© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
The expansion of the subarachnoid space is often recorded based on the results of ultrasound of the brain in children or MRI in adults. This change may be subtle or clearly visible, as in the case of hydrocephalus. In all cases, such a phenomenon requires consultation with a neurologist, finding out the causes and deciding on treatment tactics.
Enlargement of the subarachnoid space is not an independent disease. It occurs in response to past injuries, abnormalities of embryonic development, and is characteristic of infections and tumors of the brain and its membranes. In fact, this is a reflection of many pathological processes inside the skull, so treatment varies in each specific case.
The conclusion about the expansion of the subarachnoid space is often encountered by parents of newborn babies who had an ultrasound scan in the maternity hospital and discovered abnormalities. As a rule, mothers and fathers do not know how to react, where to run and what to expect from pathology in the future. Answers to their questions should be given by pediatric neurologists, who observe such children especially carefully.
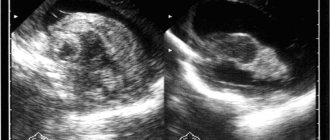
Expansion of the subarachnoid space on an MRI image
Symptoms of an enlarged subarachnoid space include a number of neurological manifestations, signs of hydrocephalus, intracranial hypertension, and possible focal symptoms in tumors. It is impossible to identify the main and strictly characteristic signs, as well as to make a diagnosis based on the clinical picture. Only additional instrumental examinations help shed light on the essence of the pathology.
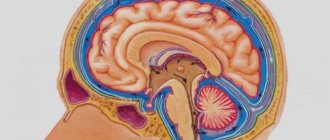
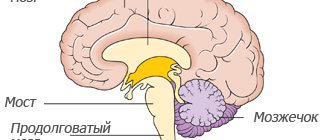
To better understand what the subarachnoid space is and how it expands, you need to remember the main features of the structure of the brain and its membranes. So, everyone knows that the central organ of the nervous system is located in the cranium. Many people remember that on the outside it is covered with membranes that protect and nourish the nervous tissue.
The outermost is the dura mater of the brain, adjacent to the bones of the skull. It is extremely dense and provides mechanical protection against damage. On the surface of the brain lies a soft membrane, rich in blood vessels, and between it and the hard one is the arachnoid (arachnoid), which, due to their close relationship, are often combined into a single whole - the leptomeninges.
Under the arachnoid and above the pia mater there is a subarachnoid space in which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. Excess cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed by the arachnoid membrane, which contains connective tissue cells, fibroblasts, glial elements and forms special trabeculae (outgrowths) that reabsorb excess fluid.
Normally, the relationship between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes is quite close, and the cerebrospinal fluid between them contains no more than 140 ml. The fluid circulating in the space between the membranes provides shock absorption to the brain, as well as nutrition, bringing useful things and taking away metabolic products from nerve cells.
With pathology, the distance between the membranes increases, there is more fluid, and on MRI there is a noticeable expansion of the corresponding intershell space, and the changes can be both local and diffuse in nature.
What is the expansion of the subarachnoid space
The human brain is surrounded by three protective membranes - hard, arachnoid and soft. The latter is directly adjacent to the medulla and provides its nutrition. The arachnoid membrane is connected to other membranes of the brain using connective tissue membranes. In areas where there are no membranes, there are cisterns.
With concomitant expansion of the subarachnoid space, arachnoiditis should be taken immediately.
The inflammatory process rapidly spreads to the brain tissue.The disease can lead to disability, serious visual impairment, hydrocephalus, and seizures.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the 4 ventricles of the brain (third, fourth and two lateral) and the subarachnoid space. Liquor performs the functions of feeding neurons, removing metabolic products, and mechanically protecting the brain.
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in children is 80-120 ml, in adults 120-160 ml. It is updated 3-5 times per day. The rate of circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is affected by the position of the body, the intensity of the heartbeat and breathing.
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs due to difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid spaces, dilating the ventricles of the brain.
The mechanisms of development of the disorder are different: the tumor mechanically blocks the paths for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, inflammation provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure may increase.
Health care
Treatment of the enlarged subarachnoid space is aimed at eliminating the causes and factors that provoked the disease. Basic therapy includes vitamins, especially groups B and D, and antibacterial drugs if infection is present.
The treatment is long-term and is prescribed for each patient individually.
The main medications include:
- diuretics , to remove excess fluid from the body (Veroshpiron, Diakarb);
- potassium-containing drugs (Asparkam);
- means for improving brain trophism (Pantogam, Cavinton);
- vitamins B and D;
- painkillers after injuries and for tumors (for example, Ketonal, Nimesil, Ketoprofen, Nimesulide);
- barbiturates (Nembutal, Phenobarbital, Amytal);
- saluretics (Acetazolamide, Furosemide, Ethacrynic acid);
- glucocorticosteroid drugs (Prednisone, Dexamethasone, Betamethasone).
