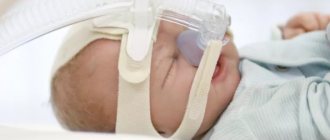
According to statistics, 2% of parents experience apnea in newborns - a disorder in which the baby stops breathing for 20 seconds or more. Apnea occurs more often in premature babies. According to various estimates, from a quarter to a half of babies born at 37-42 weeks suffer from OSA (obstructive sleep apnea syndrome).
Norm
Uneven breathing in newborns during sleep is not always a problem. Parents should not worry if breathing stops:
- occur no more than once per hour;
- breathing in a sleeping child does not cause effort;
- the baby breathes evenly and deeply during sleep;
- holding your breath for less than 5 seconds;
- the baby’s heart does not slow down, the pulse does not subside, the skin does not change color.
If your baby’s breathing causes concern, you should find time and visit a pediatric somnologist – a doctor who treats sleep disorders.
Why are adenoids dangerous?
First of all, adenoids in children are fraught with deterioration in auditory activity. The difference between the internal pressure in the middle ear cavity and the external atmospheric pressure is regulated using the Eustachian (auditory) tube. The enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil, blocking the mouth of the auditory tube, impedes the free penetration of air into the middle ear area. As a result, the eardrum loses its mobility, which is manifested by hearing loss.
Often a child may sniffle during sleep due to enlarged adenoids, which contribute to hearing impairment . Hearing loss comes in different degrees. With adenoids in children, hearing loss can develop to moderate severity. As a rule, with adenoids, there is an enlargement of the tonsils. Some children's tonsils are so enlarged that they almost connect with each other, so the child has problems swallowing food and cannot breathe freely through either his mouth or nose.
It often happens that difficulty breathing, especially when a child sniffles in his sleep, causes him to wake up in the middle of the night. The baby wakes up with a feeling of fear and is afraid that he will suffocate. Such children can be nervous and out of mood. You should not delay and wait for such an illness to go away on its own; you should immediately make an appointment with an ENT doctor who can decide when and how to effectively treat adenoids.
Adenoiditis is a chronic inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsils, which causes snoring in children. Adenoids make it difficult to breathe through the nose, contributing to the formation of inflammatory diseases, and themselves serve as an ideal environment for attacks by viruses and bacteria. For this reason, the tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil is in a state of chronic inflammation, and viruses and microbes multiply in it. A focus of chronic infection appears, from which microbes spread throughout the body.
Kinds
Infant apnea - what is it? Experts distinguish several types of this pathology.
A baby born at term may experience the following types of apnea:
- central – short-term cessation of breathing, which occurs involuntarily in infants;
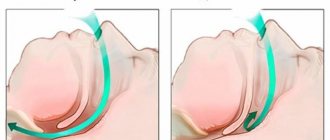
- obstructive - the child stops breathing due to obstruction (blockage) of the airways.
Premature newborns may experience:
- primary apnea - observed due to difficulty in lung function immediately after the baby is born or 3-6 months after birth;
- secondary – respiratory arrest after primary ventilation.
Secondary apnea is characterized not only by cessation of breathing, but also by a decrease in pressure and a general weakening of muscle tone. This condition can provoke the further development of complications.
Treatment of snoring in children
It is necessary to treat adenoids in children, since prolonged frequent and shallow breathing through the mouth at night (especially when the child sniffles in his sleep) can cause improper formation of the chest and lead to anemia. In addition, due to continuous mouth breathing in children, the growth of teeth and facial bones may be impaired. The development of a special adenoid type of face is especially dangerous: the mouth is half-open, the lower jaw lengthens and droops, the upper incisors protrude significantly forward.
For every parent, worrying about their own baby is unbearable torture. If you notice that your child has a stuffy nose and is breathing through his mouth, you should immediately contact a specialist doctor at the ENT-Asthma clinic. You should definitely visit an ENT doctor if your child sniffles during sleep, since timely diagnosis of the disease and effective treatment in the shortest possible time will help avoid serious complications .
