Frequent emotional overload and repeated stress can often lead to the fact that the nervous system ceases to work stably. As a result, nervous disorders of varying severity occur. Often people try to wait until all the symptoms go away on their own, but often the wait-and-see tactic leads to a worsening of the situation and the development of the disease. The difficulty of contacting a specialist for such disorders is that several highly specialized doctors deal with the nervous system. To figure out which of them treats in each specific case, you need to find out what is within its competence.
Which specialists will help?
Dysfunctions of the nervous system can be caused by a variety of reasons and have completely different manifestations. Specialists dealing with such diseases are divided into 3 main categories: neurologist, psychotherapist and psychiatrist. All of them must have a diploma of higher medical education, after which they must complete an internship within 2 or 3 years and begin independent practice.
Neurologist
A neurologist is a specialist whose field of activity covers all areas of neurology: prevention, examination and influence on the central and peripheral parts of the nervous system. Neurology studies in detail the anatomy, functioning and treatment of the nervous system.
The term “neuropathologist,” which was actively used in Soviet medicine, also belongs to this category. Now it is considered outdated and incorrect, but sometimes out of habit it is used by individual doctors.
Psychotherapist
Psychotherapist - a doctor who deals with patients with mild or moderate mental disorders is called a psychotherapist. A prerequisite for his practice is a detailed study of psychotherapy.
The psychotherapist's field of activity is mental disorders caused by childhood traumas, severe stress, or due to genetic predisposition. As a rule, patients treated by this doctor do not have organic or anatomical brain injuries, but exhibit only psychological disorders.
The question often arises as to whether there are differences between a psychologist and a psychotherapist. There is a difference, and it lies in the fact that a psychologist does not have a higher medical education, and therefore can only advise patients, while a psychotherapist has the right to make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
Psychiatrist
The scope of his activity is almost the same as that of a psychotherapist, but the psychiatrist also works with cases of the highest severity. A doctor who has studied for 6 years at a medical university and spent 2 years in an internship or is engaged in the activities of a graduate student has the right to work as a psychiatrist.
If a psychotherapist’s treatment methods are predominantly based on speech, and medications are used only as an aid, then the psychiatrist primarily carries out drug treatment and active non-drug therapy. Such methods cause stimulation of brain activity.
Diagnosis and treatment
It will not be difficult for an experienced doctor - neurologist, psychiatrist or psychotherapist - to identify asthenic neurosis, separating it from other pathological disorders. Taking into account all of the above, he needs to exclude the presence of somatic diseases, oncology and organic lesions of the central nervous system in the patient.
The specialist will collect anamnesis and talk with the patient. In the case of classic symptoms with a predominant arousal reaction
A diagnosis of hypersthenic neurasthenia is made. If there are more inhibitory reactions, including drowsiness, then there is reason to believe that this is hyposthenic neurasthenia.
Comprehensive treatment of the disorder involves, first of all, normalizing the patient’s life, as well as the use of psychotherapy and medications.
It should be noted right away that you cannot “prescribe” medications for yourself, especially psychostimulants - they can lead to addiction and increased manifestations of the disorder.
The doctor selects medications based on the presence and severity of certain symptoms (a form of neurasthenia); the dose and duration of administration are prescribed individually for each patient. These are tonic or sedatives that normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system, tranquilizers. It is mandatory to include general strengthening, restorative body functions, metabolism-improving agents, as well as vitamins C and B, antioxidants, neurorubin, etc. Plant extracts won't hurt either.
Psychotherapy includes psychoanalysis, individual and group sessions, conversations with a psychotherapist, and trainings. This allows you to identify and eliminate the causes of the disorder, change the patient’s attitude towards them, gain skills in separating the main from the unimportant and the ability to enjoy life.
Autogenic training will teach self-education and self-hypnosis, and hypnosis will help normalize heartbeat, blood circulation, and muscle tone.