If the disease progresses rapidly and the subarachnoid cavity enlarges, then the main therapy will be to find the cause of the causing disorder; if it is hydrocephalus, diuretics are used, and antibacterial drugs are used to treat infections.
Hydrocephalus as a common complication
In severe cases of the disease, when medications and physical procedures have not brought the desired result, surgical treatment is indicated.
Hydrocephalus is an extremely dangerous disease that can cause blindness or decreased vision, speech impairment and developmental delays in the child.
The principles and methods of treating the disease are carried out over a long period of time and are selected individually for each patient. Treatment will depend on the nature, severity and complications. The main task is to restore normal circulation and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the supracerebral region, which will lead to normalization of intracranial pressure, which will make it possible to improve and restore the metabolism of cells and tissues of the nervous system.
The complex also prescribes physioneuropological procedures that reduce the symptoms of the disease and speed up the recovery process.
Symptoms of the disease
The expansion of the subarachnoid space in an adult has characteristic signs:
- paralysis of the laryngeal muscles responsible for articulation and, as a result, speech impairment;
- loss of sonority ;
- difficulty swallowing;
- disturbances of visual and auditory perception;
- severe pain in the head, especially in the morning;
- nausea and vomiting accompanying headache;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness or sleep disturbances;
- dementia;
- impairment ;
- hallucinations;
- walking disorders - the patient is able to imitate walking movements in a lying position, but when standing up, walking is difficult, the gait is uncertain, shuffling;
- increased fatigue.
In young children, there is an abnormal enlargement of the skull as a result of developed hydrocephalus. Earlier symptoms are:
- increased sensitivity to sound and light stimuli;
- excessive regurgitation;
- unequal pupil size;
- strabismus;
- problems ;
- slowly overgrowing fontanel;
- swelling of the fontanel;
- restless behavior due to changing weather;
- tremor of the chin and limbs.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the causes of the disease and the severity. In the absence of adequate and timely treatment, expansion of the subarachnoid space in infants is dangerous due to the possible development of hydrocephalus.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
This disease leads to a lag in motor development, seizures, paralysis, and intellectual impairment. The effects of hydrocephalus can last a lifetime.
Treatment of external hydrocele in adults
Treatment methods are selected at a consultation with a neurosurgeon or neurologist after diagnosing the disease. Intervention must be timely, otherwise the risk of various neurological complications increases. It is important to take into account both the type of pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev practice only effective methods of treating external hydrocele of the brain. Methods are divided into two large groups: conservative (medicinal) and surgical (operative), each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
Drug treatment is only relevant at a mild stage of the disease. Special medications accelerate the outflow of fluid from the brain, increase urination, relieve inflammation and swelling, strengthen blood vessels, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To combat severe headaches, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Common groups of medications are vascular, neurotropic, venotonics, diuretics. But in acute illness they will be ineffective. Mixed hydrocephalus is poorly corrected. In this case, conservative treatment will not get rid of the disease, but will only restore or improve the functioning of individual systems and functions of the human body. Often surgical intervention is not possible.
SURGERY
If acute external dropsy is diagnosed, in most cases drainage of the cerebral ventricles is prescribed. The main technologies are endoscopy and open surgery.
In the first case, we are talking about manipulations that are characterized by minimal trauma, a very low risk of complications, and fairly rapid postoperative recovery. Endoscopy methods allow, with minor intervention, not only to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also to eliminate vein defects, hematomas, and blood clots.
Currently, open surgery is chosen only in exceptional cases. Why? It is difficult to imagine performing open surgery without craniotomy. And trepanation always means increased risks and a long postoperative recovery period.
Another way to get rid of external dropsy is bypass surgery. Doctors use a system of valves and silicone tubes to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. The fluid is redirected to other cavities of the body, in particular to the abdominal cavity, right atrium, and superior vena cava. According to statistics, the effectiveness of this technique is 85%.
Is it possible to protect against the occurrence of external hydrocephalus of the brain? This is a very difficult question. But, if you completely give up bad habits and avoid traumatic brain injuries, there is a high probability that trouble will bypass you. Another important point is the timely and professional treatment of such serious diseases as encephalitis, polio, meningitis, as well as other infectious diseases.
Reasons for expansion
In infants, the disorder occurs due to congenital malformations, birth injuries, brain tumors, and infectious diseases. In some cases, the subarachnoid space and ventricles return to normal by the age of two years. However, pathology requires constant monitoring by specialists who can determine the further prognosis of the disease and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
In adults, expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs as a consequence of a stroke, vascular pathologies, head or spinal injuries, infectious and colds, and tumor cell degeneration. Meningitis, encephalitis, ventriculitis, tuberculosis, inflammation of the sinuses are diseases that affect the brain and can cause disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
The disease may indicate concomitant leptomeningitis or arachnoiditis - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain. Long-term exposure to toxic substances, such as alcohol, arsenic, and lead, can cause inflammation.
Clinical signs
Manifestations of SAP expansion differ in adulthood and in infants.
