Central nervous system degeneration is irreversible organic and functional changes in the spinal cord and brain that lead to mental degeneration. There are many types of diseases, the consequences of which are disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Accordingly, treatment will depend on the type of disease and the causes that cause it. Unfortunately, not all diseases of the central nervous system are treatable. Successful therapy for degenerative diseases of the central nervous system is performed at the Yusupov Hospital.
Degenerative diseases of the central nervous system: general concepts
The main characteristics of the group of degenerative diseases of the central nervous system are the following criteria:
- diseases begin unnoticed; before their appearance, the nervous system could function absolutely normally;
- diseases have a gradually progressive course and can last for years or decades;
- some degenerative diseases are associated with hereditary factors and develop in several members of the same family;
- a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system is characterized by the gradual death of neurons and their replacement by glial elements;
- atrophic processes at the initial stage of pathology development occur in a specific area of one of the cerebral hemispheres; further, during the advanced stage of degeneration, atrophy in the brain becomes almost symmetrical.
Various diseases of the central nervous system, the list of which is quite long, remain under study. The reasons for the occurrence of atrophic processes during the normal functioning of the nervous system for most of a person’s life are not reliably known. However, there are a number of factors that can trigger brain degeneration:
- alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- toxic effects of pesticides and herbicides;
- meningococcal infection;
- viral encephalitis;
- deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
Organic diseases of the central nervous system
The presence of an organic disease of the central nervous system means that the brain is defective. The pathology can be congenital or acquired. Neurologists say that organic disorders of the central nervous system of the first stage can be found in 98% of the population, but they do not require treatment. The second and third stages are characterized by more serious lesions and are accompanied by significant deviations.
Congenital organic brain lesions occur during embryonic development or during childbirth as a result of birth trauma. The reasons for their appearance may be unfavorable factors that influenced the pregnant woman:
- woman's use of alcohol and drugs;
- severe influenza or other infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- the effect of certain medications;
- severe stress.
Acquired organic lesions can occur after a stroke, traumatic brain injury, alcohol and drug abuse, and infectious diseases with brain damage.
Among the diseases that are caused by organic lesions of the central nervous system, mental retardation and dementia are distinguished. With oligophrenia, mental retardation occurs. The disease occurs during fetal development or in the first year of life. Children have reduced intelligence and poorly developed speech and motor skills. With dementia, there is a loss of previously acquired skills and knowledge. Gradually, dementia leads to complete degradation of a person. Considering this disease of the central nervous system, the symptoms are the following: impaired memory, speech, orientation in space, a person cannot learn new things and loses old skills and knowledge.
Let us consider in more detail each cause of central nervous system damage.
Peri- and intrapartum pathology
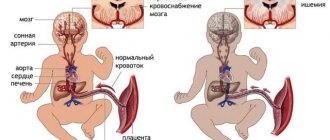
There are several critical moments during pregnancy and childbirth when even the slightest impact on the mother's body can affect the health of the child. Oxygen starvation of the fetus (asphyxia), prolonged labor, premature placental abruption, decreased uterine tone and other reasons can cause irreversible changes in the fetal brain cells.
Sometimes these changes lead to the early death of a child before the age of 5-15. If life is saved, then such children become disabled from a very early age. Almost always, the disorders listed above are accompanied by varying degrees of severity of disharmony in the mental sphere. With reduced mental potential, positive character traits are not always sharpened.
Mental disorders in children can manifest themselves:
- in preschool age : in the form of delayed speech development, motor disinhibition, poor sleep, lack of interest, rapid mood changes, lethargy; - during the school period : in the form of emotional instability, incontinence, sexual disinhibition, impaired cognitive processes.
Traumatic brain injuries
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a traumatic injury to the skull, soft tissues of the head and brain. The most common causes of TBI are car accidents and household injuries. Traumatic brain injuries can be open or closed. If there is communication between the external environment and the cranial cavity, we are talking about an open injury; if not, it is a closed injury. The clinic presents neurological and mental disorders. Neurological include limitation of limb movements, disturbances of speech and consciousness, the occurrence of epileptic seizures, and damage to the cranial nerves.
Mental disorders include cognitive impairment and behavioral disorders. Cognitive disorders are manifested by a violation of the ability to mentally perceive and process information received from the outside. Clarity of thinking and logic suffer, memory decreases, and the ability to learn, make decisions and plan ahead is lost. Behavioral disorders manifest themselves in the form of aggression, slow reactions, fears, sudden mood swings, disorganization and asthenia.
