Knowing the early signs of a concussion can help prevent or mitigate serious consequences. Children—especially those just starting to walk—fall frequently. Falls are often severe and bring parents a lot of anxiety, because babies can fall out of the crib or from a highchair.
Despite the fact that young children fall a lot, most often there is only a bump, bruise or swelling at the site of the injury. Thanks to the elastic skeletal system of the skull, a concussion in infants due to a fall is unlikely.
It is enough to apply a cold object to the bruised area, and the bruise will go away without consequences in a few days.
But there are times when, when falling, a baby can hit a sharp corner with its head, and then the first symptoms of a concussion appear.
If a large hematoma appears at the site of the injury, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- After the child falls, strong and prolonged crying appears. At the same time, he knocks his legs and waves his arms. In other cases, on the contrary, he becomes lethargic and drowsy.
- Vomiting occurs. The child refuses to eat and spits up after eating a small amount of milk.
- There is moodiness and irritability.
- Sleep is disturbed: the baby has trouble falling asleep and may wake up crying during sleep.
- Pallor of the skin is observed.
- Increased sweating and a sharp rise in body temperature may occur.
- Symptoms of visual impairment are likely - blurred vision, poor concentration.
- If a baby is seriously injured, the fontanel may swell.
At the first appointment with a specialist, they are usually immediately referred to a neurologist if fundus disorders and other neurological signs are observed.
How are head injuries in children treated?
After the child has fallen and signs of a concussion appear, emergency doctors should be called. Having determined the child’s condition, they will decide on further tactics - perhaps they will give some recommendations or decide on hospitalization for a detailed examination. There is no need to get to the hospital yourself.
Before the doctors arrive, the baby should be provided with rest, not given the opportunity to make unnecessary movements, and placed on a hard surface.
There is no need to let the child fall asleep. If he loses consciousness, turn him on his side. No medications or water should be given.
If a baby experiences loss of consciousness, you should not panic. You can bring a cotton swab dipped in ammonia and apply a cold object to your head. You should feel and count the pulse. Loss of consciousness in infants is extremely rare; signs of a concussion appear a few seconds or minutes after the fall.
Treatment of a child can be carried out both at home and in a hospital. The main condition is compliance with bed rest for several days or weeks. In some cases, surgical intervention is provided - it all depends on the severity of the condition.
The following medications may be required as therapy:
- to reduce intracranial pressure;
- to eliminate or prevent seizures;
- Diuretics may be prescribed to prevent cerebral edema;
- potassium preparations;
- analgesics for pain relief;
- sedatives;
- nootropics that improve brain metabolic processes.
The hospital will carry out the following tests to make a diagnosis:
The child is examined by several specialists - an ophthalmologist, a traumatologist, a pediatrician, and a neurologist.
Attention is paid to the patient’s consciousness, mobility, sensitivity, motor activity, and the presence of reflexes.
If the blow was not strong, then you can take your time with the inspection, but you also cannot postpone it for a long time. First of all, you should consult a pediatrician. After examining the symptoms of falls and injuries, he will decide whether to refer you to other specialists.
- If a child has injuries to the face or mouth, doctors such as a surgeon and dentist may be needed.
- A blow to the temporal lobe can lead to hearing impairment, so it is worth visiting an otolaryngologist.
- If the blow falls on the frontal lobe, you need to consult an ophthalmologist.
- If the back of the head or cervical spine is affected, consultation with a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist is required.
Symptoms from a concussion may not appear immediately, but may take several months or even years:
- weather-related headaches;
- asthenic syndrome;
- epileptic seizures;
- disruption of the cognitive (attention, memory, thinking) and emotional (irritability, depression) spheres;
- pathological changes in the muscular system.
In more severe cases, there may be disability or death (if the child is unconscious for a long time).
Small children should not be left unattended, even for a short time. Even if the child has not yet learned to roll over, he can slide off the surface of the changing table, actively moving his limbs. The crib must have bumpers. Most injuries under one year of age occur due to the carelessness of adults, so leaving a child on an open high surface (stroller, table, bed) is not allowed even for a second.
The very definition of injury - a concussion - means that a kind of “shaking of the head” occurs, in which no special changes in the structure are observed.
Moreover, if during diagnosis it was possible to look inside the skull, no specialist would notice anything specific, since changes in this injury occur at the smallest cellular level.
Let's consider the medical statistics of this pathology:
- the proportion of craniocerebral injuries in childhood occupies a leading position among all types of injuries
- Every year, about 125 thousand children become patients in the trauma department of Russian hospitals due to concussion.