A disease such as neurasthenia does not require hospitalization. When conducting therapeutic and drug treatment, specialists usually give patients the following advice:
- change the environment, walk in the fresh air more often, have a good time, travel;
- take a vacation, don’t check your email, turn off your phone - get a good rest, do something you enjoy that brings you pleasure;
- reduce emotional stress that negatively affects the psyche;
- establish a daily routine with a clear schedule that allows enough time for rest and sleep;
- strengthen the immune system, introduce a balanced diet, take vitamins;
- restore autonomic function through massage, acupuncture, warm foot baths, hot aromatic baths.
A good option for treating neurasthenia is to use traditional methods, but before doing this, you should consult with your doctor. Among the most effective options that have a beneficial effect on the autonomic and central nervous systems, we can recommend the following:
- Motherwort decoction. A tablespoon of herb is poured into a glass of boiling water, kept in a water bath for a quarter of an hour, allowed to cool and filtered. Take for a month 3 times a day.
- Hawthorn decoction. Brew berries (1 tbsp) with boiling water (a glass), filter after 45 minutes.
- Melissa and mint tea. Brewed like regular tea, this drink is soothing and promotes good sleep.
- Valerian tincture alcohol - 30 drops added to a small amount of water and drunk before going to bed.
- Lavender bath. Dried inflorescences (200 g) are placed in boiling water (5 l) and simmered for 7 minutes on fire. The broth is filtered and poured into a bathtub filled with warm water. You need to lie in it for 20 minutes.
- General strengthening mixture with raspberries, calamus root, birch leaves, chicory, strawberries, rose hips, oregano.
Reasons for contacting
Depending on the health of a particular person, his temperament and the type of personal reactions, the symptoms of nervous disorders can be very individual. But there are a number of signs that are inherent in most cases:
- long-term sleep disturbance;
- increased irritability and neuroses;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- severe unreasonable anxiety;
- constant desire to sleep;
- a sharp decrease in ability to work and activity;
- absentmindedness;
- difficulty concentrating on a specific action or object;
- noticeable deterioration of short-term memory;
- obsessive thoughts;
- panic attacks.
Often all these signs do not add up to the overall picture and are ignored for a long time by a person who needs the help of a doctor. All of the above signs can be perceived as a change in mood, emotional exhaustion, moral fatigue, etc. But for a specialist, a combination of these signs will indicate a certain disease.
Over time, physical manifestations of the disease are added to the above conditions:
- dizziness;
- severe shortness of breath;
- neuralgia;
- feeling of strong heartbeat;
- difficulty swallowing and enlarged thyroid gland;
- digestive disorders (constipation or diarrhea, stomach pain, flatulence);
- lack of appetite;
- increased body temperature after stress;
- surges in blood pressure.
The most common symptom that accompanies most mental disorders is a severe headache that occurs periodically. In severe cases, it is combined with fainting.
Symptoms
Neurasthenia manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Excessive irritability even over trifles, short temper, anger, constant dissatisfaction.
- Impatience - the desire to get everything at once, the impossibility of waiting - it literally “kills”.
- Constant feeling of fatigue, weakness.
- Pain in the temples or a sensation of encircling, squeezing pain in the head.
- Lack of ability to concentrate and do one thing for a long time.
- Violation of the sequence of thoughts, general perception of the environment.
Speaking in more detail about the symptoms of asthenoneurotic syndrome, it is more correct to consider the disorder in phases, since the intensity of its manifestation gradually increases. But more often the disease stops at a certain phase, that is, its development does not occur, which is reflected in the diagnosis.
Hypersthenic (excitable) form
This is the initial stage of the disease, which is recorded most often. It is characterized by nervousness, irritability, and excitability.
The patient is unnerved by any, even quiet, sounds (creaking and light knocking of the door, whispering, clock ticking, dripping water, etc.), bright light, the presence of people nearby and their movement. The most insignificant reason causes an outburst of emotions, uncontrollable irritation or even anger. Without realizing the reasons for aggression, a person can insult or offend someone.
The patient is impatient, strives to do several things at once, fusses, but his performance leaves much to be desired. It is not weakness or rapid fatigue that is to blame for this, but a problem with concentration and constant distraction.
The sleep pattern is disrupted: the patient is lethargic during the day, and at night he falls asleep with difficulty and sleeps poorly, with nightmares, and often wakes up. Waking up happens either earlier than usual or later.
