Diagnosing a stage 4 malignant neoplasm in a patient raises the most important question: how much time is left. Such glioblastoma cannot be treated, and at the same time, doctors face the main therapeutic task: to increase the patient’s life expectancy and the symptomatic maintenance of his body. Yes, the last stage of cancer can be considered a death sentence, but you shouldn’t give up right away. You have to fight for life, and the main weapon in this fight is knowledge.
General information
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive and most common malignant brain pathology.
This is a very dangerous disease. From the moment the patient first develops symptoms of the disease, if untreated, the person lives for about three months. By providing complex treatment (surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy ), the life of such a patient can be extended by 1-2 years. Currently, scientists are actively working to more accurately determine brain glioma - what it is, and what are the causes of this terrible disease.
So far, experts believe that the tumor develops due to malfunctions in the functioning of brain cells. This pathology is quite rare. According to statistics, per 100 thousand patients with oncological pathologies, glioblastoma is diagnosed in only one case.
What does survival depend on?
Survival for glioblastoma depends on factors such as:
- age. Children with glioblastoma live longer than adults and older adults. About 25% of young patients live 5 years or more with supportive care;
- timely detection of pathology. If the malignant process was detected at the astrocytoma stage, the chances of a favorable outcome remain;
- sensitivity of cancer cells to radiation treatment and chemotherapy. If these measures produce results, then the pathology enters the remission stage and life expectancy increases;
- localization of the tumor. Glioblastoma often develops in areas where surgery is not very convenient or poses a risk of additional complications. Tumors in the cerebellar area are much easier to remove without consequences than tumors in the brain stem. The brain stem is the most unfavorable place for tumor development, since it houses the vasomotor and respiratory centers. This makes it difficult to perform surgery in this area;
- general condition of the patient – presence of additional diseases, state of immunity;
- the patient’s lifestyle and bad habits;
- state of the environment;
- the rate of tumor growth and the disorders that it provokes.
Pathogenesis
Gliomas are any malignant brain tumors that form glial cells . When malignant transformation occurs, glial cells, namely astrocytes , become less differentiated, losing the characteristics of functional mature cells. In addition, their connection with neighboring cells is lost, and division becomes uncontrolled.
Thus, glioblastoma consists of poorly differentiated astrocytes, it has foci of necrosis and areas of vascular proliferation. A characteristic feature of this formation is a random arrangement of cells, polymorphism of cell nuclei and extensive perifocal edema. The tumor grows rapidly and invades the brain tissue. It is impossible to trace clear boundaries of the affected area. The neoplasm does not metastasize beyond the nervous system.
It is most often found in the frontal and temporal lobes. Very rarely, a tumor forms in the brain stem, spinal cord, or cerebellum.
In some cases, glioblastoma develops from anaplastic and low-grade astrocytomas, but most often this lesion is primary.
The tumor spreads to neuroglial cells, whose functions are related to the nutrition and protection of neurons. These cells do not reproduce in adulthood, but there are precursors of glial cells in the brain. If disturbances occur in their development, glioblastoma may develop.
A characteristic feature of glioblastoma, which determines its aggressive course, is its heterogeneity. The nature of the neoplasm differs in different patients. Moreover, even in one patient, the tumor can contain different cells that are not genetically similar, with different mutations. During the treatment process, cells mutate, actively evolve and develop new methods of survival.
Characteristic signs of glioblastoma
During the research, scientists noted that a significantly lower risk of developing glioma – by 40% – is observed in people suffering from various types of allergies .
Experts explain this by the fact that in such people the immune system is in an activated state and prevents tumor growth.
What are the features of the course of glioblastoma?
Glioblastoma is a type of malignant neoplasm that affects neuroglia (brain tissue). Oncology has a particularly aggressive and rapid course.
Neuroglia is the main tissue of the medulla. It is based on intercellular substance and glial cells, the number of which is almost 50 times greater than the number of brain neurons. About 40% of the total mass of the brain matter is accounted for by neuroglia.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
The tumor begins to develop from astrocytes - small, star-shaped neuroglial cells. It is formed both primarily and as a result of malignancy of a benign tumor. The favorite location of glioblastoma is the hemispheres and subcortical structures of the brain. Characteristic is infiltrative growth and transition from one hemisphere to another through ingrowth into the corpus callosum.
The main cause of the development of the disease is currently unknown, but, based on observations, it was possible to identify certain risk groups. These include:
- people whose age ranges from 40 to 70 years;
- men;
- people who have been exposed to radiation or carcinogens;
- persons who abuse alcohol or tobacco;
- neurofibromatosis;
- genetic abnormalities.
