Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system is a disease accompanied by signs of dysfunction of internal organs.
However, numerous examinations reject the presence of organic pathology: the condition is due to a psychogenic nature. Often the concept is replaced by the terms vegetative-vascular dystonia or neurocirculatory dystonia, which are not included in the official international medical classification. ICD-10 classifies somatoform dysfunction as a neurotic disorder, defining it with code F 45.3.
Formation mechanism
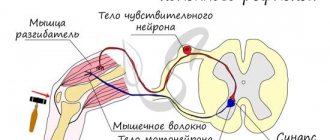
The autonomic nervous system is the main regulator of the activity of internal organs, blood vessels and glands. Therefore, this system is often called visceral. The ANS regulates the functioning of organs in accordance with changes in environmental conditions.
The autonomic system is represented by two departments: sympathetic and parasympathetic, which have mutually opposite effects:
- The sympathetic nervous system mobilizes the body's defense reactions, preparing it for vigorous activity. Intensifies metabolism, increases arousal;
- The parasympathetic nervous system restores wasted energy. Stabilizes the body's condition. Supports its work during sleep.
Both departments have opposite effects on internal organs.
| Organ | Sympathetic NS | Parasympathetic NS |
| Heart | Tachycardia, increased force of contractions | Bradycardia, decreased force of contractions |
| Arteries | Constriction of organs, dilation of muscle vessels | Dilates blood vessels of the genitals and brain; narrows the coronary and pulmonary arteries. |
| Intestines | Inhibits peristalsis and enzyme synthesis | Enhances peristalsis and enzyme synthesis |
| Pulmonary system | Bronchial dilatation, hyperventilation of the lungs | Narrowing of the bronchi, decreased ventilation |
| Bladder | Relaxation | Reduction |
| Salivary glands | Depresses work | Stimulates saliva secretion |
| Pupil | Expands | Narrows |
The opposite influence of systems with balanced work helps to balance the condition of the internal organs. The ANS is not subject to human will. For example, we cannot make the heart stop beating. But vegetative activity is subject to the influence of stress factors. This is easy to check. Remember how your heart begins to “rumble” when you are scared. The mouth becomes dry, intestinal colic appears, and the urge to urinate increases. This activates the sympathetic department, mobilizing the body's protective resources.
The fear went away - the heart calmed down, breathing returned to normal. This is the merit of parasympathetics.
Problems begin when the activities of both departments are separated. There are several reasons for this imbalance:
- heredity;
- hormonal changes;
- chronic stress;
- powerful simultaneous stress impact;
- overwork;
- chronic intoxication;
- alcohol abuse;
- radiation;
- action of high temperatures.
Disharmony in the activity of the ANS triggers the formation of somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Vegetative control over organs decreases. Their work is disrupted, giving rise to painful symptoms, but there are no organic changes. The main reason is stress.
Somatic symptoms are a way of experiencing stressful situations at a physiological level. This was also discussed by Adler, who developed the concept of the symbolic language of organs. The theory said: organ systems specifically mirror mental processes.
Causes of autonomic dysfunction syndrome
Usually this syndrome occurs as a result of constant overstrain of the nervous system. It can occur due to various factors, such as severe stress, illness, injury, and alcohol abuse. The overstrain of brain cells immediately passes into the structures of the spinal cord, then through the autonomic nerves into the autonomic nodes. Autonomic ganglia are clusters of nerve cells on the sides of the spine.
Autonomic disorders can be widespread, occurring in several organ systems at the same time, systemic, affecting one organ system, or local - when a certain area of the skin becomes red. Most often, vegetative manifestations involve the cardiovascular system, since it has the greatest psychological significance for a person.
General picture of the disorder
The main symptom of the disorder is the appearance of somatic symptoms affecting one or more organ systems.
The pathological manifestations are multiple, reminiscent of the clinical picture of a separate disease, but are characterized by blurriness, uncertainty, and rapid variability. A peculiarity of the presentation of complaints by patients is a special dramatism. Patients present symptoms emotionally vividly, exaggeratedly, using all kinds of epithets. They visit a huge number of doctors of various specialties and require examinations. When examinations refute the presence of physical pathology, the patient resists this news, is confident in the examination’s error and continues further vigorous diagnostic and treatment activities. Patients often spend years on “treatment” before a correct diagnosis is made.
Such people are quite sensitive to their own feelings, tend to exaggerate them, and often call an ambulance and are hospitalized. Numerous examinations and ineffective treatment fuel patients’ confidence in the presence of the disease. This situation causes distrust in individual specialists and medicine itself.
Let's sum it up
— Alexander Ivanovich, what could you advise patients with vegetative dystonia?
Imagine a person who has been feeling very bad for many years in a row, goes to doctors, but no medicine helps. In Soviet times, such patients were called “functional patients”; they were never taken seriously because examinations did not reveal any pathology. Our clinic can help these people understand the causes of their illnesses, and then help get rid of them. So, if no one can help you, come to our center!
Somatic symptoms of dysfunction
The main target organs of somatoform dysfunction are the heart, lungs, and digestive tract.
Frequent complaints are heart pain that is not clearly localized. Cardialgia is attributed to a different character: stabbing, cutting, aching, squeezing, pressing, “scorching.” The intensity is variable: from unpleasant to painful, depriving sleep. The pain can persist for several minutes or hours and affects the area of the shoulder blade, arm, and right side of the chest.
The cause of pain is fatigue, anxiety, and weather changes. These appear after physical activity. This circumstance is important to take into account when differentiating VNS DM from angina pectoris, characterized by the appearance of pain during physical activity.