Parents should constantly monitor the child’s health and monitor the level of air humidity in the room, since too dry air dries out the mucous membrane. Doctors-specialists of the ENT-Asthma clinic, who have a wealth of practical experience over many years, do not recommend self-medicating their children, and when the first symptoms appear, such as a child snoring or sniffling during sleep, you should immediately seek help.
Symptoms
The main alarm signal is interruptions in breathing or stopping it for more than 20 seconds. You should urgently make an appointment with a doctor if your breathing pattern does not fit into the norm, and if at least one of the following symptoms is observed:
- baby's skin becomes paler or bluer;
- cyanosis appears in the mouth and nose area due to oxygen deficiency;
- snoring (indicates an obstructive type of apnea);
- The baby suffers from restless sleep not for the first night;
- enuresis (indicates disruptions in the functions of the central nervous system);
- profuse sweating occurs during sleep;
- the child convulsively gasps for air, constantly breathes through his mouth (both in sleep and while awake);
- cannot restore smooth breathing after an attack.
Due to constant lack of sleep, the baby becomes capricious, constantly cries, and gets irritated.
The main symptoms of apnea in children born prematurely include:
- episodic interruption of breathing with pauses of 20 seconds or more;
- blue/pale skin;
- slowing of the pulse (in infants it can be heard more clearly on the shoulder or fontanelle).
Doctors are well aware of when apnea in premature babies goes away, unless there are complicating factors. This occurs by 40-45 weeks of life as the nervous and respiratory systems, as well as the respiratory control center, are finally formed.
It is more difficult to understand until what age the problem will last. Seizures can occur both in infants in the first weeks of life and in children older than six months. The prognosis is given only after a complete diagnosis.
Sources of sleep disorders
It should be immediately noted that most often periodic breathing appears in infants who are not yet six months old. For such babies this is quite normal. Doctors' intervention is not required here, even if up to 7-8 percent of the night time is paused. In the case of sleep apnea, it must be treated immediately.
As for older children, uneven breathing may appear in the following situations:
- Lack of oxygen , when possible cyanosis of the extremities, as well as the skin of the body and around the mouth. This usually affects children one year old and younger. The picture is like this: the baby is gasping for air, it is difficult for him to breathe fully.
- Diseases of infectious etiology . In children, whistling, heavy snoring, and even gurgling are also added. If there are inflammatory processes in the lungs, the rhythm of inhalation and exhalation often increases.
- Increased body temperature : the rhythm is lost, there is shortness of breath, which can also occur with cardiac problems.
- Bronchitis with obstruction and croup , which is called false. The rhythm also becomes disrupted, noisy and loud exhalation appears, and the child coughs.
In addition, adenoids and obesity, diabetes mellitus and nervous diseases, heredity and birth injuries can be the basis for respiratory disorders.
Causes and consequences
In newborns, pathology can develop due to problems:
- with lungs or heart;
- due to disorders of the respiratory functions of the central nervous system;
- due to airway obstruction.
In premature babies, the syndrome often develops due to an immature nervous system. The reasons may also be:
- unsuccessful ventilation after primary apnea;
- birth injury;
- congenital pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- intrauterine infections affecting the fetal brain;
- immaturity of the laryngeal muscles;
- craniofacial pathologies;
- weak muscular corset of the upper respiratory tract.
In addition, apnea is often a complication of hereditary diseases, as well as diseases that the child has already had - meningitis, inflammation of the adenoids, asphyxia, oxygen starvation, etc.
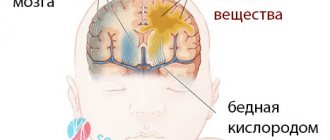
Breathing problems are extremely dangerous for the baby's health. They can also threaten his life. When breathing stops for 20 seconds, neurons begin to die. With a longer absence of oxygen, irreversible problems begin with all vital organs - heart, lungs, bronchi.
In children older than six months, neurological problems develop with chronic apnea. The child cannot concentrate. Memory deteriorates. With hyperactivity, it is extremely difficult for a child to find contact with other children. There are problems with socialization on the playground or in the nursery.
