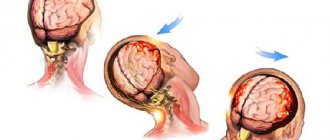
Post-traumatic headache occurs after a head or neck injury. In fact, headache is the most common symptom that people experience after even mild traumatic brain injury.
The pain may begin immediately or a week after the injury. For many patients, especially those who have had a severe injury, headaches can be a problem for months, years, or a lifetime. If headaches develop within 2 weeks of injury and persist for more than several months, it is considered to be the chronic phase of post-traumatic headache. Sometimes patients do not develop headaches until several months after the injury, but in general, headaches usually begin within hours or days after the injury.
It is very difficult to predict the possibility of developing chronic post-traumatic headache in patients who have suffered trauma. In general, patients with pre-existing headaches or migraines are at higher risk. Patients with a family history of migraine may be at increased risk of developing chronic headaches. The severity of the injury can also help with prognosis, but many patients endure months or years of severe headaches after a trivial head injury. Rear-end collisions without head trauma usually result in severe headaches and neck pain. Factors such as the angle of impact, where the patient was sitting in the car, and where the force was placed on the head are key elements in the development of headaches.
Headaches are usually of two types:
- by type of tension headaches, which can be daily or episodic
- migraine headaches, which are usually more severe.
In some patients, post-traumatic migraine pain can be a serious problem, with intermittent severe headaches lasting hours to days. In other patients, tension-type headache is the predominant problem. In many patients with PTTH, pain can be mixed.
Occipital pain is often associated with neck pain and is usually of muscular origin.
Types of Injuries that Cause Post-Traumatic Headaches
- Violence
- Car crashes
- A fall
- Sports injuries
Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Diagnostics
The International Headache Society defines criteria for post-traumatic headache such as:
- Headache that does not have typical characteristics and meets criteria C and D
- Having a head injury with all of the following symptoms:
- Without and with loss of consciousness, which lasted no more than 30 minutes
- Glasgow Coma Scale score (which is used to assess level of consciousness after traumatic brain injury) is equal to or greater than 13
- Symptoms that are diagnosed as a concussion
- Headache develops within seven days after traumatic brain injury
- One or other of the following:
- Headache resolves within three months after head injury
- The headache has not disappeared, but the injury was less than three months ago
To diagnose this type of headache, as a rule, such types of studies as MRI, CT, PET, EEG are used, since it is necessary to clearly visualize morphological changes in brain tissue and exclude life-threatening conditions.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Treatment
Medicines are the cornerstone of treatment. During the first three weeks of headache, abortifacient medications are usually used. If headaches continue after three weeks, then additional therapy is prescribed.
Abortion therapy
The choice of abortive therapy depends on the type of headache. The main medications for the treatment of post-traumatic tension-type headaches are analgesics and NSAIDs. Muscle relaxants are more effective for PTTH than for regular tension headaches due to the presence of cervical muscle spasm. But these drugs are recommended to be taken only for 1-2 weeks. If the pain persists, then preventive treatment is necessary. If post-traumatic headaches are migraine in nature, then the same drugs are used as for migraines. Antiemetic drugs are effective for many patients. Primary abortive migraines include: Excedrin, aspirin, naproxen (Naprosyn or Anaprox), ibuprofen (Motrin), ketorolac (Toradol), Midrin, Norgesic Forte, Butalbital, Ergotamines, Sumatriptan, corticosteroids, narcotics, and sedatives.
Preventative treatment
During the first 2-3 weeks after injury, abortive drugs such as anti-inflammatory drugs are usually used. Most patients do not need to take daily preventive medications, and post-traumatic headaches gradually improve over time.
The most commonly used preventative treatments are antidepressants, especially amitriptyline (Elavil) or nortriptyline (Pamelor) and beta blockers. NSAID drugs often have a dual purpose, functioning as an abortifacient and preventive treatment. Antidepressants that have a sedative effect, especially amitriptyline, often reduce daily headaches while improving sleep. In severe cases, it is necessary to use both beta blockers and antidepressants. Non-drug treatment methods may include various physical procedures and acupuncture.