There is a connection between tumor formation, frequent viral diseases and traumatic brain injuries.
Classification
The following types of tumors are identified:
- Multiform . Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common and most dangerous type of tumor. The lesion is well supplied with blood, and vascular necrosis develops very quickly.
- Giant cell . This variety is different in that the cells have not one nucleus, but several.
- Gliosarcoma . This is a tumor with a sarcomatous component.
It is important to conduct an accurate diagnosis and clearly determine the type of formation. This will make it possible to choose the most optimal treatment.
Primary and secondary types of the disease are also distinguished.
- Primary – develops very quickly, over about three months. This type is more common in older men.
- Secondary - is the result of the degeneration of benign formations. This type of disease most often develops in women after 45 years of age.
There are other, less aggressive types of brain tumors.
Four degrees of the disease are determined:
- The first is that there are no signs of malignancy, but the tumor covers new cells. There is a possibility of recovery.
- Secondly, there are already signs of glioma, the tumor is still growing quite slowly. The chances of recovery are reduced.
- Third, brain tissue is involved in the process, the tumor grows quickly and is malignant. Complete recovery occurs in rare cases.
- Fourth, the tumor grows very quickly, the symptoms are very severe. The tumor is inoperable, the prognosis is unfavorable.
The main stages of manifestation of glioblastoma
Oligodendroglioma is a glial neoplasm of the brain that develops from oligodendrocytes. This tumor grows slowly but can grow to a large size. It forms along the walls of the ventricles, grows into their cavity, as well as into the cortex. The disease lasts a long time, sometimes longer than five years. The tumor is removed surgically.
A variety of such neoplasms are:
- oligodendroglioma (has a second degree of malignancy);
- anaplastic oligodendroglioma (has a third degree of malignancy);
- mixed oligoastrocytoma (has a third degree of malignancy), later degenerates into glioblastoma .
Another type of glial tumor is optic nerve glioma .
This neoplasm develops from the glial elements of the optic nerve. It is treated with radiation or surgery.
Which treatment method will lead to recovery?
The standard treatment regimen includes neurosurgery followed by radiation and chemotherapy. Therapeutic approaches vary depending on the situation. For example, sometimes it is difficult for a patient to tolerate chemotherapy due to the side effects of the drugs, or the location of the tumor makes surgery impractical. Therefore, an individual, most favorable option for the patient is selected.
Glioblastoma grows inside the skull and does not spread beyond it. Therefore, surgical treatment in all cases involves the work of an experienced neurosurgeon. The intervention is carried out using fluorescent contrast (5-aminolevulinic acid), which accumulates in cancer cells, makes them visible and allows them to be completely removed surgically. During cancer surgery, surgeons remove a small portion of healthy tissue around the cancer. This increases the chances of a full recovery and no relapse. In the case of brain tumors, such an approach, unfortunately, is impossible, since every millimeter of tissue is important for the patient’s normal life in the future. Therefore, modern neurosurgery attaches particular importance to gentle operations - identifying cancer cells and preserving healthy cerebral tissue.
Radiation therapy helps control the proliferation of cancer cells after surgery. The course of dosed radiation lasts up to one and a half months, with radiation therapy sessions carried out 5 days a week. In some cases, radiation therapy is prescribed as the main method, for example, for inoperable tumors larger than 30 mm.
CyberKnife and Gamma Knife techniques occupy an intermediate position between surgery and radiotherapy. Essentially, these techniques are based on irradiating malignant cells with a high dose of ionizing radiation. In this case, radiologists preliminarily determine the location of the oncological formation using a stereotactic frame - a three-dimensional coordinate system. This technique ensures “surgical precision” of irradiation, when the cells of the pathological focus receive maximum radiation exposure, while healthy tissue remains safe. The robot, which controls the source of ionizing radiation during the procedure, directs the beam with an accuracy of tenths of a millimeter. Today, the Gamma Knife technique is considered the “gold standard” in the treatment of glioblastoma.
Chemotherapy is used after surgery if there is a risk of relapse or incomplete removal of the tumor (more than 90% of the volume). Patients receive chemotherapy in oral or injectable form. Another effective option is to implant plates with a chemotherapy drug into the brain, next to the main mass of neoplasm. The drug is released gradually over several weeks. At the same time, a high local dosage of the chemical destroys cancer cells.
