuralgia G53.1 * Multiple lesions of the cranial nerves in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere ( A00 - B 99 +) G53.2 * Multiple lesions of cranial nerves in sarcoidosis ( D86.8 +) G53.3 * Multiple lesions of cranial nerves in neoplasms ( C00 - D48 +) G53.8 * Other lesions of cranial nerves in other diseases classified in other sections
G54 Lesions of nerve roots and plexuses
Excluded: current traumatic lesions of nerve roots and plexuses - see • nerve injury by area of the body lesions of the intervertebral discs ( M50 - M51 ) neuralgia or neuritis NOS ( M79.2 ) neuritis or radiculitis: • brachial NOS } • lumbar NOS } • lumbosacral NOS } • thoracic NOS } ( M54.1 ) radiculitis NOS } radiculopathy NOS } spondylosis ( M47 . -)
G54.0 Lesions of the brachial plexus. Infrathoracic syndrome G54.1 Lesions of the lumbosacral plexus G54.2 Lesions of the cervical roots, not classified elsewhere G54.3 Lesions of the thoracic roots, not classified elsewhere G54.4 Lesions of the lumbosacral roots, not classified elsewhere G54 .5 Neuralgic amyotrophy. Parsonage-Aldren-Turner syndrome. Brachial shingles neuritis G54.6 Phantom limb syndrome with pain G54.7 Phantom limb syndrome without pain. Phantom limb syndrome NOS G54.8 Other lesions of nerve roots and plexuses G54.9 Lesions of nerve roots and plexuses, unspecified
G55* Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in diseases classified elsewhere
G55.0 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in neoplasms ( C00 - D48 +) G55.1 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in disorders of the intervertebral discs ( M50 - M51 +) G55.2 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in spondylosis ( M47 . -+) G55.3 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in other dorsopathies ( M45 - M46 +, M48 . -+, M53 - M54 +) G55.8 * Compression of nerve roots and plexuses in other diseases classified elsewhere rubrics
G56 Mononeuropathies of the upper limb
Excludes: current traumatic nerve injury - see • nerve injury by body region
G56.0 Carpal tunnel syndrome G56.1 Other lesions of the median nerve G56.2 Damage to the ulnar nerve. Late ulnar nerve palsy G56.3 Damage to the radial nerve G56.4 Causalgia G56.8 Other mononeuropathies of the upper limb. Interdigital neuroma of the upper limb G56.9 Mononeuropathy of the upper limb, unspecified
G57 Mononeuropathies of the lower limb
Excluded: current traumatic nerve damage - see • nerve injury by body region G57.0 Sciatic nerve damage Excluded: sciatica: • NOS ( M54.3 ) • associated with intervertebral disc damage ( M51.1 ) G57.1 Meralgia paresthetica. Syndrome of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh G57.2 Damage to the femoral nerve G57.3 Damage to the lateral popliteal nerve. Peroneal (peroneal) nerve palsy G57.4 Damage to the median popliteal nerve G57.5 Tarsal tunnel syndrome G57.6 Damage to the plantar nerve. Morton's metatarsalgia G57.8 Other mononeuralgias of the lower limb. Interdigital neuroma of the lower extremity G57.9 Mononeuropathy of the lower extremity, unspecified
G58 Other mononeuropathies
G58.0 Intercostal neuropathy G58.7 Multiple mononeuritis G58.8 Other specified types of mononeuropathy G58.9 Mononeuropathy, unspecified
G59* Mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere
G59.0 * Diabetic mononeuropathy ( E10 - E14 + with common fourth sign .4) G59.8 * Other mononeuropathies in diseases classified elsewhere
Drug-induced polyneuropathy (ICD code G.62.0)
Drug-induced polyneuropathy occurs as a result of metabolic disorders in myelin and feeding vessels as a result of taking various medications: antibacterial drugs (tetracycline, streptomycin, kanamycin, viomycin, dihydrostreptolysin, penicillin), chloramphenicol, isoniazid, hydralazine. Antibacterial polyneuropathies with symptoms of sensory neuropathy, night pain in the limbs and paresthesias, vegetative-trophic dysfunctions are detected not only in patients, but also in workers of factories that produce these medications.
At the initial stage of development of isoniazid polyneuropathy, patients are bothered by numbness of the fingers, then a burning sensation and a feeling of tightness appear in the muscles. In advanced cases of the disease, ataxia joins sensory disorders. Polyneuropathies are detected when taking contraceptives, antidiabetic and sulfa drugs, phenytoin, drugs of the cytotoxic group, and the furadonin series.
Diagnostics
Neurologists make a diagnosis of polyneuropathy based on:
- analysis of complaints and how long ago symptoms appeared;
- clarification of possible causative factors;
- establishing the presence of diseases of internal organs;
- establishing the presence of similar symptoms in close relatives;
- identifying signs of neurological pathology during a neurological examination.
