The perinatal period is the period from the 28th week of pregnancy to the 7th day after birth, inclusive. If during this period, as a result of exposure to various unfavorable factors, damage to the child’s brain occurs, accompanied by neurological symptoms, then such damage is called perinatal damage to the central nervous system or perinatal encephalopathy.
The concept of perinatal damage to the central nervous system combines several pathologies resulting from damage to brain cells in the perinatal period and leading to dysfunction. Damage to the central nervous system in the perinatal period can lead to the development of serious diseases later (cerebral palsy, delayed psychomotor and psycho-speech development, etc.).
Perinatal encephalopathy manifests itself as various disorders in motor development, impaired speech formation, and mental disorders.
Perinatal encephalopathy is a syndromic diagnosis and requires mandatory clarification. That is, it is necessary to examine the child in order to find out which specific departments are damaged and to what extent, and what functions this damage affects. A detailed examination will allow the doctor to prescribe adequate treatment and minimize the consequences of the damage.
Risk factors
The development of perinatal encephalopathy in the fetus and child can lead to
- chronic maternal intoxication and chronic diseases
- infectious diseases during pregnancy
- disorders of uteroplacental blood flow, placental abruption, fetoplacental insufficiency
- Umbilical cord entanglement
- maternal diseases associated with metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria, etc.)
- severe toxicosis;
- pathological course of labor, use of obstetric aid, weakness of labor, rapid labor
- prematurity;
- Fetal malformations
Consequences
The consequences and complications of central nervous system damage in a newborn child can be very serious, dangerous to health and life. They can be expressed as follows:
- severe forms of mental development;
- severe forms of motor development;
- cerebral palsy;
- epilepsy;
- neurological deficit.
Timely detection of the disease and proper therapy will help get rid of serious health problems and prevent complications from occurring.
(
2 ratings, average: 4.50 out of 5)
Symptoms, how PCNSL manifests itself
Perinatal encephalopathy is a very multifaceted disease. The following main clinical syndromes of PPCNSL are distinguished:
- Muscular dystonia is a pathological increase or decrease in muscle tone. Normally, all newborns have increased muscle tone of the flexors; in the process of growth and motor development, the flexor tone decreases, becoming normal. This transformation allows a newborn child to have the necessary set of protective reflexes, and during the process of growth, a decrease in flexor tone makes it possible to develop movements. In cases where muscle tone has not decreased in a timely manner or does not change symmetrically, this significantly interferes with the normal development of the child’s motor sphere, the formation of postural control and normal movements.
- Neuro-reflex excitability syndrome is a disorder of sleep and wakefulness, an overly active reaction to sounds and touches.
- CNS depression. Lethargy, apathy, decreased tone and reflexes, drowsiness.
- Intracranial hypertension. This syndrome occurs when intracranial pressure increases. Increased excitability, obsessive screaming, regurgitation, bulging fontanel and Graefe's symptom are most characteristic of this syndrome. Intracranial hypertension can lead to the development of hydrocephalus—a decrease in the volume of brain tissue and its replacement with fluid.
- Convulsions (convulsive syndrome) are involuntary contractions of the muscles of the entire body, accompanied by loss of consciousness or simply “freezing” for several seconds. Convulsive syndrome is dangerous because, if left untreated, it significantly disrupts the normal development of the brain and its function.
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose neonatal encephalopathy, a number of studies are carried out:
- blood test for glucose and electrolyte levels;
- examination of the cerebrospinal fluid for infection;
- neurosonography through the large fontanel.
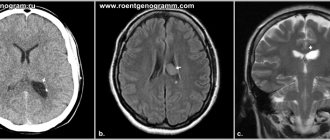
A comprehensive examination includes MRI or CT to clarify ischemia and hypoxia, encephalography for seizures, Doppler ultrasound to study the condition of blood vessels. The child requires an examination by an ophthalmologist, and with age, consultation with a psychologist and speech therapist.
Treatment and rehabilitation for PCNSL
Treatment of PPCNS begins with measures to prevent it.
Before birth, mandatory monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out and, if any abnormalities are present, treatment is immediately prescribed. In severe cases, surgical delivery may be required.
During the perinatal period, children with suspected PPCNS are observed by a neonatologist. At this stage, intensive therapy is carried out, the child is in a specialized department.
After stabilization of the condition, in the absence of a threat to life, the recovery process begins - rehabilitation. The goal of this stage is to minimize the effects of brain damage.
At this stage, medications are used that improve trophic processes in brain tissue, massage to normalize tone and stimulate tactile and proprioceptors, exercise therapy and kinesiotherapy (Bobat, Vojta, etc.) to develop motor skills and prevent the development of contractures, it may also be necessary the use of special orthopedic devices to prevent or correct limb deformities. Botulinum therapy can be used to reduce tone.
The most important thing is to remember that all rehabilitation activities are carried out for one purpose - to provide an opportunity for the child to develop skills and make him as independent as possible in adulthood. Each child’s body is unique and the result of recovery in each specific case is very difficult to predict, however, the correct and consistent use of rehabilitation methods and techniques allows you to achieve maximum results. Cases of partial or complete restoration of central nervous system functions after PCNSL are far from uncommon.