In addition to the main methods, new developments are used - immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Symptomatic treatment (painkillers and anticonvulsants, drugs against cerebral edema) is mandatory, the goal of which is to improve the general condition. A psychologist also works with the patient to help overcome fears and look into the future with confidence and a positive attitude.
Causes
Experts still do not know why glioblastoma develops. The likelihood of developing this disease increases with radiation exposure and congenital mutations. However, scientists have not yet determined a clear dependence on these factors. It is noted that the disease is not inherited, and its development is not associated with smoking, exposure to electromagnetic radiation, or poor nutrition - this has been confirmed in the process of scientific research.
However, risk factors that to varying degrees provoke the development of a tumor are:
- age over 50 years;
- male gender;
- nationality – residents of Asia, Europe, Latin America;
- the presence of genetic pathologies that increase the likelihood of developing gliomas - Turcotte syndrome , tuberous sclerosis , neurofibromatosis , etc.;
- undergoing radiotherapy;
- benign astrocytoma .
There is also an opinion that the development of this disease is increased by certain viruses: human herpes cytomegalovirus , polyomavirus .
Symptoms of glioblastoma
At the initial stage of the disease, there are practically no symptoms, so it is difficult to diagnose it in the early period. Pronounced signs are observed when the tumor has already grown significantly and puts pressure on the brain. The first manifestations of glioblastoma are common dizziness and memory impairment. In some cases, the fingertips become permanently numb.
As the disease progresses, cerebral and neurological manifestations develop.
The development of cerebral symptoms is associated with increased intracranial pressure and progression of intoxication. These are the following manifestations:
- Severe headaches that become more intense when the person lies down.
- Constant feeling of dizziness.
- Nausea that has nothing to do with eating; vomiting, after which there is no relief.
- Constant weakness, drowsiness, severe fatigue.
- Deterioration of mental abilities, lethargy.
- Depression , apathy , irritability.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. The following signs may be observed:
- Cramps.
- Impaired vision, hearing, speech, smell.
- Decreased sensitivity or paralysis of the limbs.
- Auditory and tactile hallucinations
- Movement coordination disorder.
- Respiratory depression.
Since neurological symptoms are similar to those of a stroke , this may be the reason for an incorrect diagnosis.
Unfortunately, in the later stages, when these symptoms appear, it is no longer possible to cure the patient. Doctors can only prolong his life.
Symptoms of oligodendroglioma also depend on its location. In all types of oligodendroglioma, intracranial pressure increases. Other symptoms similar to the manifestations of glioblastoma described above also develop.
Treatment options for stage 4 glioblastoma in medical
Treatment of cancer pathology in the last stage is one of the specializations of medicine (Türkiye).
The long-term cooperation of the Medical Center with the Johns Hopkins Clinic in the USA helps to provide patients with the most modern treatment at the level of world standards.
The Center employs world-famous doctors who provide highly accurate diagnostics and treatment using the most modern methods and technologies.
At the same time, the cost of medical care at Anadolu is approximately 20% lower compared to clinics in the USA and Israel, while treatment and examination are carried out at the same advanced level.
The medical institution has an International Department that helps foreign patients organize and undergo treatment, as well as stay in touch with doctors upon returning home. The clinic organizes free transfer from the airport, helps book a hotel, provides a personal coordinator and translator during treatment.
The center has representative offices in the main regions of Russia and the CIS countries. Order a call back , send a request for treatment and prices , or call us (toll-free within the Russian Federation): 8 .
The material was prepared in agreement with the doctors of the Anadolu Clinic, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Serdar Kahraman and Professor Hale Basak Chalar.
Tests and diagnostics
Development can be detected in the early stages if a person regularly attends preventive examinations and examinations. In this case, you can take timely measures at the first sign of a threat. It is very important to visit a neurologist and neurologist who can identify the disease.
If there is a suspicion of glioblastoma, a medical history, examination, and laboratory tests are performed.
Next, the doctor prescribes appropriate examinations. The patient may be prescribed the following examinations:
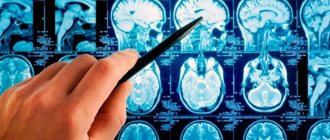
- computed tomography - makes it possible to obtain a high-quality image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- magnetic resonance imaging – using an intense magnetic field, you can obtain a clear image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- functional MRI – allows you to obtain broader information about the tumor, blood flow, tissues;
- biopsy - in the process of selecting material, taking biomaterial;
- MR spectroscopy – allows you to obtain information about metabolism in the brain;
- lumbar puncture - a sample of cerebrospinal fluid is taken;
- PET, SPECT - these studies make it possible to determine the functional activity of brain tissue;
- electroencephalography – carried out to study brain activity.
