A disorder acquired as a result of gradual progressive destruction in a patient of nerve cells that are responsible for coordination functions is known as Parkinson's disease. The initial symptoms of the disease are tremor (shivering) of muscle tissue, instability of some parts of the body at rest (hands, fingers, head). Such symptoms are most common among citizens aged 55-60 years, but there have also been cases when the disease began to manifest itself in citizens under 40 years of age. As the disease progresses, a person completely loses any physical activity and intellectual abilities, all this leads to the extinction of vital activity and death. This disease is one of the most difficult to treat. How long can a person with such a diagnosis live with modern medicine? Accommodation and care in specialized boarding houses for the elderly significantly increases life expectancy with this disease.
The emergence of Parkinson's disease
The entire system of coordination of human movements is controlled by his central nervous system, which includes the brain as well as the spinal cord. As soon as the patient thinks of making any movement, the cortex of his brain activates all parts of the nervous system responsible for physical activity. The basal ganglia is one such part. This is an auxiliary motor mechanism responsible for the speed of movement, quality and accuracy of execution.
Activity signals travel from the human cortex to the basal ganglia compartment. The ganglia are responsible for determining the specific muscles involved in the movement process, the work of each of them and the degree of their tension. All this happens so that the accuracy and purposefulness of movements corresponds to intentions.
Impulses from the basal ganglia are transmitted using neurotransmitters (special chemicals). The work of muscles depends on the amount of such substances and the process of their influence.
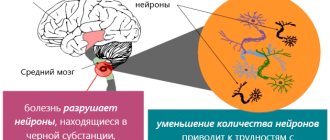
One of the most important neurotransmitters is dopamine, which helps inhibit nerve signals, controlling the accuracy and force of contraction of each muscle. In the most complex coordination of movements, part of the work is done by the “Nigral Substantia”, delivering dopamine to the striatum, thereby sending signals from the basal ganglia to the rest of the brain. “Substantia nigra” has this name because of the dark color of this brain structure, since the by-product of dopamine biosynthesis, melanin, is found there in large quantities. So, Parkinson’s disease is caused by insufficient levels of dopamine in the substantia nigra.
What is Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative brain disease that develops slowly in most cases. Over the course of many years, the symptoms of this pathology may progress unnoticed. Due to the death of a significant number of neuronal cells in areas of the basal ganglia and degradation of nerve fibers, this disease occurs. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease begin to actively manifest themselves when the functions of 80% of neural connections are impaired. In such cases, Parkinson's disease is incurable and develops over time, despite all the therapy taken.
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of diseases that develop slowly and are characterized by hereditary or acquired lesions of the central nervous system.
Another specific feature of Parkinson's disease is a sharply reduced amount of dopamine. Its quantity is no longer sufficient for the necessary inhibition of nerve impulses flowing from the cerebral cortex. Thanks to this, nerve impulses go straight to muscle tissue, stimulating its tension. This is typical for the most striking manifestations of Parkinson's disease: muscle contractions (trembling and tremors), stiffness of muscle activity due to excessively high tone, manifestations of unintentional body movements.
Life extension
When the patient has completed all the necessary diagnostic procedures, he will be given a final diagnosis. Sometimes this process is delayed, because... symptoms may be vague and similar to other diseases. Immediately after checking that a person has this particular disease, the doctor will prescribe therapy that will allow him to remain in a normal state and live as long as possible.
Treatment includes many ways to treat the disease. It is very important to follow all the measures prescribed by the doctor, because... Only this approach will achieve results. The patient is prescribed:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Physical therapy;
- Classic diet;
- Psychotherapy.
Along with this, you must take medications. They help treat the disease by reducing its impact on the brain. Various groups of drugs are prescribed. Most popular:
- "Lizuride";
- "Midantan";
- "Levodopa";
- "Pyridoxine";
- "Cyclodol".
Additionally, it is permissible to use folk remedies. To do this, you need to make an infusion of oats, thyme, lemon balm, peony, oregano or chamomile. If the disease progresses to stage 4 or 5, then you will need to care for the patient. If there are no relatives, this can be done by specialists at a rehabilitation center.
Recent medical developments make it possible to perform an operation that eliminates most symptoms and also normalizes the patient’s condition as much as possible.
Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonism
There are two types:
- "Primary parkinsonism" or Parkinson's disease. This is an irreversible, quite common case.
- "Secondary parkinsonism". Characterized by brain damage resulting from infectious or traumatic events. As a rule, it can be treated and restored. It can occur at any age under the influence of external factors.
The following can lead to secondary parkinsonism:
- Various brain injuries.
