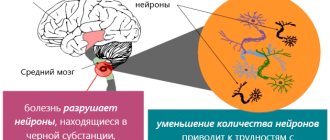
Parkinsonism, or Parkinson's disease, is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system, which in most cases results in disability and death.
Parkinson's disease is defined by four characteristic features that make up the tetralogy of parkinsonism:
- shaking (tremor) of the head, limbs,
- muscle stiffness (stiffness),
- limited movement (hypokinesia),
- changes in gait, posture (postural disorders).
Parkinsonism is a common neurological disease, affecting 120–180 people out of 100 thousand, and the disease has a pronounced age dependence.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
general information
Parkinson's disease affects men twice as often as women. In most cases, it develops after 60 years of age, but cases of early onset of the disease are recorded (at 30-40 years of age), as well as juvenile forms that develop in people in their twenties.
There are several hypotheses for the formation of pathology. It has now been precisely proven that one of the mechanisms of its development is the gradual degeneration of neurons and a decrease in the production of dopamine. It is an important neurotransmitter involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As a result, a specific set of disorders is formed, which makes it easy to make a diagnosis.
What is Wilson-Konovalov disease
The term Wilson-Konovalov disease refers to a hereditary pathology.
It occurs when parents pass on a defective gene (ATP7B) to their child. The condition is an autosomal recessive pathology, that is, it occurs if each of the parents carries a similar gene in their cells and the child inherits both genes at once - from the mother and from the father. This defective gene gives instructions for the synthesis of a protein that regulates the exchange and transport of copper within the body. When it is defective, copper accumulates in the liver, concentrates in the nerve ganglia, and is deposited in the iris of the eye. The pathology is rare and is sometimes very difficult to recognize, especially if there are no similar patients in the family.
Causes
The exact causes of Parkinson's disease have not been identified. Scientists have been able to identify only a number of factors that increase the risk of developing neurodegenerative processes:
- natural processes of aging of the body, accompanied by a decrease in the ability of tissues to regenerate;
- genetic predisposition (this is especially true for forms with early onset);
- chronic lack of vitamin D, which protects neurons from the pathological effects of toxins;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals, pesticides, alcohol;
- poor environmental conditions in the region of residence;
- taking certain medications (for example, chlorpromazine);
- chronic insufficiency of blood supply to the brain (due to atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, etc.);
- infections affecting the central and peripheral nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis, herpes viruses, influenza);
- brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- smoking;
- frequent and prolonged stress, chronic fatigue.
Make an appointment
Symptoms
Parkinson's disease is manifested by specific symptoms, which together form a clear picture of the disease:
- tremor: fine trembling begins in one hand and then spreads to both limbs and head; the movement of the fingers is somewhat reminiscent of counting coins; while performing purposeful movements (for example, while working at a computer);
- general slowness of movements (bradykinesia): the patient often freezes in one position;
- specific gait: a person moves with small, shuffling steps, as if he is constantly on very slippery ice;
- poor facial expressions: a mask effect is formed due to low mobility of facial muscles;
- monotonous, quiet speech;
- increased muscle tone (muscle rigidity): the figure becomes stooped, arms and legs are slightly bent, the head is tilted forward;
- postural instability: a person has difficulty starting and ending movements, resulting in decreased ability to maintain balance;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system: oily skin, excessive secretion of saliva and sweat;
- decreased sense of smell;
- constipation, urinary disorders.
Unlike other neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinson's disease has little effect on intelligence in early and middle stages of development. As the pathology progresses, there is a decrease in the speed of thinking and speaking, decreased mood, depression and indifference to everything that happens.
Manifestations of the disease
Muscle stiffness in Parkinson's is the most serious and unfavorable symptom. The onset of the disease with the primary development of this symptom indicates that Parkinson's disease has developed - an akinetic-rigid form that is difficult to treat and leads to profound disability. With this form, all muscle groups of the limbs and trunk are affected.
Important! At the beginning of the disease, tremor appears in one half of the body, and subsequently the lesion spreads to the other half of the body.
Clinical signs of Parkinson's disease
| Symptom | How it manifests itself | Consequences |
| Decreased motor activity due to stiff muscles | Stiff muscles make voluntary movements difficult. At the beginning of the pathological process, it becomes difficult for the patient to fasten buttons, tie shoelaces, and get up from a low chair. In the future, it is impossible to dress yourself, eat food, or perform purposeful actions. | The patient loses the ability to care for himself and move around independently |
| Speech Impairment | Speech becomes slurred and quiet due to rigid muscles of the speech apparatus | Communication and professional activities become difficult |
| Gait disorder | The patient moves in small steps, shuffles his feet | Movement speed decreases |
| Changing facial expressions | The face becomes mask-like due to stiff facial muscles | Problems with facial expressions create the impression of a lack of emotion |
| Handwriting problems | Handwriting deteriorates, and as the disease progresses, writing becomes impossible | Everyday problems due to writing disorders (inability to sign when receiving a pension, fill out utility payment receipts) |
| Emotional disturbances | Decreased depressed mood in the form of depression | The appearance of suicidal thoughts, the possibility of suicide |
| Changes in memory and thinking | At a late stage of the disease, problems arise with remembering information, thinking slows down | Difficulties in communication and socialization |
The cogwheel sign develops due to stiff muscles and occurs at the beginning of movement. Coordinated and cooperative actions are impaired in patients. It is noteworthy that when walking there is no swinging of the arms, the arms “stick” to the body.