- in 9 cases out of 10 calls for traumatic brain injury, a concussion is diagnosed
- age specificity of victims: newborns - 2%, infants - about 23-25%, children from one to 4 years old - 7-8%, preschoolers - 20-22% and schoolchildren - more than 45%
Symptoms in schoolchildren
is manifested by the following symptoms:
- obvious loss of consciousness lasting up to 15 minutes
- constant nausea and vomiting
- intense headaches
- loss of memory regarding the nature and causes of the injury
- the presence of neurological symptoms of a specific nature (for example, eye twitch syndrome)
- pronounced impairment of coordination of motor activity.
A characteristic feature of the clinical course of childhood concussion is its ability to increase. That is, immediately after the injury, the child may feel quite satisfactory, but over time the condition noticeably worsens.
First aid for children with concussion
Diagnosis of a concussion in a child If a child hits his head or falls, then in any case it is worth seeking qualified help from a specialist. If it is impossible to provide medical assistance, the following actions can be taken:
- if the child is conscious, place him on a hard surface and cover him with a blanket
- if the child has lost consciousness, then he should be laid on his right side, while for a stable position and to create conditions for proper breathing, the left leg and arm should be bent at an angle of 90 degrees
- in case of uneven breathing and slow pulsation, artificial respiration and cardiac massage can be performed if possible
- thoroughly examine the child for fractures or bruises; if there are bleeding wounds, they should be treated
The most important thing is to ensure complete rest in a horizontal position; before the doctor arrives, if possible, try to interview the child about all the symptoms that are currently bothering him in order to pass on all the information to specialists.
Diagnostic measures
If a concussion is suspected, the following measures are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis:
- X-ray - this study is prescribed in most cases to exclude skull fractures
- Ultrasound examination - this type of diagnosis allows you to assess the condition of the brain
- Neurosonography - this study is usually prescribed for children under 2 years of age, which makes it possible to diagnose the presence of the following brain disorders:
edema; hematomas; hemorrhages.
- Echo-encephalography is an ultrasound examination that allows you to identify displacements that indirectly indicate the presence of hematomas and tumors. This method is effective when used in older children, since their skull bones are already thickened. However, there are disadvantages - the method is not reliable enough
- Computed tomography is the most common and effective method; it allows you to identify all brain damage down to the smallest detail, which helps the specialist to establish a complete picture of the child’s condition
- Additional methods include magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture, electroencephalography
Treatment
The basic principle of treating a child diagnosed with this pathology is absolute rest and specialist supervision for some time.
- Inpatient observation for several days is advisable for early detection of severe injuries and the possibility of preventing complications.
- Limitation of physical activity, even when the little patient is in excellent health.
- Complete exclusion of watching TV, computer games, and sports.
Drug treatment involves prescribing the following drugs:
- Diuretics to eliminate swelling of the brain and other consequences after a stroke - Diacarb, Furosemide. These drugs are used in mandatory combination with potassium-based drugs (Asparkam, Panangin)
- Drugs that stimulate the supply of sufficient nutrients to the brain and improve its blood circulation - a group of nootropic drugs (Cavinton, Piracetam)
- Sedatives - for example, phenozepam or valerian infusion
- Antihistamines - Suprastin, Fenistil, Diazolin
- Painkillers - analgesics (Sedalgin, Baralgin)
- Medicines for the relief of nausea - Cerucal
- Vitamin therapy
Consequences and complications
Consequences and complications of concussion in children Despite the fact that this type of injury is a mild pathology, they do occur. The consequences of a concussion include:
- persistent intense headaches of a prolonged nature
- lethargy in performing usual daily activities
- periodic bouts of vomiting for no apparent reason
- irritability from games and activities that brought joy before the injury
- weather dependence - any change in weather has a depressing effect on the child, manifesting itself in headaches and malaise
- sleep disturbance, rarely insomnia
Most often, the negative symptoms of a concussion disappear over time without treatment, but if they persist, you should definitely visit a specialist to rule out irreversible damage.
Explanations of Dr. Komarovsky about concussion in children
A concussion is a medical condition that has specific symptoms in the form of a short-term loss of consciousness and does not require specialized treatment.
A sufficient condition for recovery after injury is rest and rest in a horizontal position with an absolute limitation on jumping and walking.
In children, metabolic processes occur at such a high intensity that additional stimulation, even after injury, is not required.
The risk of complications from a concussion cannot be prevented by medication.
In the video, Dr. Komarovsky answers questions about concussions in children - how to correctly diagnose a concussion and whether it is worth taking a large number of medications when treating it:
In conclusion, I would like to note that a concussion in most boys and some girls of school age is a certain stage in development and maturation, so on the one hand there is no need to panic. On the other hand, it is imperative to carry out diagnostics for the child’s speedy recovery.
