With sharp pain, the body signals the presence of a pathological process that needs to be eliminated. Quite often there are complaints of unpleasant sensations in the ear or nose that arise unexpectedly and seemingly for no reason. It is important to establish the causes of this phenomenon as soon as possible and begin full-fledged therapy, which will avoid complications.
The appearance of pain, if its cause is unknown, cannot be ignored. Often these sensations are the very first signal of illness. If you pay attention to them in a timely manner, you can eliminate health problems at the very beginning. Treatment in such a situation turns out to be much simpler and shorter. It is also worth remembering that if the disease starts, then its treatment will require spending significantly more money.
The relationship between nose and head pain
The nose is one of the sections of the respiratory system. It consists of several departments interconnected. If diseases occur on the visible part of the nose, they are easy to diagnose. However, nasal pain can be caused by damage to the internal parts that are located inside the skull. To understand why the nose hurts and radiates to the head, it is worth familiarizing yourself with its structure.
- The outer nose is the visible part. Its shape is formed by cartilage and several bones, as well as facial muscles. This is the first section into which the inhaled air penetrates, so it is initially purified from small particles and microorganisms.
- The nasal cavity is an expansion formed by bones and cartilage. Its posterior part narrows and passes into the nasopharynx.
- Paranasal sinuses (paranasal sinuses) are additional cavities that are located on opposite sides of the nasal cavity. There are anterior and posterior sinuses.
All parts of the nose are covered with mucous membrane. It is continuous, contains nerves and vessels, and connects to the epithelial layer of the oropharynx. The nasal mucosa has a distinctive feature - it contains olfactory receptors, with the help of which the nervous system is able to distinguish odors. In addition, it is the first barrier against viruses and bacteria that enter the body with inhaled air and can cause infectious diseases of the respiratory system.
Diseases that cause nasal congestion and discomfort reduce the supply of oxygen to the lower respiratory system. This causes insufficient nutrition of tissues, especially brain cells. Most colds are accompanied by a headache, which occurs due to respiratory failure. In addition, colds are accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane, inflammatory processes, and increased formation of exudate.
Diagnostics
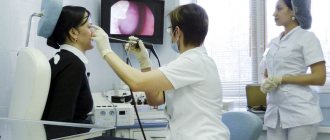
For pain in the nose, a visit to an otolaryngologist is indicated. The doctor receives information valuable for making a diagnosis when collecting complaints, visual examination and palpation of the paranasal area, assessing the amount and nature of discharge. A diagnostic search in otolaryngology requires instrumental or laboratory research methods, the most informative of which are:
- Rhinoscopy.
When examining the nasal passages, pay attention to the color and presence of swelling of the mucous membrane, atypical growths or foreign bodies, and deformation of the nasal septum. To clarify the diagnosis, a nasal endoscopy is performed using modern equipment. - Radiography.
An X-ray of the nasal bones and paranasal sinuses is the standard method for identifying sinusitis, which is visualized as darkening and narrowing of the affected sinus. In case of traumatic injury, an X-ray or computed tomography of the facial skeleton is additionally performed. - Bacteriological research
. If there are signs of inflammation, the release of cloudy mucus or pus when sneezing, a smear test for microflora is required. When a boil is detected, a smear is taken from the top of the pustule to diagnose the type of bacterial flora and determine its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. - Lab tests
. A clinical blood test shows nonspecific signs of inflammation (leukocytosis with a shift to the left, increased ESR); with massive nosebleeds, a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells is possible. Blood biochemistry is done in case of severe intoxication, for example, with an extensive burn complicated by a purulent process.
If the doctor suspects malignant transformation of cells, an endoscopic biopsy of the formation is performed, followed by histological examination. In case of multiple injuries to the bones of the skull and nose, the patient requires examination by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. If the pathological process affects the organ of vision, an ophthalmologist is involved in the diagnostic search.
For nasal pain, consultation with an otolaryngologist is indicated.
What can hurt your nose?
The most common cause of nasal pain is inflammatory reactions . They occur in response to the penetration of pathogenic microflora or mechanical damage. Inflammation can begin in any area, but often spreads to adjacent areas and affects several structures simultaneously. It often begins on the mucous membrane, as this is where the immune system's initial fight against viruses and bacteria occurs. Then the process can spread to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, cartilage tissue, blood vessels and nerves, paranasal sinuses, and nasopharynx.