- Various toxic poisonings.
- Encephalitis.
- Vascular lesions in the brain (coronary artery disease, stroke or atherosclerosis, etc.).
Signs and symptoms
How to spot Parkinson's disease?
The manifestation of the disease is characterized by a persistent loss of control over one’s own physical activity:
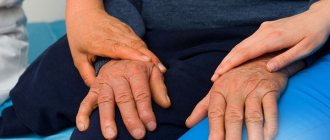
- Tremor at rest.
- Lack of mobility and muscle stiffness (rigidity).
- Reduced speed and insufficient range of motion.
- Insufficient ability to maintain balance (instability).
Rest tremor is involuntary small movements that occur in the absence of motor activity. The most common are sudden shaking of the hands and tilted movements of the head.
Signs not related to movement and coordination:
- Excessive fatigue.
- Manifestations of depression.
- Smell disorders.
- Excessive salivation.
- Increased sweating.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Negative changes in the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
- Psychoses and other psychological disorders.
- Degeneration of cognitive functions.
The most noticeable deviations in cognitive functions in parkinsonism are:
- Memory problems.
- Slowness of thought processes.
- Problems with orientation in space.
Variants of the disease in young people.
There are cases when young people from 20 to 40 years of age develop Parkinson's disease - this is the so-called “early parkinsonism”. But there are not many such patients, according to statistics from 10% to 20%. People with this diagnosis have the same symptoms of the disease, but they are less pronounced and develop much more slowly than in the elderly.
How it manifests itself in young people:
- In many patients, the disease manifests itself as painful spasms of the muscles of the extremities of the body (feet, fingers, shoulders). This symptom can complicate the diagnosis of the disease, as it is very similar to the symptoms of arthritis.
- Undesirable motor activity of the body and limbs, often resulting from dopamine drug therapy.
Further symptoms characteristic of the normal progression of the disease develop.
Diagnostics.
At this time, there are no objective tests whose results may indicate the presence of Parkinson's disease.
Based on the manifestations of the disease, the findings of a physical examination and the results of certain tests, a diagnosis is made. The attending physician can refer you for certain diagnostics (including tests), which will help to recognize and exclude other diseases that cause similar manifestations.
The main sign of the presence of Parkinson's disease is positive changes and a noticeable decrease in symptoms of the disease after the prescription and administration of anti-Parkinsonian drugs.
Also in the modern world there is another diagnostic method - this is Positron Emission Tomography (PET). In a number of circumstances, when using PET, it is possible to identify insufficient levels of dopamine in certain areas of the brain, which is the root cause of Parkinson's disease. But this technique is very rarely used for diagnostic examination of Parkinson’s disease, since it is quite expensive and not many medical institutions are provided with such equipment.
Forecast
Each patient should be especially attentive to the slightest signs of the development of such a pathology. The manifestations of Parkinson's disease and how long people live with it all depend on many factors. The disease destroys neurons in the brain, reducing their number many times over. Gradually this leads to a very serious condition, which can result in death.
The least favorable prognosis is received by older people, as well as those who are faced with the most complex forms of the disease. The latter concerns the akinetic-rigid type of Parkinson, because. it progresses very quickly and the symptoms become even more severe. Many patients with this form of the disease become disabled many times faster than other patients, and also die more often.
Previously, such a disease led to disability after 1-2 years, and the approach of death could be expected after 5-8 years. Now modern medicine has made it possible to improve the situation of patients and give them more chances. People with Parkinson's can live for about 20 years if their age is between 40 and 65 years, while younger people can expect to increase their remaining life to almost 40 years. However, the elderly, those over 65 years of age, are not able to withstand more than 5 years. Such indicators are enough for patients to die from natural causes and not from disease. It is worth noting that late stages of Parkinson's or severe forms will cause death to approach much faster and the prognosis will be poor.
Many factors influence how long a person will live. The most important of them are the following:
- Patient's age;
- Form and stage of the disease;
- Genetics;
- Intensity of therapy;
- The presence of other pathologies;
- The quality of life.
Patients often die of natural causes. However, there are frequent cases of complications, for example, bronchopneumonia, infection, heart attack or oncological pathologies. Sometimes patients experience delusions with hallucinations, which can lead to suicide.
With Parkinson's disease, a person becomes disabled. Its group depends on the stage of the disease:
- Group 3 – at stage 2 or 3;
- Group 2 – at stage 3 or 4;
- Group 1 – at stage 4 or 5.
