In this article you will learn what the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are. A component of the human system is the autonomic system, the most important function of which will be to ensure the vital functions of absolutely all organs. Consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system, aimed at providing the opposite effect on every human organ. If we talk about the vegetative system as a whole, it is the only one that is quite complex, but generally autonomous, not subject to human will. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, its anatomy, is a complex system of nerve nuclei connected by fibers and delivering impulses from stimuli to the central nervous system.
Functional significance of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is divided into two sections: peripheral and central. The central department is responsible for monitoring the functioning of internal organs and manages the work of absolutely all organs. The central department works around the clock, without breaks.
The peripheral division is divided into two subdivisions: the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system. The nervous system of every person is completely structured.
Both the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic nervous system function simultaneously. Their performance will largely depend on the needs of the body at a particular time.
Due to the multidirectionality and impact on the organs of the centers of the parasympathetic and sympathetic parts of the nervous system, absolutely all healthy people can adapt to different conditions and environmental factors, for example, in the dark, the eyes will be more concentrated in order to see and distinguish objects around a person. In cold weather, the body tries to produce more heat than in normal climatic conditions. On a hot day, the human body cools the skin through increased sweating. It is these processes and many others that are controlled by the peripheral part of the autonomic nervous system, which performs two main functions:
- Ensuring homeostasis (the performance of each organ is constantly maintained at the same level).
- Creation of full-fledged mental and physiological functioning of the human body.
Increased physical activity forces the autonomic nervous system to control the pressure in the circulatory system to prevent its drop or excessive increase. The same applies to the work of the heart, which begins to work more actively in order to ensure optimal blood circulation in the body. During periods of passivity and rest, heart contractions decrease, sending a message to the autonomic system.
How does the sympathetic nervous system differ from the parasympathetic? First of all, by the “options” carried out and the impact on the activities of individual bodies.
The central department of the autonomic parasympathetic nervous system is completely independent in its work, literally scattered throughout the brain, and therefore actively participates in all biological processes of the human body.
The central section is divided into several structures - segmental and suprasegmental. The latter combines several more subdivisions, including the hypothalamus.
Chapter 1. The nervous system as a unique natural computer
Structure of the nervous system
Imagine that you are in the cabin of an airplane, which, when landing, flies over the city so low that through the window you can see residential areas in which multi-storey buildings stand either separately or huddled together. Now also imagine that in every apartment of such houses floating under the wing of an airplane there is a computer. And, of course, each such computer can communicate with any other computer not only in the city, but throughout the world. So, one nerve cell is a whole computer, and all the computers that you can imagine at the same time are a semblance of our nervous system. And the main thing in this system is not the computer itself - the cell, but its ability to receive and transmit information.
Information from one computer to another can be transferred in two ways: connecting computers to each other using a special cord (in nerve cells this is an anatomical connection) or using the Internet (functional connections of nerve cells). Neuron
(this is the name of a nerve cell) was created solely for the purpose of receiving information and necessarily, without fail, transmitting it further.
If we continue the analogy with computers, then very soon differences will be revealed - this is understandable, a computer is only a similarity to what nature has created in the human body. The power went out and the computer screen went dark. In a natural computer, in addition to biological electricity, there is another way - with the help of chemicals - mediators, neuropeptides.
It must be said that the neuron has a very interesting structure: like any computer, it has a case - a body. And yet, this is not what the neuron is famous for; the main thing about it is its processes. The entire neuron is somewhat reminiscent of a tree, which has a developed crown and trunk. The crown of a tree is formed by branches, and in a neuron these are short processes, they are called dendrites
.
A tree has a trunk, and a neuron has a long process, an axon.
And now about the junction of nerve cells - this is
a synapse
. If two computers are connected with a cord, then the contact between the computer and the cord will be exactly the same synapse in the nervous system.
And now very good news! The nervous system is a self-programming computer! What does this mean for you personally, for example? This means the following: through training and repeated repetition, you, dear reader, can learn anything! If there is a desire, of course. Bears skate in the circus not just for the sake of our pleasure and fun, but also for clarity, so to speak! If we are bears, then us?! And all thanks to the ability of nerve cells to grow new processes and connect with the necessary nerve cells. You need it, no problem, the neuron cell begins this painstaking work of growing new dendrites-branches! You don’t need any more – no problem either, the unnecessary ones disappear.
The more you read and try to remember new things, the longer your brain remains young, the better your memory, your thinking. This is a useful thing - to move your convolutions! By the way, no joke - this is a reliable remedy for dementia in old age!
The emergence of new processes and synapses and the partial disintegration of existing ones underlie learning, adaptation, compensation and restoration of impaired functions.
The body and processes of a neuron even differ in color: the place where there are many nerve cell bodies is gray, but the accumulation of processes is white. The processes united together are already a nerve
, and the accumulation of neuron bodies is
a nerve ganglion
.
The nerve ganglion is an anatomical concept. If several neurons perform the same function, this is already a nerve center.
