Stroke is a dangerous condition characterized by impaired cerebral circulation. Brain damage of this type is the most common cause of disability, and also occupies a leading position as a cause of mortality, second only to myocardial infarction and cancer.
Neurologists distinguish between ischemic stroke, the prevalence of which is more than 80% of the total number of cases, and hemorrhagic stroke, diagnosed in 20% of cases.
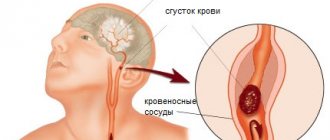
In most cases, the development of stroke is associated with blockage of the lumen of a cerebral artery by a thrombus. The quality of life and prognosis are determined by many factors, among which the most important is the adequacy and timeliness of care provided to the patient. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide emergency care to patients with signs of stroke, and also carry out comprehensive examination, treatment and rehabilitation measures.
First symptoms
A stroke is characterized by a lack of nutrients and oxygen in the brain tissue. The causes of this phenomenon are: rupture, blockage or compression of a cerebral vessel. Women and men require emergency assistance when the first signs of a stroke appear:
- sudden dizziness and headache that occur for no apparent reason;
- confusion;
- visual impairment, speech impairment;
- uncoordinated movements, gait disturbance;
- numbness, weakness in the limbs on the affected side.
Patients who have suffered a stroke resemble people who are intoxicated. The following requests can be used to identify an acute condition:
- stick out your tongue, in case of a stroke the tongue will fall to the side;
- smile; when smiling, facial asymmetry may appear;
- utter a simple phrase, after a stroke the patient is unable to speak;
- raise your arms, this action is aimed at identifying asynchrony of movements and weakness of the limb on the affected side.
The listed signs are a serious reason to call an ambulance. After a stroke, the patient’s life is in danger, so treatment measures must be organized in the shortest possible time. Neurologists draw patients' attention to the fact that during a microstroke or ischemic attack, similar symptoms may also occur, but they are less intense and pass quickly.
Main symptoms of stroke
Important elements in diagnosing a stroke are a person's smile, conversation and movements.
- Smile. If you suspect a stroke, you need to ask the person to smile. In most cases of stroke, there is a distortion of the smile, all this happens because paralysis of one side of the face occurs.
- Speech. You just need to ask the person to tell you a complex sentence. For example: “Birds are singing outside.” If you hear unclear, lisping, or slurred speech, you should be wary of a stroke.
- Movements. You need to ask the person to raise both hands. If you have a stroke, your arms will be at different levels, or one arm will not rise at all.
causes of stroke
In addition, there are two more options for how to recognize a stroke :
- You need to ask the person to stick out his tongue. Due to the same nerve paresis, the tongue will be crooked or have an irregular shape. In addition, it can deviate to one side.
- You need to ask the person to extend his hand forward, palm up, and close his eyes. Also repeat with the second hand. If one of them begins to descend, then most likely the person is having a stroke.
Note! If you notice symptoms of a stroke in a person, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Signs of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke
A stroke, depending on the mechanism of its occurrence, can be ischemic or hemorrhagic, the first signs of which are significantly different. Hemorrhagic stroke has symptoms such as headache, impaired consciousness, dizziness, convulsions and vomiting. This type of stroke is characterized by focal symptoms:
- cranial nerve palsy;
- bulbar, meningeal and pyramidal symptoms;
- speech dysfunction;
- decreased sensitivity.
With hemorrhage in the brain, general cerebral symptoms first appear, which are then combined with focal signs of the disorder.
The development of ischemic stroke occurs rapidly, within a few seconds. Ischemic stroke is characterized by focal neurological disorders in which speech, motor, and cognitive functions are affected. If the cerebellum or brainstem is affected, there is a sharp headache, confusion and intense vomiting.
Neurologists conduct an examination and instrumental diagnostics to identify the type of stroke in a patient.
A stroke is a circulatory disorder in the brain caused by blockage or rupture of blood vessels. This is a condition when a blood clot - thrombus - or blood from a ruptured vessel interferes with blood flow to the brain. Lack of oxygen and glucose leads to the death of brain cells and impairment of motor functions, speech or memory.
