© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Focal changes in the brain substance are areas of atrophic, dystrophic, necrotic changes that arise against the background of impaired blood flow, hypoxia, intoxication and other pathological conditions. They are recorded on MRI and cause anxiety and fear in patients, but do not always cause any symptoms or are life-threatening.
Structural changes in the brain substance are more often diagnosed in the elderly and serve as a reflection of natural aging. According to some data, more than half of people over 60 years old have signs of focal changes in the brain. If the patient suffers from hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, then the severity and prevalence of dystrophy will be greater.
Focal changes in the brain substance are also possible in childhood. Thus, in newborns and infants, they serve as a sign of severe hypoxia during the prenatal period or during childbirth, when a lack of oxygen provokes the death of immature and very sensitive nervous tissue around the ventricles of the brain, in the white matter of the hemispheres and in the cortex.
The presence of focal changes in nervous tissue, established by MRI, is not yet a diagnosis. Focal processes are not considered an independent disease, so the doctor is faced with the task of finding out their cause, establishing a connection with the symptoms and determining tactics for managing the patient.
In many cases, focal changes in the brain are detected by chance, but patients tend to associate their presence with a variety of symptoms. In fact, these processes do not always disrupt brain function, provoke pain or anything else, so treatment is often not required, however, most likely, the doctor will recommend follow-up and MRI annually.
Causes of focal changes in the brain
Perhaps the main cause of focal changes in the brain substance in adults can be considered the age factor, as well as its accompanying diseases. Over the years, natural aging occurs in all tissues of the body, including the brain, which somewhat decreases in size, its cells atrophy, and in some places structural changes in neurons are noticeable due to insufficient nutrition.
Age-related weakening of blood flow and slowdown of metabolic processes contribute to the appearance of microscopic signs of degeneration in brain tissue - focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. The appearance of so-called hematoxylin balls (amyloid bodies) is directly associated with degenerative changes, and the formations themselves are once active neurons that have lost their nucleus and accumulated the products of protein metabolism.
Amyloid bodies do not resolve; they exist for many years and are found diffusely throughout the brain after death, but mainly around the lateral ventricles and vessels. They are considered one of the manifestations of senile encephalopathy, and there are especially many of them in dementia.
Hematoxylin balls can also form in foci of necrosis, that is, after cerebral infarction of any etiology, or trauma. In this case, the change is local in nature and is detected where the brain tissue was most damaged.
amyloid plaques in the brain during natural aging or Alzheimer's disease
In addition to natural degeneration, in older patients a noticeable imprint on the structure of the brain is left by concomitant pathology in the form of arterial hypertension and atherosclerotic vascular lesions. These diseases lead to diffuse ischemia, degeneration and death of both individual neurons and their entire groups, sometimes very extensive. Focal changes of vascular origin are based on a total or partial disruption of blood flow in certain areas of the brain.
Against the background of hypertension, the arterial bed is primarily affected. Small arteries and arterioles experience constant tension, spasm, their walls thicken and become denser, and the result is hypoxia and atrophy of the nervous tissue. With atherosclerosis, diffuse brain damage is also possible with the formation of scattered foci of atrophy, and in severe cases, a stroke occurs like a heart attack, and focal changes are local in nature.
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory nature are precisely associated with hypertension and atherosclerosis, which almost every elderly inhabitant of the planet suffers from. They are detected on MRI in the form of scattered areas of rarefaction of brain tissue in the white matter.
Focal changes of a post-ischemic nature are caused by previous severe ischemia with necrosis of brain tissue . Such changes are typical for cerebral infarctions and hemorrhages due to hypertension, atherosclerosis, thrombosis or embolism of the cerebral vascular bed. They are local in nature, depending on the location of the site of neuronal death, and can be barely noticeable or quite large.
