Organic lesions of the central nervous system are a group of various neuropsychic disorders that develop as a result of the influence of various pathological factors on the brain at different stages of ontogenetic development. This pathology has many variations and different development mechanisms.
Pathogenesis and, accordingly, clinical manifestations of cerebral-organic disorders depend on:
- from the causes of the defeat;
- the period in which the brain damage occurred;
- localization, intensity and depth of damage to brain structures;
- the time that has passed since the onset of the disease that led to brain damage.
If unfavorable factors impact the fetus at the embryonic stage of development, severe developmental defects incompatible with life may occur.
Damage to the central nervous system can occur in a child at different periods: during fetal development (antenatal), during childbirth (intranatal) and after the birth of the child (postnatal).
The classification of organic lesions of the central nervous system in children in the modern world is usually based on the causes and mechanisms that can lead to damage to the central nervous system in newborns or older children. According to this classification, there are 4 groups of perinatal central nervous system disorders:
- traumatic lesions of the central nervous system in newborns. Such a case is a leading accompanying factor in damage to the tissues of the central nervous system during childbirth or the first hours of a child’s life;
- hypoxic damage to the central nervous system: the main factor of damage is lack of oxygen;
- toxic-metabolic and dismetabolic lesions of the central nervous system in newborns: the damage factor in this condition is a metabolic disorder in the child’s body during the prenatal period;
- damage to the central nervous system in children due to infectious diseases: the main damaging effect is exerted by an infectious agent (usually a virus).
Causes
Damage to the central nervous system in children can occur at the embryonic stage of development, during childbirth, and also after birth. Among the reasons are:
- Somatic diseases of the mother, taking medications, stress and bad habits during pregnancy, previous infectious diseases, pathologies of pregnancy;
- Birth injuries, immaturity of the woman’s body, pathological course of childbirth;
- Head injuries in children, neuroinfections, strokes, tumors of the brain and spinal cord.
Opening hours: 8:00 to 20:00
Telephone
Sign up
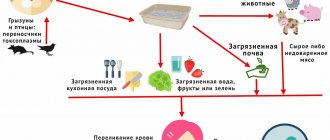
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system
There are a fairly large number of agents that can cause damage to the central nervous system. The main ones are the Coxsackie virus, herpes infection, ECHO. They can provoke the occurrence of meningitis, arachnoiditis, and encephalitis. The central nervous system can also be affected by HIV infection, when the disease is in its final stage. It most often manifests itself in the form of abscesses and leukoencephalopathies.
Mental disorders provoked by infectious pathology can manifest themselves as follows:
— Asthenic syndrome : weakness, fatigue, significant decrease in performance. — Complete or partial psychological disorganization. — Affective disorders. — Violations of personality integrity. — Psychoses: paranoid, hypochondriacal, hysterical. — Intoxication
Intoxication can be caused by uncontrolled use of drugs, alcohol, nicotine, as well as poisoning by mushrooms, salts of heavy metals, and carbon monoxide. Poisoning is also possible with an overdose of drugs. Clinical consequences depend on the specific substance used. The development of neurosis-like disorders is also possible.
If poisoning occurs due to the use of diphenhydramine, atropine, and various antidepressants, it manifests itself as delirium. If a psychostimulant was used, intoxication paranoid is possible. Characteristic for this type of intoxication are visual, auditory and tactile hallucinations and delusions. A manic-like state is also possible, which is manifested by euphoria, sexual and motor disinhibition, and accelerated thinking processes.
If intoxication is chronic, the patient will encounter the following manifestations:
— Exhaustion, lethargy, hypochondria, a noticeable decrease in performance, various types of depressive disorders. — Memory impairment, decreased intelligence level, attention impairment. — Vascular diseases
Vascular diseases of the brain include:
- Hemorrhagic stroke. - Ischemic stroke. - Encephalopathy.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to blood seeping through the walls of blood vessels or a rupture of an aneurysm. As a result, hematomas are formed. Ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of a vessel by a blood clot, an atherosclerotic plaque. As a result, a lesion is formed that is deprived of a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients.
Discirculatory encephalopathy can develop with hypoxia, which is chronic. At the same time, a large number of lesions are formed throughout the brain. reasons that provoke the development of tumors in the brain :
— Genetic predisposition. — Exposure to chemicals. — Ionizing radiation.
Today, doctors are actively discussing the likelihood of the negative impact of bruises, cell phones and various injuries to the head.
If vascular pathology , various mental disorders may develop. As a rule, they directly depend on the location of the outbreak. As practice shows, they most often occur when the right hemisphere is affected.
