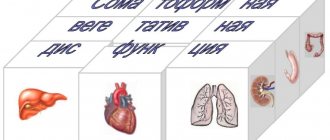
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system is a disorder in which there are symptoms of dysfunction of internal organs, but the results of all tests and studies show that the person is healthy. Diagnosis and treatment of the disorder is carried out by a psychotherapist.
Important
Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) as a term is not included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), but in general corresponds to the picture of a somatoform disorder of the VNS.
Factors that contribute to somatoform dysfunction of the ANS:
- predisposition of the nervous system and personality of the patient, heredity;
- unfavorable course of pregnancy and birth injuries;
- mental and physical stress, stressful situations;
- hormonal disorders, bad habits, infectious and somatic diseases.
Somatoform autonomic disorder causes constant anxiety and anxiety in the patient. The person cannot think about anything other than their symptoms. Performance decreases, it becomes difficult to communicate with others. All this significantly reduces the quality of life. An experienced specialist will understand the problem and provide the necessary assistance, help get rid of discomfort and return to normal life.
VD with somatoform disorders
With somatoform dysfunction, the patient sincerely considers his problem to be some kind of physical, somatic ailment. He doesn’t just think so, but actually “feels” pain, heaviness, discomfort in various parts and organs of the body. He looks for (but does not find) various serious illnesses. The patient undergoes the same examinations and tests many times. However, as a rule, there are no significant changes in them that would indicate a disruption in the functioning of the organs. Ultimately, an inattentive doctor may attribute the patient’s complaints to hypochondria.
However, a full diagnosis in this case should include a full examination of the ANS (autonomic nervous system): a thermal imager and analysis of heart rate variability. With VD, there are no disorders directly in the organs, but the functioning of the ANS, which controls blood circulation, metabolism, heat exchange, and most importantly, the activity of all internal organs, is disrupted. In this regard, a patient with VD may indeed experience such somatic symptoms.
General poor health, local discomfort in the organs, tension in one or another part of the spine during VD indicate functional stress in a specific vegetative node. A thermal imager image will show a deviation in the operation of the unit due to a failure of the temperature regime in this area. Since the ANS is responsible for heat exchange (thermoregulation), a thermal imager is one of the most effective ways to diagnose its problem areas.
Thus, when a person diagnosed with VD “hurts,” the “illness” is not imaginary. However, only a full diagnosis of the VNS will help to detect it, which should be carried out after a general examination has been carried out and a conditional diagnosis of “completely healthy” has been made. Next we will see what symptoms indicate the need to undergo such an examination.
Illness without illness, or Psychovegetative syndrome
A truly gentle spring sun will shine, and gloomy people with a pained expression on their faces appear one after another in the neurologist’s office...
Many symptoms, no disease
These people are usually brought to the doctor by vegetative symptoms, which, with all their diversity, make up a completely characteristic set in the patient’s card:
- cardiovascular system:
rapid heartbeat, tachycardia, extrasystole, discomfort or pain in the chest, fluctuations in blood pressure, lightheadedness, hot or cold flashes, sweating, cold and wet palms; - respiratory system:
feeling of a lump in the throat, “failure” or lack of air, shortness of breath, uneven breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation; - nervous system
(pseudo-neurological symptoms): dizziness, headaches, lightheadedness, tremors, muscle twitching, shuddering, paresthesia (unpleasant sensations in the skin), muscle tension and pain, sleep disturbances; chills and causeless low-grade fevers (slight increase in temperature); - gastrointestinal system:
nausea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, flatulence, appetite disturbances; - genitourinary system:
frequent urination, decreased libido, impotence.
And all this against the backdrop of a general poor condition:
- the patient is tired and tired, irritable and weak at the same time, suffers from weakness combined with motor restlessness and fussiness, inability to relax, muscle stiffness and tension in the body;
- suffers from impatience and loss of self-control, restlessness and inability to concentrate physically and mentally, memory deteriorates, and it is impossible to learn new things;
- sleep is disturbed, there are difficulties falling asleep and waking up;
- low mood, depression, tearfulness and tearfulness, loss of appetite, anxiety or guilt, a feeling of hopelessness;
- Anxieties and fears worsen.
Surprisingly, with such an abundance of symptoms, making a diagnosis is not at all easy...
Elusive diagnosis
In the diagnosis from the therapist (who carefully searched for at least some specific disease in this subject, but did not find it), one can see such terrible words as “asthenic syndrome”, “neurocirculatory” or “vegetative-vascular dystonia”, “chronic fatigue syndrome”...
Moreover, usually the patients themselves see these words not for the first time, because the described problems have bothered them since childhood. Concerned about the health of their weak and pale children, parents drag them to the “luminaries of medicine” and do a bunch of examinations. Doctors call this "diagnostic panic."
Causes of the disease
Photo: freepik.com
- What causes this failure?