If you want to read all the most interesting things about beauty and health, subscribe to the newsletter!
Did you like the material? We will be grateful for reposts
Head impacts and blows to the head occur repeatedly in every child's life.
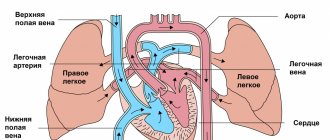
A fundamental feature of children in the first year of life is the fact that the amount of fluid in the cranial cavity is much higher than that in older children and (or) adults. In addition, the baby’s brain is not tightly closed in the cranium, since there are fontanelles, as well as pliable and movable sutures between the bones of the skull. All this creates the possibility of shock absorption and to some extent reduces the risk of impacts to the head and head.
The vast majority of head injuries end safely and are not accompanied by any serious consequences. However , any blow to the head (to the head) has the potential to be taken seriously.
, since very dangerous damage to the brain substance and bleeding in the cranial cavity are possible.
A very common specific condition that occurs after a head injury is called a concussion.
.
Medical science still does not know exactly what happens to the brain during a concussion. It is assumed that during an injury, the brain substance is shaken and hits the skull from the inside. As a result, connections between brain cells and its parts are disrupted. All this is accompanied by very specific symptoms, primarily disorders of consciousness. The fundamental point is that the integrity of the brain tissue is not damaged during a concussion.
A head injury may be accompanied by damage to the brain substance with the development of edema and hemorrhage. In this case, they talk about a brain contusion
.
Severe swelling of brain tissue and intracranial hematomas lead to a very dangerous condition - compression of the brain
.
Shake
,
bruise
and
compression
of the brain are united by such a concept as
traumatic brain injury
.
Traumatic brain injury can be closed
(without violating the integrity of the bones of the skull) and
open
(respectively, with violating the integrity of the bones).
Between the inner surface of the skull bones and the brain matter itself is the dura mater. Open traumatic brain injury with damage to the dura mater is called penetrating
.
If, as a result of the impact, only soft tissues are damaged (skin, subcutaneous tissue above
bones of the skull) and there is no disorder of consciousness, then this condition is called
head contusion
.
All of the technical terms listed are medical diagnoses. The diagnosis is made by a doctor.
However, there are very clear symptoms that indicate that a head injury is potentially dangerous and requires mandatory medical attention.
The task of parents is to know these symptoms and provide emergency assistance.
Attention!
Seek medical help if following a head injury:
Regardless of the symptoms, seeking medical help is necessary if a head injury was sustained while intoxicated or under the influence of drugs.
ATTENTION!
Dangerous symptoms may not appear immediately, so parents should closely monitor their child for at least 24 hours after a head injury, even if the injury appears to be minor.
If after the injury the child calms down and falls asleep, he should be woken up every 2-3 hours and asked simple questions (what is your name?, etc.).
Once again, any head injury is potentially dangerous. The slightest doubt - see a doctor!
Emergency care for head injury
There are no dangerous symptoms:
- calm the child down;
- try your best to limit physical activity (lay down and read, avoid active games, etc.);
- Apply cold
to the injured area.
If dangerous symptoms are detected:
- Assess the state of breathing and circulation, and in critical condition, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation;
- if breathing and blood circulation are preserved, but there is no consciousness, try to keep the child in a supine position, on a hard, flat surface, support the head with your hands; carefully monitor breathing: if in this position breathing is difficult due to vomiting or excess saliva, place the child in a stable position on his side
. When turning, hold your head, trying to avoid its rotation, excessive throwing back and lateral tilt; - while waiting for help (optimally in the supine position, even before turning to a stable lateral position), it is advisable to immobilize the cervical spine
; - if the child is conscious, wait for help in the supine position without a pillow;
- do not give food or drink;
- Do not move the child unless absolutely necessary.
When stopping bleeding:
- follow the general rules for stopping bleeding
and
treating a wound
; - at the slightest suspicion of damage to the skull bones, categorically avoid direct pressure on the wound - cover the wound with a dressing material, do not remove foreign bodies from the wound.
(This publication is a fragment of the book by E. O. Komarovsky “Handbook of Sensible Parents. Part 2. Emergency Care” adapted to the format of the article.)
Concussions occur in 90% of all head injuries in children. This is the least dangerous damage possible, but this does not mean that special attention should not be paid to it. It is important to take timely measures to prevent serious consequences for the child.
How dangerous is a concussion for a child?