Obtaining a disability group is not an easy process. The patient will have to undergo a lot of diagnostics, and then regularly confirm his diagnosis for a special commission. In some cases, when Parkinson's disease symptoms and prognosis for life are unfavorable, disability can be assigned permanently, which will prevent it from being confirmed in the future.
Stages of development of Parkinson's disease
"1st stage"
Some disturbances in the movements of one of the hands. Nonspecific manifestations also occur: decreased sensitivity of smell, chronic fatigue, sleep disturbances and mood abnormalities. When nervous, tremors appear in the fingers. As the tremor progresses, it intensifies and tremor appears at rest.
"One and a half" or "intermediate stage"
Strong manifestations of signs of illness in one of the parts of the body or arm. Constant trembling, disappearing only in sleep. The quality of fine motor skills of the hands deteriorates, manifested in changes in handwriting. Stiffness in the neck and part of the upper back becomes noticeable, and the swinging movements of both arms when walking are limited.
"2nd stage"
Symptoms of deviations in the regulation of movements occur on both sides of the body. Trembling of the lower jaw and tongue is also possible. Disturbances in joint movement, noticeable changes in facial expressions and speech inhibition. Changes in sweating: skin is too oily or, conversely, too dry. Sometimes the patient has the ability to control involuntary movements. The patient can perform simple tasks and actions, but the speed of their execution slows down significantly.
"Zya stage"
Muscle stiffness (rigidity) and hypokinesia become much more noticeable. The gait changes noticeably, which has the appearance of a “puppet”, expressed in parallel feet and small steps. The facial expression takes on the appearance of a “mask”. Head shaking may appear as swaying movements (vertically or horizontally). The posture that often appears noticeably changes: half-bent legs, a semi-squat position of the pelvis, a hunched back with the head pressed and lowered forward, while the arms are slightly bent at the elbows and pressed against the body (the “beggar” pose). Characteristic movements in the joints are jerky. Deviations in speech develop - a person begins to fixate on the same words. The person is still able to take care of himself, but experiences enormous difficulties in doing so. It is difficult to fasten buttons and get your hands into the sleeves. Much more time is spent on simple hygiene procedures.
"Stage 4"
Postural instability begins to be noticeable - it is difficult for a person to balance when landing or getting out of bed (there is a high probability of falling forward). If you slightly push a patient who is standing at rest, he will move by inertia in the direction of the push until he hits an obstacle. There are falls that end in broken limbs. During sleep, changing the position of the body is especially difficult. The patient’s speech degrades – it becomes quieter and has a “blurred” character. Acute manifestations of depression, expressed in suicide attempts, are possible. There is a possibility of progression to dementia. Without outside help, a person can no longer cope with everyday worries and self-care activities.
"Stage 5"
This is the last stage of development of Parkinson's disease, and it is characterized by the development and intensification of all movement disorders. The person is no longer able to walk, sit or stand independently. Is not able to feed on his own - this happens not only due to trembling in the limbs and stiffness in the muscles, but also due to the inability to swallow food on his own. Loss of urinary control. His speech becomes extremely incomprehensible and the person begins to need constant care and help from others. Often these manifestations are accompanied by severe attacks of depression and dementia.
Dementia is a disease characterized by damage to cognitive functions to a much greater extent than occurs with aging. It manifests itself in the loss of the ability to learn and acquire new information with the loss of previously acquired knowledge.
Is there a chance of recovery with proper treatment?
Parkinson's disease, if symptoms and signs in women are confirmed by diagnosis, is difficult to treat. Therapy helps keep tremors under control, ease movement and improve coordination. The difficulty of treatment lies in replenishing dopamine, a brain neurotransmitter that is lacking in this disease.
The main directions of therapy make it possible to cope with the following symptoms:
- imbalance;
- impaired control over body position;
- decreased mobility;
- muscle weakness;
- trembling of limbs.
Therapy regimens prescribed by a doctor can support the patient’s body and provide improvement, but it is impossible to completely overcome the disease with their help.
Parkinson's disease is an incurable disease that is not a death sentence and allows you to live for many years. But without quality treatment, the patient’s condition worsens, up to the first group of disability, in which the person is unable to care for himself. That is why it is so important for patients to use supportive therapy and follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Causes of Parkinson's disease
Doctors and scientists are unable to recognize and identify specific root causes of the development of Parkinson's disease, however, there are several facts that may provoke the progression of this disease:
- One of the reasons may be aging . Since with aging, the number of nerve connections and cells sharply decreases, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in the required amount of dopamine in parts of the brain (in the basal ganglia).
- Hereditary factor . The genetic predisposition has not yet been proven, but 20% of people with this disease have relatives with manifestations of parkinsonism.
