The main methods for diagnosing epilepsy are magnetic resonance imaging and electroencephalogram. The article will talk about EEG of the brain: what it is, decoding in children.
An encephalogram is a method for studying the bioelectrical activity of the brain. This study allows us to determine the activity of neurons in various parts of the brain, the presence of pathological patterns (discharges) that indicate pathology. The harmlessness of the diagnosis allows it to be widely used in childhood. Based on the results of the study, epileptiform activity, indications for MRI and the direction of further treatment are determined.
Epileptiform activity on the EEG in a child - what does it mean? The term epileptiform activity refers to electrical oscillations recorded on the EEG in the form of sharp waves and peaks that differ from the general activity by more than 50%. The presence of epileptiform activity on the EEG may indicate the presence of epilepsy.
Causes of cortical dysarthria in children
The defect develops as a result of damage to those areas of the cerebral cortex that regulate the tone and contractions of the muscles of the cheek, pharynx, jaw, soft palate, lips and tongue.
The cause of the disorder may be:
- perinatal pathology is the main cause of brain damage in childhood. Hypoxia, intrauterine infection, and asphyxia of the newborn are important. The likelihood of these conditions is increased by a complicated obstetric history, oligohydramnios, gestosis, and rapid labor;
- traumatic brain injuries - in children, birth injuries play an important role, which occur due to inadequately chosen labor management tactics. Injuries at an early age are dangerous due to falls and impacts. Brain damage in older children and adolescents can also cause speech disorders;
- space-occupying formations lead to compression of the cerebral cortex, sometimes to germination and destruction, that is, destruction;
- neuroinfections - consequences of ARVI, rubella, herpes, measles, sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis, abscess, syphilis, tuberculosis.
The mechanism of development of the cortical form of dysarthria is associated with damage to the anterior central gyrus or the area behind it. In the first case, central paresis of the articulatory muscles develops. In the second, the processing of information about the state of the organs of articulation is disrupted, which is why there is no correction of the movements of the muscles involved in speech. This is how apraxia occurs - a failure in the sequence of muscle contractions.
BRT in the complex treatment of children with activity and attention disorder (ADHD)
25.12.2018 14:33 Author: Reflexologist Mamatova Vera Aleksandrovna
Relevance of the problem.
Currently attention disorder with hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (ICD-10)
is one of the most important problems in pediatric neurology. The widespread prevalence of the disease, which accounts for 5-10% of the child population, high comorbidity with various childhood disorders, and the increasing incidence of this pathology attracts the attention of a wide range of specialists to develop new and adequate treatment methods aimed at increasing the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures.
Considering the presence of various specialists in our Center involved in the rehabilitation process, the equipment with which it is possible to diagnose and treat patients, repeated rehabilitation courses that make it possible to qualitatively monitor the dynamics in the treatment of children - all this together is a good basis for searching and experimenting with new methods in treatment of children with ADHD.
Etiological factors of ADHD.
1. Perinatal factors
This is a polymorphic syndrome. The occurrence of ADHD is due to the immaturity of the developing organism, and in particular the central nervous system (CNS), which is most sensitive to harmful influences. Brain damage in the early stages of development may be preceded by disorders, the main of which are: prematurity, morphofunctional immaturity, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, underweight of the child, premature birth, physical and emotional trauma to the mother during pregnancy and childbirth.
2.Genetic factors
There has been a high incidence of ADHD symptoms in childhood among parents of children suffering from this disease. Hyperactivity is an innate characteristic along with temperamental characteristics.
3. Socio-psychological factors
Along with the immaturity of the central nervous system (CNS), there are socio-psychological factors leading to ADHD, for example, insufficient education of parents, single-parent families, deformation of maternal care, alcoholism, drug addiction, depression.
4.Nutritional factors
Of particular interest is the influence of dietary factors and unbalanced nutrition on the manifestations of ADHD symptoms. Deficiencies of magnesium, zinc, iodine, and iron contribute to the onset or intensification of ADHD symptoms.