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system
The range of infectious agents that cause brain damage is quite large. The main ones among them are: Coxsackie virus, ECHO, herpes infection, staphylococcus. All of them can lead to the development of meningitis, encephalitis, and arachnoiditis. Also, lesions of the central nervous system are observed during HIV infection in its final stages, most often in the form of brain abscesses and leukoencephalopathies.
Mental disorders due to infectious pathology manifest themselves in the form of:
- asthenic syndrome - general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance; — psychological disorganization; — affective disorders; — personality disorders; — obsessive-convulsive disorders; - panic attacks; - hysterical, hypochondriacal and paranoid psychoses.
Intoxication
Intoxication of the body is caused by the use of alcohol, drugs, smoking, poisoning with mushrooms, carbon monoxide, salts of heavy metals and various medications. Clinical manifestations are characterized by a variety of symptoms depending on the specific toxic substance. The development of non-psychotic disorders, neurosis-like disorders and psychoses is possible.
Acute intoxication due to poisoning with atropine, diphenhydramine, antidepressants, carbon monoxide or mushrooms most often manifests itself as delirium. In case of poisoning with psychostimulants, intoxication paranoid is observed, which is characterized by vivid visual, tactile and auditory hallucinations, as well as delusional ideas. It is possible to develop a manic-like state, which is characterized by all the signs of a manic syndrome: euphoria, motor and sexual disinhibition, acceleration of thinking.
Chronic intoxication (alcohol, smoking, drugs) manifests itself:
- neurosis-like syndrome - the phenomenon of exhaustion, lethargy, decreased performance along with hypochondria and depressive disorders; - cognitive impairment (impaired memory, attention, decreased intelligence).
Vascular diseases of the brain and neoplasms
Vascular diseases of the brain include hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, as well as dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when brain aneurysms rupture or blood seeps through the walls of blood vessels, forming hematomas. Ischemic stroke is characterized by the development of a lesion that lacks oxygen and nutrients due to blockage of the supply vessel by a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque.
Discirculatory encephalopathy develops with chronic hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and is characterized by the formation of many small foci throughout the brain. Brain tumors arise from a variety of causes, including genetic predisposition, ionizing radiation and exposure to chemicals. Doctors are discussing the impact of cell phones, bruises and head injuries.
Mental disorders in vascular pathology and neoplasms depend on the location of the lesion. Most often they occur with damage to the right hemisphere and manifest themselves in the form of:
— cognitive impairment (to mask this phenomenon, patients begin to use notebooks and tie knots “for memory”); - reducing criticism of one’s condition; - nighttime “states of confusion”; - depression; — insomnia (sleep disturbance); — asthenic syndrome; - aggressive behavior.
Vascular dementia
Separately, we should talk about vascular dementia. It is divided into various types: stroke-related (multi-infarct dementia, dementia due to infarctions in “strategic” areas, dementia after hemorrhagic stroke), non-stroke (macro- and microangiopathic), and variants due to disorders of the cerebral blood supply.
Patients with this pathology are characterized by slowing down, rigidity of all mental processes and their lability, and a narrowing of the range of interests. The severity of cognitive impairment in vascular lesions of the brain is determined by a number of factors that have not been fully studied, including the age of the patients.
Demyelinating diseases
The main disease in this nosology is multiple sclerosis. It is characterized by the formation of lesions with destroyed nerve endings (myelin).
Mental disorders in this pathology:
— asthenic syndrome (general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance); — cognitive impairment (impaired memory, attention, decreased intelligence); - depression; - affective insanity.
Neurodegenerative diseases
These include: Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. These pathologies are characterized by the onset of the disease in old age.
The most common mental disorder in Parkinson's disease (PD) is depression. Its main symptoms are a feeling of emptiness and hopelessness, emotional poverty, decreased feelings of joy and pleasure (anhedonia). Dysphoric symptoms (irritability, sadness, pessimism) are also typical manifestations. Depression is often combined with anxiety disorders. Thus, symptoms of anxiety are detected in 60-75% of patients.
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system characterized by progressive decline in cognitive function, personality disorder, and behavioral changes. Patients with this pathology are forgetful, cannot remember recent events, and are unable to recognize familiar objects. They are characterized by emotional disorders, depression, anxiety, disorientation, and indifference to the world around them.