Sleep-disordered breathing in children
Yulia Ivanovna Zhavinina
Nurse of the highest category, department of functional diagnostics of diseases of the nervous and muscular systems of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution "Diagnostic Center of the Altai Territory" 656063 Altai Territory, Barnaul, st. V. Kashcheeva 7, apt. 131 +7-962-822-5225 [email protected]
Now I am addressing parents whose children have difficulty waking up in the morning, fall asleep in class, fight during breaks, snap at teachers, and do not learn the school curriculum well. Or maybe your heir has enuresis or talks in his sleep, suffers from night terrors and sweats a lot? Dear moms and dads, I think in such cases you take your child to a neurologist, psychologist, psychiatrist, or even “treat” him with a belt to no avail. And if you notice that your child looks small compared to his peers or is gaining weight, despite a diet and active lifestyle, then contact an endocrinologist! I can already hear your question: “What do you propose to do?” I suggest first listening to how your child sleeps!
Did you know that 10-15% of children aged 2 to 8 years snore in their sleep? How does snoring occur? During sleep, the muscles of the soft palate and the walls of the pharynx gradually relax. They begin to vibrate when a stream of air passes and create the sound phenomenon of snoring. But snoring is different! What happens if your child has enlarged tonsils, adenoids, a deformed facial skeleton, or suffers from allergic rhinitis, i.e. diseases accompanied by narrowing of the upper respiratory tract? Then a further deepening of sleep and a decrease in muscle tone leads at a certain moment to a complete collapse of the pharynx and the development of an acute episode of suffocation, which leads to awakening of the brain and, as a result, a deterioration in the quality of sleep. I have now described obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) - this is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition for the patient. In the morning, the child may complain of a dry throat and headache. But not all snorers have sleep apnea, although the risk of developing it is significantly higher in snorers than in non-snoring people.
Central apnea is also common in children - a lack of air flow due to a temporary lack of impulse from the central nervous system to activate respiratory effort. This form of apnea occurs in children with disorders of the central mechanisms of breathing regulation and requires serious and long-term observation by specialists (neurologist, somnologist).
Severe forms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children have dire consequences. In the deep stages of sleep, growth hormone is produced, and with poor quality sleep, the deep stages of sleep are absent, and the production of “growth hormone” is significantly reduced, so the child lags behind his peers in growth.
A decrease in blood oxygen saturation at night leads to a decrease in academic performance, because... the functions of attention and intelligence suffer. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children causes learning problems due to hyperactivity and attention deficit, and if a child cannot study normally at the age of 5-12 years, then it will be almost impossible to make up for this gap in the future.
Fluctuations in blood pressure during apnea change the hemodynamic system, which subsequently leads to the early development of cardiovascular diseases.
Activation of the striated muscles, which occurs at the end of apnea, is a trigger for sleep talking and sleepwalking, and changes in intra-abdominal pressure provoke episodes of enuresis.
And if a child is diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, parasomnias, minimal brain dysfunction, nocturnal enuresis, then it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive sleep study - polysomnography. At the same time, indicators of blood oxygen saturation, snoring, chest excursion (which makes it possible to differentiate obstructive from central apnea), and EEG sleep indicators are recorded.
There is a method for diagnosing OSA that is simpler, but quite accurate - this is pulse oximetry - a method of long-term non-invasive saturation of arterial blood hemoglobin with oxygen and pulse.
The diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is considered confirmed if 1 or more episodes of apnea-hypopnea are recorded per hour of sleep.
It is very important to consult a doctor in time and accurately establish the diagnosis, because obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) and primary snoring are treatable. A doctor who deals with the problem of sleep disorders is a somnologist. Such specialists work in many large medical centers. Treatment tactics depend on the combination of causes and severity of snoring and OSA. Treatment methods are varied and can be divided into the following categories:
1) General preventive measures and situational relief of snoring:
- weight loss;
- ensure sleeping on your side, because When sleeping on the back, the tongue retracts, especially in patients with deformation of the facial skeleton (retro- and micrognathia). To do this, sew a pocket between the shoulder blades onto your nightwear and place a tennis ball in it;
- ensure an elevated position of the headboard. An elevated position of the torso reduces the retraction of the tongue even in a supine position, and fluid in the body shifts downward, which leads to a decrease in swelling of the mucous membrane at the level of the nose and pharynx and an increase in their lumen. But don't use tightly stuffed pillows! The head should be positioned as parallel to the body as possible, so it is better to use flat pillows or special contour pillows;
- Training the muscles of the tongue and lower jaw:
A. push the tongue forward and backward as much as possible. Hold it in the extended position for 1-2 seconds and pronounce at this moment the drawn-out sound “i”. This exercise increases the tone of the muscles of the soft palate and uvula.