- Environment . It can lead to toxic brain poisoning due to the presence of toxic compounds, poisonous substances, pesticides and heavy metals in the air, water or food, which can lead to the death of a large number of nerve cells and lead to illness.
- Use of medications . Antidepressants and other antipsychotic medications that alter the metabolism and production of dopamine in the central nervous system can cause side effects very similar to the symptoms of parkinsonism.
- Diseases and brain injury . Concussions, various head contusions, viral or bacterial encephalitis - all this can lead to damage to parts of the basal ganglia and trigger the progression of Parkinson's disease.
- Lifestyle . Improper sleep patterns (lack of sleep), regular stress, unhealthy diet, lack of vitamins in the body and other factors can cause some pathologies.
- Other diseases . For example, atherosclerosis, various malignant tumors in the brain, and disorders of the endocrine gland can also provoke complications leading to Parkinson's disease.
Causes, symptoms
No disease can appear without the presence of certain causes or factors in a person’s life. Parkinson is no exception. To avoid such an unpleasant situation, you should try to avoid the maximum number of possible causes of the disease. Symptoms are not limited to impaired mobility with tremor and have a direct impact on how long people with Parkinson’s live.
Causes
Several factors can influence the development of the disease. Most often, the direct cause can be identified at the diagnostic stage, but sometimes treatment is prescribed without information about what exactly caused the problem.
The reasons for the development of the disease include:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Senile age, age-related changes within the body;
- Endocrine diseases, damage to the nervous system or blood vessels, infections;
- Traumatic brain injuries, vascular diseases;
- Wrong lifestyle, bad habits, alcoholism, lack of sleep, stress;
- Environmental pollution in the place of residence, work in a factory;
- Taking antipsychotics during long-term treatment for other diseases.
Any of these reasons can provoke the development of Parkinson’s, and even a completely healthy person can become ill.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease bring a lot of problems even in cases where the degree of Parkinson's development is not so dangerous. They can significantly limit the patient’s capabilities and also deprive him of a full life.
Signs of the disease may consist of the following symptoms:
- Slowness of movements;
- Constant muscle tension;
- Tremor of the limbs;
- Slight stoop;
- Change in gait;
- Painful sensations in the joints;
- Slurred speech;
- Intellectual inhibition;
- Apathy, depression;
- Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Disorders of the genital organs.
Either just a few symptoms or all of them can appear. Their brightness depends on the form and stage of the disease. If they are accompanied by other violations, then the development of complications is possible.
Particularly severe symptoms may leave the patient unable to move, requiring regular care from another person.
How is Parkinson's disease treated?
- In the early stages of Parkinson's disease, it is treated with medications, introducing substances that are lacking into the body. The main target of drug (chemical) therapy is the “substantia nigra”. When using this method of treatment, almost all patients experience a noticeable reduction in symptoms and they have a lost opportunity to live a normal life.
- But there are cases when patients do not improve, even after taking medications for a long time and increasing their dosages. In such cases, brain surgery is used to implant a stimulator into the brain.
This operation takes the form of high-frequency stimulation of the basal ganglia with electric current through an electrode connected to an electrical stimulator:
- When using local anesthesia, two electrodes are sequentially introduced into the patient’s brain (along a path determined in advance by a computer), producing deep stimulation of parts of the brain.
- Under anesthesia, an electrical stimulator connected to electrodes is implanted into the chest area under the skin.
Drugs used for treatment:
"Amantadine" or "Midantan". These are the drugs used to start the treatment of Parkinson's disease. This medication stimulates the release of dopamine, helps reduce its reuptake by blocking glutamate receptors, protects the “substantia nigra,” and also has other positive properties. Amantadine significantly reduces the manifestations of hypokinesia and rigidity (stiffness and limited movement), however, it almost does not reduce tremor and trembling. These medications are well tolerated and have almost no side effects.
Rotigotine or Newpro. It is an agonist of the dopamine receptor group. Available in the form of a patch that is applied to the skin. This patch is a transdermal therapeutic system with dimensions of 10-40 cm², used once a day. Such medications are sold exclusively by prescription and are used for independent (without combination with other drugs) treatment of Parkinson's disease in the early stages.
The use of this form of drugs has significant advantages: the dosage is smaller, but more effective, and the side effects are less pronounced.
"Leftfall." It has long been considered one of the best medical drugs for the treatment of Parkinsonism. This compound is a chemical precursor to dopamine. But it is worth remembering that this substance has a significant number of side effects, such as psychological disorders. It is prescribed, as a rule, in combination with “carbidopa” or “benserazide”. They lead to better absorption of “levodopa” and reach areas of the brain and help reduce side effects.