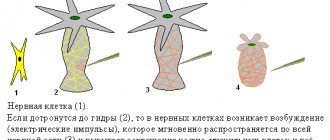
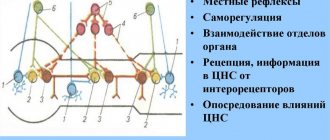
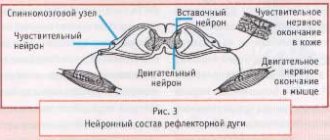
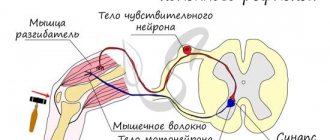
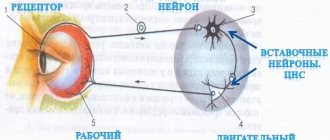
In order to understand how the nervous system works, let's look at an example. Surely there has been a time in your life when, through carelessness or inexperience, you touched something hot with your hand. Remember, before you had time to think of anything, your hand pulled back on its own. This is the simplest reflex, and this kind of work of the nervous system, when an action is carried out as if by itself, without your thinking, is called reflex.
As you understand, such activity is simply vital.
How is it carried out? The skin contains special nerve endings called receptors that distinguish, for example, a cold touch or a hot touch. A long process of a neuron approaches these receptors, and the neuron itself is located in the central nervous system, in the spinal cord, and specifically in the intervertebral node.
Receptors are able to convert mechanical stimulation into an electrical impulse that runs along the process and reaches the body of the neuron. A neuron receives information and transmits the potential further to the body of another neuron, like one computer to another through an electrical cord. Of course, the neuron, which is located in the spinal cord, also has a long process that goes from the spinal cord directly to the muscle. The muscle perceives the impulse and does what it knows how to do - it contracts. The hand withdraws. The path from skin receptors through the spinal cord to the muscle is called a reflex arc. Essentially, when we pull our hand away from a hot surface, we are thinking with our spinal cord!
Spinal cord
- This is already a department of the central nervous system, and the body takes great care of it. He, like a treasure, is packed in armor made of vertebrae. Very reliable protection, both durable and mobile.
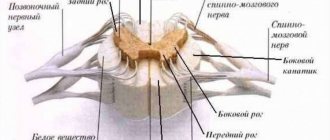
The spinal cord itself is a cylindrical cord 41-45 cm long. The most remarkable thing about it, that is, what is immediately noticeable, are its roots. These roots are very cleverly arranged: they extend from the spinal cylinder in front and behind, and on the side of it they join together, forming the spinal nerve, which in turn passes through the hole between two adjacent vertebrae.
In total, such nerves extending from the lateral surface of the spinal cord, spinal roots,
31 pairs. The functions of the remarkable roots of the spinal cord were discovered through an experiment by two outstanding scientists - the Scot Bell and the Frenchman Magendie. It turned out that cutting the anterior roots leads to the inability to move the limbs, that is, they become completely immobile, paralyzed, but the sensitivity in them remains completely intact. When the dorsal roots are cut, on the contrary, sensitivity in the limbs is lost, but movements in them are preserved.
The spinal cord collects all information from the skin, muscles, blood vessels, intestines, and genitals through these roots. And all this information is processed by the spinal cord without our conscious participation and transmitted to the muscles of the skeleton (arms, legs, torso, everything except the face), and internal organs. The work, one might say, is in full swing, but we don’t feel it at all, and that’s wonderful.
There is another curious detail related to the unconscious, i.e., reflex, activity of the spinal cord. It turns out that we can feel quite alert when our skeletal muscles are toned, that is, not relaxed. And this tone is maintained by special impulses through the motor neurons of the same spinal cord.
Perhaps some of you, dear readers, have noticed that you feel better in sunny weather, for example, but for others, on the contrary, give it some rain, and longer! This phenomenon is called meteosensitivity, and it is realized with the help of special flows of information coming from above, from our personal power plant, the reticular formation, located in the brain and directly related to another part of the nervous system - the part of the autonomic nervous system. Work or don’t work your muscles, and if the reticular formation in our head is lazy and does not have enough strength to send impulses to special motor neurons in the spinal cord, then you won’t find a feeling of vigor during the day, lethargy and laziness result.
And yet, scientists were very curious about what kind of activity is inherent in the spinal cord itself, without the influences of the head, so to speak, regardless of the influences of the brain. To do this, a special experiment was carried out on animals: the brain was separated from the spinal cord. Such an animal has no voluntary movements, it has ceased to feel and breathe. The respiratory function was supported by artificial devices. But some things still remained: the reflex activity of the skeletal muscles was preserved (i.e., the animal could not run away from the scientists, but pulling back a limb is welcome), blood pressure, urination reflexes, defecation, and some sexual intercourse were normal. reflexes.
This is how we quietly approached the definition of the functions inherent in the spinal cord. This is already familiar to us reflexive, i.e. automatic, activity, and, in addition, conductive - from the brain and back.
I hope you have already understood that the central nervous system includes not only the spinal cord, but also the brain, which, like the spinal cord, is reliably protected, completely covered by the skull and has a shock absorption system - a special liquid, cerebrospinal fluid, which circulates between the membranes brain. The connection between the brain and the spinal cord is through the foramen magnum of the skull.
But this is not the whole division of the nervous system - into the central
and
peripheral
.
There is also a division into somatic and vegetative. The somatic nervous
system contains the root "soma" in its name, which means "body". That’s right, this system is mainly responsible for the functioning of the skeletal muscles.