Diagnosis of ADHD
Diagnosis is based on international criteria, which include lists of the most characteristic and clearly visible signs of this disorder.
1. Occur before 8 years of age
2. Identified in two or more areas of activity (at school, at home, at work, in games)
3. Not caused by psychotic, anxiety, affective disorders
4. Cause significant psychological discomfort and maladjustment
5. The presence of inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity that do not correspond to age norms
6. Disorder of school skills (writing, counting, reading)
7. The disorder is more common in boys.
The relative prevalence among boys and girls is from 3:1 to 9:1.
In 30-70% of cases, the disorder syndromes progress into adulthood, and the risk of developing antisocial psychopathy, alcoholism and drug addiction is high.
The first signs of ADHD appear already in the newborn period with disturbances in the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness, increased excitability, and general restlessness. At the age of 3 years, when the active development of speech, memory and attention occurs, a lag in neuropsychic development appears. Disobedience and stubbornness appear in the character of children with ADHD. By the age of 5, clinical polymorphism of the structure of the syndrome develops. The main manifestations of ADHD syndrome are a violation of the child’s ability to control his behavior, increased distractibility, instability of attention, impulsiveness and hyperactivity. With a normal level of intellectual development, cognitive impairment, anxiety disorders, fears, fatigue, and movement disorders such as tic hyperkinesis are added. Enuresis and encopresis are often observed. At the age of 6-9 years, it manifests itself as low self-esteem, hot temper, and aggressiveness. All this significantly affects the processes of learning and adaptation of the child in the team.
Goal of the work.
To determine the effectiveness of exogenous BRT for the treatment of children with ADHD.
The main idea of using resonance in medicine is that with the correct selection of the frequency of the therapeutic effect, it is possible to enhance physiological or weaken pathological fluctuations in a biological system.
In the exogenous BRT method, treatment is carried out by exposure to one or a set of specific frequencies, the values of which are selected experimentally and tested in laboratory and clinical conditions. Exogenous BRT predominantly uses alternating or pulsed magnetic fields
BRT, unlike most known methods of physiotherapy, is not associated with tissue heating, which allows us to classify this method as “low-intensity therapeutic factors.”
The patient can be exposed to electric current (contact) using metal electrodes or a magnetic field (non-contact) using inductors, loops, belts.
The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of exogenous BRT is due to the introduction of an external signal of an electrical or electromagnetic nature into the body, which causes a response in it. In this case, the frequency of the external signal causes a response in the body if the external signal has a tendency to interact with a large number of rhythmic processes, i.e. to synchronization.
The frequency of the external signal (synchronizing) affects the frequency of the body (synchronizing), encoding and transfer of information are carried out, which contributes to the formation of a therapeutic effect.
Methods and equipment:
In the treatment of this group of patients, we used the therapeutic capabilities of the equipment: “MINI-EXPRESS-DT” with software. Method of vegetative resonance testing (VRT).
Own research.
215 preschool and school-age children with ADHD syndrome were observed and treated.
Of these, 56 girls (26%), 159 boys (74%),
children from 3 to 7 years old girls 51 boys 144
over 7 years old 20 children girls 5, boys 15
All children had a complicated history of intrauterine development and were observed with a diagnosis of perinatal encephalopathy in the first year of life. At the time of admission to rehabilitation, in most cases, these are the consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in the form of hyperexcitability syndromes, impaired activity and attention, hyperkinetic syndrome, vegetative-vascular dystonia, intracranial hypertension syndrome, enuresis, encopresis.
In addition to consulting a neurologist, all children underwent a comprehensive examination, which included:
1. Electroencephalography (EEG)
2. Diagnostics using the vegetative resonance test “IMEDIS” method
3. Psychological research aimed at assessing intelligence and the emotional-volitional sphere
4. Speech therapy examination in children with speech development disorders
5. Psychiatrist
6. Audiologist
At the time of treatment, all children received drug treatment in the form of nootropic and sedative therapy, attended speech therapy classes, group or individual sessions with a psychologist.