According to WHO, stroke is the cause of death for 6.7 million people a year worldwide, and is second only to coronary heart disease. In most countries of the world, doctors consider stroke to be one of the most common causes of neurological disorders, leading to varying degrees of disability, and therefore incapacity for work .In Russia, no more than 20% of patients return to work after suffering a stroke, and one third of those with stroke are people of working age. Recently, stroke in Russia has ceased to be a diagnosis only for older people; doctors are increasingly recording this disease not only in 25-30 -year-old Russians, but also among children.
A stroke can affect anyone. Some risk factors, such as developing an aneurysm or developing a blood clot from injury, are difficult to control. However, a significant number of factors are mainly due to lifestyle.
These factors include:
- high blood pressure;
- high cholesterol;
- diabetes;
- obesity and overweight;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- smoking;
- drug use;
- alcohol consumption.
In addition, stroke is more likely to develop in people over 55 years of age and those whose close relatives have already suffered from a stroke. In the age range from 45 to 55 years, stroke occurs twice as often in men as in women.
Three quarters of all cases of the disease are ischemic stroke. This term refers to a condition in which a blood clot obstructs a vessel and blocks blood flow to a certain part of the brain. Typically, a blood clot forms somewhere in the peripheral vessels of the body, breaks off and travels through the bloodstream to the brain. There it gets stuck in the small vessels of the brain and blocks the blood flow in them.
The second type of stroke – hemorrhagic – is much less common. It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. If the vessel is on the surface of the brain, the leaked blood fills the space between the brain and the skull. This is called subarachnoid bleeding. And if a vessel bursts in the deeper structures of the brain, blood from it fills the surrounding tissues.
Damage to a small area of the brain leads to minor impairments – weakness of the limbs. Impaired blood circulation in large areas of the brain causes paralysis and even death: the degree of damage depends not only on the scale, but also on the location of the stroke.
Many people who have had a stroke are left partially or completely paralyzed on one side of the body, and have difficulty speaking and controlling urination and bowel movements. Intellectual abilities - memory, cognitive functions - also suffer.
The onset of a stroke is usually asymptomatic. But after a few minutes, brain cells, deprived of nutrition, begin to die, and the consequences of the stroke become noticeable.
Common symptoms of a stroke:
- sudden weakness in the face, arm, or leg, most often on one side of the body;
- sudden confusion, problems speaking or understanding speech;
- sudden vision problems in one or both eyes;
- sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination;
- sudden severe headache of unknown cause.
It is very important to immediately recognize its symptoms in order to call an ambulance as quickly as possible. After all, the earlier treatment is started, the better a person recovers from a stroke. Delayed seeking help leads to severe complications and disability.
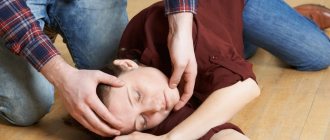
Providing first aid for a stroke is not just important, it is vital. And if suddenly you are near a person who has shown obvious signs of a stroke, there are several actions you should immediately take. The life of this person depends on them.
- As soon as you realize that a person has all the signs of a stroke, immediately call an ambulance. This must be done immediately so as not to miss time. Cerebrovascular accidents are most effectively treated in the first 3 hours. So don't waste your time.
- Remove unnecessary people from the room if business is taking place indoors. If outside, ask everyone to step aside and not interfere with the flow of fresh air. Only those who can help should remain nearby.
- Do not disturb the person under any circumstances. Is it dangerous. The patient must be left where the attack occurred. Do not transfer to the bed.
- Elevate the patient's upper body and head (about 30 degrees). It is best to add several pillows. Unfasten or remove all clothing that constricts and interferes with breathing (belt, collar, belt, etc.).
- Provide fresh air.
- If vomiting begins, turn the victim's head to the side and clean up the vomit properly, otherwise the person may suffocate.
- Sometimes it happens that a stroke is accompanied by epileptic seizures. Moreover, they can follow one after another. In this case, turn the person on his side, insert a spoon, comb, or stick wrapped in a handkerchief into his mouth and, lightly holding the patient’s head with your hands, wipe away the foam. The most important thing in this case is not to press the person. You just need to hold it lightly and that’s it. And even more so, you can’t bring ammonia. The consequences can be terrible - cessation of breathing and death.