How to detect glioblastoma?
If a brain tumor is suspected, the doctor, usually a general practitioner, refers the patient to a neurologist and neurosurgeon . After assessing the neurological status, doctors move on to instrumental diagnostic methods. Technical advances in modern medicine make it possible to see the brain in great detail and evaluate its functions.
Imaging studies ( MRI, CT, PET, SPECT ) show the doctor the structural features of the brain and the presence or absence of tumors here. Additionally, you can assess the condition of the skull bones and, if necessary, prepare for radiosurgical techniques - determine the location of the tumor according to the stereotactic coordinates frame. Such a frame is placed on the patient’s head before the examination and provides clear guidelines for the localization of the pathological focus in the cerebral tissue. Angiography plays a special role among imaging studies . Angiography “highlights” the blood vessels of the brain and tumors in the image. This allows you to avoid massive blood loss during surgery.
Functional studies include:
- Functional MRI, which determines the type of blood flow inside the neoplasm
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy, which determines metabolic activity in brain tissue
- Electroencephalography (EEG), which records the electrical activity of the brain and reflects the tendency to have seizures
Biopsy is considered the “gold standard” in diagnosing all types of cancer. Only a biopsy makes it possible to examine the neoplasm tissue under a microscope and accurately determine its nature. With glioblastoma, the suspicious tissue is always located inside the skull, so a biopsy involves neurosurgical intervention.
After conducting the necessary studies and comprehensive assessment of the results, a multidisciplinary team of doctors draws up an individual treatment plan.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the case of glioblastoma, traditional methods can only be additional treatments aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms. If you replace the traditional treatment regimen with folk remedies, a quick death is inevitable.
- Radish compress – grate the radish and add salt. When the juice begins to stand out, rub the mixture on your head and wrap it with a towel. The course lasts three weeks.
- Soda solution - dissolve 3 g of soda in 100 g of water and drink this solution. Gradually increase the amount of soda to 5 g.
- Chamomile tea - it is prepared from dried chamomile flowers (15 g of raw material per glass of boiling water). Drink instead of tea.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention is regular attendance at preventive examinations, which make it possible to identify problems at an early stage. It is especially important to undergo annual examinations for people over 45 years of age, because with age the likelihood of this dangerous disease increases.
To reduce the risk of developing this disease, you must follow the recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle:
- Get a full night's rest - healthy sleep and its sufficient duration are important.
- Spend time outdoors – you need to walk as much as possible every day.
- Avoid stress and emotional turmoil.
- Give up bad habits - do not smoke, do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Do not abuse spending time with various gadgets.
- Eat right - lots of vegetables, fruits and grains, be sure to have legumes, high-quality proteins, and unsaturated fats. Harmful foods - fast food, smoked meats, soda, confectionery, etc. - must be excluded.
Diet for glioblastoma
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
With this disease, the patient needs to eat more fat and less carbohydrates. This diet is called a ketogenic diet. Its essence is that the tumor receives less energy for its growth. People are allowed to consume more protein and fatty foods than on a regular diet.
But for now, scientists are studying the mechanism of action of such a diet in malignant brain tumors.
At the same time, it is important to consume foods that will help cleanse the body, strengthen the immune system , improve blood counts and give the body additional strength.
But in general, the following nutritional rules are relevant for oncology:
- Do not make too drastic changes in your usual diet.
- Make adjustments to your diet gradually.
- Monitor how the body reacts to certain foods.
- Do not eat food that you absolutely do not like.
- Do not practice low-calorie diets.
- Try to eat food that does not contain artificial additives and preservatives.
- Be sure to include vegetables, fruits, dairy, legumes, vegetable fats, grains, seafood, green tea, and nuts in your diet.
But in general, it is important that the diet is healthy and does not contain harmful foods and dishes.
Forecast
Survival and life expectancy in this disease directly depend on the type of glioblastoma, its location, and the general condition of the patient.
If proper treatment is not given, only about 10% of people survive more than three months after diagnosis.
With the most aggressive form of the disease - glioblastoma multiforme - even with a competent approach to therapy, a person rarely lives more than one year. However, the likelihood of a favorable prognosis largely depends on the completeness of tumor resection and on some tumor biomarkers.
Complete recovery, provided proper treatment, is possible only with grade 1 or 2 glioblastoma. Treatment will require a very large number of different procedures, and the likelihood of relapse with a fatal outcome will remain.