In the neurological status, 191 children (89%) had scattered focal microsymptoms; revitalization of tendon reflexes with expansion of reflexogenic zones, hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet, coldness of the hands and feet, “marbling” of the skin. In 13 (6%) boys, tic hyperkinesis was observed such as blinking, twitching of shoulders, and coughing. Speech impairment was detected in 157 (73%) children in the form of general speech underdevelopment and dysarthria. 23 (11%) children suffered from enuresis, 3 of them had encopresis.
During psychological testing, significant conflict experiences and disturbances in the emotional-volitional sphere, disturbances in the cognitive sphere, difficulties in acquiring educational skills, memory disorders, weakness of thought processes with a normal level of intelligence development, and impaired relationships with peers and adults were revealed.
All children were tested using the IMEDIS-TEST ART method.
In 87% of cases, psychovegetative stress of grades III-IV, mental stress of grade II-III-IV was tested in children; in 27 (13%) children, mental stress of grade 6-8 was tested. Mental stress or psychovegetative stress is the result of prolonged exposure to a psychotraumatic factor on the child’s body, leading to the occurrence of pathological disorders in various organs and systems.
In 81% of cases, tension of the autonomic nervous system was tested, which is confirmed by a burdened perinatal history.
More than half of the children (76%) showed indications of grade I-IV tension. or depletion of the I-III immune and endocrine systems, and such children had a history of various somatic disorders: allergic reactions, biliary dyskinesia, chronic tonsillitis, bronchial asthma, eczema, etc.
All children underwent a diagnostic electroencephalographic study with visual assessment of EEG and spectral analysis before or at the beginning of BRT treatment and after treatment, after 3-4 months.
The electroencephalogram was recorded using a 19-channel electroencephalograph Neuron-Spectrum-3.
Ten five-second EEG segments were analyzed, where average values for frequency, amplitude and index were calculated for each of the main rhythms.
In 15% of cases, no deviations from the norm were detected.
In 85% of cases, the dynamics took into account changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain in the background recording, during photostimulation and hyperventilation, and when opening and closing the eyes.
As a result of the analysis of the EEG before treatment, a predominance of the beta rhythm was revealed in the fronto-central and temporal leads, the alpha rhythm was represented by weakly modulated, somewhat deformed and high-amplitude areas.
Regional differences are erased and distorted by layers of fast and, to a greater extent, slow activity.
Against the background of rhythmic photostimulation, the assimilation of rhythm at the proposed frequencies turned out to be unclear.
In a number of cases, bursts of alpha and theta waves were recorded with generalized paroxysms of high-amplitude slow waves against the background of hyperventilation (7%).
All these changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain, recorded before treatment, indicated the immaturity of the functional state of the neurons of the cerebral cortex and the presence of irritation phenomena.
In young children (up to 7 years old), noteworthy is the conclusion about the immaturity of the cerebral cortex in the absence of focal changes, typical forms of epileptic and paroxysmal activity. EEG results over the age of 7 years show in most cases, along with diffuse changes in the BAM, signs of dysfunction of the mid-brain structures.
Therapeutic influences used:
The main direction of application of therapeutic effects is the removal of mental and psycho-vegetative stress.
For this we used:
1. Exogenous bioresonance induction therapy.
One of the types of exogenous BRT is induction therapy - the impact of the physiological frequency spectrum, which is represented by: Beta rhythm, Alpha rhythm, Theta rhythm, Delta rhythm on the electromagnetic fields of the brain and serves as a stimulus for their normalization and restoration.
Magnetic therapy devices (MMT) were used in the treatment: a “loop” with fixation on the head, the intensity during the session was from 10 units. up to 30 units taking into account the age of the child. Based on the testing results, the following programs were used most often: alpha rhythm (P1), rest (P5), children's program (P7), cerebral (P15), learning (P16), memorization (P17), muscle relaxation (P20), Schumann waves (P22 ), stress (P8), sleep program (P6, P18).