- It may happen that the victim's heart stops and breathing stops. In this case, you will have to immediately begin chest compressions and artificial respiration.
Stroke prevention is based on the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- Know and control your blood pressure - it should not be more than 140/90 mmHg.
- Don't start smoking or stop smoking as soon as possible.
- Add as little salt as possible to your food and avoid canned and processed foods that contain excess salt.
- Monitor your blood cholesterol levels - the maximum allowable level is 5 mmol/l.
- Follow the basic principles of a healthy diet - eat more vegetables and fruits (at least 500 g per day), avoid added sugar and saturated animal fat.
- Don't drink alcohol. The risk of stroke is highest in the first hours after drinking alcohol.
- Exercise regularly. Even moderate physical activity (walking outdoors for 30 minutes a day) reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
A disease is a process that develops gradually in the body, quietly forming over the years before manifesting itself as sensations and symptoms. Only the sick person himself thinks that the disease arose suddenly. In fact, it takes a long time for painful changes in the body to become apparent. That is why disease prevention and knowledge of the principles of a healthy lifestyle are necessary - the basis of good health.
Emergency help
The stable functioning of brain structures is ensured by metabolic processes characterized by high speed. Irreversible changes in the affected area during a stroke occur due to a violation of their mechanism. The area affected by a stroke is outlined by a penumbra formed by cells that can be restored with adequate and modern therapeutic measures. The patient’s quality of life and the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures depend on how successfully first aid is provided.
It is possible to restore the functioning of some cells within 4 hours after the first signs of an acute disorder appear. At the moment, the support of loved ones and relatives is of particular importance, since patients often do not realize the events happening to them. When symptoms of a stroke appear, loved ones should not only call an ambulance, but also provide first aid, regardless of where the person is: at home or on the street.
First aid for hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke involves performing the same actions. After calling an ambulance, it is important to understand whether the person is conscious, since with severe lesions, patients fall into a coma; epileptic seizures and stupor are also possible. If there is no response, it is important to periodically bring the patient to consciousness, as well as ensure his safe placement.
Another vital point is to check the person's heartbeat and breathing. In some cases, the patient’s life can be saved by resuscitation measures carried out before the doctors arrive. If a person breathes on his own and his heart is beating, then he should be laid on his back or side, to ensure air flow, his neck and chest should be freed from constricting clothing and accessories.
When a patient wears removable dentures, they should be removed from the oral cavity. Vomiting during stroke is common and can obstruct the airway, so it is important to remove the vomit while the patient is unconscious.
The next step in first aid is to check the blood pressure level, if it is elevated, you should not give the person water or any medications. Before doctors arrive, paralyzed limbs should be massaged and the person covered with a blanket.
The participation and care of people around you can save a person’s life. The adequacy and efficiency of first aid provided determine the effectiveness of subsequent treatment and rehabilitation measures. After the ambulance arrives, the patient is hospitalized in a medical facility equipped to combat the consequences of a stroke.
What to do before the ambulance arrives?
Don't just stand there until the ambulance arrives. First of all, you need to put the person on a flat surface in a horizontal position. If a person has fallen, then you just need to give him a more comfortable position. It is important to control your breathing. If it is completely absent, place the person on his side, clean the oral cavity of food debris, vomit or dentures. They can be a barrier to normal breathing. To make breathing easier, you also need to unbutton your blouse or other tight items. It is advisable to loosen the belt. Open a window and allow fresh air to flow.
what to do before the ambulance arrives
If you have a tonometer at hand, you should immediately measure your blood pressure and record the readings. With high pressure, you need to raise your head, and with low pressure, you need to raise your legs. If a person has convulsions, under no circumstances should you try to restrain the person. Just put something soft under your head to avoid injuring your head. The only thing worth doing at the end of a seizure is to turn the person on his side.
It is strictly forbidden to unclench your jaw, try to insert any objects into your mouth, or fix your tongue. Such actions will only lead to harm to the person providing assistance. You should not worry about asphyxia through tongue swallowing; this is not possible during a convulsion.