A concussion is a mild degree of brain damage that is not accompanied by fractures of the skull bones. In children, such injuries occur very often, and with the right approach, complications rarely occur. A distinctive feature is a short loss of consciousness after the blow. Changes in the brain occur at the cellular level and are not detected in studies.
Concussions are common among children and can have serious consequences.
This condition is especially dangerous for newborns and babies in the first year of life, since at this age the symptoms may not be noticed, and the body is not yet ready for such stress. Older children can report how they are feeling and the signs of a concussion are more obvious.
If symptoms appear, it is important to take immediate action and call an ambulance to rule out more serious head injuries. The specialist prescribes diagnostic measures, and if there are indications, may recommend hospital treatment.
Symptoms of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is usually manifested by the following symptoms:
Feeling of a lump in the throat
The sensation of a lump in the throat is a fairly typical symptom of pharyngitis. First, the throat dries out, then a feeling of discomfort arises, as if something is preventing you from taking a sip.
A sore throat
The development of the disease leads to the feeling of discomfort in the throat turning into pain. Upon examination, it is clear that the throat is red. The mucous membrane of the throat may be covered with a film or purulent discharge. The tongue may be coated (covered with a white coating).
Cough
A cough with pharyngitis usually begins with a sore throat. I want to cough all the time. The development of the disease leads to a persistent and long-lasting cough. Cough with pharyngitis can be different - dry, throaty, bronchial. Quite often, the cough gets worse at night. The most common form of cough with pharyngitis is a dry cough.
More about the symptom
Temperature
An increase in temperature is typical in acute pharyngitis and may not be observed in the chronic form of the disease. With acute pharyngitis, the temperature can rise to 38°C.
More about the symptom
Classification
Traumatic brain injuries can be open or closed (depending on the presence and degree of damage to the skull bones). The nature of the damage is also taken into account:
- Brain contusion is a dangerous condition that causes brain swelling. Can occur with both open and closed trauma. It provokes an increase in intracranial pressure and requires immediate medical intervention.
- A fracture of the skull bones is an equally serious injury that can result in mechanical injury to the soft tissues of the brain.
- A concussion in most cases does not pose a serious danger; symptoms disappear within a few days.
There are three degrees of severity of concussion:
- Mild - consciousness is absent for no more than 5 minutes;
- Average - loss of consciousness from 5 to 15 minutes;
- Severe - prolonged absence of consciousness, may progress to coma.
The latter condition is the most dangerous, as it can cause irreversible changes in the brain.
Causes and development factors
Concussions in children are common. Can occur after a blow to the head or to the head. And sometimes “shaken baby syndrome” occurs, when injury occurs without a blow. This can happen due to excessive shaking of an infant in a stroller or other rough handling of the baby.
Infants who are not yet walking often suffer from parental inattention.
The fourth and fifth months are especially dangerous, when the baby just begins to roll over onto his stomach. Adults may simply not expect this from the baby, and leave him unattended on the sofa, changing table or other elevated area.
Parents of babies who have just learned to roll over should be especially attentive.
Older children, starting to walk, try to climb higher and higher, but the vestibular apparatus is not yet fully formed. Therefore, falls and, as a result, head impacts occur.
Children are more prone to head injuries because the head is proportionately larger and heavier than adults. Among other things, the child’s fear of falling or damaging something is often not fully realized, which contributes to the search for new heights. At a younger age, the baby is not yet able to put his hands up in time when falling from a height, which also favors “landing” on his head.
Symptoms
Small children often fall and hit their heads. It is important to remain calm in such moments and objectively assess the situation. Knowing the symptoms, you can easily identify a head injury. In other cases, there is no need to panic, but carefully monitor the child for the next 24 hours.
The first and fundamental sign of a concussion is considered to be loss of consciousness after a blow.
When the child regains consciousness, he may not remember several minutes before the fall. Other main symptoms of brain injury are:
- vomiting, most often multiple times (if the child vomited only once, this may be the body’s reaction to stress);
- confusion (inadequate answers to simple questions, lack of understanding of what is happening);
- post-traumatic blindness (rare, occurs only in children, goes away after a few minutes or hours);
- headache;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness;
- apathy or overexcitement;
- capriciousness.
If loss of consciousness does not occur, this does not always mean that there is no cause for concern. This may be another traumatic brain injury, the symptoms of which appear with some delay.
In case of a concussion, all symptoms disappear on their own after a few days, if you follow the recommendations of doctors and take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
A concussion can be caused by a blow or push directly to the head and trigger chemical changes in the brain. Another problem is that concussions in young children can be difficult to identify because children may not always be able to describe what they are feeling.
Are concussions in children different from concussions in older children and adults?