Sleep disorder
Patients suffer from a distortion of the sleep formula, which is manifested by the inability to fall asleep at night. During the day there is drowsiness. Waking up at night with attacks of panic and fear often occur. Lack of night sleep increases lethargy and apathy. To correct insomnia, patients are shown medications based on melatonin, which should be taken only in the dark.
Changes in other organs
The following changes are observed in the internal organs and blood vessels:
- decrease in blood pressure (especially pronounced when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position);
- urinary retention or incontinence;
- constipation;
- decreased appetite;
- excess skin greasiness.
Negative manifestations require mandatory correction, as they worsen the patient’s condition and contribute to the progression of neurological symptoms.
Stages of development
Currently, doctors distinguish 5 stages of Parkinson's disease, manifested by a certain set of symptoms:
- Stage 0: no clinical manifestations;
- Stage 1: there are slight difficulties in moving one arm, a slight tremor, first with excitement, then at rest; the sense of smell and sleep are disrupted, fatigue and apathy appear;
- Stage 2: disturbances involve the second hand, trembling of the tongue and lower jaw appears; salivation; hypokinesia is formed; the ability to self-care is preserved;
- Stage 3: stiffness and impoverishment of movements increases, facial expressions are almost absent; a specific gait and posture is formed; during a conversation, the patient begins to get stuck on the same word; self-care is difficult, but possible;
- Stage 4: postural instability develops, the patient begins to fall frequently; the intellect begins to suffer, depression increases; At this time, suicide attempts are common; a person needs help to perform simple actions;
- Stage 5: manifestations reach their climax, the person cannot sit down, stand up and walk independently, eating is difficult due to swallowing disorders; loss of control over bowel movements and urination; the patient requires constant care.
Results and discussion
General characteristics of the group
SP was detected in 498 (82.59%) patients, i.e. Every 6th applicant did not have parkinsonism.
In the remaining 105 (17.4%) cases, ET was diagnosed - in 75 (12.4%) patients, psychogenic parkinsonism - in 16 (2.7%) and dyscirculatory encephalopathy without parkinsonism - in 14 (2.3%). It should be noted that before contacting a specialized clinic, 71.4% of patients were not diagnosed with ET, which confirmed the existing difficulties in the differential diagnosis of ET and trembling forms of PD.
In the structure of the syndromic diagnosis “parkinsonism,” 407 (81.7%) cases were associated only with PD. We have not observed a single case of juvenile parkinsonism. In 140 (34.4%) patients, the diagnosis of PD was established for the first time.
Among 48 (9.64%) patients with secondary parkinsonism, the most common was vascular parkinsonism, identified in 32 (6.43%) patients, which is consistent with literature data [2, 7, 8]. Drug-induced parkinsonism was detected in 7 (1.41%), toxic parkinsonism caused by manganese intoxication - in 6 (1.20%), parkinsonism with normal pressure hydrocephalus - in 3 (0.60%) patients. As is known, drug-induced parkinsonism most often predominates within secondary parkinsonism (from 5 to 22% of cases) [3]. The low level of drug-induced parkinsonism in the present study is due to the fact that only patients with rapidly progressing and severe complications as a result of taking various antipsychotic drugs visited the clinic.
Neurodegenerative diseases from the parkinsonism-plus group were identified in 43 (8.63%) patients. Of these, dementia with Lewy bodies was observed in 10 (2.0%) people, multiple system atrophy - in 7 (1.41%), hepatolenticular degeneration - in 6 (1.20%), progressive supranuclear palsy - in 4 (0. 80%). Fahr's disease and the juvenile variant of Huntington's disease each represented 3 (0.60%) patients. This group also included very rare forms of parkinsonism, identified in 10 (2.00%) patients: ALS-parkinsonism - in 2, and 1 patient each with hemiparkinsonism-hemiatrophy syndrome, frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism, dementia with Lewy bodies in combination with dementia of the Alzheimer's type. In addition, in 5 (1.0%) patients, the nosological form of the disease could not be clarified due to the atypical picture of parkinsonism in combination with other signs of central nervous system damage (pyramidal and cerebellar syndromes, apraxia, severe pelvic disorders, cognitive impairment). The difficulties in clarifying the nosological form in these patients were also explained by the short period of follow-up.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is made based on the characteristic clinical picture. The patient is examined by a neurologist who notes typical signs. Complaints must be clarified and an anamnesis of the disease (history of the appearance of symptoms) and life history (information about previous injuries, chronic diseases, surgical interventions) is collected. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are used to clarify concomitant pathology and exclude other causes of neurological disorders.