Autonomic nervous system,
on the contrary, it regulates the functioning of internal organs, and with the help of two different, opposite influences, which are successfully carried out by two subsections of the autonomic nervous system - sympathetic and parasympathetic.
The somatic and autonomic nervous systems differ in function, like the animal and plant worlds. Even in the names of these subsystems one hears and writes “soma” (“body”) and “vegetatics” (“plant”). These analogies will help us better understand the subtle differences in their functional activities.
So, only an animal has eyes, ears, a throat, it is alive while it moves, and can find food for itself as long as its body is preserved. This is not the case with a plant - the tree sheds its leaves for the winter, and the life in it is, as it were, packed away until spring. The plant is alive as long as it has roots, and new shoots can grow in place of a broken branch or even a cut trunk.
Somatic nervous system
belongs to the cerebral cortex,
and the autonomic
part belongs to the subcortex, the stem part of the brain. Somatics dominates during the day, and vegetatives dominates at night. That is, the tone of the somatic nervous system during the daytime prevails over the tone of the autonomic nervous system. Knowing this, we can easily understand in the future why some people experience palpitations more often at night.
During the day, the muscles of the body recharge the centers of the autonomic nervous system with energy, thereby allowing it to have the necessary resource for normal functioning. Do I need to add after this how important reasonable physical exercise is! And if, nevertheless, your work, which requires nervous tension, does not leave you the opportunity for physical activity, is it any wonder that at night there is no sleep, and your heart suddenly seizes?
By the way, stress is realized through the somatic nervous system and is triggered when a large focus of excitation occurs in the cerebral cortex. More often these are some difficult or completely unsolvable social problems. At this moment, all other functions of the body seem to be suppressed, while stress very quickly devastates the autonomic nervous system, and these are the energy batteries of the whole body. And then depression is just around the corner - beware of stress!
High aspirations, touchiness, and aggressiveness are not compatible with the rational functioning of the nervous system.
Somatic nervous
The system, unlike the vegetative one, has very strong protection in the form of the skull and spine
.
The autonomic system lives like a vine, resting on the spine and passing next to it. Of course, protection in the form of bone cases is reliable, but over time these cases turn into sarcophagi! The bones of the skull completely lose mobility, the holes between the vertebrae collapse, become smaller, are walled up with cholesterol, and become overgrown with bone formations. But it is through these openings that the arteries go to the brain. And what? The blood supply to the brain and its nutrition deteriorate, the brain simply starves, and the somatic nervous system, under its leadership, begins to function weakly, the heart does not receive support from the head, the autonomic system is also left without energy, since the muscles no longer charge it!
Control in the body becomes headless, and the person, sadly enough, loses to the microflora, which in his body begins to unpack its growth and reproduction programs and blooms wildly! This is how diseases begin.
Only a person can exploit his body so mercilessly, busy with the constant, restless solution of social problems, forgetting that the autonomic nervous system at this time is left without energy and quickly works out. And what does she do in response to such an appeal to her? The tree shedding its leaves for winter, remember? That's right, it's the same with us: the autonomic nervous system, not receiving energy from the muscles, declares stress mode and packs up.
We cannot live with ourselves in peace and harmony, we do not hear the quiet voice of reason - we get, like the tomb of a pharaoh, a sarcophagus of osteochondrosis and depression. It seems like they’re still alive, but there’s no time for love!
Let's remember! Functions of the somatic nervous system
, which provides us with behavior, motor activity, learning, protection, receiving information about the environment through the channels of central analyzers - all this depends on the nutrition of the brain and the quality of its bone protection! It would seem that the neck began to creak when turning the head, well, doctors diagnose osteochondrosis, but our adaptation suffers! But not only chondrosis! And the injuries! Did you fall on your tailbone from a bicycle as a child? Did you hit the wall with your head? That's the same! After injuries, pockets of inflammation remain that can disrupt the flow of blood and lymph.
Somatic nervous system
The somatic nervous system is cross-controlled: the muscles on the left are controlled from the right hemisphere of the cerebral cortex, and the muscles on the right are controlled from the left hemisphere. The somatic nervous system, in addition to innervating the muscles, also affects the organs that are located next to these muscles.
If, for example, you do physical exercises for the muscles of the arms and upper shoulder girdle, then you also nourish your heart! The organs are fed from the same arteries as the muscles located next to them. I hope that from now on you will be imbued with greater respect for physical exercises, and after reading the book to the last page, you will begin to perform these exercises with pleasure!
But the main thing is for you to understand now that with the power of the somatic nervous system, which nourishes the muscles, we can support our internal organs, despite the fact that they are under the jurisdiction of a completely different department of the nervous system - the autonomic one.
This is very important when the nutrition of these organs suffers due to disruptions in brain regulation. Osteochondrosis, for example, does not go away immediately, but the heart should always receive good nutrition.
So, we won’t talk any more about the benefits of therapeutic exercises. Everyone has already understood that reasonable, gentle training should become your daily routine. Doctors don’t talk about this, and it’s clear: they don’t have time, they’re treating diseases. And you and I want to stay healthy as long as you want. Again, we are not talking about sports training, but about reasonable, gentle exercises. This is a fundamental difference, and it is very important, since sport itself can lead to stress, here you cannot do without experienced sports doctors and trainers, but we don’t need that.