"Modopar". It is a combination drug containing both “leovdopa” and “benserazide”. Produced in various forms. "Madopar GSS" is produced in special capsules, the shell density of which is significantly less than that of gastric juice. This ensures that the substance enters the body slowly and evenly, because such a capsule dissolves in the stomach from 5 to 12 hours. “Dispersible Madopar” is also available, which has a liquid form, thanks to which it acts much faster. This option is more suitable for patients with limited swallowing function.
"Miralex". This drug is produced as tablets, which are used both as a stand-alone drug in the early stages of the disease, and as a combination therapy with levodopa in the later development of Parkinson's disease. Miralex has fewer side effects than non-selective agonists, but at the same time more than amantadine. Such side effects can manifest themselves as nausea, pressure surges, excessive drowsiness, changes in the balance of enzymes secreted by the liver, and swelling of the lower extremities. Hallucinations are also possible in patients diagnosed with dementia.
"MAO inhibitors." They significantly slow down the oxidation of dopamine, located in the “striatum” of the brain, due to this its concentration in synapses increases. The most common use in the treatment of the disease is Selegiline. In the first stages of Parkinson's disease, Selegiline is used as an independent therapy (without the use of other combination drugs). Many patients report significant improvements when using these products. Undesirable effects from the use of Selegiline are rare and mild.
Treatment with Selegiline can delay the prescription of lepodopa for a period of 9 to 12 months. In the last stages of the disease, Selegiline is used as an addition to Levodopa, which allows the latter to increase its effectiveness by a third.
"Mydocalm." This drug greatly reduces the abnormally large tone of muscle tissue. This property is used in Parkinson's disease as an auxiliary. "Mydocalm" is available in tablets, for oral use and ampoules, for intravenous and intramuscular use.
"B vitamins." This group of vitamins is often used to treat diseases of the central nervous system. In order for L-Dopa to be safely converted into dopamine, nicotinic acid and vitamin B6 are needed. Also, “Thiamin” (vitamin “B1”) is used to increase the content of dopamine in parts of the brain.
Classification
The disease is a neuro-physiological one, which makes it quite dangerous. It causes the gradual death of brain cells, as well as the cessation of the production of dopamine, which is very important for humans. The main consequence of the disease is a state of degeneration of body and brain functions.
Stages
For Parkinson's disease, there are two classifications according to stages. The first is according to Hen-Yar, and the second is classical. Both of them are used by doctors to make a diagnosis, because allow you to describe the patient’s condition as accurately and concisely as possible.
According to Khen-Yar, 3 stages are distinguished:
- Early. The brain is slightly damaged, symptoms are minimal, and tremors of the upper extremities may occur.
- Expanded. The brain damage is more serious, the symptoms manifest themselves quite actively, and it is difficult to normalize the condition even with high-quality treatment.
- Late. The brain works ineffectively, the patient cannot get up and move, socialization is very low.
The second classification by stages consists of 5 stages of the disease:
- The first stage is characterized by the manifestation of symptoms on one side.
- The second stage is accompanied by the spread of symptoms to the second part of the body.
- The third stage is characterized by the appearance of minor postural instability.
- The fourth stage partially limits a person’s ability to move fully.
- The fifth stage deprives you of the ability to move, forcing you to lead a recumbent lifestyle.
The amount of time people with advanced Parkinson's disease live largely depends on the stage. Therefore, its determination is of great importance for making a future prognosis and planning therapy.
Forms
Parkinson's disease is classified not only by stages, but also by forms. Moreover, over time, one can flow into another, which will force the doctor to change the previously made diagnosis and adjust the treatment plan.
There are 6 forms in total:
- Rigid - all muscle tissues are constantly tense, the ability to move is limited.
- Trembling - no rigidity is observed, but is manifested by severe tremor of the limbs.
- Akinetic – there are no involuntary movements, the limbs are under control of the patient.
- Rigid-trembling – accompanied by tremor, combined with muscle tension.
- Trembling-rigid - there is a tremor during movements, the rest of the time it is absent.
- Akinetic-rigid - the limbs do not suffer from tremor, the symptoms consist of non-motor manifestations.
By determining the shape, doctors are able to find out the extent of the disease. With mild types of Parkinson's, the chances of saving life remain relatively high, but with severe types, for example, akinetic-rigid, the prognosis will be unfavorable.
Determining the form and stage of the disease is the most important task for a doctor whose patient is suspected of having Parkinson's disease.