Causes of pain in the nose and head
Pain in the nose that radiates to the head is the result of a number of pathological processes. They can be associated with internal or external factors that cause inflammation of the nasal structures or disruption of their anatomical integrity. Based on the exact location of the painful focus, its cause can be assumed. According to the mechanism of development, several main groups of diseases are distinguished:
- inflammatory processes - often occur with viral and bacterial diseases, but can also be associated with autoimmune processes and allergic reactions;
- injuries - accompanied by mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, skin and subcutaneous tissue, as well as cartilage tissue and other structures;
- Poor circulation in certain areas of the nose or nasopharynx is a less common cause of nasal pain and is associated with aseptic cell necrosis (death without the participation of pathogenic microflora).
Another classification distinguishes several groups of causes, depending on the location of the main cause of nasal pain. These include:
- diseases of the external nose - often represent damage to the skin and subcutaneous tissue (furuncle, carbuncle, erysipelas, eczema);
- diseases of the inner nose - can affect both the mucous membrane and bone and cartilage tissue, and also occur due to the ingress of foreign objects and injury to internal structures;
- diseases of the paranasal sinuses - represent a separate group of diseases that involve infection and inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- diseases that can simultaneously affect several structures of the nose - these include both viral and catarrhal rhinitis, as well as more dangerous pathologies (tuberculosis, granulomatosis).
It is important to determine the primary cause of nasal pain in order to select an effective treatment regimen. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain will make an accurate diagnosis in a short time, based on the results of the examination. Treatment tactics will differ for injuries, infectious diseases, allergic and autoimmune processes.
Rhinitis
One of the most common reasons why the nose and head hurt is rhinitis, or runny nose, inflammation of the nasal mucosa. It is a symptom of most colds caused by viruses and bacteria. Pathogenic microflora penetrates the nasal mucosa, where the main fight of the immune system against infection occurs. The process is accompanied by inflammation, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, and increased secretion of exudate.
The main symptoms of rhinitis include:
- runny nose, nasal congestion – excessive exudation makes breathing difficult;
- pain in the nose - more often they are concentrated at the site of inflammation;
- headaches - occur due to difficulties with breathing, as well as as a result of deterioration in general well-being;
- itching and burning in the nose.
Treatment for rhinitis depends on its cause. If the disease is caused by a viral infection, it is important to strengthen the immune system and provide the patient with bed rest. To make breathing easier, the doctor will select medications in the form of nasal drops or spray. They contain anti-inflammatory and antiviral components, as well as substances that constrict blood vessels and reduce the appearance of a runny nose.
Sinusitis
Diseases of the paranasal sinuses can occur independently or as a complication of colds. Normally, paranasal sinuses are aseptic formations in which there is no pathogenic microflora. If viruses or bacteria penetrate the mucous membrane of the sinuses, inflammatory processes begin. The danger of the disease is that normally there is no fluid in the sinuses, so draining the exudate is difficult. The cavities can be filled with liquid contents or pus, depending on the cause and type of inflammation.
There are several main types of sinusitis, which develop in different paranasal sinuses:
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses. They are located to the left and right of the nasal cavity and connect to it. Sinusitis is the most common form of sinusitis, accompanied by pain in the nose, bridge of the nose and head.
- Frontitis is inflammation of the frontal sinuses. They are located above the nasal cavity, in the thickness of the frontal bone. They are paired, but connected to each other by a common partition. Frontal sinusitis is diagnosed less frequently than sinusitis, but is also a common type of sinusitis.
- Sphenoiditis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinuses, a rare pathology. These sinuses belong to the posterior ones and are located in the thickness of the sphenoid bone. Their lower wall is the upper arch of the inner nose. Despite the fact that sphenoiditis occurs rarely, it is considered a dangerous disease. This is due to the deep location of the sinuses, the difficulty of accessing them and difficult drainage of fluid.
- Ethmoiditis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the ethmoid bone. Their number is not constant, in different people it can range from 8 to 10. The sinuses are cells of the ethmoid bone. Ethmoiditis rarely develops as an independent disease; it often accompanies other forms of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
A lingering runny nose, pain in the head and bridge of the nose, behind the eyes often indicates the onset of sinusitis. Other inflammatory diseases of the sinuses are diagnosed less frequently. It is useful to know about one characteristic symptom of sinusitis, with which the disease can be recognized even at home. To do this, you need to bend over sharply and lower your head to the ground. If at the same time acute pain begins in the nose and head, in the forehead and bridge of the nose, inflammation of the maxillary sinus can be assumed.
Treatment of sinusitis is prescribed individually. The most common method is nasal rinsing combined with a course of antibiotics. These drugs destroy bacterial microflora, thereby eliminating the symptoms of purulent inflammation. However, in acute forms of sinusitis, drainage of the maxillary sinuses may be necessary. The procedure consists of puncturing them, removing purulent contents and treating the mucous membrane with antiseptic solutions.