They can appear in the form of:
— Cognitive impairment (to disguise this impairment, patients use notebooks where they record all the necessary information). — Significant reduction in the level of criticism of one’s own condition. - Prolonged depression. - Sleep disorders. — Manifestation of aggressive behavior. - Asthenic syndrome. — Vascular dementia
Separately, it is worth considering vascular dementia . Today it is divided into several types:
- Stroke-related. - Non-stroke. — Variants caused by disturbances
Patients with the pathologies described above have rigidity of all or most processes and their lability. There is also a significant decrease in the range of interests. The severity of cognitive impairment is determined by a number of characteristics, which may even include the age of the patient.
Demyelinating disease
One of the main diseases is multiple sclerosis. The lesions are formed with the destruction of the membranes of the nerve endings.
Mental disorders may include the following:
— Increased levels of fatigue, weakness, significant decrease in performance. — There is a decrease in intelligence, memory, and absent-minded attention. - Affective insanity. - Depression. — Neurodegenerative diseases
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease may fall into this category . Symptoms usually appear in old age.
Depression is the most common condition in Parkinson's disease. It is accompanied by a deep feeling of emptiness, emotional poverty. A person’s ability to feel joy and enjoyment also decreases. A person may behave overly aggressively, become sad, or show unjustified pessimism. Depression can be supplemented by various anxiety disorders (in 70% of patients).
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative disease that causes marked decline in cognitive function, as well as changes in behavior and personality structure.
People with Alzheimer's disease are unable to recognize familiar objects, familiar people, and are forgetful and confused. They quickly fall into a state of depression, experience disorientation, anxiety, and emotional distress.
Residual ZPR: reviews
| Positive | Negative |
| I was very sick during pregnancy, which caused my daughter to suffer greatly. From birth we were noticeably lagging behind in development. When all the children our age were actively trying to roll over on their stomachs or sit up, we just lay there and did not show the slightest interest even in rattles. Even then we became alarmed and began to look for “our” doctor. Today we are 3, and we just learned to hold a spoon in our hands on our own; we started at 2.5 years old, and we learned to get up from the floor ourselves at 2.7. We have a real struggle for every skill, but we believe that complex therapy will show more effective results. Mommies, endurance and perseverance to you. (Alla) | I also understand different types of therapy, but stuffing me with medications is an absolute no-no! (Rita) |
| Our mental retardation began to manifest itself after our son, at the age of one, fell and hit his head hard, causing a concussion. After that, we lost speech instantly and completely forgot our self-care skills. We all went through it all over again. Today we are 4 and everything is fine with us. By the way, hippotherapy and drug treatment work wonders. (Sonya) | Often children with residual mental retardation are fed nootropics or sedatives, which simply inhibit development and completely kill the ability to concentrate. Just spend more time with your child and don’t stuff him with medications. (Anna) |
| The reason for everything is a genetic predisposition, and yes, we are constantly on medications that change course after course, while we take the medications - we see the result, take a break and there is a stop in development. And every disease rolls back all our achievements significantly. We are waiting for more powerful medications to be released to nourish and stimulate brain function. (Galina) | We had a hematoma in the head after birth, which resolved on its own, but the doctors tried to prescribe something, especially sedatives, but I persistently refused. And now we have noticeable signs of mental retardation, but we are successfully fighting them through ABA therapy. We are used to feeding children pills for any deviation from the norm. (Alice) |
| It is important not to let everything take its course and everything will definitely work out. By the way, in the absence of corrective work, the child’s condition with residual mental retardation will only worsen and be complicated by more serious diseases. (Nina) | Well, they gave us a diagnosis, well, they outlined what kind of therapy we need to attend, and what the price for these classes is - simply unaffordable for the average family. That is why you have to study hard at home, which is not so effective. (Irina) |
| Our son was completely silent until he was 2 years old, we were diagnosed with residual mental retardation, we selected a course of treatment and therapy, there was no change for six months, and then it broke through and began to fill his vocabulary like a sponge. Treatment is very important. (Galina) | In our city, people with a diagnosis of mental retardation are not admitted to kindergartens, regardless of the background of the disease, or to schools. The question arises, how can we socialize and develop our children? As always, no one needs children with special needs. (Yana) |
Conclusion
Although there is no cure for organic mental disorders, many of these conditions can be treated through psychotherapy and prescription medications.
Unfortunately, not all patients will respond to treatment in the same way. In most cases, it will take weeks or even months before treatment starts to work. In some cases, medications may have little effect on symptoms caused by an organic mental disorder.