Constant headaches are called “neurasthenic helmet” - they are compressive and very debilitating. Pain when turning and tilting the head moves along the spine to the back. Mental or physical stress makes them more intense.
Irritable weakness (intermediate form)
This phase combines severe irritability with a rapid decrease in the body's resources. In principle, this is a reflection of the clinical essence of the disorder.
Attacks of irritation are the most intense, outbursts of anger instantly turn to a stream of tears, completely unusual for the individual. Such tearfulness arises from the patient’s inability to overcome overwhelming discontent. The mood changes instantly: sometimes gloom, sometimes joy.
The patient is often lethargic, he is not interested in anything, his appetite becomes worse or disappears altogether. Digestion suffers, which is reflected by diarrhea, constipation, belching, and heartburn. The heart rate increases, pulse and blood pressure fluctuate. The limbs become sluggish, instability and so-called floaters appear before the eyes, a rush of heat is replaced by chills, redness of the skin is replaced by pallor. Libido decreases and men may experience problems with erectile function. There may be a frequent urge to urinate.
Hyposthenic (inhibitory) form
At this stage, depression, weakness, gloom, and lethargy are especially pronounced. I don’t want to do anything, but I don’t feel anxiety or melancholy. The patient’s thoughts are focused only on his own unpleasant sensations in the body, and he, assuming that he has some kind of serious illness, turns to doctors, who, naturally, do not find it.
Very often, neurasthenia can be eliminated with good rest. But if this does not help and the disease has gone too far, then you will have to leave yourself in the hands of professionals.
Causes of nervous disorders
Most people believe that mental and neurological disorders are caused solely by nervous breakdowns and difficult emotional conditions. This is not true at all, the reasons may be:
- injuries resulting in damaged nerves (most often head injuries);
- acute or chronic hypoxia, leading to oxygen starvation of the brain and other tissues of the nervous system;
- osteochondrosis;
- prolonged overheating or hypothermia of the body (in this case, the degree of damage directly depends on the time of exposure to high or low temperatures);
- poisoning with neurotropic substances that selectively affect cells of the nervous system;
- factors that have an aggressive effect on the body - electric current, prolonged vibration, electromagnetic field;
- metabolic disorders with damage to the central or peripheral parts of the brain;
- suffered serious illnesses (most often of the endocrine system);
- hereditary factors - depression, bulimia or anorexia, schizophrenia, alcoholism, severe neuroses or Alzheimer's disease in one of the blood relatives;
- the presence of tumors in the body;
- inflammatory or parasitic diseases of the brain.
Why you shouldn’t bother yourself with such questions
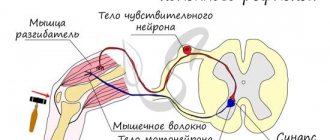
When we organized our clinic, we proceeded from the fact that our body is one system where everything is connected. The nervous system controls the entire body, it gives us movement, sensitivity, emotions, thinking and consciousness. And in diseases of the nervous system, manifestations will be in all areas: motor, sensitive, mental.
We gathered a team of psychiatrists, psychotherapists, neurologists and organized a hospital where we can fully provide assistance for mental disorders and neurological diseases, as well as for conditions where both of these areas have been affected by the disease. We help both children and elderly patients.
With us, in one place, you can undergo an examination and, if necessary, receive treatment for diseases of the mental, psychosomatic and neurological spheres. Our specialists: psychiatrists, psychotherapists, neurologists, psychologists, therapists, rehabilitation specialists.
The modern system of medical care has divided diseases of the nervous system into different areas. Psychiatry separately, psychotherapy separately, narcology separately, neurology separately, rehabilitation separately, hospitals separately, dispensaries and clinics separately, psychological assistance - in itself.
Our clinic successfully combines all these areas, so it can safely be called:
- neurological,
- psychotherapeutic,
- neurological, psychoneurological dispensary,
- hospital for crisis and borderline conditions,
- center for the treatment of mental illness, a place of psychological support,
- a children's psychiatric hospital, a clinic for the treatment of age-related changes in the nervous system,
- family clinic...
... and other and other names.
How to get an appointment
If the patient understands which doctor to contact, then this must be done as soon as possible. If the patient has doubts, then it is advisable to go to a therapist, who will identify a specialist.