Injuries
One of the causes of pain in the nose and head is injury . Nasal fractures, damage to the nasal septum and other factors lead to disruption of tissue integrity and hemorrhages, deterioration of blood supply and innervation of certain areas. Injuries to the internal structures of the nose can also be caused by foreign bodies entering the nasal passages. The process is dangerous, since pathogenic microflora multiply in damaged areas, tissue suppuration and necrosis occur. In addition, if recovery is not performed correctly, the patient may find it difficult to breathe even after a long time.
Treatment for injuries is prescribed based on the results of the examination. If the bones and cartilage remain intact, and only damage to the skin, subcutaneous tissue and mucous membranes is detected, it is important to regularly treat these areas with antiseptics. In case of displaced fractures, an operation is prescribed, during which the bone fragments are returned to the anatomically correct position. With proper rehabilitation, breathing returns to normal without consequences.
Inflammatory diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue can appear on both the outer and inner surfaces of the nose. They are often associated with the entry of pathogenic microflora and its reproduction in a favorable environment. In addition, inflammation develops as a result of microtraumas. There are several formations that can appear in different parts of the external nose, causing headaches and breathing problems.
- Furuncle - formed when the sebaceous gland is infected with staphylococci or streptococci. It is a small, painful raised area above the surface of the skin containing pus. Most often, boils appear on the skin, in the area of the tip or wings of the nose.
- A carbuncle is a larger formation that occurs when the sebaceous gland, one or more hair follicles are simultaneously infected. The process spreads to the skin, subcutaneous tissue and mucous membranes, causing their purulent melting. A carbuncle is a dense, painful formation of a red or bluish tint that causes acute pain and fever.
- Eczema is an allergic inflammation, but its exact cause has not been established. The skin of the tip and wings of the nose is often damaged. It becomes dry, turns red, cracks, ulcers and blisters filled with transparent aseptic content may appear on it. Due to a violation of its integrity, boils, carbuncles and other manifestations of skin suppuration may form in the affected areas.
- Erysipelas (erysipelas) is an infectious disease that affects the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It is caused by specific microorganisms, hemolytic streptococci. They cause inflammation, redness of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, as well as hardening of these structures. These areas are painful, and in many patients they are separated from the healthy skin of the nose by a noticeable ridge.
In infectious diseases, redness of the skin, swelling and an increase in local temperature are observed. Limited formations are less dangerous because the purulent contents are enclosed in a capsule. To get rid of them, a simple procedure is carried out in which the abscess is opened, cleaned and treated with antibiotic solutions. Diseases in which the pus is in a diffuse state require complex treatment using broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs.
Allergy
If your head and nose constantly hurt, or a chronic runny nose does not stop, this may be the first sign of an allergy. It is a pathological reaction of the immune system to various stimuli. If in a healthy person the immune factors react only to viruses and bacteria, then in an allergic person they react to any substances. Thus, dust and pollen, animal hair, household chemicals and dyes, and certain products often become allergens. When they enter the body, characteristic allergy symptoms appear:
- pressing headaches, dizziness;
- runny nose, difficulty breathing;
- deterioration in general health;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- irritation and redness of the skin, itching, burning and rash.
At the first symptoms of an allergy, it is important to determine what caused it. The easiest way is to track what new substances the patient has been in contact with recently. Allergy tests are considered the most accurate method. Concentrated allergens are injected under the skin in the forearm and the reaction is observed for several days. If inflammation develops at the injection site and a painful swelling appears, it can be argued that this substance is an allergen. Antihistamines are used for treatment, which suppress the immune system's reactions.
A specific type of allergy is autoimmune reactions . They arise in response to internal factors and the body’s own tissues. Manifestations of these processes also include headaches, inflammatory reactions, damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Treatment is selected individually, its main stages are reducing the sensitivity of the immune system and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Herpes
Herpes is a viral disease with a chronic course. It can cause various diseases, including damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Small blisters form in the nose area, the skin becomes red and inflamed, and an itching and burning sensation appears. The bubbles are located close to each other, in a limited space. They open on their own, leaving behind small ulcers.
The herpes virus is present in the body of most people, but occurs in a latent form. An exacerbation is caused by a decrease in immunity, and therefore may be associated with colds. Antiviral and restorative drugs are used to treat it. However, after recovery, immunity is not formed. In addition, the virus continues to be present in the body, so another exacerbation can occur at any time.