When a toddler has a concussion, it is different from what happens to older children and adults. For kids this happens because:
- The skull is softer
- The head is larger compared to the body
- Neck muscles are not developed enough to support
- Baby's bones are not fully developed and they have less control over their movements.
Causes of concussion in young children
Causes of a concussion may include:
- A fall
- A bump on the head
- Head contact with an acute angle
Other causes of concussion can occur when the body is struck. Although the head is not physically affected, it may be affected by the impact of a blow to the body.
Common signs of a concussion in a child
When a child has a concussion, symptoms do not always appear immediately. They usually develop within 24-72 hours after injury.
Most babies don't have the ability to clearly express how they feel, so they are likely to express their symptoms through crying, frustration, or irritability. These actions may appear later and last longer. It is important to closely monitor your baby for any changes in behavior.
- Headache
When a child has a concussion, headache is a symptom. For babies, because they have difficulty verbalizing their pain, it is important to pay attention to signs in behavior and any changes. Your baby may cry excessively, want to cuddle more, hang their head down, or hold their head up frequently because of the pain they are experiencing.
- Stunned look
If your baby seems slow to respond or withdraws from his usual activities, it is important to monitor this behavior very closely. Another symptom is a distant look or glassy eyes. The baby may also seem tired or lethargic.
- Lethargy
When a baby is floppy, he or she may feel heavier or experience a feeling of heaviness when carried during sleep. The child will also be less interested in playing or exploring.
Most babies are curious and love to touch and pick up things. When they have a concussion, they have less interest and participation in activities they would normally enjoy.
- Irritability and crying
There are normal situations and reasons why a baby cries. This is usually associated with hunger, changes in daily routine, fatigue and/or new surroundings.
A concussion can cause excessive irritability and crying.
- Loss of balance
Babies sometimes wobble. As they develop walking skills, leg strength tends to improve. If you have a concussion, look for additional signs that your baby is walking poorly or moving differently than usual.
It is natural for a baby to fall due to the proportion of his legs. If there is obvious cause for concern or they are moving differently than usual, there may be a problem.
- Changing your sleep pattern
Depending on the baby, changes in sleep can range from: having trouble falling asleep/sleeping more than usual/not sleeping as much before.
Other symptoms include difficulty waking up or falling asleep quickly after waking up after only a few hours of sleep.
- Uneven or dilated pupils
The pupils usually dilate when the fight or flight response is triggered. Dilated pupils are not a clear sign of a concussion. However, a sign of structural brain injury is when one pupil is more dilated than the other. This requires immediate emergency care.
- Refusal to breastfeed or eat
Your baby may be delayed in his natural ability to consume breast milk or eat at all. It is important to monitor your eating habits after an injury.
FAQ
Is it okay to let my baby sleep after hitting his head?
If your child hits his head and it is serious, take him to the emergency room. Unless the condition is severe, it is usually normal for the child to fall asleep, but monitor sleep patterns and movements during sleep.
If your baby is sleeping and cannot be awakened, take him to the emergency room.
Can a child get a concussion without hitting their head?
A concussion can occur when there is an impact to the body, where it can shake the brain back and forth. Although the head is not physically affected, it may be affected by the impact of a blow to the body. If the brain hits the skull, the nerves inside the brain can be damaged due to ruptured blood vessels. It can also lead to a concussion.
How long does it take for signs of a concussion to appear after a child hits their head?
Signs of a concussion are noticeable within 24-72 hours.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
It is impossible to diagnose a concussion using any tests, so the diagnosis is made based on the overall clinical picture and symptoms. The sequence is always this: the child hit himself, lost consciousness, and symptoms appeared.
You need to respond quickly to symptoms of a concussion in a child.
Diagnostic measures are carried out in a hospital setting so as not to miss more severe injuries.
The following studies may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the head. They are carried out to assess the condition of the skull bones; this is the simplest and most mandatory procedure.
- Neurosonography. This is an ultrasound of the brain. The procedure is indicative for children under two years of age, when the skull bones are still thin. With its help, you can detect a brain contusion, if any.
- Computed tomography (CT). Allows you to clearly see all the damage and assess the condition of the skull and brain matter. However, this method is not always used due to the lack of equipment in the hospital.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This test is rarely performed for head injuries because it is very expensive. The method is accurate and helps to detect any, even the most minor, damage. An MRI may be prescribed if concussion symptoms persist for a long time, despite treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
Other examinations may be prescribed for special indications and are rarely performed in children.
Treatment
A concussion requires an immediate call for an ambulance.