If breathing and heartbeat stop, CPR should be started immediately. All resuscitation actions must be performed until the ambulance arrives.
First aid for stroke
For ischemic stroke, if the patient was taken to the hospital within the first 4 hours, thrombolysis is performed using a plasminogen activator substance. The drug urokinase is used when there are indications for intra-arterial thrombolysis. The introduction of warfarin is possible after overcoming the acute period; this drug prevents recurrent stroke. To patients diagnosed with ischemic stroke, neurologists administer cardiomagnyl, ACC thrombo and aspirin-cardio.
With the development of cerebral edema, the efforts of specialists are aimed at reducing body temperature, eliminating oxygen deficiency in tissues and reducing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. First aid for cerebral edema resulting from a stroke is carried out:
- hyperventilation;
- intravenous administration of drugs that have a dehydrating effect;
- drainage of cerebrospinal fluid;
- a surgical procedure during which the surgeon opens the skull and removes part of the bone, resulting in access to the brain.
First aid for hemorrhagic stroke is aimed at maintaining the patient’s vital functions. In this case, a minimally invasive or neurosurgical operation can achieve a positive result.
Causes of formation and mechanism of development of pathology
Content:
- Causes of formation and mechanism of development of pathology
- Types of brain strokes
- Symptoms and signs of stroke: clinical picture
- Stroke: how to recognize and determine brain damage
- First aid for stroke: algorithm of actions
Brain damage due to stroke, today, is one of the most common causes of disability in the population - this is evidenced by data from the World Health Organization. Approximately 70-80% of people who have suffered a stroke become disabled, of which 20-30% require constant outside care.
Men and women are susceptible to the development of pathology approximately equally, and the likelihood of a stroke increases as a person reaches the age of 30-35 years and older.
Why might a stroke develop? The general principle of the development of pathology is the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system, which directly affect blood circulation in the brain. A significant role in the development of stroke is played by factors such as arterial hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease - against the background of these diseases, apoplexy can develop if this is facilitated by poor nutrition, smoking, alcohol consumption, frequent stress, taking hormonal contraceptives, and dyslipidemia. Moreover, stress and the use of contraceptives negatively affect the female body. Obesity is also dangerous for women; for men, the problem of alcoholism is more pressing. Family members with a history of strokes also increase the likelihood of brain damage.
As for the mechanism of development of strokes, each of the types of pathology known to medicine is formed differently. Thus, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are characterized by fundamentally different mechanisms of occurrence. The ischemic type of damage occurs approximately 4 times more often than hemorrhagic.
Ischemic stroke is also called cerebral infarction - it develops as a result of obstruction of the patency of the cerebral arteries. Due to insufficient blood supply, a person experiences prolonged cerebral ischemia, after which irreversible changes begin in the tissues of the organ, affecting the blood exchange zone of the affected artery.
A hemorrhagic stroke is formed according to a slightly different pattern - as a result of an atraumatic rupture of a cerebral vessel, hemorrhage occurs in the brain tissue.
Ischemic strokes are more common in people over the age of 55, while the hemorrhagic type of pathology also occurs in younger people.
Medical care at the Yusupov Hospital
At the Yusupov Hospital, we are ready to provide specialized care only on the third day. We do not provide emergency hospitalization for stroke.
If necessary, our employees are ready to quickly arrange the transfer of a patient from one medical institution to ours.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are supervised around the clock by medical staff and receive proper treatment, care and subsequent rehabilitation.
One of the structural divisions of the Yusupov Hospital is the neurology clinic, where patients receive highly effective medical care, professional care and comprehensive restoration of lost functions. Neurologists know how to combat even severe forms of the disease, so they do not refuse help to such patients.
By calling the Yusupov Hospital you can find out the procedure for hospitalization, call an ambulance, or make an appointment with a neurologist.
Make an appointment
If the stroke is hemorrhagic
Symptoms that speak in favor of hemorrhagic stroke:
- arose abruptly at the height of physical or psycho-emotional stress;
- there is no consciousness;
- have convulsions;
- the neck muscles are tense, it is impossible to bend the head;
- high blood pressure.