Autonomic nervous system
Now it's time to talk about the autonomic nervous system.
It is really responsible for the growth of the body, for receiving energy through the lungs and intestines, for blood circulation, and is connected with the rhythm of the heart. Again, she is in charge of bringing to life, implementing the stress regime, which is launched from the centers of the somatic nervous system for flight and fight.
But we just don’t run, because erosion in the intestines and stomach can appear, and neurodermatitis. But the nature of stress may be different, internal, so to speak. For example, after a traumatic brain injury. Like a damaged telephone: the “damaged” brain begins to give completely wrong commands.
But it is with signals emanating from internal organs that the autonomic nervous system works, regulating vascular tone and the movement of blood and lymph. Moreover, these signals are quiet, of small amplitude, and the brain, in which thoughts about where to get money are always spinning, is unlikely to hear them. Of course, this is a joke, but the science of maintaining the autonomic nervous system and its rational management came to us from the East, from China. This is the doctrine of meridians, biologically active points, as well as a wonderful healing method - acupuncture. Now let’s try to remember some parts of the autonomic nervous system: hypothalamus, pituitary gland, vagus nerve, nerve nuclei in the back of the head (head control), sacral nuclei (return blood to the heart), cardiac plexuses (providing a cardiac impulse), thoracic, celiac, lumbar nerves plexus.
The autonomic nervous system relies on three areas in the brain: the nuclei of the cranial nerves, especially the vagus nerve, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the pineal gland. The control organs of the autonomic nervous system are symmetrical: the left nuclei control the left organs, the right ones control the right ones.
Autonomic nervous system
to a very large extent depends on the volume of blood that circulates through the vessels, on the quality of the skull, spine, pelvis, on the condition of the throat, sinuses and forehead, lungs, and liver.
This nervous system has two subdivisions : sympathetic and parasympathetic
.
Sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
The sympathetic division, in the form of two trunks, runs on both sides of the spine. The left trunk nourishes the organs of the left side, the right – the right. The exceptions are the liver, stomach and heart; they are fed by both sympathetic trunks. Moreover, if the nerves of the spinal cord have protective sheaths, then the sympathetic trunks are “naked” and can literally be pinched and switched off.
The main part of the network of the autonomic nervous system is located in the organs, its nerve centers are removed from the bone case of the skull and spine, live and work in close proximity to the spine, skull, near arteries, veins, in the walls of organs, where, of course, both viruses and bacteria. Those nerve centers that are located in the central nervous system have common protections, the same for everyone: bone sheaths, the blood-brain barrier, and the peripheral centers protect themselves, individually, so to speak. The first is dangerous due to a concussion, and the second is due to flooding (inflammation in the organ disables the nerve plexus located in it).
Now let's digress a little. Just an interesting hypothesis. You must have heard about the mysterious Russian soul? We don’t know what it is, we just feel it. It is in this ability to feel what is not seen or heard that the Eastern mentality lies, and these are well-functioning meridians, biologically active points. Touch. As you remember, this is the autonomic nervous system. Western mentality is about animal analyzers, that is, the somatic nervous system: hearing, vision, smell.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Now remember: in a state of rest, the parasympathetic nervous system dominates. It constricts the pupil, slows the heart rate, dilates blood vessels, lowers blood pressure, enhances the secretion of glands and intestinal motility, and relaxes the sphincters. When stressed, the sympathetic nervous system comes into force, which dilates the pupil, increases the heart rate, constricts blood vessels, increases blood pressure, reduces the secretion of glands, slows down the peristalsis of the intestines and stomach, and contracts the sphincters.
The autonomic nervous system forms a number of plexuses: solar, pericardial, mesenteric, pelvic, which innervate the internal organs. Higher control is carried out from the nuclei of the hypothalamus, the limbicoreticular complex. Management is the integration of mental and somatic functions. By the way, during emotions of fear, anger, anger, the sympathetic nervous system is excited. Now it’s clear why your heart is pounding, your mouth is dry, your pupils are wide? If you need to empty the gallbladder, bladder and rectum, the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, but when blood sugar decreases, the sympathetic nervous system is activated. At the same time, it stimulates the adrenal glands, which release adrenaline into the blood, which, entering the liver, converts glycogen into glucose, and blood sugar levels normalize. The body's performance is directly related to the tone of the sympathetic nervous system: the higher it is, the more active a person is.
Now let's briefly return to the topic of stress. The stress mode is activated when there is a lack of resources to solve current problems in the environment and in the body itself. It occurs when demands are high or when one is aware of one’s troubles. Sometimes it is rage due to humiliation, sometimes it is the inability to achieve a goal. And the more significant this goal is, the greater the stress. Love, hunger, rivalry, as well as beliefs and the desire for comfort - these are all sources of stress, as well as inadequate reactions to signals from reality. This is called stupid behavior. The situation is assessed as hopeless, and the hypothalamus launches a stress program, whether you want this program or not.
And the resources for the survival program (this, by the way, is a huge expenditure of energy) are taken from the cells of the immune, digestive and reproductive systems. Have you probably encountered a situation where, after exams, students start to get sick, like during a flu epidemic? And these protective cells, which provided immunity, went into the energy cauldron of those who regarded passing exams as stressful. The body simply digested these cells to obtain additional energy.