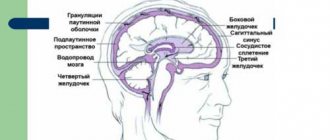
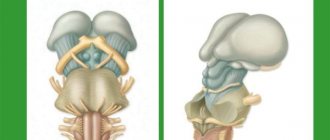
A brief excursion into the anatomy of the central nervous system
The human brain is a complex organ responsible for the functioning of the entire organism. There is a clear hierarchy in the structure of the brain, which allows the entire body to work effectively. The central nervous system can be divided into several main parts:
- The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher nervous activity, i.e. thought processes, speech, memory, writing, hearing and many other functions.
- Subcortical structures that form the midbrain. The midbrain is responsible for the primary reflex units and the formation of unconditioned reflexes.
- The bridge is a connecting link between all parts of the central nervous system and the cerebral cortex.
- Cerebellum. It is located in the lower occipital part of the head and is responsible for human coordination in space.
- The medulla oblongata connects the brain with the spinal cord and is its continuation. The medulla oblongata contains vital centers: vasomotor and respiratory.
Organic mental disorders: conditions and symptoms
Symptoms of organic mental disorders vary depending on the type of disorder the patient is suffering from. For example:
- Those who suffer from bipolar disorder will experience severe mood swings, ranging from feelings of euphoria to feelings of despair.
- Those with autism will have problems with social development.
- People diagnosed with schizophrenia often experience delusions and hallucinations.
A qualified psychiatrist can accurately determine the type of organic mental disorder a patient is suffering from based on the symptoms presented.
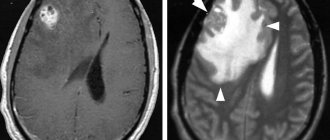
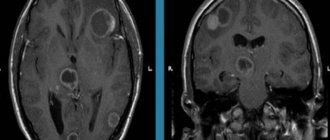
In some cases, organic mental disorders can be diagnosed using blood tests, EEG, MRI and CT scans. Unfortunately, laboratory tests cannot always diagnose mental retardation on a residual basis, and patients must rely on the assessment of a qualified psychiatrist to obtain an accurate diagnosis. A psychiatrist can evaluate a patient by providing a comprehensive psychological evaluation and asking the patient to answer various questionnaires.
Treatment of organic mental disorders
Treatment for organic mental disorders depends on the underlying cause. Drug treatment or rehabilitation therapy may be given to help patients regain function in the parts of the brain affected by OPD.
Advice: in order to reduce the percentage of a child’s lag in mental and speech development, it is recommended to surround him with positive emotions, attention, love, as well as an active speech environment: fairy tales, cartoons, songs, reading books, commenting on his actions (to develop the child’s subject-personal connections).
Types of ZPR on a residual organic background:
- catatonic - they are characterized by problems associated with motor skills or muscle malfunction;
- mood disorder - deep emotional problems may be caused by an organic mood disorder, which can cause depression or mania;
- anxious - those who have problems with anxiety in public places;
- dissociative - characterized by problems with awareness, identity, memory, perception, or a combination of these;
- emotionally labile - wild mood swings in both directions;
- personal - associated with problems that lead to the fact that people do not fit into most of society in an extreme form;
- post-concussion syndrome - problems that can occur after a concussion due to a blow to the head;
- unspecified - the entire spectrum of syndromes that are not listed above can be classified as unspecified, but are just as serious.
Convulsive syndrome
The tendency to have seizures in the first months of a child’s life is due to immaturity of the brain. Convulsions occur only in cases where the spread or development of a disease process in the cerebral cortex occurs, and have many different causes.
In each specific case, the cause of the convulsive syndrome must be identified by a doctor. Effective assessment often requires a number of studies and manipulations: instrumental studies of brain function (EEG), brain circulation (Dopplerography) and anatomical structures (brain ultrasound, computed tomography, NMR, NSG), as well as biochemical blood tests.
From the point of view of localization, cramps are not the same - they can be generalized, that is, covering the entire body, and localized, which are associated with individual muscle groups.
Convulsions are also different in nature: tonic, when the child seems to stretch out and freeze for a short time in a certain fixed position, and clonic, in which twitching of the limbs and sometimes the entire body occurs.
Parents should carefully monitor their child in the first months of life, because... convulsions in children can become the onset of epilepsy if you do not immediately contact a specialist and do not carry out proper treatment. Careful observation and a detailed description of emerging seizures on the part of the parents will greatly facilitate the doctor’s diagnosis and speed up the selection of treatment.