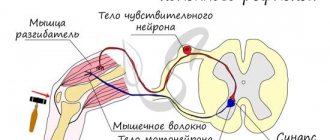
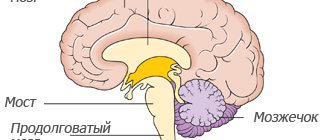
As a rule, this occurs due to systematic overstrain of the nervous system. It can be triggered by various factors: severe stress, illness, injury, alcohol abuse, etc. Overload of brain cells is automatically transmitted to the structures of the spinal cord, and from there along the autonomic nerves to the autonomic nodes. Autonomic ganglia are clusters of nerve cells on the side of the spinal column.
— What are vegetative nodes responsible for?
Each vegetative node has its own sphere of activity, which is called a metamer. In this territory, he controls all blood vessels (constricts and expands them depending on external circumstances), tissue nutrition, and their thermoregulation. It is also important that the activity of those organs of the human body that are associated with them depends on the work of the vegetative nodes.
— What happens when the vegetative node is tense?
If the vegetative nodes are overly excited, this can lead to a malfunction in their functioning. I think you have noticed that each person describes a situation of severe stress in his own way: someone’s heartbeat quickens, someone’s “throat catches,” someone’s “stomach cramps.” This means that those vegetative nodes in the body that are responsible for the activity of the corresponding organs are weakened.
— It turns out that those who say that all diseases are caused by nerves are right?
Not all, but very many. Imagine a person living in constant stress. He regularly feels that his heartbeat is uneven. He goes to the doctor to check what is wrong, but the examination shows that the heart is absolutely healthy. Both the doctor and the patient simply do not realize that the problem is not with the heart, but with the autonomic node, which is responsible for cardiac activity.
Horner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome is a neurotic syndrome, a combination of 3 symptoms that arise from disorders of the sympathetic nervous system in the neck area. The sympathetic nervous system is a set of nerves and nerve ganglia that regulate certain functions of the body that do not depend on the will of a person. The cervical sympathetic system also controls the eyes.
Causes
There are many causes of cervical sympathetic nerve damage. In addition to neck injuries, some locally growing tumors are involved in the genesis, such as thyroid and lung cancer growing in the upper lobe of the lung (Pancoast tumor). Symptoms consistent with Horner syndrome may also occur with disorders such as:
- multiple sclerosis;
- spinal cord damage due to syringomyelia;
- thrombosis of the cavernous canal;
- migraine (temporary).
Manifestations
The most common signs of sympathetic damage:
- constriction of the pupil (miosis);
- drooping eyelid (ptosis);
- visible slight recession of the eye into the orbital fossa (enophthalmos).
The most noticeable constriction of one pupil. There may also be facial redness on the affected side. This phenomenon is caused by the dilation of subcutaneous blood vessels in this area of the skin.
Treatment
A patient with Horner's syndrome should be examined by a neurologist; As part of the diagnosis, it is important to exclude brain disease (CT or MRI), compression of the nerve structures in the neck (ultrasound, CT).
Treatment of the syndrome depends on the underlying disease. If the disease is treatable and the nerve damage is not irreversible, the condition can be corrected through strengthening techniques and medications.
Causes of the disorder.
A single cause of ANS dysfunction has not yet been discovered. But the danger of earning it is simply enormous. To understand why the diagnosis of “nervous system disorder” is being made more and more often today, just read the list of possible root causes:
- Genetic predisposition, heredity.
- Difficult pregnancy, birth trauma.
- Poor nutrition, overeating.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Workaholism, chronic stress.
- Low self-esteem, excellent student syndrome.
- Hormonal imbalance, age-related disorders.
- Bad habits (smoking, alcoholism).
- Head injuries.
- Self-medication, drug abuse.
- Allergy, chronic infection.
- Mental, physical, mental stress.
According to statistics, manifestations of autonomic dysfunction make themselves felt already in adolescence and are much more common than colds. In men, the disease is diagnosed two times less often than in women. But this is only because women monitor their health more carefully and seek medical help more often.
Autonomic dystonia syndrome
Autonomic dystonia syndrome is all forms of disturbance of autonomic regulation, most often secondary manifestations of various pathologies.
There are 3 forms of SVD:
- psychovegetative – a feeling of tightness in the chest, changes in heartbeat, stomach pain, frequent vomiting, headache, dizziness, neuralgia of various locations, problems with urination, increased sweating, changes in the menstrual cycle, feeling cold;
- peripheral autonomic failure syndrome - (see autonomic failure);
- angiotrophalgic - vascular (marbling of the skin, redness, pallor, cyanosis, feeling of numbness, tingling), trophic (peeling and thinning of the skin, spots of pigmentation or depigmentation, ulcers, more often in the area of the hands and feet, brittle nails) and painful manifestations (paroxysmal prolonged pain , having a shooting, aching, burning, tingling, etc. character.
The source of all diseases
It often happens that a person feels sick, goes to doctors, does many examinations, but no one can diagnose him.
Why is this happening? As medical practice shows, the symptoms of various diseases often hide one thing - vegetative dystonia. Many people have heard about this disease, but few know anything specific. Photo: kuprevich / freepik.com
We talked about why vegetative dystonia is dangerous, how to identify it and how to treat it with Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category, medical director Alexander Ivanovich Belenko .