In order to choose a qualified doctor, you need to pay attention to the following features:
- sufficient practical experience in the treatment of nervous disorders;
- an integrated approach to determining the patient’s condition;
- It is desirable to have scientific articles or works in the area that the patient is faced with;
- sufficient initial consultation time (at least 30 minutes).
At the appointment, the doctor will determine the further direction of the examination, if necessary. Having all the necessary data, he will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe drug or non-drug treatment. If necessary, the patient will be recommended a course of treatment in a hospital.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Insomnia and sclerosis
Sleep disorders can be associated with regular lack of sleep, depression, and a heavy work schedule. As a result of insomnia, fatigue, a feeling of weakness, nervousness, and decreased work activity are noted. Chronic insomnia can occur due to problems with metabolism, prolonged stress, and neurosis. If you can’t fall asleep after a hard day, you can take a moderate dose of sleeping pills. You can use this method for no more than 2 weeks, as it may become addictive.
For prevention purposes, you should follow the following rules:
- do not eat after 19.00;
- Avoid drinking alcohol and coffee in the evening;
- take a walk before bed, take a relaxing bath;
- drink a glass of warm milk with honey;
- fall asleep before midnight.
Sclerosis is not an independent disease, but is caused as a result of problems with blood flow, impaired metabolism, and age-related changes.
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis:
- memory impairment;
- rapid fatigue, decreased work activity;
- nervousness, anxiety;
- speech problems;
- hearing impairment;
- insomnia.
A person should pay attention to their diet, active pastime, and give up bad habits.
In the initial stages, you can take sedatives and vitamins.
How to get out of this state? Will it take a lot of time?
– If a person understands that he has recently lived and worked at an accelerated pace, then the logical first aid would be to slow down the pace, normalize the rest regime, take a short vacation, and have a proper diet with a predominance of fruits and vegetables and easily digestible foods.
A great addition can be yoga, meditation, relaxation, pleasant communication with loved ones and pets. And for each person, recovery time is very individual.
Reproduction of CityDog.by materials is possible only with the written permission of the editors. Details here.
Photo: heroine’s archive, unsplash.com.
Hysteria and depression
Mental illness is associated with a specific personality type. There are seizures, convulsive laughter, in addition to the manifestation of tears, nervousness and spontaneous behavior. It is more common among the fair sex. Such people try in every way to stand out from the crowd so that they will be noticed. They often create conflicts, are emotionally unbalanced, and experience sexual dissatisfaction.
Such a person needs a special approach and attention from others. Most often, hysteria appears in childhood as a result of improper upbringing. Parents should pay more attention to the development of their child, talk about his fears and experiences.
Depression is manifested by retarded mental activity, depression, weakness, and deep disappointment. Women are also more prone to this condition. There is a feeling of melancholy, anxiety, a feeling of uselessness, pessimism and indifference to what is happening. Appetite may disappear, insomnia and exhaustion may appear. The reasons may be related to personal experiences and grievances.
What is the difference between nervous exhaustion and a nervous breakdown?
– Nervous exhaustion is the price to pay for living a life of wear and tear. When responding to stress, especially if it is severe and prolonged, our body's resources are depleted, and in this sense we consider it as a process. That is, we “spend” to a greater extent than we recover.
Many people notice that when there is a surge of stress hormones, they “hold on well,” react quickly, and the body functions at “high speed.” And then, at the moment of relaxation, they get sick. This means that, unbeknownst to them, they spent more energy than they could afford. Such overload and its result - nervous exhaustion - are felt by a person as severe fatigue, lack of energy, asthenia.
A nervous breakdown may or may not be part of the stress response. If the stress is strong enough and long-lasting, but the person copes with it emotionally (feels that he has defeated the “enemy” or at least is winning), then there will be no breakdown, but nervous exhaustion is quite possible later.
We will see a “full negative set” if the stress is serious and there is no feeling of coping with it. Then, at the exit or even along the way, a nervous breakdown and at the same time exhaustion may occur.