2. Exogenous bioresonance therapy with fixed frequencies.
Non-contact therapy with an alternating magnetic field was used using a (UMT) “loop” with fixation in the head area from 10 units. up to 30 units Programs for diseases of the central nervous system and psyche were used: (E97) antisocial behavior, (E2) insomnia, (E58) stuttering, (E34) fear, (E22) cerebrasthenic syndrome, (E29) depression, etc.
Results:
1. Positive dynamics were identified in 206 (96%) children.
There was no provocation of hyperexcitability by the action of induction programs.
2. The best results were achieved in the group of children who underwent 3-4 courses of treatment with an interval between courses of 2-3 months
3. During control testing, there was a decrease in mental and psycho-vegetative stress to degrees I-II.
4. The positive effect of therapy was confirmed by an improvement in the bioelectric activity of the brain: After treatment, EEG in 100% of cases showed an improvement in the form of a decrease in the beta rhythm index in the parietal and temporal leads, and an increase in the alpha rhythm index in the occipital leads. The alpha rhythm became more regular, more modulated with fewer layers in the form of fast and slow activity. A weakening of the phenomena of irritation of the cerebral cortex was also observed.
5. The effectiveness of therapy was also noted by the children’s parents: a decrease in hyperactivity and impulsivity, a decrease in fears, an improvement in attention, mood, sleep, a decrease in play impairment, and an increase in performance.
Conclusions:
From all of the above, we can conclude that the use of the method of exogenous therapy, a program of induction therapy with brain rhythm frequencies, significantly increases the effectiveness of medical, psychological and pedagogical rehabilitation of children with ADHD.
The process of rehabilitation of children with ADHD is long, difficult for all specialists, and not always completed. However, significant positive dynamics make it possible to take a big step towards the social adaptation of these children.
The plasticity of the child’s nervous system and the ability to compensate for impaired function determine the importance of the early start of comprehensive rehabilitation of children with ADHD, which will prevent the occurrence of developmental deviations.
BRT allows you to speed up the rehabilitation processes of children with ADHD.
The results of dynamic EEG analysis during treatment of children suggest the possibility of this method influencing both cortical structures (reduced irritation, slow-wave activity index) and subcortical structures (generalized discharges of high-amplitude slow waves).
Thus, the data from the study indicate a change in the bioelectrical activity of the brain in children with ADHD against the background of BRT.
An electroencephalographic study allows us to establish a positive effect and, if necessary, adjust treatment depending on the changes.
Classification of cortical dysarthria in children
Depending on the location of the pathological focus and the mechanism of development, two types of pathology are distinguished:
- Cortical kinetic dysarthria (efferent) is associated with damage to the central zone of the anterior cortex. Due to the proximity of the area that controls hand movements, hemiparesis may occur. Characterized by slowness of speech and lack of rhythm. Some children speak in syllables;
- Kinesthetic (afferent) dysarthria is associated with damage to the postcentral zones. It is characterized by discoordinated work of the organs of articulation and movements of the muscles of the hand on the opposite side.
Based on severity, there are 4 forms of the defect. In the first degree there is no clear clinical picture, then their severity increases. Grade 4 may be accompanied by complete anarthria, that is, lack of speech.
Mixed variants of the disease are possible, for example, cortical-subcortical dysarthria, when in addition to the cortical part, the subcortical parts of the brain are also affected.
Preparing children for EEG
The key point in preparing a child of any age is the need to remain as calm as possible during the study in order to obtain the most reliable result.