Atherosclerosis is the cause of decreased blood flow to the brain. In the chronic process, small focal/diffuse changes in brain tissue develop. In case of acute blockage, an ischemic stroke may develop with the subsequent formation of a necrotic focus in the surviving patient
In addition to natural aging and vascular changes, other causes may lead to focal damage to brain tissue:
- Diabetes mellitus and amyloidosis - cause degeneration of predominantly vascular origin due to hypoxia and metabolic disorders;
examples of demyelination foci in multiple sclerosisInflammatory processes and immunopathology - multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, vasculitis in rheumatic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, for example) - both demyelination (loss of cell membranes) and microcirculation disorder with ischemia occur;
- Infectious lesions - toxoplasmosis, “slow infections” (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Kuru), herpesvirus encephalomyelitis, borreliosis, tick-borne viral encephalitis, HIV infection, etc. - focal changes are based on the direct cytopathic effect of pathogens, the death of neurons with the formation of diffuse scattered lesions, inflammation and necrosis;
- Osteochondrosis and congenital pathology of the spine and blood vessels, leading to ischemic changes and decreased blood flow;
examples of foci of brain leukoaraiosisAcute and chronic intoxication with narcotic substances, alcohol, carbon monoxide - diffuse irreversible degeneration and death of neurons occurs;
- Brain injuries - focal changes of a local nature at the site of application of the traumatic factor or diffuse areas of demyelination and microinfarctions in severe bruises;
- Metastatic brain damage from tumors of other organs;
- Congenital changes and perinatal severe hypoxia are considered in the context of the pathology of early childhood and represent multiple focal changes in the nervous tissue mainly around the lateral ventricles (leukoaraiosis and leukoencephalomalacia).
Stages and symptoms of disease development
The disease is progressive. It is characterized by a paroxysmal course, with sharp rapid deterioration. Discirculatory focal changes have several stages of development.
Sinusitis is a type of sinusitis, a disease of the maxillary sinus (sinuses) of the nose, caused by various types of infections or as a complication of other inflammatory processes in the ENT organs. Read more in the article: “antibiotics for sinusitis in adults.”
Initial
Minor processes of tissue change begin in small areas of the brain. Their occurrence is facilitated by mild dysfunction of the vascular circulatory system.
Advertising:
Symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- recurrent headaches;
- easy absent-mindedness;
- increased emotional sensitivity (irritability and tearfulness);
- noise in the head, frequent dizziness;
- partial loss of non-professional memory;
- concentration on performing one type of activity;
- mild ataxia.
Average
The blood supply to the brain deteriorates significantly. Blockage of blood vessels provokes necrotization of cells in the superficial structures of the brain (gray matter).
The symptoms of the initial stage worsen, the following signs are added:
- Sleep disturbances. The patient sleeps more often during the day, and sleep lasts longer than at night.
- Interest in new knowledge disappears, intelligence becomes dull.
- Behavior becomes aggressive, character becomes self-centered.
- There is a lack of coordination of movements (staggering gait, uncertain hand movements).
- There is a progressive loss of memory and professional skills.
Heavy
Due to the development of chronic dyscirculatory encephalopathy in the lesion, most of the cells of not only gray matter, but also white matter die. This causes disturbances in brain function.
Advertising:
At this stage, neurological changes reach their peak. The clinical picture is disappointing. All previous symptoms become irreversible, which entails consequences such as:
- complete loss of ability to work and self-care;
- loss of memory and skills, development of dementia (dementia);
- loss of control over motor and speech functions.
Early diagnosis of the disease is difficult because at its initial stage there are no pronounced symptoms. Delayed diagnosis makes treatment more difficult.
If the blood flow per minute slows down to 10 ml/100 g and below
, the process of instant destruction of brain tissue, which is irreversible, starts.
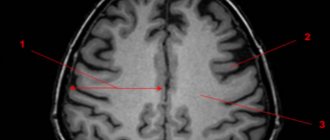
Features of MRI diagnostics of focal changes in the brain substance
As a rule, the presence of focal changes in the brain substance becomes known after the patient has undergone an MRI. To clarify the nature of the lesion and differential diagnosis, the study can be performed with contrast.
Multiple focal changes are more typical for infections, congenital pathology, vascular disorders and dysmetabolic processes, multiple sclerosis, while single focal changes occur after strokes, perinatal lesions, certain types of injuries, and tumor metastasis.
Doctors' recommendations
Quit tobacco products or get rid of addiction. Do not drink alcohol or drugs. Move more, do exercises. The permissible intensity of physical activity is determined only by a doctor. Sleep 7-8 hours a day. Doctors advise increasing sleep duration when diagnosing such disorders.
You need to eat a balanced diet; it is preferable to develop a diet together with your doctor in order to take into account all the nutritional components that help with destructive processes in the brain. Neurons need to be nourished with useful substances.