In addition to standard care, such patients need:
- The position is strictly with the head end elevated (except for convulsions or resuscitation).
- Applying an ice pack to the head (preferably to the half in which hemorrhage is suspected - opposite to the immobilized tense limbs).
Comprehensive examination of patients
An examination using high-precision and sensitive equipment at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out upon admission of patients with signs of stroke. A comprehensive diagnosis of a patient’s condition may include both computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. However, to exclude hemorrhage, the first-priority method is CT, since it is the fastest test.
MRI results allow the doctor to determine the source of the disorder and its size. This method helps visualize small lesions localized in the brainstem and cerebellum. When performing CT, these lesions are poorly visualized.
A comprehensive examination after a stroke at the Yusupov Hospital may also include:
- multislice tomography;
- angiography;
- magnetic resonance angiography;
- duplex scanning of the carotid and vertebral arteries;
- transcranial Dopplerography of arteries.
Specialists at the diagnostic center of the Yusupov Hospital record an electrocardiogram to detect ischemia, heart rhythm disturbances and myocardial disorders. Transthoracic electrocardiography is performed if intracardiac thrombus, cardiomyopathy and ventricular aneurysm are suspected.
Features of providing assistance at home or in any enclosed space
If a stroke occurs indoors (at home, in an office, in a store, etc.), then in addition to standard first aid, pay attention to:
- Free access of fresh air to the patient: open the window, door.
- Release your chest and neck.
- If possible, measure your blood pressure. If it is elevated (more than 150/90 - 160/100 mmHg), you can give antihypertensive drugs under the tongue (Captopress, Farmadipin, Metoprolol), lightly press on the solar plexus or on closed eyes. If it is low, raise your legs, but do not lower your head, massage the area of the carotid arteries on the sides of the neck.
How to provide first aid for a stroke indoors
Stages of treatment
The Yusupov Hospital treats patients after stroke in accordance with international standards.
- First stage.
Basic therapy is based on the organization of round-the-clock care, which involves the prevention of pulmonary congestion, bedsores and mobility impairment.
- Second phase.
The next stage of recovery is activities that involve passive movements in the joints. Breathing exercises are also of particular importance. If swallowing disorders are detected, the patient is given intravenous mixtures that provide the body with nutrients.
- Third stage.
Highly qualified neurologists create individual treatment programs that involve drug therapy and the use of non-drug methods. In case of arterial hypertension, patients are prescribed antihypertensive drugs.
An important area of treatment for patients after acute circulatory disorders is the regulation of water-salt balance in the body, osmolarity of blood and urine, and electrolyte content, for which infusion therapy is organized. Drug treatment may also include the use of glucocorticoids and diuretics for cerebral edema. Patients who have suffered a stroke, in the absence of contraindications, are prescribed anticoagulants.
The use of thrombolytic drugs by neurologists is carried out to restore blood flow and dissolve formed blood clots. Data from modern studies confirm the high efficiency of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator, which provides thrombolysis.
Rehabilitation
In modern medicine, there are stages of the post-stroke period, according to which treatment and rehabilitation are organized:
- the first 3-4 weeks belong to the acute stage;
- the first 6 months form the early recovery stage;
- period from 6 months to 1 year – late recovery stage;
- The residual stage lasts more than 1 year.
The periodization of the early recovery stage includes two intervals:
- during the first interval, the duration of which reaches 3 months, a cyst is formed, strength and movement are restored in the paralyzed limbs;
- the second stage, lasting from 3 to 6 months, is the period of restoration of motor function.
Types of brain strokes
All manifestations of pathology, its characteristic signs, pathogenesis and etiology determine the division of the concept of “stroke” into several types:
- ischemic;
- hemorrhagic;
- lacunar;
- extensive;
- spinal;
- spicy;
- repeated.
What is ischemic stroke
This type of lesion is formed as a result of an obstruction in the flow of blood through the blood vessels in the brain. In this case, the intracranial and extracranial vascular subsystems may be affected. So, in 30% of cases of ischemic stroke, it develops due to occlusion of the carotid arteries.