In adults
A large amount of fluid in the space limited by the bones causes an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The symptoms of this pathology consist of the following disorders:
- headache that does not respond to painkillers;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of pressure on the eyes.
These signs appear suddenly or gradually intensify, with periodic subsidence and exacerbation possible. With brain atrophy, the pressure inside the skull may not increase, so the detection of SAP expansion is an incidental finding during instrumental examination.
These include:
- unsteadiness when walking;
- dizziness;
- instability when changing position;
- difficulty coordinating movements;
- sensation of tinnitus.
Visual disturbances are manifested by decreased acuity, loss of fields, and congestive changes in the fundus. Long-term hydrocephalus leads to blindness due to atrophy of the optic nerves.
The neurological consequences of expansion of the subarachnoid space include:
- decreased motor function of the limbs - paresis (partial immobility) and paralysis;
- increased tendon reflexes and muscle tone;
- muscle spasm, which leads to contractures (limited mobility) of the limbs;
- in severe forms – loss of consciousness, convulsions.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be made after a comprehensive examination. To study the state of brain structures, the following methods are used:
- Computed tomography is a method for diagnosing pathologies of the brain and central nervous system using x-rays. It is highly informative and accurate. The disadvantages of the method are high cost and health risks from irradiation. Although the x-ray dose is much lower than permissible, the method is contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most effective diagnostic methods; it allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer picture of each part of the brain. MRI with contrast is used to examine the condition of the vessels of the head and determine disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Before the procedure begins, the patient is given a contrast agent intravenously. The disadvantages of the method are the high cost and the presence of contraindications: MRI is not performed if the patient has metal implants or a pacemaker.
- Cisternography is a type of X-ray diagnostic examination used in combination with CT to study the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Requires injection of air or contrast agent.
The patient is prescribed a general and biochemical blood test, urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests. To collect cerebrospinal fluid and measure intracranial pressure, a lumbar puncture is performed - a puncture of the spinal cord membranes at the lumbar level.
When examining cerebrospinal fluid, the concentration of protein and glucose, the number and structure of cells are determined, and a bacterioscopy of a Gram-stained fixed drop is performed. Additionally, an examination of the fundus is performed. If tumor cell degeneration is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
The neurologist also studies the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination and makes a conclusion based on all the data.
Features of brain examination in children
CT and MRI are considered the most effective modern diagnostic methods, however, their use is undesirable for young children. It is difficult for a child under one year of age to lie still for a long time. Therefore, in cases where there is still a need to resort to CT or MRI, children are given anesthesia.
To detect expansion of the subarachnoid space in children, the following is used:
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of brain structures. To conduct the examination, the child must have a non-ossified fontanel. The procedure is safe, takes no more than 15 minutes, can be performed repeatedly, and does not require special preparation. A sonologist interprets the results.
- Echoencephalography is a method of examining the brain using ultrasound, used in children with already overgrown fontanelles and in adults. Can be carried out in one- and two-dimensional modes. Allows you to determine the damage to the brain and its displacement relative to the bones of the skull under the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid. Does not require preliminary preparation and is not harmful to health. The disadvantage of the method is its low accuracy.
To prevent brain damage due to birth injuries, hypoxia, and infectious diseases, neurosonography is performed in maternity hospitals. Pediatricians also monitor the growth of the skull in children - this simple procedure allows them to detect hydrocephalus.
Examinations for lesions of the frontal and parietal lobes
Manifestations of hydrocephalus are quite recognizable at the stage of medical examination. Instrumental diagnostics are prescribed to detect the cause of its occurrence
Radiography
Detects thinning of the bones with divergence of the sutures of the skull. With a narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct, the volume of the posterior fossa is reduced, and with a congenital cerebral cyst, it is increased. If the communication between the ventricles is closed, the frontal and parietal lobes on one side will be larger than on the other.
X-ray for hydrocephalus
In a child of the first year of life, it can be carried out through the fontanel; this diagnosis is called ultrasonography. It helps determine the degree of intracranial hypertension (increased pressure) and the risk of developing complications of cerebral hydrops.
MR picture
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most accurate research method. It helps to detect a tumor, a cyst, an inflammatory process, swelling of brain tissue, a congenital malformation, or a place where the cerebrospinal fluid outflow tract is blocked.
MRI signs of complications of hydrocephalus are:
- swelling of the cortex (thickening);
- unclear border between gray and white matter;
- changing the shape of SAP;
- areas of brain tissue displacement.
If a circulatory disorder is suspected, MRI is combined with angiography.
MRI for hydrocephalus
Additional Methods
Patients are advised to consult an ophthalmologist to determine visual acuity, fields and condition of the fundus. If diagnosis is difficult and there are no signs of brain displacement, a puncture is prescribed. It can alleviate the condition of patients a little, and examination of the cerebrospinal fluid helps in diagnosing inflammation and hemorrhage. In case of congenital infection, a PCR test is performed to determine the pathogen.