It should be borne in mind that conducting an EEG (like any other diagnostic method) for a child of any age can be associated with anxiety and stress. Therefore, a number of neurologists advise taking with you the child’s favorite things that can please, distract and calm him, and it is also recommended to conduct “preparatory” games and conversations with him a few days before the test. The game will be most relevant for preschool children, and it must include putting on a “magic hat”. For newborns, it is possible to schedule a study during feeding, and the electrodes are applied before feeding begins. This is explained by the newborn falling asleep more easily after feeding, which is significant in view of the large number of artifacts when recording while awake. It is not recommended to discontinue or prescribe new medications without consulting a doctor, which is associated with possible distortion of the results. You should also try to prevent your child from falling asleep while waiting for the procedure and refrain from sitting for long periods while waiting for the examination. It is necessary that the child’s hair is washed in advance, while braids (if any) should be combed, and various clips, hairpins and metal jewelry should be absent. It is also necessary to avoid unnecessary excitement and abstain from foods that can cause digestive disorders. 23
Only if all the rules and recommendations of the doctor for preparing the patient are followed, will it be possible to obtain a diagnostically significant and reliable result of the study.4
Symptoms of cortical dysarthria in children
Characteristic symptoms of cortical dysarthria are disturbances in the tempo-rhythmic component of speech: there is a slow pace of expressive speech, lack of fluency and automatism. From the outside it seems that it is difficult for the child to move his tongue and lips.
The most difficult sounds are the anterior lingual sounds. The baby replaces or skips problematic sounds. Because of this, speech is blurred and slurred. But there are no problems with the semantic part, that is, the vocabulary is sufficient, children correctly use words in sentences and correctly express their thoughts.
Cortical-subcortical dysarthria is characterized by violent involuntary movements at rest and during conversation.
Afferent cortical dysarthria
Signs of this variant of cortical dysarthria are the search for the correct articulatory structure when pronouncing sounds, which causes pauses. The voice, due to stress during conversation, is loud with a decrease in voiced consonants. Due to the slowness of speech, intercalary sounds appear.
The baby pronounces affricates (consonants made of two sounds) separately or pronounces only a separate part. For example, “t” or “s” or the prolonged “ts” from instead of the sound “ts”. It also replaces some sounds with others: fricative consonants with stop consonants. The child cannot name the place on the face that the speech therapist touches.
Efferent cortical dysarthria
Cortical kinetic dysarthria is characterized by slowness of speech due to problematic transitions between sounds. Stressed vowels are lengthened, and consonants, if they are at the beginning and end of a word, too. The pronunciation of “l”, “sh”, “r”, “zh” suffers: this requires the participation of the tongue, and the child’s tongue movements are difficult. He can replace them with “d” or “t”.
It is difficult for a child to fix the desired articulatory position, so there are unnecessary insertions and omissions of sounds. Children may wrinkle their forehead, stick out their tongue, close their eyes, and lick their lips when talking.
Electroencephalogram for autism: reviews
| Positive | Negative |
| In order not to injure the child, we asked for a CT and MRI of the brain, albeit with anesthesia, but quickly, accurately and without any problems. The only negative is that these studies are much more expensive than electroencephalography. If it were possible to reach an agreement with my son, we would go through with what was prescribed, but... alas. (Nina) | For us, all these suction cups on our heads are a total nightmare; our daughter won’t let us attach them to anything, and we also have to sit motionless for a long time. A neurologist prescribed an EEG for us, we went to a psychiatrist to find out how to cope with fear, and he told us that all these studies for autism are completely useless, since autism is diagnosed solely by behavioral indicators. Now I don’t even know what to do. (Anya) |
| We had an electroencephalogram performed at the age of 1.5 years. We were lucky that we slept soundly, so we drove around the city for an hour in a car to lull us to sleep, then they carefully carried us into the office, and we did everything. As the neurologist explained to us, it is necessary to exclude factors that could cause symptoms similar to autism. The diagnosis was confirmed, appropriate treatment was prescribed, which, by the way, is already showing positive results. (Sofia) | We are categorically against such torture for autistic children! This is incredibly stressful for them. Especially when they are wrapped in a towel or diaper and held by several doctors - it’s just darkness! (Taya) |