A sharp deterioration in blood supply can occur due to the presence of vascular spasm and thromboembolism. The formation of emboli occurs against the background of pathologies in the heart:
- after a heart attack;
- with atrial fibrillation;
- due to acquired or congenital heart valve defects;
- with myocarditis, endocarditis;
- for rheumatism.
Blood clots that form in the heart area, due to the blood flow, move into the cavity of the cerebral vessels, clogging them. In this case, a part of an atherosclerotic plaque that breaks away from the vascular wall can act as an embolus. Getting into a narrow cerebral vessel, it provokes its occlusion.
What pathogenetic types can an ischemic stroke have? Doctors highlight:
- cardioembolic, which is formed due to cardiac arrhythmia, the presence of valve disease, or a previous heart attack;
- atherothrombotic: its root causes are atherosclerosis of large arteries and arterio-arterial embolism;
- lacunar: develops due to occlusion of small arteries;
- of unknown origin, which include pathologies with an unknown cause of occurrence, when an accurate diagnosis cannot be established.
More rarely, another type of ischemic apoplexy occurs, caused by hypercoagulation of the blood, non-atherosclerotic vasculopathies, and dissection of the arterial wall.
Periods of development of ischemic type of brain damage
Ischemic stroke can occur due to the following diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- amyloidosis;
- collagenoses;
- systemic vasculitis;
- angiitis;
- drug addiction.
The normal course of the disease involves a person going through several periods:
- acute, which is observed in the patient during the first three days. In this case, the first five hours are considered the so-called “therapeutic window”, during which it is advisable to use thrombolytic drugs;
- acute, which lasts up to 4 weeks after the attack;
- early recovery – up to 6 months;
- late recovery – about 2 years after the onset of pathology.
After the rehabilitation period ends, the residual effects of a stroke can manifest themselves throughout the rest of their lives.
Hemorrhagic stroke: what is it, why does it appear?
This type of brain damage is associated with diffuse or isolated cerebral vascular pathology. The vascular wall becomes thinner and loses elasticity.
Often hemorrhagic stroke occurs against the background of uncorrectable arterial hypertension, hypertensive crisis. With a sharp increase in pressure, the pressure on the wall of the vessel increases - it bursts. Blood flows into surrounding tissues.
Provoking moments are:
- stress;
- lack of sleep;
- hyperthyroidism;
- pathology of the adrenal glands.
Other factors that provoke the appearance of pathology are developmental anomalies and arteriovenous malformation of the brain. This process leads to the formation of an aneurysm, that is, a protrusion of the arterial wall. At this point, the vascular wall becomes very thin and therefore easily ruptures due to increased blood pressure.
Hemorrhagic strokes can occur due to blood clotting disorders, as well as with inadequate drug therapy, which affects coagulation parameters.
It is considered the most severe form of stroke - death occurs in approximately 70% of all cases.
The following stages of formation of hemorrhagic strokes are distinguished:
- ruptures in the walls of blood vessels lead to the accumulation of a blood clot and the formation of necrosis in the tissues;
- a hematoma forms, which mechanically compresses the brain tissue;
- an ischemic zone is formed in the compressed area;
- the combination of hematoma and ischemia triggers a chain of irreversible processes of brain damage in the organ;
- under the pressure of a hematoma, areas of the brain can shift, which is a life-threatening condition.
Characteristics of other types of strokes
Extensive
This category characterizes the so-called massive strokes - severe lesions with pronounced cerebral manifestations:
- depressed state of consciousness;
- swelling of the brain;
- paresis of gaze towards the paralyzed side of the body;
- hemiparesis;
- speech disorder;
- loss of part of the visual field;
- vegetative disorders;
- trophic disorders that occur after a year or two on the affected side;
- changes in pupil size, weakening of the pupil's reaction to light;
- squint.
In addition, the patient experiences spasms of the tonic muscles. The extensor muscles may experience a marked increase in tone.
A major stroke is a lesion that often leads to a person’s death or complete disability.