Glioblastoma grade 4 is most often inoperable. To increase life expectancy, doctors prescribe drug therapy and special procedures. Patients with this pathology are most frightened by the question of how they die from glioblastoma of the brain. Having learned about the diagnosis, a person is frightened by the thought of dying from this malignant disease in severe pain. In such a situation, doctors prescribe painkillers and other medications to alleviate the person’s condition.
Where is the best place to treat glioblastoma?
There is no denying that glioblastoma is a serious disease that requires expert knowledge and skills from the medical team. The technical side is no less important - the possibility of using neuronavigation, stereotactic techniques and radiosurgery. The availability of modern chemotherapy drugs and targeted therapy is also important. Only in this case can the goal of treatment be achieved - to increase life expectancy and improve its quality.
Nowadays, the possibilities of medicine are not limited to the borders of the patient’s home country. This is important because health systems in developing countries often fail to offer patients the level of care they need. If we are talking about an integrated approach to the treatment of glioblastoma, decent technical equipment of clinics, effective neurological rehabilitation and reasonable cost of therapy, then the best option is treatment in Germany.
The experience of German neurosurgeons is beyond doubt - specialists participate in advanced training of colleagues from other countries, develop new techniques and demonstrate the best success rates of operations. The German pharmaceutical market offers chemotherapy drugs and targeted therapies that have only recently passed the stage of clinical trials. Most importantly, the latest Gamma Knife models are available in Germany, the use of which allows you to avoid invasive surgery. Thus, specialists from the Gamma Knife and Radiation Therapy Center Krefeld and the Gamma Knife and Radiation Therapy Center Hanover annually accept thousands of patients with glioblastoma for radiosurgical treatment.
Naturally, the provision of medical services to international patients differs from medical care to German citizens. Therefore, international patients come here with the assistance of a certified medical tourism operator - Booking Health. The company’s specialists annually help hundreds of patients with glioblastoma receive timely treatment from experienced international specialists. The company's work meets the high requirements of the international quality control certificate ISO 9001:2015.
In order to start preparing for your trip, you need to submit an application with medical documents on the official Booking Health website. After reviewing your application, you will be contacted by a patient manager who will help you with such important points as:
- Issuing an invitation for treatment to quickly obtain a medical visa
- Make an appointment at a time convenient for you
- Preliminary organization of a comprehensive examination and discussion of the upcoming treatment plan
- Transfer from the airport to the clinic and back to the airport
- Translator and personal medical coordinator services
- If necessary, assistance in organizing further surgical treatment
- Providing health insurance against complications with a coverage amount of 200,000 euros
- Preparation and translation of medical statements and recommendations from the clinic
- Assistance in subsequent communication with your attending physician, including consultations on repeated examinations through the unique E-doc medical document management portal
The company’s specialists take an active part in the life of each patient, support and instill faith in recovery. We rejoice at your successes together with you and help you maintain your health for many years. Send us your request!
List of sources
- A.P. Romodanov, N.M. Mosiychuk. Neurosurgery. - Kyiv: Vyshcha School, 1990. - P. 16. - 105 p.
- Zemskaya A.G. Glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. - L: Medicine, 1976.-S. 192.
- Pishel Y.V. Glioblastomas of the brain. (Pathomorphology, clinical picture, diagnostics, comparative assessment of treatment methods): Abstract of thesis. dis. . Dr. med. Sci. - Kharkov, 1971. P. 32.
- Savchenko A.Yu. Brain gliomas. Omsk: Publishing house. Omsk State Pedagogical University, 1997. - P. 312.
- Fadeev B.P., Zhabina PM Combined treatment of glial and metastatic brain tumors // Bulletin of Surgery named after. I.I. Grenova. - 2005. - No. 1. — P. 80-82.
Diagnostic measures
The main method for diagnosing glioblastoma is brain MRI. Experts also use stereotactic tissue biopsy to determine the degree of malignancy of the process and select effective treatment tactics. It is possible to prescribe magnetic resonance spectroscopy and positron emission tomography. MR spectroscopy opens up wide opportunities for the neurosurgeon, making it possible to create preoperative models of the patient’s brain in 3D format, think through each stage of the future operation, assess the condition of healthy tissues and the characteristics of their contact with the pathological focus. To obtain additional information about the patient’s health status, laboratory tests of blood and urine are performed. It is possible to schedule a consultation with specialized specialists, especially in the presence of concomitant internal diseases.