Upon arrival, the doctor will necessarily take the child to the hospital for examination and consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
When diagnosing a concussion in children, hospital treatment is strictly recommended. First of all, this allows for medical supervision during the first days after the injury. It also helps the child stay in a calm environment with an established routine. Parents may refuse to leave their baby in the hospital if they are absolutely sure that they can create the necessary conditions for him at home.
First aid
If loss of consciousness occurs after hitting the head, it is necessary to lay the child on his side. If there is bleeding, it is stopped with an ice compress. Something cold is also applied to the site of impact.
If a child loses consciousness after hitting his head, he must be placed on his side.
When the baby has come to his senses, he must be calmed and not allowed to engage in physical activity. It is important to prevent him from falling asleep for at least an hour immediately after the injury. In this way, possible violations can be detected.
Even if no symptoms of a concussion are detected in the first hours, it is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s behavior. On the first night after the incident, you need to wake up the baby several times to assess his condition.
If you suspect a concussion, be sure to call an ambulance.
Even if it is a “false alarm”, it is better to be safe.
Treatment with drugs
Therapy in the hospital and while staying at home is aimed at preventing possible complications. The following groups of medications are usually used:
Related measures
The main condition for a quick recovery is rest, preferably bed rest.
. For young children, it is not always possible to comply with this requirement. It is necessary to reduce activity as much as possible - engage the child in quiet play, read books to him.
Watching TV, sitting at the computer, or using any other gadgets is completely excluded. The eyes should not be strained to allow the brain to rest as much as possible from the shock.
After an injury, watching TV is completely excluded
As for nutrition, it is better to exclude heavy foods during treatment. It is not recommended to use:
- strong tea;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- fat;
- roast;
- spices;
- salty.
These foods increase intracranial pressure and promote fluid accumulation, which can cause cerebral edema. The influence of food is not too great, but sticking to such a diet for a few days will not hurt.
Consequences of concussion in children
In most cases, this injury does not cause serious complications.
If you follow the regimen and doctor’s recommendations, all symptoms disappear within 1–2 weeks. However, with incorrect or untimely treatment (and sometimes regardless of this factor), the following consequences may occur:
- the impact of weather changes on general well-being;
- irritability, moodiness;
- lethargy;
- frequent headaches;
- insomnia and other sleep disorders;
- periodic causeless bouts of vomiting;
- epileptic seizures are very rare.
In rare cases, such complications may bother the child for another 1–2 months after the concussion, and sometimes longer. If such residual effects are detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor for consultation and development of further treatment tactics.
Treatment methods for pharyngitis
Pharyngitis
Treatment of pharyngitis is usually carried out at home, but if you cannot quickly cope with the symptoms of pharyngitis on your own, you should consult a doctor. You should not let things get to the point of chronic pharyngitis.
The choice of treatment for pharyngitis depends on what caused the disease. If pharyngitis is infectious, the basis of treatment is suppression of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
It is also important to eliminate the factors that contributed to the development of pharyngitis (first of all, eliminate smoking during the period of treatment). You should definitely take steps to strengthen your immune system.
With chronic pharyngitis, it is important to make sure that recovery has actually taken place. Therefore, at the end of the course of treatment, you may be scheduled to take tests again. If this is not done, there is a possibility that the activity of the infectious agent is simply suppressed by the medications taken, and after stopping the medication, the disease will return again.
Antibacterial therapy
Antibiotics may be used to treat pharyngitis. Antibiotics for pharyngitis are effective only in the case of a bacterial infection, so the use of antibiotics should be preceded by a bacteriological analysis.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can be used as an additional auxiliary treatment method for pharyngitis. For this purpose, electrophoresis with the use of antiseptics, UHF and darsonvalization can be used.
More information about the treatment method
Prevention of pharyngitis
In order to prevent pharyngitis, doctors at Family Doctor advise:
- Make sure that your breathing is predominantly nasal. If adenoids, nasal polyps, or a deviated nasal septum are identified, it is advisable to eliminate the cause of mouth breathing;
- strengthen the immune system, harden the body;
- humidify the air in the room. Normal humidity is 50-60%;
- Change your toothbrush more often. A toothbrush can accumulate harmful microorganisms;
- If a runny nose or other signs of acute respiratory infections appear, begin treatment immediately.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Prevention
In children, it is difficult to take sufficient measures to prevent falls. But you can do the maximum possible:
- do not leave infants unattended at elevated locations;
- use a helmet when cycling and other active sports;
- isolate sharp corners in a house where there is a child under three years old. And also limit access to any heights - window sills, tables, cabinets, etc.;
- talk to older children and explain the danger of injury;
- try to avoid a large number of objects in the house that can cause you to trip;
- use non-slip shoes or socks for the child if the floor in the apartment is slippery - linoleum, tiles, etc.