Autoimmune aggression. Autoimmune process
Some diseases of the nervous system are associated with the body's aggression against itself, namely, with an attack of the immune system on the tissues of its own nervous system (demyelination). Some autoimmune diseases are triggered by infection. Before drawing up a treatment plan, we will examine your immune status and infectious background in detail.
Our main task is to find the cause of autoimmune aggression and prevent its further development. In many cases, it is possible to put the autoimmune process into long-term remission or stop it completely.
Examples of autoimmune diseases of the nervous system:
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Disseminated encephalomyelitis;
- Polyneuritis, polyneuropathy, polyneuropathy;
- CIDP (demyelinating polyneuropathy);
- Guillain-Barre polyneuropathy;
- Polyneuropathy in rheumatic diseases;
- Encephalopathy and polyneuropathy due to viral hepatitis;
- Fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Similar phenomena are observed in rheumatic diseases, when immune aggression is directed against joints, ligaments, muscles, and blood vessels.
Causes of autoimmune processes
Why do autoimmune diseases appear? This is usually due to the unfortunate coincidence of three main factors:
- Hereditary characteristics – autoimmune reactions occur more easily in people with certain genetic characteristics.
- Increased activity and decreased “intelligibility” of the immune system , which often occurs under the influence of stress, lack of sleep, operations, injuries, infections.
- The introduction of an infectious agent (virus, bacterium, parasite, fungus), similar in its antigenic structure to the myelin protein (sheath of nerve fibers). In such a situation, immune antibodies to the infectious agent will also be aggressive towards healthy tissue of the body.
The “phenomenon of myelin decompaction” is known, when, as a result of infectious or autoimmune damage, deep-lying myelin antigens are exposed, with which the immune system normally does not contact at all. These antigens are perceived by the immune system as foreign, and autoreactive immunocompetent cells and antibodies (autoantibodies) are formed to them, triggering further immune aggression.
Molecular mimicry and autoimmune reaction. The antigens of some microbes are similar to the autoantigens of healthy body cells. 1-Immune cell; 2-Infectious agent; 3-Nerve; 4-Identical receptors.
The resulting aggressive autoantibodies can participate in cross-autoimmune aggression to other tissues of the body . Therefore, in patients with demyelinating diseases, we often find other autoimmune processes:
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland);
- Fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue;
- Inflammation of tendons and joints;
- Antibodies to insulin and beta cells of the pancreas (risk of diabetes and obesity).
Treatment of autoimmune diseases
Treatment of any autoimmune disease involves reducing autoimmune aggression.
We get the most convincing treatment results from influencing three parts of the autoimmune process at once:
- Suppression of infection;
- Stimulation of weakened and suppression of “overheated” parts of the immune system;
- Regulating the functioning of the nervous system: restoring normal night sleep, reducing stress.
Our rehabilitation programs for PCNSL
We provide comprehensive treatment for the consequences of perinatal CNS damage.
Typically, a rehabilitation program includes:
- Observation by a neurologist. The participation of this doctor is necessary, since the child’s condition must be monitored during the process of rehabilitation measures
- Observation by a physical therapy doctor (rehabilitation specialist). The basis of any rehabilitation is the development and restoration of motor skills. A physical therapy doctor will examine a small patient and plan the rehabilitation process, helping to prioritize physical treatment.
- Observation by a neuropsychologist and sessions with a neuropsychologist. The participation of a neuropsychologist in rehabilitation after PCNSL is necessary starting from 2 years of age. The tasks of a neuropsychologist include diagnosing disorders of higher nervous activity in a child, planning and implementing measures to correct them. Neuropsychologists conduct group and developmental classes with children to develop memory, attention, motivation, and thinking. The neuropsychologist also provides family counseling.
- Exercise therapy and kinesitherapy. We are proficient in various exercise therapy techniques. It is impractical to single out just one among them. Exercise therapy techniques are tools in the hands of a doctor and instructor. We try to select the appropriate instrument for each of our patients. The most commonly used methods in children are Bobath therapy and Vojta therapy. We also use PNF, Neurac, manual therapy techniques and many others in our work.
- Massage. Massage plays an important role in the rehabilitation of children. Naturally, it is not an independent procedure, but its reasonable use allows the child to become more aware of his body and helps him learn to control it. In addition, massage in rehabilitation solves many auxiliary problems - eliminating swelling, improving muscle nutrition, temporary decrease in tone, etc.
- Physiotherapy. We widely use physiotherapeutic treatment in rehabilitation after PCNSL. The objectives of physiotherapy are very diverse and depend on the characteristics of the disease. The most commonly used are medicinal electrophoresis, IR dipole, phototherapy, and magnetic therapy.
- If necessary, a speech therapist may be included in the rehabilitation team. Typically, the need to involve this specialist arises when there is a delay in speech development or alalia.
If you have any questions or want to sign up for a rehabilitation program, call us at: +7 (812) 309-67-26 or leave a request through the contact form on the website.
Prevention of central nervous system damage
In order to prevent the occurrence of a serious and dangerous disease, it is necessary to prevent damage to the infant’s central nervous system. To do this, doctors recommend planning your pregnancy in advance, undergoing the required examinations in a timely manner and giving up bad habits. If necessary, antiviral therapy is carried out, all necessary vaccinations are given, and hormonal levels are normalized. If damage to the baby’s central nervous system does occur, then it is important to provide assistance to the newborn from the first hours of his life and to constantly monitor the baby’s condition.