Questions and answers
Can true parkinsonism be cured?
Modern pharmacology and medicine do not have the means to completely cure Parkinson's disease. The treatment regimens used are aimed at slowing down destructive changes, relieving the main symptoms and improving the quality of life of people suffering from parkinsonism. Treatment methods for Parkinson's disease and the causes of this pathology are still being closely studied by the world's leading scientists. It is possible that in the foreseeable future there will be a breakthrough in medicine.
How to predict the life expectancy of a patient with Parkinson's disease?
The prognosis is formed by the attending physician based on the clinical picture, chronic pathologies of the patient and the results of diagnostic procedures. Assessing the prospects for treatment is a difficult task, since neurologists cannot predict in advance the human body's response to drug therapy.
Is it possible to eliminate the possible causes of Parkinson's disease in youth and avoid the development of pathology in adulthood?
Neurologists believe that parkinsonism is a genetically determined pathology. For this reason, the development of an effective set of preventive measures is not possible. Note that the symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease in the early stages remain insufficiently pronounced to take emergency measures.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
At the moment, successfully selected treatment for Parkinson's disease can stop the process of degradation and reduce the severity of pathological symptoms. The disease begins to progress more slowly, which allows patients to stay in good shape longer.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at restoring the balance of dopamine in the central nervous system. The following drugs are used:
- Levodopa and its analogues: serve as the basis for the production of dopamine;
- dopamine receptor agonists: stimulate receptors similar to a natural neurotransmitter and reduce the severity of symptoms;
- MAO-B inhibitors: reduce the breakdown of dopamine;
- COMT inhibitors: prescribed in combination with levodopa and reduce its breakdown;
- anticholinergics: aimed at reducing symptoms.
There are combination products that combine several active ingredients for the fastest possible effect.
Non-drug treatment
Drug treatment is complemented by physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage. Physiotherapy is used to activate metabolic processes and increase blood flow in the brain. Depending on the patient’s condition and concomitant diseases, the following may be prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound stimulation;
- electrosleep;
- mineral baths;
- acupuncture.
The massage is aimed at improving motor activity. Intensive muscle kneading and passive gymnastics reduce muscle stiffness and have a general strengthening effect.
Physical therapy exercises allow you to:
- reduce muscle stiffness and strengthen it;
- increase sense of balance;
- improve the patient's emotional state.
Most exercises are aimed at training the sense of balance. The complex is selected individually depending on the patient’s condition, age and concomitant diseases.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is relevant in the last stages of the disease. The most effective and safest operation is the installation of a brain stimulator. The intervention does not require opening the skull. Thin electrodes are inserted into the brain and a small stimulator is placed under the skin of the collarbone. The device is programmed for a specific pulse frequency; in addition, the patient and his relatives can change the settings depending on the condition. Using a stimulant allows you to reduce the dosage of medications and keep symptoms under control for a long time.
Other surgical treatment options require working on an open brain:
- thalamotomy: destruction of part of the thalamus, allowing to get rid of tremors, but maintaining other symptoms;
- pallidotomy: partial removal of one area of the brain (globus pallidus), significantly reducing all the main symptoms of the pathology.
Symptoms of pathology
Destructive processes in the central nervous system provoke the development of the main symptoms:
- tremor;
- rigidity;
- hypokinesia (limited mobility);
- violations of translational regulation.
True parkinsonism is characterized by recurrent or constant episodes of tremors. The pathology is characterized by a looped movement of the patient’s limbs at rest.
In the early stages of the syndrome, muscle rigidity remains relatively unnoticed. As other symptoms develop, constant muscle tone causes more and more discomfort to the patient. Asymmetry in muscle tension remains one of the main diagnostic markers in the early stages of Parkinson's disease.
Neurologists distinguish several stages in the development of pathology. In the educational literature for medical universities, the classification of Hoehn and Yahr is often given. Its basic provisions are presented in the table.
| Stage | Description |
| Zero | There are no motor symptoms of parkinsonism |
| First | Pathology manifests itself unilaterally |
| Second | A complex of bilateral symptoms is formed |
| Third | Noticeable translational instability develops, but the patient retains the ability to care for himself independently |
| Fourth | Rapid degradation of motor activity, the patient can only stand and move short distances without assistance |
| Fifth | The patient cannot leave the chair or bed without the help of doctors or relatives |
Symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease are the same in women and men. Gender and age differences in the diagnosis of pathology turn out to be insignificant.