When stressed, the organs that use insulin to absorb glucose from the blood suffer. When stressed, they remain hungry and without energy. And this is immunodeficiency, impotence, erosion of the gastrointestinal tract. If stress is chronic, then diseases of these organs occur.
Chronic stress is stress that is produced by the adrenal hormone cortisol. By the way, aggressiveness is also realized with the help of cortisol. And love.
How do we lose weight when we fall in love, you know? With the help of the stress hormone cortisol, which is also a catalyst for fat metabolism in the cell. Who would argue that love is a disease!
After stress, the liver and heart suffer. The volume of circulating blood decreases, and foci of inflammation appear. The blood becomes thick and does not “get through” into the capillaries. The cells experience cold, hunger and sadness. If you do nothing, you can get seriously ill.
Please limit your desires, tame your pride, fight not with others, but with yourself. Peace in your soul is your concern; maintain it, and it will save strength and strengthen the nervous system. God bless you!
What is the hypothalamus?
The lower part of the human brain is called the hypothalamus. The shape and structure do not have clearly defined boundaries, smoothly transitioning into the tissues of other brain regions.
Consisting of many small cell nuclear groups (to date, only thirty-two nuclear pairs have been studied), the hypothalamus generates impulses that reach other areas of the brain along special pathways. The formed nerve impulses work to control the respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems. It is from the uninterrupted operation of the hypothalamus that the body regulates the process of maintaining water-salt balance, normalizes body temperature, and during the hot season and with increased physical activity, active sweating occurs in order to cool the skin and prevent overheating.
In addition to transmitting nerve impulses, the hypothalamus produces releasing factors - hormonal substances. Thanks to their production in the postpartum period, the woman “starts” the production of milk in the glands; childbirth, due to hormonal changes, ensures full contractile movements of the uterus to move the fetus along the birth canal, etc.
The hypothalamus performs its function only due to the close relationship of this part of the brain with the pituitary gland, which is the main organ of the endocrine system and continuously links together the work of the two systems.
The hypothalamus is divided into several zones:
Trophotropic
Located in the near zones of the hypothalamus and maintaining a constant internal environment, it normalizes the functioning of the heart and blood vessels during the rest period, and removes decay products of human activity. The main effect occurs through the parasympathetic department. When this zone is stimulated, the production of sweat and saliva increases, the heart rate slows down, blood pressure decreases, etc.
Ergotropic
Responsible for the ability of the human body, regardless of age, to adapt to changing environmental conditions, carrying out adaptation of the body and implemented through the sympathetic department.
The result of the functioning of the ergotropic system and the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system on cardiac activity: blood pressure, blood glucose levels, increased heart rate, and respiratory function increase. The ergotropic zone is located in the posterior part of the hypothalamus.
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system controls:
- lacrimation;
- pupil enlargement/decrease;
- production of saliva.
It also affects the functioning of internal organs (bronchopulmonary system, cardiac muscle, gastrointestinal tract, etc.).
Instead of a preface
“All illnesses come from nerves!” Is this true or not? Exaggeration or sad reality? And what kind of diseases are these that are caused by nerves? For clarity, I will allow myself to cite one case from my medical practice.
I work in a clinic, where, as you know, in addition to local doctors, doctors of other specialties - “narrow specialists” - also see patients. This, by the way, is Western technology, when it is not a person who is treated, but his illness, and accordingly, each disease has its own specialist. But we are already accustomed to this and cannot even imagine how it could be otherwise.
So, one day a middle-aged man came to an appointment; after a conflict at work, a stomach ulcer opened up, a rash appeared on his hands, his blood pressure rose, and he couldn’t sleep at all! And instead of sleep, sadness appeared, and anxiety. His stomach was treated by a gastroenterologist, his skin rash by a dermatologist, and his blood pressure by a therapist. And everything would have been fine, as they say, but when the man remembered the conflict, everything was repeated again, and the doctors, sensing something was wrong, referred him to a psychotherapist.
It should be said that the human brain is designed like the most perfect computer; or rather, the computer is designed in a similar way to the nervous system. In the human body, the channels for inputting information are the eyes, ears, skin, there are receptors that react to the biochemical composition of the blood, etc. So, the brain reacts very sensitively to a word, and a rude word can cause a whole storm in the body, just like this happened in our case: the central nervous system responded to psychological stress with a powerful release of biologically active substances as its defense, and one of these substances was histamine, which caused stomach ulcers and neurodermatitis.
Moreover, with each memory of what happened, the brain reacted with a new release of the same active substances, as if it were not a simple memory, but a repeated event.
Yes, this is how our nervous system works: memories are as real to the brain as the events that gave rise to them. To help that man, it was necessary to influence the central nervous system, which triggered a defensive reaction in the form of the release of certain substances that acted on the stomach, and on the skin, and on blood pressure, and on sleep, and on mood, and acting like you understand, not in the most successful way. Which is what was done. Along with sadness, all other illnesses soon disappeared.