Review other bad habits. It is better to get rid of regular stressful situations. It is better to change your job if it is a little stressful. Relax more often, choose the most suitable ways for this. Visit the doctor for examinations at the specified frequency in order to timely record changes in pathological processes and timely apply therapeutic techniques.
Nervous tissues are characterized by increased vulnerability. Neurons die when there is a lack of oxygen, so you need to treat your body with special attention.
Natural degeneration during aging
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature against the background of age-related involution are represented by MRI signs:
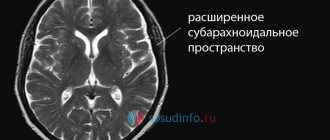
- Periventricular (around the vessels) “caps” and “stripes” - found outside the lateral ventricles, arising due to the breakdown of myelin and expansion of the perivascular spaces, proliferation of glial cells under the ependyma of the ventricles;
- Atrophic changes in the hemispheres with expansion of the grooves and the ventricular system;
- Single focal changes in the deep white matter.
Multiple focal changes of a discirculatory nature have a characteristic deep location in the white matter of the brain. The described changes will be more pronounced, and the symptoms of encephalopathy will progress with age-related hypertension.
changes in the brain with age (younger → older): leukoaraiosis around the ventricles of the brain, atrophy, focal changes
Depending on the prevalence of age-related changes, the following are distinguished:
- Mild degree - single focal changes in the white matter of point sizes in the deep parts of the brain;
- Middle - drainage pockets;
- Severe - large confluent, scattered foci of damage to nervous tissue, mainly in deep sections against the background of vascular disorders.
At-risk groups
If there are no signs of the disease, it is preferable to find out about risk groups. According to statistics, focal disease more often manifests itself in the following disorders: atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, VSD, diabetes, heart muscle disease, regular stressful situations, work without movement, abuse of alcohol, tobacco, drugs, obesity.
As a result of age-related changes, brain damage occurs. After reaching 60 years of age, minor lesions of the disorder appear.
Discirculatory changes
Focal changes in the white matter of the brain due to impaired vascular trophism are the most common occurrence when analyzing MRI scans in older patients. They are considered to be caused by chronic hypoxia and dystrophy due to damage to small arteries and arterioles.
decreased blood flow is one of the main causes of age-related changes in the brain
MRI signs of vascular lesions:
- Multiple focal changes in white matter, mainly in the deep structures of the brain, not involving the ventricles and gray matter;
- Lacunar or border areas of necrosis;
- Diffuse lesions in the deep sections.
foci of lacunar microstrokes in the brain
The described picture may resemble that of age-related atrophy, therefore it can be associated with dyscirculatory encephalopathy only if the corresponding symptoms are present. Lacunar infarctions usually occur against the background of atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels. Both atherosclerosis and hypertension give similar changes on MRI in a chronic course, can be combined and are characteristic of people after the 50th birthday.
Diseases accompanied by demyelination and a diffuse dystrophic process often require careful differential diagnosis, taking into account symptoms and medical history. Thus, sarcoidosis can simulate a variety of pathologies, including multiple sclerosis, and requires contrast-enhanced MRI, which shows characteristic focal changes in the basal ganglia and meninges.
In Lyme borreliosis, the most important facts are a tick bite shortly before the onset of neurological symptoms and a skin rash. Focal changes in the brain are similar to those in multiple sclerosis, measure no more than 3 mm and are combined with changes in the spinal cord.
Modern methods of therapy
Therapeutic measures are necessary to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease that provokes brain disorder. You will have to use medications that inhibit the development of pathology.
Vascular medications such as pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, cinnarizine, and dihydroergocriptine are required . They have a beneficial effect on the blood supply to brain tissue, stabilize the functioning of capillaries, increase the plasticity of red blood cells, and make the blood liquid. The drugs help eliminate vascular spasm and increase the resistance of arteries and veins to hypoxia.
Cytoflavin and piracetam are used as antioxidant and antihypoxic drugs. Treatment with vestibulotropic drugs stops dizziness, eliminates unsteadiness during movement, and improves the quality of life of patients. At high blood pressure levels, constant monitoring of pressure numbers and contraction frequency is required, stabilizing them according to indications.
