Reception is conducted by:
Belyakova Alla Vasilievna -
pediatric neurologist
Make an appointment
Fainting is a clinical situation accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness. Pathology develops due to metabolic disorders in brain cells and oxygen deficiency. The corresponding problem is rarely an independent disease. In 90% of cases it accompanies pathology of other internal organs. The specialists of the Profimedica clinic will help in such a situation and tell parents how to behave in the future.
Causes of fainting in children
Children of any age are susceptible to fainting. The key to this issue is a sudden decrease in the flow of blood or glucose to brain cells, which causes neurocytes to temporarily “turn off.”
Possible reasons:
- severe pain syndrome;
- very strong emotion (joy, fear);
- prolonged fasting;
- massive blood loss;
- infectious diseases accompanied by intoxication shock;
- mental overload. Due to the immaturity of the brain, the baby cannot always withstand the pressure usual for an adult patient.
A common cause of this situation is traumatic brain injury. The baby may fall and hit himself hard, causing him to lose consciousness.
First aid for a child with fainting
At the moment of an attack, it is necessary to put the child down and raise his legs
First aid for a teenager and an adult in case of fainting (pre-syncope) is completely identical.
In most cases it is enough:
- Prevent the victim from falling and injuring himself by pre-sitting or adjusting.
- If fainting has already occurred, it is necessary to lay the child on a flat surface, slightly raise his legs, placing something under them, and unbutton tight clothes.
- If there are open injuries and bleeding, they should be eliminated. Naturally, there is no need to give any medications to the victim. Stop using a tourniquet for severe blood loss or applying gauze to the wound site.
If after 1-2 minutes after loss of consciousness the teenager has not regained consciousness, you need to:
- Call an ambulance immediately.
- Bring the victim into a stable lateral position.
By the way, to implement the last action, you need to lay the person on his side, extend his left arm forward, place his right hand with the hand up under his cheek, and slightly bend his upper leg at the knee. This position is the safest and most optimal for an unconscious teenager, and therefore should be used to wait for doctors.
Danger signs and risks of complications
After any fainting in a teenager, it is advisable to take him to the clinic for a thorough examination.
You can hesitate slightly in contacting a doctor only if the loss of consciousness happened once, was short-lived and without serious consequences.
Frequent fainting can be signs of serious and dangerous pathologies
The following are considered dangerous signs:
- prolonged fainting
- accompanied by foam at the mouth and convulsions
- development of health problems related to loss of consciousness
Since there are many causes of fainting, its occurrence with dangerous symptoms requires immediate consultation with a doctor. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing serious complications. The latter include both relatively harmless disorders at the level of the brain or cardiovascular system, as well as coma and death.
Symptoms of fainting
The clinical picture of the corresponding pathology can be divided into the pre-fainting stage, the phase of loss of consciousness and the post-fainting state.
The following symptoms are warning signs of a problem:
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- paleness of the skin;
- slow breathing;
- nausea;
- darkening of the eyes;
- cold sweat.
After this, the child loses consciousness. In the post-harvest state, the patient complains of weakness and general poor health. The duration of the unconscious period depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. The baby may not come to his senses from several seconds to several minutes.
Types of fainting
The classification of fainting is based on the causes of loss of consciousness. There are three main types of fainting:
- neurogenic;
- cardiogenic;
- hyperventilation.
Among neurogenic syncope, in turn, a distinction is made between vasodepressor and orthostatic. The first ones are the most common, usually occurring in fairly young patients in stuffy conditions, stress, fatigue, or lack of nutrients.
Orthostatic fainting occurs when there is a sudden change in body position (usually during a sudden rise or standing). It may also be caused by taking certain medications.
Cardiogenic loss of consciousness occurs when the heart rhythm is abnormal and can accompany a heart attack. Cardiogenic syncope accounts for up to a quarter of all cases of loss of consciousness, especially among the elderly population.
Hyperventilatory syncope occurs due to rapid breathing. This symptom is characteristic of panic attacks and anxiety attacks. Sometimes this condition is called a vegetative crisis.
Self-help for arrhythmia
If palpitations occur, it is important to quickly determine the heart rate. If it is very high (180-250 beats per minute), then in the first 10-15 minutes:
- You need to pinch your nose and mouth and strain sharply. Do this several times.
- There is a pulsating vessel on the neck that can be easily felt (this is the area of the carotid sinus). During an attack it often pulsates. You need to first massage it on one side, then on the other. But you can’t massage it on both sides at once, as the pressure may drop significantly. Tense yourself 2-3 times - massage.
- Pressing on the root of the tongue is very effective. This technique is often able to interrupt the arrhythmia.
- A sharp cold on the face can also stop an attack.
- To stop an arrhythmia, a two- and three-year-old child can simply be lifted upside down and given a regular enema.
But if ventricular arrhythmia occurs, it is often accompanied by loss of consciousness. In this condition, only those around you can provide help.
First of all, you need to determine whether there is a heartbeat or not (palpate the carotid artery in the neck, put your ear to the chest).
If the patient is breathing and there is a heartbeat, then emergency measures are not needed, but an ambulance must be called.
If the pulse is not detected, then you need to immediately start cardiopulmonary resuscitation - perform artificial respiration. While one is performing CPR, someone must call an ambulance.