Causes of pharyngitis
Normally, a person breathes through the nose. The human nose is designed in such a way as to prepare the inhaled air for its further movement inside the body. The nasal passages have sufficient volume so that the inhaled air continues to flow with some delay; this allows it to warm up and moisturize - due to interaction with the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. In the nose, the air is also cleared of dust, particles of which linger on the mucous membrane and the eyelashes growing on it.
Mouth breathing is a backup option built into our body in case breathing through the nose is impossible. At the same time, unprepared air enters the throat, preserving the properties of the external environment. It may be cold, dry, contain dust, infectious agents, etc.
Pharyngitis
Therefore, the main factor contributing to the development of pharyngitis is impaired nasal breathing . If a person has a stuffy nose (and this can happen for many reasons, for example, due to the growth of adenoids, nasal polyps, a runny nose), then he is forced to breathe through his mouth. In this case, the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, exposed to direct exposure to atmospheric air, quickly dries out, easily becomes hypothermic and can be infected with pathogenic microorganisms that are always present in the air.
Quite often, pharyngitis occurs against the background of a runny nose caused by a viral infection (ARVI). This happens because the mucus that flows down the nasopharynx during a runny nose contains a virus, the causative agent of the disease, and contributes to the expansion of the source of inflammation.
But mouth breathing alone is not enough to cause pharyngitis. Much depends on the general condition of the body. If the body is weakened as a result of previous illnesses, overwork, lack of vitamins, or poor nutrition, it becomes more vulnerable to infection.
Also factors contributing to the development of pharyngitis are smoking and alcohol abuse, vitamin deficiency, diabetes mellitus, unfavorable environmental conditions (prolonged exposure to dust, hot and dry air, smoke, chemical fumes, etc.).
The most common pharyngitis is of viral origin, more rarely - bacterial, fungal, allergic and traumatic pharyngitis.
Video: Dr. Komarovsky about concussion in children
All children, starting from the first steps, fall and hit their heads. It is not necessary to run to the hospital or call a doctor every time. The main thing is to observe the child’s behavior and not give in to panic. The child, seeing his parents’ excessive concern, may become frightened himself. Any sign or even suspicion of a concussion or other traumatic brain injury requires medical attention. If you go to the hospital in a timely manner, there is virtually no risk of complications.
Among critical conditions in childhood with dangerous consequences requiring emergency assistance, traumatic brain injuries, in particular: concussions in a child, come first.
First aid for a concussion in a child:
- provide the child with peace and horizontal position
- call an ambulance (mandatory consultation with a traumatologist or neurologist is required)
The consequences of a traumatic brain injury can occur several hours later, with a sharp deterioration in the condition that requires. What to do when the symptoms of a child’s concussion are hidden and deceptive? Komarovsky recommends: after any head injury, the first step is to seek help from a traumatologist and neurologist.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this acute disorder, due to the anatomical features of the immature organism, differ from the manifestations of a crisis in adults.
In an infant under 1.5 years of age, the symptoms of a concussion are not pronounced or intense. What to do when there are no exact signs of injury, but the consequences are very dangerous? In infants, the following may indicate a condition requiring first aid:
In a child 2, 3, 4 years old and older, a concussion is accompanied by the following symptoms:
In an infant and a child over 1 year of age, a concussion can cause a short-term loss of consciousness, which requires first aid. What to do when the above symptoms are absent? According to the experience of Dr. Komarovsky: signs of a dangerous crisis in older children may be a feeling of stupefaction, post-traumatic blindness, pain in the eyes during exertion, which develop some time after.
Forms of pharyngitis
What does pharyngitis look like?
There are acute and chronic pharyngitis.
For acute pharyngitis
The following symptoms are typical:
- dryness and sore throat;
- pain when swallowing, especially when swallowing saliva (the so-called “empty swallow”);
- Sometimes a rise in temperature to 37.5-38°C and general weakness are observed.
Chronic pharyngitis
usually occurs at normal temperatures. Quite often a dry cough is observed, and there is a constant desire to cough and “clear” the throat. The patient has to swallow mucus all the time, which causes pain. As a result, irritability increases, attention and performance decreases, and sleep is disturbed.
Causes
As Dr. Komarovsky explains, the main cause of such injuries in young patients is increased motor activity, which is characteristic of children from 1 year to adulthood. All babies from 1 year to 8 years are restless and curious creatures. At the same time, the level of coordination of movements and motor skills in children from 1 year to adulthood is in the stage of development and formation. Another reason for a concussion in a child: the head of a one-year-old baby and children under 5 years old weighs significantly more than the proportions of an adult. At the same time, infants do not at all know how to protect themselves when falling by moving their upper limbs forward. Therefore, infants and older children fall in most cases on their heads, and not on the support - outstretched arms.
