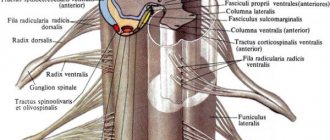
NS classification
The nervous system is divided into: central and peripheral.
The central nervous system is the main part, which includes the spinal cord and brain. Both of these organs are reliably protected by the skull and spine. The PNS is the nerves responsible for movement and sensory. It ensures human interaction with the environment. With the help of the PNS, the body receives signals and reacts to them.
There are two types of PNS:
- Somatic - sensory and motor nerve fibers. Responsible for coordination of movement; a person can consciously control his body.
- Autonomic - divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic. The first gives a response to danger and stress. The second is responsible for peace and normalization of the functioning of organs (digestive, urinary).
Despite their differences, both systems are interconnected and cannot work autonomously.
Types of rationality
Published: 09/29/2018
Researchers of rationality today propose to distinguish three types of it: the classical type of rationality, the non-classical type of rationality, the post-non-classical type of rationality.
Types of rationality manifest themselves not only in the high spheres of scientific comprehension of the world, but also in ordinary life. Types of rationality describe the most characteristic principles of organizing and processing information, principles of constructing a picture of the world and decision-making mechanisms. Classic type of rationality Classic... no comments
What are signaling systems
The signaling system is a set of reflexes that connect the body with the environment. They serve as a step in the formation of higher nervous activity.
There are two signaling systems:
- reflexes to specific stimuli - light, sound (available in animals and humans);
- speech system - developed in a person in the process of work.
Personality types according to E. Fromm
Published: 09.29.2018
This American psychologist believed that early childhood and family relationships are the determining factors in the formation of personality. Therefore, the five personality types he identified (consumer, exploitative, accumulative, market and productive) rather reflect the influence of social rather than innate factors (E. Fromm, 1964). Consumer type A person believes that the source of all benefits is external, and is determined to...
no comments yet
Evolution of the central nervous system
The evolution of the functions of CNS cells occurred in several stages:
- improvement of individual cells;
- the formation of new properties that can interact with the environment.
The main stages of phylogenesis that the nervous system went through are:
- The diffuse type is one of the oldest; it is found in organisms such as coelenterates (jellyfish). It is a type of network that consists of clusters of neurons (bipolar and multipolar). Despite its simplicity, the nerve plexuses, in response to irritations, give a reaction throughout the body. The speed at which excitation propagates through the fibers is low.
- In the process of evolution, a stem type emerged - a number of cells gathered into trunks, but diffuse plexuses also remained. It is represented in the group of protostomes (flatworms).
- Further development led to the emergence of the nodal type - some of the cells of the central nervous system are collected in nodes with the ability to transmit excitation from one node to another. The improvement of cells and the development of reception apparatuses occurred in parallel. Nerve impulses arising in any part of the body do not spread throughout the body, but only within the segment. Representatives of this type are invertebrates: mollusks, arthropods, insects.
- Tubular - the highest, characteristic of chordates. Multisynaptic connections appear, which leads to qualitatively new relationships between the organism and the environment. This type includes vertebrates: animals that differ in appearance and have different lifestyles, and humans. They have a nervous system in the form of a tube that ends in the brain.
Personality types according to A. Miller
Published: 09/29/2018
A. Miller (1991) created a typology based on a combination of personality traits. He used three dimensions of personality traits: cognitive, affective, and conative. Cognitive dimension - analyticity - holisticity (in other concepts it is analyticity - syntheticity), i.e. the tendency to focus on the whole or parts. The affective dimension is represented by emotional stability—instability, which is determined through the intensity of emotional reactions.…
no comments yet
Varieties
The scientist Pavlov conducted laboratory research for many years, studying the reflexes of dogs. He concluded that in humans, the type of nervous system mainly depends on innate characteristics. It is the nervous system, its properties, that physiologically affect the formation of temperament.
However, modern scientists argue that this is influenced not only by hereditary factors, but also by the level of upbringing, training and social environment.
Thanks to all the research, the following types of nervous system have been identified, depending on the processes of excitation, inhibition and balance:
- Strong, unbalanced - choleric. In this type, excitation of the nervous system predominates over inhibition. Cholerics are very energetic, but they are emotional, hot-tempered, aggressive, ambitious and lack self-control.
- Strong, balanced, agile - sanguine. People of this type are characterized as lively, active, easily adapt to different living conditions, and have high resistance to life's difficulties. They are leaders and confidently move towards their goals.