Complex regional pain syndrome
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a term used to describe a variety of regionally localized pain conditions that are primarily the result of trauma. They are characterized by clinical changes with a maximum distance from the primary affected area.
Manifestations
The process of SRPS is divided into 3 stages, each of which has its own clinical picture.
Acute stage (decreased sympathetic activity):
- increased blood circulation;
- temperature increase;
- sweating;
- acceleration of body hair and nail growth;
- local swelling;
- redness;
- decreased mobility.
Dystrophic stage (increased sympathetic activity):
- decreased blood circulation and skin temperature;
- slower hair growth, brittle nails;
- expansion of edema;
- more pronounced limitation of range of motion;
- spotted osteoporosis.
Atrophic phase (irreversible):
- deepening tissue changes;
- damage to all tissues, leading to irreversible disruption of the configuration and position of the joints;
- joint deformities with severe mobility impairment;
- necrosis.
Causes
This dysfunction of the nervous system has both external and internal causes.
External factors:
- injuries (skeleton, soft tissues, nerves);
- operations;
- burns;
- frostbite;
- overload of muscles and ligaments;
- inappropriate and painful treatment methods (tight cast, painful rehabilitation, incorrectly prescribed physical therapy), especially in a child.
Internal factors:
- inflammation (nonspecific, specific);
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- tumor hyperemia;
- barbiturate intoxication;
- anti-tuberculosis therapy.
Treatment
Treatment of SRPS should be comprehensive, including regimen measures, rehabilitation, physical therapy, pharmacotherapy and invasive means. Treatment of advanced disease always requires a specialized approach in the field of neurology. Only stages 1-2 of the disease have a good prognosis (hope for a positive functional result).
The basic principle is pain relief with analgesics and physical means. The affected segment should not be overloaded even during rehabilitation.
Today there are no generally accepted criteria for the treatment of this serious disease based on medical evidence. This reflects the fact that only a few randomized treatment trials have been published in this area to date.
Treatment and rehabilitation
Healing energy of light
— Alexander Ivanovich, but autonomic dystonia is manifested not only by heart problems?
Exactly. I always tell my patients: “You don’t have several diseases, but one, it just manifests itself in different ways.” In general, modern medicine lacks an integrated approach to treatment. Some doctors deal with heart problems, others with digestive problems, and still others with problems with the nervous system. But very often they treat only external symptoms, not realizing that all these problems are interconnected.
Many doctors do not like patients with such diverse manifestations of the disease, they consider them almost malingerers - after all, no serious violations of the relevant organs can be found! As a result, people suffer for years and go from doctor to doctor, but no one helps them.
- What should they do then?
We have developed our own method for treating vegetative dystonia, which has proven its effectiveness over many years of practice. Our main task is to ensure that the body’s nervous system receives an impetus for self-healing. As our medical experience shows, such an impulse that stimulates the body is light. Under natural conditions, photons of light participate in physiological reactions within the body, passing from the eyes to the hypothalamus, the main autonomic center of the brain. Academician Bekhterev established in 1916 that by exposure to light of different wavelengths, disorders of the nervous system can be effectively treated.
— What wavelength is needed to treat vegetative dystonia?
Each wavelength has a different color, so for example, blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light. Moreover, the therapeutic effect of light on the body directly depends on the wavelength. Modern light therapy devices are divided into two types. The first type is laser therapy devices. Which allow you to receive light of a given wavelength. It must be supplied to the body at a certain frequency corresponding to the fluctuations of vegetative structures. We determine this frequency using the cardiorhythmography method. It turns out that during therapy we supply light taking into account the physiological rhythms of the autonomic nervous system.
Recently, new light therapy devices have appeared that use high-power LEDs, which also emit light of a given wavelength.
— How does light influence the body?
There are two main methods. In the first case, the light is directed to the area where problem points were identified during thermal imaging diagnostics. We connect the emitter, set the power, frequency and time of exposure to light. In the second case, we carry out the method of intravenous photolaser therapy, that is, we actually introduce red and blue light into the vein using a special light guide. This light affects the vessel wall and blood cells, giving them additional energy, red blood cells are enriched with oxygen, and vascular tone is restored. I should note that this method has practically no side effects.
— How long should such therapy last?
We provide IV treatments of 10 to 15 minutes, although they typically last twice as long around the world. The fact is that we have developed a technique for the combined effects of local and intravenous laser: the total session time is reduced and the efficiency is increased. Typically, a course of treatment consists of ten such sessions.
Recovery process
— After this, the work of the autonomic system is restored?
Yes. It is very important that recovery occurs according to the universal rules of self-healing of the body, laid down by nature itself. The body goes through several stages of recovery: at some point there will be drowsiness and lethargy, at some point there will definitely be an exacerbation of symptoms. There is no need to be afraid of this. This is not a complication of treatment, but one of the important stages of recovery. We are talking about the sacrament of recovery.
— How long does the recovery process take?
The results of a ten-day course of treatment can be judged no earlier than after 2.5-3 months. After the end of the sessions, recovery continues, the person feels that healing processes are taking place in his body. In most cases, one course of treatment is sufficient, but in particularly advanced cases a repeat course may be required.