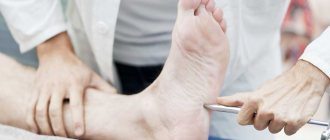
An obligatory component of the diagnostic program is an examination of the lower extremities in order to identify autonomic failure:
- thinning of the skin of the legs;
- dryness;
- hyperkeratosis;
- osteoarthropathy;
- trophic ulcers.
During a neurological examination, if the nature of the polyneuropathy is unclear, doctors palpate the available nerve trunks.
To clarify the cause of the disease and changes in the patient’s body, the Yusupov Hospital determines the levels of glucose, glycated hemoglobin, protein metabolic products (urea, creatinine), perform liver tests, rheumatic tests, and toxicological screening. Electroneuromyography allows one to evaluate the speed of impulse transmission along nerve fibers and determine signs of nerve damage. In some cases, a nerve biopsy is performed for examination under a microscope.
If there are indications, instrumental methods for studying the somatic status are used: radiography, ultrasound. Cardiointervalography allows identifying violations of autonomic function. A study of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out if demyelinating polyneuropathy is suspected, and when searching for infectious agents or an oncological process.
Vibration sensitivity is examined using a biotensiometer or a graduated tuning fork with a frequency of 128 Hz. The study of tactile sensitivity is carried out using hair monofilaments weighing 10 g. Determination of the threshold of pain and temperature sensitivity is carried out using a needle prick and a Tip-therma thermal tip in the skin of the dorsal surface of the big toe, dorsum of the foot, medial surface of the ankle and lower leg.
Basic principles of therapy
In case of acute polyneuropathy, patients are hospitalized in a neurology clinic, where the necessary conditions for their treatment have been created. For subacute and chronic forms, long-term outpatient treatment is carried out. Prescribe drugs to treat the underlying disease, eliminate the causative factor in case of intoxication and drug-induced polyneuropathies. In case of demyelination and axonopathy, preference is given to vitamin therapy, antioxidants and vasoactive drugs.
Rehabilitation specialists provide hardware and non-hardware physiotherapy using modern techniques. Patients are advised to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, heavy physical activity, and contact with chemical and industrial poisons. If you have signs of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, you can consult a neurologist by making an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
CEREBRAL PALSY AND OTHER PARALYTIC SYNDROMES (G80-G83)
G80 Cerebral palsy
Included: Little's disease Excluded: hereditary spastic paraplegia ( G11.4 )
G80.0 Spastic cerebral palsy. Congenital spastic palsy (cerebral) G80.1 Spastic diplegia G80.2 Infantile hemiplegia G80.3 Dyskinetic cerebral palsy. Athetoid cerebral palsy G80.4 Ataxic cerebral palsy G80.8 Another type of cerebral palsy. Mixed syndromes of cerebral palsy G80.9 Cerebral palsy, unspecified. Cerebral palsy NOS
G81 Hemiplegia
Note • For initial coding, this category should be used only when hemiplegia (complete) (incomplete) is reported without further specification or is stated to be established for a long time or has existed for a long time, but its cause is not specified • This category is also used for coding for multiple reasons to identify types of hemiplegia due to any cause. Excludes: congenital and cerebral palsy ( G80.- ) G81.0 Flaccid hemiplegia G81.1 Spastic hemiplegia G81.9 Hemiplegia, unspecified
G82 Paraplegia and tetraplegia
Note • For primary coding, this category should be used only when the listed conditions are reported without further clarification or it is stated that they have been established for a long time or have existed for a long time, but their cause is not specified • This category is also used when coding for multiple reasons for identifying these conditions due to any cause. Excludes: congenital or cerebral palsy ( G80.- )
G82.0 Flaccid paraplegia G82.1 Spastic paraplegia G82.2 Paraplegia, unspecified. Paralysis of both lower limbs NOS. Paraplegia (lower) NOS G82.3 Flaccid tetraplegia G82.4 Spastic tetraplegia G82.5 Tetraplegia, unspecified. Quadriplegia NOS
G83 Other paralytic syndromes
Note • For primary coding, this category should be used only when the listed conditions are reported without further clarification or it is stated that they have been established for a long time or have existed for a long time, but their cause is not specified • This category is also used when coding for multiple reasons for identifying these conditions due to any cause. Includes: paralysis (complete) (incomplete), except as specified in sections G80 - G82
G83.0 Diplegia of the upper limbs. Diplegia (upper). Paralysis of both upper limbs G83.1 Monoplegia of the lower limb. Paralysis of the lower limb G83.2 Monoplegia of the upper limb. Paralysis of the upper limb G83.3 Monoplegia, unspecified G83.4 Cauda equina syndrome. Neurogenic bladder associated with cauda equina syndrome Excludes: spinal bladder NOS ( G95.8 ) G83.8 Other specified paralytic syndromes. Todd's palsy (post-epileptic) G83.9 Paralytic syndrome, unspecified