Cardialgia is accompanied by anxiety, restlessness, weakness, and lethargy. There is a feeling of lack of air, internal trembling, tachycardia, increased sweating.
You may feel a change in rhythm. Tachycardia is usually limited to 90-140 beats per minute, but is situational. It is provoked by changes in body position, drinking strong tea, coffee, alcoholic beverages or smoking. It goes away quickly. Often there is a feeling of fading, interruptions in the heart.
Pressure during somatoform dysfunction rises to reasonable limits, changes many times during the day, at night and stabilizes in the morning.
An indicative symptom of the respiratory system is shortness of breath, caused by a state of emotional stress. There is a pressing sensation in the chest. It's hard to take a breath. The patient experiences shortness of breath. Experiencing this, a person suffering from somatoform dysfunction constantly ventilates the premises and feels discomfort when being in closed spaces.
Patients are accompanied by frequent, shallow breathing, interrupted by periodic deep sighs. Attacks of neurotic cough occur.
Changes in the digestive system are characterized by:
- epigastric pain that occurs regardless of food intake;
- difficulty swallowing;
- stool disorder. The patient suffers from constipation or diarrhea;
- poor appetite;
- belching, heartburn, vomiting;
- improper salivation.
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system may be accompanied by hiccups, which are intrusive and quite loud.
VNS diabetes provokes urinary disorders. The urge becomes more frequent, and there is a need to empty the bladder in the absence of a toilet. Difficulty urinating in public toilets is typical.
Other signs of the disorder include low-grade fever, joint pain, fatigue, and decreased performance. Patients often suffer from insomnia, they become irritable and excitable.
It should be noted that the symptoms of somatoform dystonia are provoked by stress, nervous strain and are not caused by circumstances that cause the manifestations of an actual disease.
Somatoform dysfunction of the ANS has the following features:
- multiplicity of symptoms;
- non-standard nature of the symptoms shown;
- strong emotional reaction;
- discrepancy with the results of objective diagnostics;
- too intense severity of symptoms or, conversely, lack of brightness of symptoms;
- lack of response to standard provoking factors;
- futility of somatotropic therapy.
Sources
- Draskau MK., Rosenmai AK., Scholze M., Pedersen M., Boberg J., Christiansen S., Svingen T. Human-relevant concentrations of the antifungal drug clotrimazole disrupts maternal and fetal steroid hormone profiles in rats. // Toxicol Appl Pharmacol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.115554; PMID:33910022
- Gürler EB., İriboz E., Kaya ÖTÇ., Türkaydin D., Öveçoğlu HS. Acute dental pain elevates salivary oxytocin in women: a risk factor during pregnancy. // Gen Dent - 2021 - Vol69 - N3 - p.73-77; PMID:33908883
- Pérez Corral O., Danet Danet A. . // Gac Sanit - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33906792
- Olmos-Ortiz A., Olivares-Huerta A., García-Quiroz J., Zariñán T., Chavira R., Zaga-Clavellina V., Avila E., Halhali A., Durand M., Larrea F., Díaz L. Placentas associated with female neonates from pregnancies complicated by urinary-tract infections have higher cAMP content and cytokines expression than males. // Am J Reprod Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.e13434; PMID:33905581
- Santymire RM., Adkin A., Bernier D., Hill B. Validating the use of fecal glucocorticoid metabolite analysis to assess the adrenocortical activity of the zoo-housed Sichuan takin (Budorcas taxicolor tibetana). // Zoo Biol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33905549
- Archiza B., Leahy MG., Kipp S., Sheel AW. An integrative approach to the pulmonary physiology of exercise: when does biological sex matter? // Eur J Appl Physiol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33903937
- Bartolone S., Mayrovitz HN. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy: Role of Baby's Sex on Itch Severity and Bile Acid Levels. // Cureus - 2021 - Vol13 - N3 - p.e14089; PMID:33903845
- Luo M., Jiang YL., Yao FX., Tian QJ. . // Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi - 2021 - Vol56 - N4 - p.251-256; PMID:33902236
- Song T.Y., Deng J., Fang F., Chen CH., Wang XH., Wang X., Zhuo XW., Dai LF., Wang HM., Tian XJ. . // Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi - 2021 - Vol59 - N5 - p.387-392; PMID:33902223
- Karim SI., Irfan F., Saad H., Alqhtani M., Alsharhan A., Alzhrani A., Alhawas F., Alatawi S., Alassiri M., MA Ahmed A. Men's knowledge, attitude, and barriers towards emergency contraception : A facility based cross-sectional study at King Saud University Medical City. // PLoS One - 2021 - Vol16 - N4 - p.e0249292; PMID:33901184
Associated mental disorders
Somatoform dysfunction is accompanied by other mental disorders.
The disease is often accompanied by phobic disorders . Characterized by fear of death, agoraphobia, cancerophobia, fear of blushing.
Panic attacks are an extremely common companion to the disorder. It is caused by a state of extreme fear and emotional stress. Characterized by an increase in the intensity of symptoms of the disease. It often provokes the development of depersonalization, fear of loss of consciousness, madness, and death.
Generalized anxiety disorder causes extreme tension, anxiety, and fears about the future. In addition to the characteristic manifestations of the disease, it contributes to the development of ideological and emotional phenomena. Worried about dizziness, weakness, feeling of lightheadedness. It is possible to develop derealization, when existing objects seem unreal, as well as depersonalization. The individual becomes hypersensitive, reacts sharply to extraneous stimuli, expecting danger.