Today, doctors pay a lot of attention to substances that block calcium channels, stabilize blood pressure, and act as neuroprotectors. Cerebrolysin helps restore cognitive functions.
Manifestations of focal changes in brain matter
The brain is supplied with blood from two vascular basins - the carotid and vertebral arteries, which already have anastomoses in the cranial cavity and form the Circle of Willis. The possibility of blood flow from one half of the brain to the other is considered the most important physiological mechanism that allows one to compensate for vascular disorders, so the clinical picture of diffuse small-focal changes does not appear immediately and not in everyone.
At the same time, the brain is very sensitive to hypoxia, so long-term hypertension with damage to the arterial network, atherosclerosis, which impedes blood flow, inflammatory changes in blood vessels and even osteochondrosis can lead to irreversible consequences and cell death.
Since focal changes in brain tissue occur due to a variety of reasons, the symptoms may be different. Dyscirculatory and senile changes have similar features, but it is worth remembering that lesions in relatively healthy people are unlikely to have any manifestations.
Often changes in brain tissue do not manifest themselves at all, and in elderly patients they are even regarded as an age-related norm, therefore, with any MRI conclusion, its result should be interpreted by an experienced neurologist in accordance with the symptoms and age of the patient.
If the report indicates focal changes, but there are no signs of trouble, then there is no need to treat them, but you will still have to see a doctor and periodically monitor the MRI picture in the brain.
Often, patients with focal changes complain of persistent headaches, which are also not necessarily associated with the identified changes. You should always rule out other causes before you start “fighting” an MRI picture.
In cases where the patient has already been diagnosed with arterial hypertension, cerebral or neck atherosclerosis, diabetes, or a combination of these, it is very likely that an MRI will show corresponding focal changes. Symptoms may include:
- Emotional disorders - irritability, mood swings, tendency to apathy and depression;
- Insomnia at night, drowsiness during the day, circadian rhythm disturbances;
- Decreased mental performance, memory, attention, intelligence;
- Frequent headaches, dizziness;
- Disorders of the motor sphere (paresis, paralysis) and sensitivity.
Initial signs of dyscirculatory and hypoxic changes do not always cause concern in patients. Weakness, fatigue, bad mood and headaches are often associated with stress, overwork at work and even bad weather.
As diffuse changes in the brain progress, behavioral inappropriate reactions become more pronounced, the psyche changes, and communication with loved ones suffers. In severe cases of vascular dementia, self-care and independent existence become impossible, the functioning of the pelvic organs is disrupted, and paresis of certain muscle groups is possible.
Cognitive impairment almost always accompanies age-related degenerative processes with brain dystrophy. Severe dementia of vascular origin with multiple deep foci of rarefaction of nervous tissue and atrophy of the cortex is accompanied by memory impairment, decreased mental activity, disorientation in time and space, and the inability to solve not only intellectual, but also simple everyday problems. The patient ceases to recognize loved ones, loses the ability to produce articulate and meaningful speech, becomes depressed, but can be aggressive.
Against the background of cognitive and emotional disorders, the pathology of the motor sphere progresses: gait becomes unstable, trembling of the limbs appears, swallowing is impaired, paresis increases up to paralysis.
Focal changes of a post-ischemic nature are usually associated with strokes suffered in the past, so symptoms include paresis and paralysis, disorders of vision, speech, fine motor skills, and intelligence.
In some sources, focal changes are divided into post-ischemic, dyscirculatory and dystrophic. You need to understand that this division is very arbitrary and does not always reflect the symptoms and prognosis for the patient. In many cases, dystrophic age-related changes accompany dyscirculatory changes due to hypertension or atherosclerosis, and post-ischemic foci may well arise from existing disseminated vascular origin. The emergence of new areas of neuronal destruction will aggravate the manifestations of existing pathology.
Diseases of vascular origin
Here it should be clarified: vascular genesis is an indication of the origin of the disease, and not the disease itself. When talking about brain diseases of vascular origin, we mean changes associated with circulatory disorders - in venules, arteries, veins, and so on.
These types of violations are divided into several main groups.
- Transient cerebral circulatory disorders are distinguished between general cerebral and focal. The first are characterized by headache, nausea, vomiting; focal ones are responsible for short-term disturbances in motor functions and sensitivity of certain parts of the body. A distinctive feature of this vascular disorder is reversibility . Treatment promises complete restoration of function.