The specific factors that provoke a concussion in a child, the symptoms and consequences of this condition, vary depending on the age of the child. Newborns and infants most often become victims of the inattention of mothers and fathers. Older babies - infants under 1 year of age receive traumatic brain injuries as a result of falling from heights, for example: from a changing table, stroller, bed. Therefore, in order to avoid dangerous consequences, the toddler must be under the constant supervision of his parents.
When a small person masters walking, between the ages of 1 and 1.5 years, the child's risk of experiencing concussion symptoms decreases. The cause of injuries between the ages of 1 year and 4–5 years are falls from a height, for example from a swing, slide, ladder, or window sill.
Children under 8 years of age often become victims and develop “shaken” syndrome, when a child receives a concussion as a result of exposure to brute force, for example: during fights with peers. Moreover, preschool children prefer to remain silent about their feelings and report them only when the condition requires immediate first aid. The peak development of head injury symptoms coincides with the school years.
Shaken baby syndrome
Everyone knows that mothers simply need rest (just like other people who regularly care for a small child). Today we will raise the topic of what can happen if a mother does not rest for a long time and, as a result, burns out.
Babies cry a lot in the first year of life. Sometimes mothers cannot stand it and, in response to prolonged crying, begin to do things that they could not even think of before: they shake the child violently or throw him against something.
After this, 2 scenarios may follow:
1. The baby will be lucky - he will get away with only a minor fright, a couple of bruises and abrasions.
2. The baby will be unlucky - the baby will develop shaken baby syndrome, which poses a threat to his health and life.
What is shaken baby syndrome?
A small child has weak neck muscles, and if the baby is shaken, his head begins to hang freely, and its contents begin to bang against the skull. This causes multiple damage to brain tissue and supply vessels.
Note that the consequences from shaking are much more serious than from a blow when a child falls from a small height.
Of course, shaken baby syndrome can also develop with increased swinging, throwing up and other situations in everyday life. However, this is much less common than what is defined as child abuse.
What's next?
The child has difficulty breathing, convulsions, lethargy and drowsiness. When parents contact a medical institution, the correct diagnosis is made, at best, within a day.
Late diagnosis is usually associated with the following reasons:
1. The parents did not even understand that the symptoms that arose in the child could be the result of shaking, so they kept silent about this fact.
2. The parents realized that the child was experiencing symptoms due to shaking and, fearing the consequences, kept silent about this fact.
Without truthful evidence, it is quite difficult to diagnose pathology, because with a concussion there are usually no external injuries. But it is at this stage that lost time can cause death.
The baby is usually brought to the hospital with nonspecific symptoms: difficulty breathing, drowsiness, vomiting, convulsions, loss of consciousness. In this case, the fact of injury is denied, and there are no external injuries.
Much later, it turns out that the symptoms appeared immediately after shaking (in more than 90% of cases) and this was not the first time the child was shaken (in 70% of cases).
What diagnostics are needed?
The following methods are used to diagnose shaken baby syndrome:
1. Neuroimaging methods (MRI or CT) are necessary to identify hemorrhages and areas of ischemia.
2. CSF analysis - used to confirm the presence of hemorrhage and rule out meningitis (due to the similarity of symptoms).
3. General and biochemical blood test.
4. Ultrasound and radiography – necessary if additional damage is suspected.
The most important and at the same time difficult task for a doctor is to prove that brain damage is associated with an act of abuse, and not just with an injury resulting from a fall (for example, when a baby is just learning to walk and often gets hit).
And it is impossible to determine what is worse - not recognizing an adult who harms a child or blaming an innocent person, thereby destroying a family.
How to help a child?
Shaken baby syndrome is often accompanied by retinal hemorrhage, as well as other manifestations of domestic violence - fractures, hematomas, damage to internal organs, etc.
A child who has suffered a concussion should be treated in intensive care. Doctors need to try to preserve as much brain tissue as possible in the first minutes (by removing the accumulation of blood, sometimes surgically, to eliminate breathing and circulatory disorders). Let us note that about 39% of children require emergency resuscitation upon arrival at a medical facility.
Unfortunately, medical care cannot always help avoid tragedy:
- about 23% of children with shaken baby syndrome die;
- up to 55% of children remain with neurological pathologies;
- up to 65% subsequently suffer from visual impairment.
Thus, the best option is not to let it get to this point and try to find enough time for proper rest.