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system are among the most common neurological pathologies. CNS diseases caused by infection are very dangerous. They have a severe course, leave serious consequences and significant neurological deficits. Infectious diseases of the central nervous system can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungal diseases. Most often, diseases develop when meningococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, ECHO and Coxsackie enteroviruses, mumps, and candida enter the body. The entry gates for infection are the ENT organs; it is also transmitted by contact, hematogenous, lymphogenous, and perineural routes.
The infection can affect the nervous system as a primary disease or occur secondarily as a result of the development of an infectious process outside the central nervous system. Infectious diseases of the central nervous system include:
- meningitis,
- encephalitis,
- polio,
- syphilis of the nervous system,
- toxoplasmosis of the nervous system,
- neurological manifestations of HIV infection,
- parasitic diseases of the nervous system.
Reasons for the development of residual mental retardation
ZPR of residual organic origin are disorders that can be caused by:
- injury or disease affecting brain tissue;
- chemical or hormonal disorders;
- exposure to toxic materials;
- neurological disorders or abnormal changes associated with aging;
- diseases of the liver, kidneys or thyroid gland;
- vitamin deficiency.
Concussions, blood clots, or bleeding in or around the brain from injury can lead to organic brain syndrome. Low oxygen levels in the blood, high amounts of carbon dioxide in the body, strokes, brain infections and heart infections can also lead to organic mental disorder.
Degenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and multiple sclerosis may also be contributing factors.
Vascular diseases of the central nervous system
Poor circulation in the brain provokes the development of vascular diseases of the central nervous system. These pathologies are extremely dangerous because in most cases they lead to disability. Also, vascular diseases of the central nervous system have a high mortality rate. Brain damage occurs as a result of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, transient ischemic attacks, and spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhages. The causes of such pathologies are:
- aneurysms,
- thromboembolism,
- vascular atherosclerosis,
- hypertonic disease,
- acute toxic damage to the walls of blood vessels,
- chronic degenerative diseases of the walls of blood vessels.
The trigger for the development of strokes can be severe stress, seizures, alcohol intoxication, and sudden changes in body temperature. Vascular disease of the central nervous system most often occurs spontaneously and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment and diagnosis of degenerative diseases of the central nervous system
The danger of degenerative diseases of the central nervous system is that they are difficult to predict. If there are provoking factors in a person’s life, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle and regularly visit a neurologist for preventive examinations. If you suspect signs of a central nervous system disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of slowing down the progression of degenerative processes in the brain.
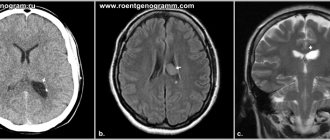
Diagnosis and treatment of degenerative diseases will depend on the type of pathology. Having determined the clinical picture of the disease, the doctor will prescribe tests to clarify the patient’s condition. These may include laboratory tests, ultrasound, MRI, CT, and psychological tests to determine the status of cognitive skills.
At the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow there is a neurology clinic, where highly qualified neurologists and doctors of sciences provide assistance. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating degenerative diseases of the central nervous system and use the latest methods of therapy and rehabilitation in their work, which allows them to take on the most complex cases.
You can ask for help, make an appointment and get advice from specialists by phone.
Symptoms of damage to the central nervous system
- Speech disorders. There is a late development of speech, a poor vocabulary, and in severe cases, a complete absence of speech skills: children with this type of central nervous system damage are able to pronounce only sounds and some single words.
- Motor impairment. Children with organic pathology of the central nervous system later begin to hold their heads, sit, and walk. Voluntary movements are impaired, which causes difficulty in eating, playing, and self-care.
- Mental disorder. An organic lesion of the central nervous system in a child is indicated by his poor performance in school and kindergarten.
In parallel, the following problems may arise: impaired memory, logical thinking, developmental delays, intellectual disability (from a slight decrease in intelligence to debility, idiocy, mental retardation), defects in the perception of the surrounding world, new information, inability to learn. Damage to the central nervous system in children must be treated immediately by making an appointment for diagnostics at our medical center. The sooner complex treatment of lesions of the central nervous system in children is started, the higher the chances of a completely successful outcome.
Such children are characterized by increased excitability or, conversely, inertia.
Possible outcomes of organic brain damage:
- Almost complete recovery. This is said in the absence of any noticeable defects in the presence of damage to the central nervous system in newborns
- Manifestations that do not pose a threat to life, but to one degree or another limit work activity and self-care.
- Gross violations - a person is bedridden and needs constant outside care.
The outcome of the disease directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis, correct comprehensive treatment, and also on the age of the patient.