It turns out that the nervous system is really the head of everything? Of course, that's why she's a head! And you, of course, have experienced how much it hurts at least once in your life. The central nervous system is, of course, just a part of the nervous system, but without a doubt it is its main part. That is why it is so carefully packed by the skeletal system. And we will talk about this later.
So what needs to be done to maintain the health of our most advanced computer - the nervous system? Well, first of all, it should be said that what a person does not know, he does not own. Secondly, today any of us should have an idea of how the human body works. You need to rely on doctors, but do not forget that they treat diseases, and the science of health is different. And here everyone needs to work for themselves: no one can take responsibility for your own health for you.
Now is the time when doctors share with you, dear reader, all their knowledge and accumulated experience so that you take on the task of maintaining your own health. This is exactly what your humble servant, a psychotherapist, is going to do for you. I hope that this will be not only useful for you, but also interesting. Are you interesting to yourself?
You need to know your own body in order to help it, treat it with care, so that the problems of the body do not overshadow the abilities and needs of the soul for creativity and love. Therefore, do not consider it difficult to find out how the holy of holies of our body - the nervous system - works, how to avoid its breakdowns, and if they do happen, eliminate them. Together with the doctor. We're together right?
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work? Features and main differences
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, its structure is unique and individual for each person. The activity of the departments will largely depend on age and health status. The neural impulse moves in a strictly specified direction. This movement is based on a reflex arc in the form of a closed chain of neurons. The work of the departments can be seen using a clear example: receptors on the skin detect an irritant in the form of cold, transmit the received data along nerve fibers to the central nervous system, where it is analyzed and evaluated. After which it is these two main departments that make the decision on the impact on the emerging stimulus. In our example, this is a person’s need to warm himself so as not to get too cold and protect himself from the cold. The impulse is transmitted along the nerve endings to the central section, and from there to the peripheral, where the impact occurs as a result of the stimulus - the skin becomes “goosey”, active muscle contraction occurs, aimed at warming the whole body under the influence of cold.
Disorders and pathologies
The structure of the autonomic system as a whole is a complex plexus of nerve fibers that act together to maintain stability within the body. Therefore, even minor damage to one of the centers will negatively affect the innervation of internal organs as a whole. For example, with a high tone of the sympathetic nervous system, a huge amount of adrenal hormones constantly enters the blood of people, which provokes surges in blood pressure, tachycardia, sweating, hyperexcitation, and rapid exhaustion of strength. While lethargy and drowsiness, increased appetite and hypotension will be signs of disruption in the autonomic department.
Clinical signs of diseases of the peripheral nervous system are directly related to the level at which the nerve fiber is damaged and the cause - inflammation, infection, or injury, tumor process. Characteristic symptoms of inflammation are tissue swelling, pain, increased temperature, and movement disorders in the part of the body that the segment innervates. The specialist must take into account the possibility of irradiation of signs - their distance from the primary focus of the disease. For example, changes in the oculomotor nerve can be expressed in drooping eyelids, increased tear production, and difficulty moving the eyeball.
If the sympathetic nervous system suffers in the pelvic area, which is typical for children, then enuresis and intestinal obstruction are formed. Or problems with the reproductive system in adults. In case of injuries, the clinical picture will be dominated by tissue damage, bleeding, and subsequently paresis and paralysis.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for?
The human body tends to adapt to stimuli that surround us at almost every step. Moreover, adaptability in each specific case will look different and have the opposite character. For example, the summer heat would have an adverse effect on the human body, if not for its ability to cool down due to increased sweating; in the cold season, sweat production stops and the mechanism of maximum heat retention in the cells is activated. Therefore, the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are different and opposite, aimed at the body’s ability to turn on or off a certain “option” at a certain moment.
Principles of treatment
Suspicions of disorders of the sympathetic system or parasympathetic department must be confirmed by an examination by a neurologist, the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Only after assessing the general health of a person and identifying the causes of the disease, a specialist will select the optimal treatment regimen. If a tumor is diagnosed, it will be removed surgically or subjected to radiation or chemotherapy. To speed up rehabilitation after an injury, the doctor will prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, drugs that can accelerate regeneration, as well as means to prevent secondary infection.
If the sympathetic nervous structure suffers from an excess of hormones, the endocrinologist will select medications to change their concentration in the bloodstream. Additionally, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs with a calming effect are prescribed - lemon balm, chamomile, as well as mint and valerian. According to individual indications, they resort to the help of antidepressants, anticonvulsants or antipsychotics. The names, doses and duration of treatment are the prerogative of the neurologist. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable.
The sanatorium-resort treatment has proven itself to be excellent - mud therapy, hydrotherapy, hirudotherapy, radon baths. Complex effects from the inside - rest, proper nutrition, vitamins and from the outside - healing wraps with herbs, mud, baths with medicinal salt, bring all parts of the peripheral nervous system back to normal.
Differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, as a result of its work, activates different “effects”.
Sympathetic:
– dilation of the pupils when exposed to a stimulus (bright light or darkness), protrusion of the eyes;
– narrowing of blood vessels;
– decreased secretion of saliva, which acquires increased viscosity and thickness;
– increased frequency of contractions of the heart muscle;
– noticeable increase in blood pressure;
– rapid breathing;
– dilatation of the bronchi with a simultaneous decrease in excretory function;
– deterioration of intestinal function;
– spontaneous ejaculation or its stimulation;
- "goose pimples".