| We were prescribed this test at the age of 8, and we could negotiate with our son and keep him occupied for half an hour. So diagnosis was not a problem for us. As for expediency, I think everything that concerns the head needs to be fully examined in order to understand exactly what is happening to your baby. (Yana) | |
| MRI cannot show the neural patency of the brain, therefore, EEG is the only option to look at how impulses move through the brain and what abnormalities exist. We were tested in front of a monitor with bright pictures and cartoons. We can “get stuck” like this for hours, while the brain was in an active state, and the picture was painted in full. | |
| A good study, but while we went through it, we suffered, as a result, our son was given some kind of injection, which completely slowed him down and turned him into a “vegetable” - to say that I was scared is to say nothing. But, thank God, after 30 minutes the son began to behave as usual, and we passed the diagnosis. The diagnosis was confirmed as “Autism due to damage to the occipital part of the brain.” (Rita) |
Complications in children
Speech defects affect the development of speech in general, the state of the nervous system and cognitive functions. Children do not develop their vocabulary well, and they have a general underdevelopment of speech. Attention and memory deteriorate. A pronunciation defect causes a deterioration in the perception of phonemes. Such violations are fraught with learning problems: written speech and reading suffer.
At older ages, the likelihood of psychological problems is high. School-age children have a hard time with speech disorders, become withdrawn, and may show aggression and irritability. Depression may develop. The situation becomes more complicated if there is a lack of understanding and help from parents.
Does EEG show autism?
Why are electroencephalograms often recommended for people with neurological conditions such as autism, intellectual developmental disabilities, or global developmental delay?
The occurrence of seizures in individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders is significantly higher than in the typically developing population. For example, epilepsy occurs in 1-2% of the general population, but in 20-40% of patients with autism. Abnormal EEG occurs in approximately 2-4% of the general population, but in 50-80% of patients with autism.
Why do seizures occur so often in autism and other nervous system disorders? Brain dysfunction that results in developmental delays also predisposes to the development of seizures. Thus, the EEG does not show autism, but the presence or absence of epileptic activity, and based on this and other indicators, a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of cortical dysarthria in children
The diagnosis is made based on an examination by a neurologist, speech therapist and the results of instrumental research methods:
- A neurological examination can reveal paresis of facial and articulatory muscles, facial asymmetry, and deviation of the tongue to one side. Difficulties in performing sequential actions at the request of a doctor are also identified;
- The speech therapist identifies not only the symptoms of cortical dysarthria, but also its characteristics and causes. Determines the degree of disturbance, the presence of its components: replacement of sounds, slowness and unevenness of speech;
- Hardware research methods make it possible to evaluate the structure of the brain and identify pathological foci: space-occupying formations, hematomas, consequences of traumatic brain injuries. Depending on the situation, an MRI or CT scan may be prescribed;
- Lumbar puncture is performed if a neuroinfection is suspected. This method allows you to evaluate the properties and amount of cerebrospinal fluid and identify the pathogen.
If necessary, the patient can be examined by other specialists. For example, in case of extensive education - an oncologist and neurosurgeon, in case of neuroinfection - an infectious disease specialist, a phthisiatrician.
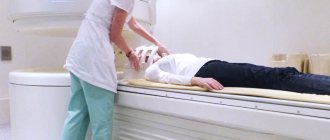
How are brain MRIs done for children?
If necessary, the baby is changed into a hospital gown (if the clothing you choose does not meet the requirements) and placed on a pull-out table.
After this, the table is pushed into the magnetic capsule and diagnostics begin. If the procedure takes place without medicinal immersion in sleep, then during it it is recommended to talk with the child so that he does not get nervous.
If a child begins to feel unwell, notices nausea, dizziness, or other strange sensations, he can immediately inform the doctor about this via the built-in intercom to stop the tomograph.