Other reasons
The exact cause of the pain in the nose, which radiates to the head, can only be determined as a result of a complete examination. If viral rhinitis remains the most common diagnosis, then diagnostics may also reveal more rare and dangerous pathologies. To identify them, it is important to pay attention to all the signs and carry out the necessary tests.
The examination may reveal the following abnormalities:
- dental diseases (caries, abnormal growth and position of teeth);
- tuberculosis is a chronic disease caused by mycobacteria, which manifests itself, among other things, in the destruction of nasal structures and acute pain in the head;
- granulomatosis is a systemic autoimmune disease in which normal tissues are destroyed and replaced by dense connective tissue;
- neoplasms - can be found in any area;
- abnormalities in the structure of the nose, often manifested by a deviated nasal septum and difficulty breathing.
When diagnosing, the doctor takes into account all possible options, but is guided by the data of the examination and questioning of the patient. You should not be afraid of dangerous diseases if your complaints include a runny nose and headaches.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
First aid for a burn to the nose is to rinse the affected area with cool water. In case of nasal bleeding, it is necessary to sit the patient down, slightly tilt his head down and apply ice wrapped in cloth to the bridge of the nose. If a boil forms, under no circumstances should you try to open it or squeeze it out. Effective and targeted treatment for nasal pain is carried out after determining its cause, so a person needs to see a doctor.
Conservative therapy
Pharmacological drugs that relieve nasal pain are selected based on the etiology of the disease. To treat sinusitis and purulent lesions of the nose, antibacterial therapy is carried out, which is selected taking into account the type and sensitivity of the pathogen. To make the patient feel better and improve nasal breathing, nasal decongestants in drops (naphazoline, xylometazoline) are used.
In case of traumatic injuries, severe pain is felt, for the relief of which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, narcotic analgesics, and local anesthetics are prescribed. Drug treatment for nasal burns includes infusion therapy aimed at detoxifying the body. Severe neurological pain requires the use of ganglion blockers, novocaine blockades or local administration of drugs using electrophoresis.
Surgery
The entry of large foreign bodies into the nasal passages is an indication for their endoscopic removal under local anesthesia. For young children, the procedure is usually performed under anesthesia, which simplifies the doctor’s work and prevents accidental injury to the baby’s nasal passages. In rare cases, when a foreign object is too large and cannot be manipulated endoscopically, the ENT surgeon resorts to surgery.
In case of injuries to the septum and nasal bones, reposition is performed under local anesthesia, and to eliminate old injuries (more than 10 days), rhinoplasty or septoplasty is necessary. In case of abscesses, prompt opening of the abscess and washing of the cavity with antiseptic solutions is required. To avoid possible complications, treatment of nasal boils also involves opening and draining the abscesses.
For large benign neoplasms that interfere with nasal breathing, their removal using an electrocoagulating loop, a radio knife, or using laser radiation is indicated. Large vascular neoplasias are excised after preliminary ligation of the artery so as not to provoke massive bleeding. In case of cancer, radical surgery is performed, supplemented by chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Diagnostic methods
Before starting treatment, the doctor will prescribe an examination that will determine the cause of pain and poor health. As a result of the examination, swelling, redness of the skin and mucous membranes of the nose, rash and other characteristic signs of a number of diseases can be detected. The patient needs to clarify when and under what conditions the first symptoms appeared. However, additional techniques will be required to make a final diagnosis.
- Rhinoscopy is one of the simplest procedures that allows the doctor to examine the internal structures of the nose using a mirror. To examine the anterior parts of the nose, it is enough to use a nasal speculum. It is wide and is used to assess the condition of the nasal turbinates and septum, as well as the mucous membrane. If necessary, the doctor uses a nasopharyngeal speculum. It is small, placed on a thin metal stick. Access to the tissues under study is carried out from the oropharynx.
- Endoscopy is a more invasive, but informative procedure. It is performed using an endoscope. It is a miniature camera on a thin, flexible tube that easily follows the movement of the nasal passages. Endoscopy allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the internal structures of the nose, identify injuries and neoplasms, and also take samples for biopsy.
- Diaphanoscopy is a method of examining the paranasal sinuses. It is performed in a dark room, with a special glowing lamp in the patient’s mouth. Normally, the sinuses are filled with air, so they are visible during diaphanoscopy. However, when they are filled with liquid or purulent contents, they become dark.
- Ultrasound diagnostics - prescribed for suspected sinusitis and frontal sinusitis. However, for most diseases of the inner nose, this technique is ineffective.