- Strong, balanced, inert - phlegmatic. He is the opposite of sanguine. His reaction to everything that happens is calm, he is not prone to violent emotions, and I am sure he has great resistance to problems.
- Weak - melancholic. A melancholic person is not able to resist any stimuli, regardless of whether they are positive or negative. Characteristic signs: lethargy, passivity, cowardice, tearfulness. With a strong irritant, behavioral disturbances may occur. A melancholic person is always in a bad mood.
Interesting: psychopathic disorders are more common in people with a strong unbalanced and weak type of GND.
COVID-19 and B vitamins
A detailed study of the mechanisms of PNS damage in COVID-19 allows us to reasonably assume the key role of immune disorders in the initiation and subsequent progression of PNS damage. Taking into account the role of various vitamins in normal and pathological conditions, there is understandable interest in studying the characteristics of their metabolism in patients with COVID-19, as well as the possibilities of correcting their content in the body in order to improve disease outcomes. This direction of research is justified and promising, since the undoubted role of vitamins, in particular group B, in the functioning of the PNS under normal conditions, as well as their positive significance in its diseases is known [20, 21]. Thus, the relationship between the content of vitamins C, D and B vitamins and the nature of the course of COVID-19 was studied [22]. A reasoned assumption has been made that the immune response to a certain extent depends on the sufficient content in the body of a number of substances necessary for its normal functioning, in particular B vitamins [23]. Vitamin deficiency may be one of the reasons for the imbalance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, changes in the control mechanisms of epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone modification, post-translational modification [24, 25].
Violations of vitamin metabolism are of particular importance in patients with concomitant somatic disorders that aggravate vitamin deficiency or increase the need for them (in particular, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, inadequate diet). As a rule, disorders of the metabolism of B vitamins occur in elderly and senile patients; they require additional vitamins into the body [26]. It has been suggested that cyanocobalamin deficiency is the key link linking risk factors for an unfavorable outcome of COVID-19 (diabetes mellitus, overweight and old age) and a more severe course of COVID-19 [27]. In addition to the well-known consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency, such as disruption of the structure and trophism of nerve cells, the damaging effects of excessive homocysteine formation, its role in the development of COVID-19 may be associated with immune disorders. Thus, it has been shown that in conditions of vitamin B12 deficiency, humans experience lymphopenia, a decrease in the level of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, an imbalance in the synthesis of a number of cytokines, and other disorders of the immune status [28, 29]. It has also been established that when vitamin B12 deficiency is compensated, these disorders regress. Factors leading to changes in vitamin metabolism in patients with severe COVID-19 and concomitant diseases are dietary disorders caused by parenteral or tube nutrition, taking certain medications (metformin, proton pump inhibitors, H2-histamine receptor blockers, etc.) leading to impaired absorption of vitamin B12 [30]. It should be remembered that older age, one of the important risk factors for poor outcome of COVID-19, is also closely associated with vitamin B12 deficiency due to impaired absorption in the elderly [31].
Of undoubted interest is the information that hyperhomocysteinemia (more than 15.5 μcol/l) directly affects the course of COVID-19. When observing a group of 273 patients, it was shown that elevated blood homocysteine concentrations are closely associated with the progression of changes in lung tissue (identified by X-ray computed tomography) and disease outcome [32]. The results of experimental studies indicate that methylcobalamin is able to inhibit the activity of RNA-dependent polymerase, limiting the replication of SARS-CoV-2 [33]. Data have also been obtained on increasing the effectiveness of treatment of patients with hepatitis C when vitamin B12 is included in the therapeutic regimen [34].
To date, there are reports that the use of vitamin B12 in complex therapy of patients with COVID-19 can have a positive effect on the course and outcome of the disease. Thus, observation of a group of patients with COVID-19 of moderate severity (n=17, age 50 years and older), who, in addition to the main therapy, received a complex of vitamin D, magnesium sulfate and vitamin B12, allowed us to establish that they were less likely to need respiratory support and/or treatment in the intensive care unit compared with patients receiving standard care only (OR 0.152, 95% CI 0.025–0.930, p=0.041) [35]. Results from another cohort study (n=162) demonstrated that lower blood folate levels were associated with more severe COVID-19 (p=0.005). Notably, this study found that high blood levels of vitamin B12 were associated with more severe COVID-19 (p=0.039) [36]. Unfortunately, the lack of adequate statistical analysis of the results obtained does not allow us to objectively assess the significance of the conclusion made.