During the procedure, the device scans the body and transmits all data to a special computerized device. After performing a tomography and obtaining an image, the radiologist interprets the image. If the patient was under the influence of medications, then after the tomography he should remain in the hospital for about half an hour under the supervision of doctors so that they can monitor his condition after anesthesia.
Deciphering an MRI of a child’s head will take some time; the result and conclusion will be given to you either on the same day or the next day.
Treatment of cortical dysarthria in children
Correction of cortical dysarthria begins with pathogenetic treatment of the disease that led to a speech defect. Without this step, no amount of speech therapy help will help restore speech.
Complex treatment includes:
- drug therapy aimed at stimulating metabolism in the brain and restoring its functions. Prescribe nootropic drugs, vitamins, metabolites. In difficult cases, sedatives, tranquilizers, and antidepressants may be needed;
- speech therapy correction of cortical dysarthria - speech therapy massage, articulation gymnastics, development of fine motor skills of the hands, production of sounds. If necessary, a psychologist is involved in the treatment process;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, reflexology, massage, physical therapy help eliminate muscle paresis and improve blood flow throughout the body;
- Relaxation techniques - art therapy, aromatherapy, music therapy help relieve stress and improve the emotional background.
Conventional treatment is long-term. Specialists prescribe several courses of therapy, during which they can adjust the program taking into account the body’s response to therapeutic measures.
How is the research conducted?
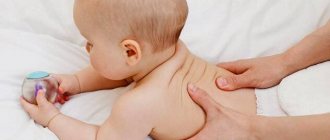
Electrodes are installed on the scalp in the projection of different parts of the brain; there are usually 19 of them in total; they are attached symmetrically on both sides of the head and in the center; a “cap” can be immediately put on, without the need to attach each electrode separately. An ECG sensor is also attached to the chest area; additional sensors (myographic) are often needed. At the same time, the child leads a normal lifestyle: walks, eats, plays sedentary games (mosaics, dolls, etc.), and smart technology records the activity of the baby’s brain.
The day before, the mother needs to prepare the child for the examination:
- Wash your hair, as excess sebum disrupts the tight contact of the electrode with the scalp and distorts the examination result.
- Remove jewelry (earrings, hair clips, piercings).
- If the child is very small or shows aggression or is too restless, then it is recommended to premedicate, which includes sedatives.
- Sometimes sleep deprivation is recommended, which is carried out in order to increase the information content of the study.
- It is not recommended to feed your child energy foods on the eve of the test: chocolate, strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, and so on.
- Warn the functional diagnostics doctor about all medications that the child receives in detailed dosages and frequency of use.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely initiation of therapy using a comprehensive individual approach and the absence of complex neurological pathology are the main conditions for complete speech restoration. The child overcomes his speech impediment and in the future leads a normal life typical for his age. He can study in a regular school and successfully master the school curriculum.
If cerebral palsy or another neurological disease is present, or there is a space-occupying lesion, the prognosis is difficult. In any case, with a competent approach, it is possible to improve speech and reduce the severity of the defect.
Prevention of the cortical form of dysarthria consists of planning pregnancy, giving up bad habits during pregnancy, timely treatment of emerging problems, and preventing complications of pregnancy and childbirth. It is important to choose a method of delivery in advance to prevent birth injuries.
Evaluation of results
The activity of brain cells is reflected on the display. This allows the doctor to print the data and interpret the readings more accurately. The data obtained greatly facilitates and speeds up the diagnosis of the patient.
Do not try to understand the results of the encephalogram on your own. Each person's impulse speed is different, this especially applies to children.
When making a diagnosis, the neurologist will also take into account the child’s medical history and the results of additional studies.
Oscillation assessment
Based on the examination data, the encephalogram displays the rhythms of the brain:
- The main rhythm or alpha rhythm is recorded in the occipital regions.
- Beta oscillations are maximally detected in the frontal region.
- Theta and delta rhythms are maximally recorded during the child's sleep.