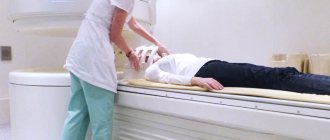
- CT, MRI - are used when injuries, neoplasms, or structural anomalies of the internal structures of the nose are suspected. The procedures are planned and prescribed when standard diagnostic methods are insufficiently effective.
The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the capabilities for full diagnostics. The doctors have high-quality, modern equipment and many years of experience in treating diseases of the nose and head. They can ensure that the examination will involve a minimum number of tests to help determine the cause of the pain and the stage of the disease.
Causes of severe ear pain
Severe ear pain occurs most often due to damage to the middle ear. In such a situation, inflammatory processes or mechanical tissue damage may occur. It is also impossible to exclude the presence of acoustic trauma, when damage to the ear occurs due to a very loud sound.
Mechanical injuries include punctures of the eardrum, the entry of caustic chemicals into the ear, and the penetration of a foreign body into the ear. In this case, the pain is especially severe, accompanied by hearing impairment. Other causes of ear pain are:
- disturbance of intra-ear pressure due to a failure in the process of its regulation through the auditory tube - in such a situation, sharp pain appears at the moment of take-off due to the plane’s sharp climb to altitude and rapid pressure drop, as well as during a rapid dive to depth;
- excessive sensitivity of the ear to cold - in this case there are no pathological changes, but as soon as a person leaves the warmth for the cold, he develops a sharp pain in the ear. The exact reason for this phenomenon has not been established. Presumably it is associated with an excessive number of nerve endings in the tissues of the auditory canal;
- otitis – most often develops otitis media, in which inflammation affects the middle ear. In most cases, the problem is diagnosed in a child, but an adult can also encounter it. Otitis externa, in which inflammation affects the skin of the ear canal, appears much less frequently. The usual cause of external otitis is water entering the ear from an open, standing body of water, which contains a large number of pathogenic bacteria;
- mastoiditis - with this disease, inflammation affects the mastoid process of the temporal bone. More often, this phenomenon occurs as a complication of untreated acute otitis media;
- tumors in the ear;
- inflammatory diseases of the temporomandibular joint - the pain is very severe and appears at the slightest movement of the jaw. It is often mistaken for ear pain due to the proximity of the nerve endings, since the joint is located behind the front wall of the ear;
- dental diseases and incorrectly selected dentures - due to the fact that the same third branch of the trigeminal nerve is responsible for the sensitivity of the teeth and ears, it is not uncommon for pain to appear in the ear as a result of problems in the oral cavity. She can be very harsh and strong;
- the presence of tumors in the throat - quite often it is a sharp pain in the ear when swallowing that is the first symptom of the disease. At the same time, ear pathologies are not detected by examination, and therefore a mandatory examination is required to identify a hidden tumor process. A person may not feel other manifestations of the tumor;
- sinusitis - due to a rapid increase in pressure in the ear sinuses, sharp pain in the ears often appears when the body position changes. In such a situation, especially severe pain is observed in the ears during frontal sinuses, when inflammation affects the frontal sinuses.
Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of ear pain. It is impossible to diagnose the problem on your own. Sharp pain in the ear, the cause of which has not been established, is an extremely serious signal and requires a full examination of the body.
Treatment of pain in the head and nose
Treatment tactics are selected individually, depending on the exact diagnosis and the nature of the disease. Most diseases can be treated with medication, but in some cases surgery is necessary. The course may include the following stages:
- taking antibiotics is a mandatory measure for bacterial diseases, purulent inflammation, injuries, sinusitis;
- supportive treatment, which includes anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor drugs, antipyretics and analgesics;
- antiviral drugs;
- surgical treatment - consists of opening and washing abscesses, boils, as well as sanitizing the paranasal sinuses for sinusitis.
Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain will select the most effective treatment regimen, which will include only the necessary steps. The drugs can be taken on schedule at home, only in some cases treatment in a hospital is indicated. The patient remains to follow all recommendations and regularly return for re-examination.
Prevention methods
Doctors have several recommendations on how to prevent the manifestation of the disease, which causes pain in the nose and head. They include the following activities:
- support for general immunity, including proper nutrition, sufficient vitamins, regular physical activity;
- tests for suspected allergies to identify the irritant and stop contact with it;
- timely diagnosis to identify sinusitis, neoplasms and other dangerous diseases that may progress over time.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of all types of headaches, including those associated with nasal diseases. To receive recommendations for treatment and prevention, all you need to do is make an appointment and undergo a full examination. Our center is equipped with modern tools for diagnostics and treatment procedures, and our doctors are experienced specialists in a narrow and broad profile.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 3 votes
Share article on social networks