Nervous exhaustion is dangerous primarily because it can affect the health of the whole organism. A malfunction will put a person out of action for an indefinite period. It is unknown which system will fail or require attention, it is unknown what resources will be needed to recover, and it is impossible to predict what social and emotional consequences may occur.
I don’t want to force the picture, because often people “get off” with several colds in a row and move on with their lives. But in any case, timely self-care will not harm anyone and will help maintain health.
SDVNS in children
Often, somatoform autonomic disorder appears in children at puberty, that is, during the period of maturation. This is due to a hormonal surge and intensive growth of the body.
The following factors can provoke the process:
- heredity;
- stress;
- mental, physical stress;
- infections;
- bad habits;
- surgical interventions;
- large body weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- staying at the computer for a long time.
The appearance of teenagers is typical. If sympathy predominates, then the skin of such children is moist and oily, with acne. She alternately turns red and pale. A bluish tint appears. Cold, with a marbled pattern called a vascular necklace. When pressed with a finger, the skin turns pale and red dermographism is observed.
When parasympathetics dominate, the skin is dry, with pink or white dermographism. These children have an increased appetite, but they do not gain weight.
The disorder is accompanied by a sudden rise in temperature under the influence of stress. A typical occurrence is fainting.
All characteristic changes in internal organs are present.
The psycho-emotional sphere is also undergoing changes. Such a child becomes distracted and nervous. He quickly gets tired, drowsiness and apathy appear, and his memory deteriorates.
In most cases, the course of the disease is stable. But periodically panic attacks and crises occur:
- sympatho-adrenal - accompanied by tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, headaches, thirst, chills and hyperthermia. Anxiety and feelings of fear develop;
- vagoinsular – migraine-like attacks, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal area. Hyperhidrosis, decreased blood pressure and fainting, slow heart rate, increased urine output, breathing disorders;
- mixed.
The attack can last up to several hours.
How can I tell if I'm having a nervous breakdown?
– Various sources include the following symptoms as neurotic manifestations of a “nervous breakdown”:
- increased emotional sensitivity, which was not there before, irritability, anxiety;
- feeling of helplessness, hopelessness, feeling small, weak, defective, wounded, bad;
- craving for a state of “oblivion” (you want to get drunk, fall asleep, “disconnect from life”);
- impulsive suicidal thoughts, acute desire to harm oneself;
- insomnia or, conversely, excessive drowsiness;
- complaints of cognitive failure (when it’s hard to think, remember, impossible to concentrate);
- a state of acute anxiety, panic, constant rapid heartbeat or frequent increase in heart rate;
- loss of interest in everyday activities, work, friends, hobbies, clothes, etc.;
- decreased or loss of sexual desire;
- loss of sense of humor;
- nervous and physical exhaustion, noticeable weight loss or gain;
- physical ailments, signs of decreased immunity,
- marked deterioration in social functioning, need for isolation;
- other individual reactions that were not there before with their negative subjective assessment.
Somatization and chronic somatoform pain disorder
Somatized dysfunction, in addition to organ manifestations, causes a decrease in the functioning of analyzers: vision, hearing, touch, smell. Coordination of movements is impaired: patients become clumsy and have an unsteady gait. Movement disorders manifest themselves in the form of paresis and paralysis.
They describe failures in the functioning of internal organs colorfully and with charm. For example, my head hurts, as if a hoop was put on it and was gradually being squeezed. Or your stomach is swollen like a balloon.
Unlike a hypochondriac, who expresses anxiety about his health, such a patient responds more rudely and persistently. He is convinced that he is sick. And if the doctor tries to hint at the psychogenic nature of the disorder, he screams and is indignant, rejecting what was said, and demands additional examination. This patient is constantly dissatisfied and complains.
The course of the disease is chronic, with wide variability of symptoms that persist for 2 years or more.
Often, a person, due to his anxiety and aggressiveness, experiences social maladjustment and family conflicts.
A pain disorder is distinguished by the presence of severe, debilitating pain that occurs for no reason. Usually it has a clear localization - the stomach, the heart. The pain characteristics do not change, there are no other symptoms.
During somatoform dysfunction, an undifferentiated disorder is also distinguished. With it, a person suffers all the typical symptoms of the disease, but it is not possible to classify them into any known group.