- Blockage of the arteries - narrowing of the working channel in any case leads to deterioration of nutrition, which significantly affects the functionality of the served areas of the brain, and can cause changes of an ischemic nature. Here treatment may even include surgery.
- Rupture of a cerebral aneurysm, cerebral hemorrhage – in fact, a stroke of ischemic or hemorrhagic origin.
What to do if MRI shows signs of focal lesions?
The question of what to do in the presence of focal changes in the brain substance on MRI is most troubling to those people who do not have any significant neurological symptoms at all. This is understandable: for hypertension or atherosclerosis, treatment has most likely already been prescribed, but if there are no symptoms, then what and how to treat?
The foci of changes themselves are not treated; doctors’ tactics are aimed at the main cause of the pathology - high blood pressure, atherosclerotic changes, metabolic disorders, infection, tumor, etc.
For age-related dystrophic and dyscirculatory changes, experts recommend taking medications prescribed by a neurologist or therapist (hypotensives, statins, antiplatelet agents, antidepressants, nootropics, etc.), as well as lifestyle changes:
- Adequate rest and night's sleep;
- A balanced diet with a limit on sweets, fatty, salty, spicy foods, coffee;
- Elimination of bad habits;
- Physical activity, walks, feasible sports activities.
It is important to understand that existing focal changes will not disappear anywhere, however, through lifestyle, monitoring blood levels and pressure, you can significantly reduce the risk of ischemia and necrosis, progression of dystrophic and atrophic processes, while prolonging active life and performance for years.
Treatment of cognitive pathologies
Donepezil is used to improve memory, concentration, and performance. The medicine stimulates the production of neurotransmitters, improves the quality of the passage of impulses as intended. The activity of patients during the daytime improves, apathy disappears, hallucinations and meaningless mechanical repetitions of the same actions are eliminated.
Rivastigmine should not be used by people with ulcers, problems with the intestines, cardiovascular system, or respiratory disorders.
For typical emotional disorders, doctors advise using antidepressants. Selective inhibitors perform remarkably well during treatment. These products are available only with a doctor's prescription.
Normal magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
MRI of the brain, normal
The normal MRI of the brain is a relative concept, depending on the age, gender of the patient, changes in tomograms are necessarily compared with symptoms. The doctor evaluates the symmetry of the lobes, the size of the ventricles, blood vessels, the uniformity of their filling with a contrast agent, the absence of neoplasms, malformations, and much more. A computer program builds layer-by-layer images, after examination they are printed onto films and examined by placing them on a X-ray viewer. Next, fill out a conclusion form indicating the preliminary diagnosis. It is hardly possible to decipher an MRI of the brain on your own without special training: an inexperienced person, even if he sees a lesion, will not figure out what caused its appearance. All questions can be asked to the doctor who conducted the study. In unclear situations with ambiguous results, obtaining a second opinion is justified. Often patients, having read the words “neoplasm, tumor, NEO” in the conclusion, try to immediately find out the prospects of the disease from the radiologist, which fails. These questions can be answered by a neurosurgeon after receiving the biopsy results. Sometimes, to complete the picture, it is necessary to additionally do an MRI of the cervical spine.
Symptoms
Clinically, focal brain damage can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- epilepsy attacks;
- mental disorders;
- dizziness;
- congestion in the vascular bed of the fundus;
- frequent headaches;
- sudden muscle contractions;
- paralysis.
The main stages in the progression of cerebral vascular disorders can be identified:
- At the initial stage, the person and the people around him practically do not notice any deviations. Only attacks of headaches are possible, which are usually associated with overload and fatigue. Some patients develop apathy. At this time, the lesions are just emerging, without leading to serious problems of nervous regulation.
- At the second stage, deviations in the psyche and movements become more and more noticeable, and pain becomes more frequent. People around you may notice outbursts of emotion in the patient.
- The third stage is characterized by massive death of neurons, loss of control of the nervous system over movements. Such pathologies are already irreversible; they greatly change the patient’s lifestyle and personality. Treatment can no longer restore lost functions.
There are often situations when changes in the blood vessels of the brain are detected completely by chance, during a diagnosis prescribed for another reason. Some areas of tissue die asymptomatically, without significant disruptions in nervous regulation.