Lacunar
It is classified as a separate variety. During the process of life and development, a person develops a limited lesion of the perforating arteries of the brain - small vessels (up to 2 millimeters in diameter, no more than 10 centimeters in length). They connect larger vessels to each other. At the site of the infarction, a round-shaped cavity appears, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The lacunar variety represents approximately 30% of all ischemic strokes. It is characterized by:
- impaired body coordination on one side;
- impaired clarity and intelligibility of speech;
- disappearance or impairment of motor activity of one arm or leg.
The most common cause of this type of lesion is a combination of atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. In addition, a lacunar stroke can be of an embolic nature - such a pathology is more difficult for the patient, since a significant area of the brain is involved in the damage mechanism.
Spinal
It is a circulatory disorder in the spinal cord, which is formed against the background of a typical cerebral stroke or an infectious process, tumor, metastases, or autoimmune diseases. Spinal stroke is usually localized in the cervical or lumbar enlargement, namely in the large-diameter arteries, as well as in the small reticulomedullary arteries. This type of damage most often occurs in older people, whose body has difficulty coping with the condition of impaired blood supply to the brain.
How to determine the formation of a spinal type of pathology in a person? Doctors pay attention to the presence of such signs:
- unexplained pain in different parts of the body;
- chronic spinal insufficiency;
- severe pain in the head that is constant;
- the presence of noise and a feeling of heaviness in the head;
- loss of consciousness when trying to get up;
- feelings of dizziness;
- memory loss;
- increased fatigue;
- sleep disorders.
A person feels numbness in his legs due to long walking, but there is no pain in his limbs. The discomfort disappears after rest.
Spicy
Acute stroke is the initial period of development of a pathological condition. On average, it lasts for three weeks. The patient experiences an increase in the pathogenetic process in the brain, especially in the first 6 hours.
Acute stroke goes through several stages:
- after damage to organ cells, the nucleus of a brain infarction is formed;
- the area of metabolic changes around it increases (by about 80% in 6 hours);
- the beginning of the death of organ cells (necrosis);
- spread of neurological disorder in the form of generalized and focal manifestations.
Repeated
Appears due to cerebrovascular diseases, dementia disorders, against the background of impaired heart rhythm, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, after a previously diagnosed stroke of the brain.
Rehabilitation after a stroke at the Yusupov Hospital
At the Yusupov Hospital, rehabilitation activities begin early. All necessary activities are organized by a multidisciplinary team of doctors.
Data obtained during a comprehensive examination about the degree of damage and dysfunction allow specialists to create an individual rehabilitation program.
- Early start of rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation activities can be organized in the first hours after the patient’s admission to the Yusupov Hospital.
In this case, passive gymnastics and massage are performed. Early recovery reduces the likelihood of patient disability and reduces the severity of symptoms and complications. - 24/7 monitoring.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital monitor the patient’s condition around the clock. When the parameters of the cardiovascular system are normalized, the patient can be gradually transferred to a vertical position. For this purpose, the rehabilitation department has all the necessary latest equipment. - Passive and passive-active rehabilitation.
One of the areas of rehabilitation is the suppression of involuntary movements. For this purpose, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use passive and passive-active exercises, an example of which is walking along a wall bars, which is subsequently replaced by a four-legged support, then a regular cane. The result of these exercises is that the patient begins to move without assistance. - Physiotherapy.
Physiotherapeutic methods are used to reduce muscle spasticity. - Speech restoration.
Speech rehabilitation begins with simple methods involving word recognition and situational speech; when a positive result is achieved, work with complex phrases begins. At this stage, written speech recognition skills are also developed. The transition to dialogue is a later stage. At the final stage of speech rehabilitation, the patient is asked to compose stories and highlight the meaning of the text read. - Drug therapy.
Another consequence of a stroke is cognitive impairment. Patients experience difficulties with fixating attention, remembering information, recognizing objects, and their intelligence also decreases. Correction of these disorders is carried out using medications.
Of course, we must not forget that family members play a special role in the recovery process. They take part in additional classes, formation and restoration of self-care skills, and involvement of the patient in performing feasible everyday activities.
You can seek help from specialists at the Yusupov Hospital by making an appointment by phone.