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system performs functions, consider them in the table:
| Eyes | Constriction of the pupil |
| Excretory function | Increased salivation. |
| Heart | Reducing blood pressure and reducing the number of heart beats. |
| Bronchopulmonary system | The amount of secretion in the bronchi increases, breathing becomes calm and measured, the bronchi narrow |
| Intestines | Peristalsis increases, spasmodic pain may appear |
| Digestive system | There is a noticeable increase in secretion production in the digestive gland |
| Genitourinary system | Spontaneously occurring stimulation of the clitoris in women and the onset of erection in men |
In general terms, the activity of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system leads to a general “excitation” of human organs and vital systems, intensifying their work due to the influence of irritating factors.
As can be seen from the data in the table, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems differ from each other in terms of the “options” they perform. However, despite all their differences, the autonomic nervous system - sympathetic and parasympathetic - are closely interconnected. However, some functions of the human body are subject to the influence of only the sympathetic department and vice versa. For example, only the sympathetic department is responsible for the work of blood vessels, glands that reproduce sweat, and the adrenal glands, while the parasympathetic department of the nervous system has no effect.
Functions
Nature has determined that the sympathetic department takes an active part in many important processes in the human body - especially the motor state. It is primarily assigned the role of mobilizing internal resources to overcome various obstacles. For example, it activates the sphincter of the iris, the pupil dilates, and the flow of incoming information increases.
When the sympathetic nervous system is excited, the bronchi expand to increase the supply of oxygen to the tissues, more blood flows to the heart, while at the periphery the arteries and veins become narrow - a redistribution of nutrients. At the same time, the stored blood is released from the spleen, as well as the breakdown of glycogen - the mobilization of additional energy sources. The digestive and urinary structures will be subject to oppression - the absorption of nutrients in the intestines slows down, the bladder tissue relaxes. All efforts of the body are aimed at maintaining high muscle activity.
The parasympathetic effect on cardiac activity will be expressed in the restoration of rhythm and contractions, normalization of blood regulation - blood pressure corresponds to the parameters familiar to a person. The respiratory system will be subject to correction - the bronchi narrow, hyperventilation stops, and the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream decreases. At the same time, motility in the intestinal loops increases - products are absorbed faster, and hollow organs are freed from contents - defecation, urination. Additionally, parasympathetic activity increases saliva secretion but reduces sweating.
The parasympathetic nervous system increases the tone of some organs, but decreases others.
In a person who has no health problems, does not suffer from nervous breakdowns, or anorexia, the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, despite their differences, work on the principle of balance. Normally, there is a slight predominance of one of the systems with a certain effect on the body.
The predominant activity of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system is called vagotonia, and the sympathetic part is called sympathicotonia.
Due to age-related changes occurring in the human body, the role of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system can change noticeably, reducing the performance of their functions.
Let’s say that in adolescence, the activity of all organs and systems is significantly increased than in senility. The functional significance of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems is different. For example, the activity of the sympathetic system is expressed by shine in the eyes, enlarged pupils, increased blood pressure, and a high probability of difficulty during bowel movements.
Structural units
The main centers of the vegetative system are localized:
- mesencephalic section - in the structures of the midbrain, from which they arise from the fiber of the oculomotor nerve;
- bulbar segment - in the tissues of the medulla oblongata, which is further represented by both the facial and vagus nerves, the glossopharyngeal nerve;
- thoracolumbar region - lumbar and thoracic ganglia in the spinal segments;
- sacral segment - in the sacral region, the parasympathetic nervous system innervates the pelvic organs.
The sympathetic division removes nerve fibers from the brain to the border segment - the paravertebral ganglia in the spinal cord area. It is called the symptomatic trunk because it contains several nodes, each of which is interconnected with individual organs through nerve plexuses. The transmission of impulses from nerve fibers to innervated tissue occurs through synapses - with the help of special biochemical compounds, sympathins.
The parasympathetic division, in addition to the intracranial central nuclei, is represented by:
- preganglionic neurons and fibers - lie as part of the cranial nerves;
- postagglionic neurons and fibers - pass to innervated structures;
- terminal nodes - located near intracavitary organs or directly in their tissues.
The peripheral nervous system, represented by two sections, is practically beyond conscious control and functions independently, maintaining the constancy of homeostasis.
Structure and types of the nervous system: structural classification
To simplify the structure of the nervous system, in medicine there are several classification options depending on the structure and functions performed. Thus, anatomically, the human nervous system can be divided into 2 broad groups:
- central (CNS), formed by the brain and spinal cord;
- peripheral (PNS), represented by nerve ganglia, endings and nerves themselves.
The basis of this classification is extremely simple: the central nervous system is a kind of connecting link in which the analysis of the incoming impulse and further regulation of the activity of organs and systems is carried out. And the PNS serves to transport the received signal from the receptors to the CNS and the subsequent activator, but from the CNS to the cells and tissues that will perform a specific action.
central nervous system
The central nervous system is a key component of the nervous system, because it is here that the main reflexes are formed. It consists of the spinal cord and brain, each of which is reliably protected from external influences by bone structures. Such thoughtful protection is necessary, since each part of the central nervous system performs vital functions, without which it is impossible to maintain health.