Are you experiencing symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Complications
Restriction of muscle function in Parkinson's disease inevitably leads to a decrease in the intensity of blood flow and a decrease in the level of metabolism. Already in the middle stages of the development of the disease, the risk of blood clots and the development of dangerous conditions increases significantly:
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, heart failure;
- pulmonary embolism.
Bedridden patients often face severe complications associated with a recumbent position:
- congestive pneumonia;
- aspiration pneumonia (due to impaired swallowing, food enters the respiratory tract);
- bedsore infection and sepsis.
Most patients experience apathy and severe depression, which lead to suicidal thoughts. Some patients carry out plans and commit suicide.
Correctly selected treatment significantly reduces the risk of complications, which is why it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Material and methods
The paper summarizes 4 years of experience in monitoring patients with SP by a specialist in movement disorders. Outpatient visits to patients with extrapyramidal pathology have been carried out since the beginning of 2008 at the university clinic of nervous diseases by employees of the Department of Neurology of Saratov State Medical University. In especially difficult cases, patients were hospitalized in a hospital to clarify the nosological form of the disease. During this time, 603 patients were examined with suspected parkinsonism, among whom 504 (83.6%) were referred by neurologists at clinics, and 99 (16.4%) referred independently.
Prevention
Prevention of Parkinson's disease includes:
- proper nutrition with a minimum amount of preservatives and artificial additives, a sufficient amount of vitamin D, omega-3, antioxidants;
- regular physical activity to prevent physical inactivity;
- adequate sleep of at least 8 hours a day, adherence to a work and rest schedule;
- minimizing stress and fatigue;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- regular medical examinations, compliance with all doctor’s recommendations;
- timely contact a specialist if any suspicious symptoms appear.
Make an appointment
Causes of Wilson-Konovalov disease in adults
The key process in this pathology is the inheritance of a defective gene from parents.
It is located on chromosome 13 and regulates copper metabolism. On average, the body of adults contains approximately 50 - 70 mg of copper and per day it needs no more than 2 mg of the element, which comes from food.
The vast majority of the microelement (95%) is transported in close association with the plasma protein – ceruloplasmin. It is constantly produced by the liver, and only about 5% of copper is transported along with albumin.
Copper is needed to participate in metabolic processes, including oxidative ones. If Wilson's disease develops, its elimination is impaired, the concentration in the plasma increases, and from there it spreads to the tissues. The main accumulation of copper occurs in the brain, in the iris, inside the liver, and also in the kidneys. Excess microelement has a toxic effect.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will come to the rescue at any stage of Parkinson’s disease. We offer comprehensive treatment in accordance with modern standards:
- selection of drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, laser treatment, etc.;
- therapeutic massage courses;
- Exercise therapy directly in the clinic;
- training in physical exercises for exercise at home;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment if indicated;
- training relatives in the rules of caring for the sick;
- work with a psychologist and psychiatrist if necessary.
Treatment
Treatment of the akinetic-rigid form of Parkinson's disease can be carried out using the following methods:
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- herbal treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy.
Dopamine-based medications that replenish the neurotransmitter deficiency must be taken constantly. Rigidity in Parkinson's is relieved by medication, but therapy is symptomatic.
During drug treatment, complications may arise in the form of violent movements and outbursts of aggression. In some cases, the patient “freezes” after physical activity and becomes completely motionless.
Surgical treatment using a laser allows you to stop the progression of the disease in the early stages. Traditional medicine methods and physiotherapeutic effects are of auxiliary value and are designed to relieve tension in stiff muscles.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic has experienced doctors, skilled nurses and modern equipment for diagnosing and treating various diseases. We offer:
- diagnostics using instrumental, functional and laboratory studies;
- consultations with experienced specialists in various fields;
- obtaining the opinion of foreign colleagues if necessary;
- individual selection of treatment;
- complex therapeutic regimens using medications, physiotherapy and other methods;
- extensive screening programs for early diagnosis of diseases;
- detailed consultations on disease prevention;
- any certificates and conclusions.
Parkinson's disease begins very slowly, but it is almost impossible to stop the process. If you or your family have suspicious signs, do not delay contacting a doctor. Sign up for diagnostics at the Energy of Health clinic.
Forecast
If left untreated, Parkinson's disease has a negative prognosis. During the first 5 years, 25% of patients experience disability and/or death, and within 7–10 years this figure exceeds 50%.
This is why early diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson's disease is so important. But even at a late stage of the disease, modern methods used in the international clinic Medica24 help to significantly improve a person’s condition.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yuryevna, a neurologist at the International Clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.