Prevention
To prevent fainting in adolescent girls, it is recommended to carry out their prevention in a timely manner. The girl should have a full breakfast. During the period of puberty of a teenager, parents are recommended to provide him with a balanced diet , which will ensure the supply of vitamins and microelements in sufficient quantities.
In the summer, when the air temperature is excessively high, the girl is recommended to go outside only in a hat. It is recommended to organize the correct daily routine, observing the alternation of stress and rest. The girl should avoid excessive physical activity. Long-term travel by vehicle is not recommended.
Fainting is a symptom in teenage girls, which indicates the impact of unfavorable environmental factors or the occurrence of serious diseases in the body. If a symptom appears frequently, it is recommended to consult a doctor to undergo diagnostics and determine the causes. This will allow us to prescribe effective therapy for the girl.
How to understand that you have arrhythmia
Until a certain time, children do not feel rhythm disturbances. An adult can feel 10 extrasystoles (interruptions in the heart), and each one feels like cardiac arrest. Teenagers only from the age of 13 feel extrasystole, and then in 10-12% of cases.
Heartbeat is not the most reliable criterion for arrhythmia, only if it is non-paroxysmal tachycardia, when a very rapid heartbeat suddenly starts at 180-200 beats per minute, and fainting occurs.
With paroxysmal tachycardia, the child’s neck vessels and chest pulsate, the baby usually gets scared and says that he feels like a bear is jumping on him. I advise parents to immediately feel the pulse - it will beat strongly.
Fainting should alert you and prompt you to be examined by a cardiologist. In general, any fainting requires examination, but if it occurs against the background of physical activity, it is especially important.
First, a standard cardiological examination is carried out: ECG, ultrasound of the heart, 24-hour Holter monitoring.
The next method is the turntable test. The child is placed on the table and connected to the devices. The table rises smoothly and remains in position at an angle of 60 degrees. This is called a passive orthostatic test.
Its mechanism is that at this time the blood moves to the lower extremities, and if the child has a weakness in the reflex, which ensures the blood rises upward, then little blood flows to the brain and it gives the command to turn off, like a computer.
In a state of fainting, the brain consumes less oxygen, and this does not lead to damage to nerve cells.
If the reflex is weak, there may be not only fainting, but also dizziness when standing up suddenly or standing for a long time in a stuffy room.
On the turntable, the patient experiences such conditions - and we can determine the mechanism of fainting.
To establish the cause of fainting, a conversation with the parents and the child himself is also important. This largely determines the direction of further diagnostic search.
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures
After collecting anamnesis, the patient is prescribed additional examination methods.
Diagnostic measures include the collection of anamnestic data, patient complaints, examination, and additional research techniques. During an attack, the doctor assesses the presence of breathing, heartbeat, skin color, heart rate, and conducts auscultation (listening) of the lungs and heart. To clarify the causes of fainting, the patient is examined. The patient is prescribed a clinical blood test, urine test, and biochemical analysis (creatinine, urea, liver tests).
Additional examination methods:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain (detects volumetric, structural pathologies of the brain);
- computed tomography (CT);
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head (USDG) (examines the speed of blood flow in the brain);
- electroencephalography (EEG) (measures the electrical activity of the brain);
- electrocardiography (ECG) (shows the nature of the heart rhythm);
- EchoCG (ultrasound examination of the heart) (diagnoses organic heart disease);
- Holter ECG monitoring (assesses the rhythm pattern over a period of 24 hours or more).
Do I need to be examined after fainting and how exactly?
It has already been noted more than once that after fainting, diagnosis in a medical institution is necessary for any person. Its importance is especially high when a teenager has problems. For help, you should contact a general practitioner, who, by collecting an anamnesis, will determine the need to contact other specialists and the general danger of the incident.
If certain health problems are suspected or for the purpose of reinsurance after fainting, the following are often prescribed:
- routine and extended blood tests
- urine and stool examination
- profile examinations of the cardiovascular system
- CT or MRI
You can learn more about how to provide first aid in case of fainting from the video:
Only based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis is a final verdict made on why the teenager fainted, how dangerous it is and whether it requires treatment. It is impossible to answer the questions posed at home, so it is highly undesirable to delay contacting the clinic. Do not forget that even a short-term loss of consciousness is an indicator of a malfunction in the body, which can be more than dangerous.
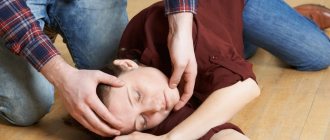
Providing first aid
If a child faints, it is recommended that he be given first aid in a timely manner. The tone consists of performing sequential actions:
- The child is placed on the bed on his back. The legs are raised so that they are at an angle of 30 degrees. For this purpose, a pillow is placed under them. This position ensures a full flow of blood to the head, which increases the amount of oxygen in the brain.
- It is recommended to provide access to fresh air in the room where the patient is located. The child needs to remove clothes that are constricting his body.
- If a child faints, you need to help him come to his senses. They pat him on the cheeks or splash his face with cold water. If these measures do not bring results, then the whiskey is lubricated with ammonia. It is recommended to give this medicine to the child to sniff.
- After that. Once the child comes to his senses, it is strictly forbidden to put him on his feet. He should remain in a lying position for several minutes, which will ensure complete restoration of blood supply to the brain.
- The victim is recommended to take sweet tea or juice, which will speed up the recovery process.
Proper provision of first aid will help get rid of syncope in children in a short time.