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Take care of your head
The consequences of a concussion can be very serious. A concussion is damage to the bones of the skull or soft tissues, such as brain tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and meninges. An accident can happen to a person in which he can hit his head on a hard surface, this is precisely what entails such a thing as a concussion. In this case, some disturbances in brain function occur that do not lead to irreversible consequences. All traumatic brain injuries are divided into open and closed. Open injuries are those that damage the soft tissues of the head (skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia) and the bones of the skull. Closed injuries are somewhat less dangerous, but still unpleasant. They, in turn, are divided into concussion, contusion and compression. Among all brain injuries, concussion ranks first in frequency. Moreover, according to the observations of traumatologists, it occurs more often in women. Although, perhaps they simply seek professional help more often than men. A concussion can be caused by bruises, blows, or sudden movement (either acceleration or deceleration). The most common cause of concussion is road traffic accidents, work-related, sports or household injuries. Problems of recognition What exactly happens to our brain as a result of a concussion, doctors are still finding it difficult to answer unequivocally. After all, if you examine the injured brain using computed tomography, then practically no organic disorders will be detected. Most likely, as a result of a concussion, certain problems arise with the functioning of nerve cells in the brain. At the same time, their nutrition may deteriorate, a slight displacement of the layers of brain tissue may appear, and the connection between some brain centers may be disrupted. A severe concussion can rupture blood vessels and seriously injure certain areas of the brain. The main danger with traumatic brain injuries is intracranial bleeding, since leaked blood can compress and permeate brain structures, disrupting their function and viability. In addition, injury can lead to another serious complication - cerebral edema. Particularly severe are brain injuries complicated by shock and injuries affecting the brain stem, where breathing and blood pressure are regulated. A severe concussion is dangerous because it can cause serious injury to certain areas of the brain or rupture of blood vessels inside the skull. Fell, woke up After an injury, a person often loses consciousness. This can last from a few seconds to several minutes. The time spent in this state may be one indicator of the severity of the concussion. The extreme degree of loss of consciousness is coma. When a concussion occurs, a person often does not understand where he is, what happened, and has difficulty recognizing the people around him. Another important indicator by which one can judge the severity of brain damage is memory loss: whether a person remembers the moment of injury, and if not, how much of the time before the injury has disappeared from his memory. The greater the memory loss, the more serious the injury. When the victim comes to, he may feel sick and vomit. He often turns pale, feels dizzy and has a headache, there is noise in his ears, it is difficult for him to focus his eyes, his breathing becomes rapid, and his pulse jumps. In the first hours after a concussion, the victim’s pupils are dilated or constricted - a traumatic brain injury of any severity leads to disruption of the nerve pathways responsible for the functioning of the eyes. Surely in the movies you have seen more than once how, when examining an unconscious person, a doctor directs a flashlight beam into the victim’s eyes. This is done to determine the reaction of the pupils. With a mild concussion, the pupils react to light, but sluggishly, and with a severe concussion, there is no reaction at all. In this case, the dilation of only one of the pupils and the lack of reaction in the second is a formidable symptom and may indicate severe damage to one of the hemispheres of the brain. In the first hours or days after a concussion, the victim turns pale, complains of weakness and dizziness, and tinnitus. The headache is pulsating and localized in the back of the head. Nausea and vomiting may appear, breathing becomes more rapid, and the pulse may change towards faster or slower. After some time, these indicators normalize. Depending on the injury itself and the accompanying stress factors, blood pressure can either quickly return to normal limits or increase. Body temperature remains unchanged. Due to dysfunction of the nerve cells of the brain after a concussion, negative phenomena in the organs of vision are observed: pain when moving the eyes, difficulty focusing the gaze, constricted or dilated pupils, pupils of different sizes, divergence of the eyeballs when reading. There may be other symptoms: sweating, flushing, discomfort or sleep disturbances. Symptoms in children In infants and young children, concussion occurs without loss of consciousness. During the impact, the skin (especially the face) turns pale and the heart rate increases. A little later, drowsiness and lethargy appear. When feeding, regurgitation and vomiting occur more often than usual. Sleep disturbances and general anxiety are noted. In preschool children, all symptoms of a concussion disappear within two to three days. Young and middle-aged people lose consciousness at the time of injury much more often than children and the elderly. At the same time, representatives of the older generation exhibit pronounced disorientation in space and time. Typically, for most people, the neurological symptoms of a mild concussion resolve within a few weeks. However, after any concussion, energy metabolism in the brain remains in an altered state for a long time (a year or longer). First aid If you suspect a concussion, you must provide first aid to the victim. First, you need to provide the person with complete peace, put him on the bed in a quiet, darkened room. It is better to raise your head slightly. It is very useful to apply cold compresses to the head. Drinking a lot if you have a concussion is not recommended. If the victim is thirsty, make him sweet tea. Alcohol is strictly contraindicated! And, of course, be sure to call a doctor, since it is possible that the brain damage is more severe than it seems at first glance. If the patient is in shock, carefully monitor his breathing and blood pressure before the ambulance arrives. In emergency cases, begin artificial respiration and chest compressions. Only a doctor can conduct a complete diagnosis and make an accurate diagnosis. He will examine and interview the patient, check reflexes, prescribe an X-ray of the skull, and if more complex brain damage is suspected, refer him for a consultation with a neurologist. There, the patient will undergo a full-scale examination: electroencephalography (EEG), echoencephalography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels, and spinal puncture. An MRI of the spine may be needed to rule out spinal problems. It must be remembered that a person who has suffered even a mild concussion may develop post-traumatic neurosis or other more serious complications, such as epilepsy. Therefore, some time after recovery, you should definitely visit a neurologist and undergo electroencephalography. Treatment for more serious traumatic brain injuries depends on their severity. In some complicated cases, the help of neurosurgeons may be required. After a concussion, victims are required to regularly visit a neurologist for a year. Patients with a concussion should remain in bed for at least several days. However, you cannot read, listen to loud music or watch TV. It is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions and carefully take the medications prescribed by him. During the first two weeks, the general condition of the victim improves. However, it should be borne in mind that health problems can last much longer. For example, headaches in those who suffer from hypertension are particularly intense. Be healthy! Prepared by Irina TENDLER, neurologist of the Tomsk State Budgetary Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 3" The material was published in the newspaper "Tambov Courier"
Indications for hospitalization
A doctor may refer you for hospitalization if there are the following grounds:
- post-traumatic amnesia;
- prolonged loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- epileptic seizure;
- bleeding;
- disorientation;
- obvious disorders of the nervous system;
- the patient is pregnant (even if she feels normal).
During treatment for TBI, the patient's condition may fluctuate. Periodically, the symptoms intensify and subside. Predictions can only be made after a full course of therapy. Unfortunately, the mortality rate for TBI reaches 25%. The main cause of death is inadequate first aid and reluctance to go to the hospital.