Spinal cord
This structure is contained within the spinal column. It is responsible for the simplest reflexes and involuntary reactions of the body to stimuli.
In addition, spinal cord neurons coordinate the activity of muscle tissue, which regulates defense mechanisms. For example, upon feeling an extremely hot temperature, a person involuntarily withdraws his palm, thereby protecting himself from a thermal burn. This is a typical reaction controlled by the spinal cord.
Brain
The human brain consists of several sections, each of which performs a number of physiological and psychological functions:
- The medulla oblongata is responsible for the vital functions of the body - digestion, respiration, blood movement through the vessels, etc. In addition, the nucleus of the vagus nerve is located here, which regulates the autonomic balance and psycho-emotional reaction. If the nucleus of the vagus nerve sends active impulses, a person’s vitality decreases, he becomes apathetic, melancholic and depressed. If the activity of impulses emanating from the core decreases, the psychological perception of the world changes to a more active and positive one.
- The cerebellum regulates the precision and coordination of movements.
- The midbrain is the main coordinator of muscle reflexes and tone. In addition, neurons regulated by this part of the central nervous system contribute to the adaptation of the sensory organs to external stimuli (for example, pupil accommodation at dusk).
- The diencephalon is formed by the thalamus and hypothalamus. The thalamus is the most important organ that analyzes incoming information. The hypothalamus regulates the emotional background and metabolic processes; there are centers responsible for the sensation of hunger, thirst, fatigue, thermoregulation, and sexual activity. Thanks to this, not only physiological processes are coordinated, but also many human habits, for example, the tendency to overeat, the perception of cold, etc.
- Cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is a key link in mental functions, including consciousness, speech, perception of information and its subsequent comprehension. The frontal lobe regulates motor activity, the parietal lobe is responsible for bodily sensations, the temporal lobe controls hearing, speech and other higher functions, and the occipital lobe contains the centers of visual perception.
Peripheral nervous system
The PNS provides interconnection between organs, tissues, cells and the central nervous system. Structurally, it is represented by the following morphofunctional units:
- Nerve fibers, which, depending on the functions performed, are motor, sensory and mixed. Motor nerves transmit information from the central nervous system to muscle fibers, sensitive nerves, on the contrary, help to perceive information received through the senses and transmit it to the central nervous system, and mixed nerves are involved to one degree or another in both processes.
- Nerve endings, which are also motor and sensory. Their function is no different from fiber structures with the only nuance - the nerve endings begin or, conversely, end the chain of impulses from the organs to the central nervous system and back.
- Nerve ganglia, or ganglia, are clusters of neurons outside the central nervous system. The spinal ganglia are responsible for transmitting information received from the external environment, and the autonomic ganglia are responsible for transmitting information about the state and activity of the internal organs and resources of the body.
In addition, all peripheral nerves are classified depending on their anatomical features. Based on this characteristic, there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves that coordinate the activity of the head and neck, and 31 pairs of spinal nerves that are responsible for the torso, upper and lower extremities, as well as internal organs located in the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
Cranial nerves originate from the brain. The basis of their activity is the perception of sensory impulses, as well as partial participation in respiratory, digestive and cardiac activity. The function of each pair of cranial nerves is presented in more detail in the table.
| No. | Name | Function |
| I | Olfactory | Responsible for the perception of various odors, transmitting nerve impulses from the olfactory organ to the corresponding center of the brain. |
| II | Visual | Regulates the perception of visual data by delivering impulses from the retina. |
| III | Oculomotor | Coordinates the movement of the eyeballs. |
| IV | Block | Along with the oculomotor pair of nerves, it takes part in the coordinated movement of the eyes. |
| V | Trigeminal | Responsible for sensory perception of the facial area, and also participates in the act of chewing food in the oral cavity. |
| VI | Abductor | Another nerve that regulates the movements of the eyeballs. |
| VII | Facial | The nerve that coordinates facial contractions of the facial muscles. In addition, this pair is also responsible for taste perception, transmitting signals from the papillae of the tongue to the brain center. |
| VIII | vestibulocochlear | This pair is responsible for the perception of sounds and the ability to maintain balance. |
| IX | Glossopharyngeal | Regulates the normal activity of the pharyngeal muscles and partially transmits taste sensations to the brain center. |
| X | Wandering | One of the most significant cranial nerves, the functionality of which determines the activity of internal organs located in the neck, chest and abdominal wall. These include the pharynx, larynx, lungs, heart muscle and digestive tract organs. |
| XI | Dorsal | Responsible for contractions of muscle fibers of the cervical and shoulder regions. |
| XII | Sublingual | Coordinates the activity of the tongue and partially forms speech skills. |
The activity of the spinal nerves is classified much more simply - each specific pair or complex of pairs is responsible for its assigned area of the body with the same name:
- cervical - 8 pairs,
- infants - 12 pairs,
- lumbar and sacral - 5 pairs respectively,
- coccygeal - 1 pair.
Each representative of this group belongs to mixed nerves, formed by two roots: sensory and motor. That is why the spinal nerves can both perceive an irritating effect, transmitting an impulse along the chain, and intensify activity in response to a message from the central nervous system.