A randomized, blind comparative study is currently ongoing, during which patients with COVID-19 (the main group) receive a combination of vitamins A, C, D and B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, cyanocobalamin, etc.), and patients in the comparison group receive only basic therapy [37]. According to the authors, based on the available results of experimental and clinical studies, combination treatment with the administration of an extensive complex of vitamins allows for a milder course of COVID-19 and improves both early and long-term outcomes of the disease.
Vitamins B6 (pyridoxine) and B9 (folate), as well as vitamin B12, play a certain role in the implementation of the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity, and therefore their content in food products is regulated in the European Union [38]. Vitamin B6 inhibits the proliferation of T-lymphocytes and their functional state, reduces the release of cytokines/chemokines [39]. Vitamin B9 deficiency is associated not only with the development of megaloblastic anemia, but also with a pronounced inhibition of T-lymphocyte proliferation, panhypogammaglobulinemia, and impaired synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines [40]. These disorders, as a rule, can be completely eliminated by introducing folate into the body.
The key function of vitamin B1 (thiamine) is participation in energy metabolism (the conversion of pyruvate into acyl-coenzyme A with subsequent entry into the Krebs cycle) and the metabolism of NADPH and glutathione, an important antioxidant defense system in various tissues [41]. In clinical settings, the effectiveness of using thiamine in combination with other drugs (ascorbic acid, glucocorticosteroids, etc.) in the treatment of patients with severe pneumonia and sepsis has been demonstrated [42]. The treatment provided less damage to internal organs and reduced mortality.
The results of experimental studies and the accumulated empirical practical experience of using B vitamins in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 are widely discussed in the literature, and the feasibility of their wider use in the treatment of such patients is being considered [43]. The diverse effects of B vitamins have been convincingly demonstrated and well studied in both experimental and clinical settings. Thus, their ability to reduce the severity of peripheral nerve damage caused by various causes has been shown. In addition to the direct positive effect on the condition of neurons, B vitamins, in particular cyanocobalamin, stimulate the processes of growth and differentiation of Schwann cells and activate their inclusion in the processes of myelination of peripheral nerve fibers [44]. Subsequent studies demonstrated that activation of the processes of proliferation of Schwann cells and the subsequent formation of the myelin sheath of surviving axons due to the use of cyanocobalamin are associated with activation of the synthesis of a number of neurotrophic factors [45]. Later it was found that the restoration of the integral structure of the myelin sheath of the axon, as well as the restoration of its functional properties, in particular the normalization of impulse conduction speed, are dose-dependent [46]. The most pronounced and complete morphofunctional restoration is observed when high doses of cyanocobalamin are prescribed for a long time.
A complex preparation for intramuscular administration, including B vitamins, is Milgamma®: one ampoule (2.0 ml) contains 100.0 mg of thiamine hydrochloride, 100 mg of pyridoxine hydrochloride, 1000 mcg of cyanocobalamin and 20.0 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride. In clinical practice, these components have proven themselves well in the treatment of patients with various diseases (mono- and polyneuropathies of various origins), traumatic lesions of the PNS, pain syndromes (musculoskeletal pain syndrome, neuropathic pain) [47–49]. The effectiveness of the drug and its good tolerability give reason to believe that its use in patients with PNS damage caused by coronavirus infection SARS-CoV-2 will be in demand.
How to determine a person's temperament
It is not easy to determine what type of nervous system a person has, since this is influenced by the cerebral cortex, subcortical formations, the level of development of signaling systems and intelligence.
In animals, the type of NS is influenced to a greater extent by the biological environment. For example, puppies from the same litter but raised in different environments may have different temperaments.
Exploring the central nervous system and human psychology, Pavlov developed a questionnaire (test), after passing which, you can determine your belonging to one of the types of GNI, provided that the answers are truthful.
The nervous system controls the activity of all organs. Its type affects a person’s character and behavior. People with a common type are similar in their reactions to certain life situations.
Personality types according to D. Keirsey
Published: 09/29/2018
Another approach to the classification of personality types is the approach of D. Keirsey (1956). Keirsey developed and supplemented the concept of Carl Gustav Jung, taking into account the latest achievements of both cognitive-behavioral and existential-humanistic psychology. As a result, he created an idea of four integral types of temperament, differing in the most significant and stable psychological characteristics - from the value-motivational structure to the observed style of behavior. Author…
no comments yet