B. Press the chin with your hand and forcefully move the lower jaw back and forth. With this exercise we train the muscles of the lower jaw that push it forward. Perform all 2 exercises 30 times in the morning and evening.
B. Press the wooden or plastic stick firmly with your teeth and hold it for 3-4 minutes. Do this exercise before bed, because... This exercise causes tonic tension in the masticatory and pharyngeal muscles, which persists for 20-30 minutes, which significantly reduces snoring in the initial stage of falling asleep.
- Use an ultrasonic humidifier in the bedroom. During the heating season in winter, humidity drops below 30% with an optimal level of 60%.
2) Facilitation of nasal breathing. To do this, you can use special nasal strips to expand the nasal passages “YurizRight”.
3) Use of intraoral devices
4) The use of pharmacological agents that alleviate snoring.
Nasonex nasal spray - locally tones, has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. Nasonex is safe and approved for use in children over 2 years of age.
Many different anti-snoring remedies are also advertised, most of which contain various herbal ingredients.
5) Application of electromechanical stimulation devices
- These are devices in the form of wrist bracelets that detect the sounds of snoring and send weak electrical or mechanical impulses that irritate the nerve endings in the arm and, thus, awaken the patient's brain.
6) Surgical treatment of snoring and OSA
– elimination of obvious anatomical defects at the level of the nasopharynx. But the benefits and potential risks of surgical treatment must be carefully weighed, so the decision to surgically treat snoring and OSA should be made by a qualified ENT surgeon.
7) Use of a respiratory support device - CPAP therapy.
This method is effective for severe forms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. The essence of the method is to maintain constant positive pressure in the upper respiratory tract, which will prevent the walls of the respiratory tract from collapsing and vibrating.
Unfortunately, there is currently insufficient information available about the impact of OSA on the health of the child and little attention is paid to diagnosis. Meanwhile, parents who listen to the dreams of their little angels can prevent serious complications, and timely contact with a specialist will significantly improve the child’s quality of life.
Bibliography:
- Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and other sleep disorders. A course of multimedia lectures. R.V. Buzunov. – M., 2012
- Sleep apnea syndromes. A.P. Zilber. – Petrozavodsk, 1994. – p. 184
- Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Yu.I.Feshchenko. L.A. Yashina and others - Kyiv, 2009
- Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in adults and children. Practical guide for doctors. R.V. Buzunov, I.V. Legeyda, E.V. Tsareva. – M., 2012. – p. 121
- Snoring and sleep apnea in pediatric practice. M.G. Poluektov. – M., 2010.
Diagnostics
Sleep apnea is not a death sentence, and to understand how to treat it, it is enough to consult a doctor. Parents of a premature baby should make an appointment with a neonatologist. The rest go to a pediatrician, who will refer you to a specialist. The task of the otolaryngologist, neurologist, pulmonologist, cardiologist will be to identify the causes that provoked the disorders.
In newborns
Polysomnography is the main method that helps to identify pathology in children born at term. Diagnosis is carried out during sleep. Electrodes and sensors are connected to the baby’s body, which record the functioning of the respiratory system. The doctor visually monitors breathing pauses, their number, frequency and duration.
Additional examinations are carried out to identify the causes. For example, if you suspect:
- For obstructive apnea, anterior rhinoscopy is prescribed, which makes it possible to detect the causes of complicated nasal breathing;
- for disturbances in the functioning of the heart - ECG, ultrasound of the heart and brain;
- for pneumonia - radiography.
The doctor may also prescribe an MRI, CT scan, brain encephalogram and other examinations.
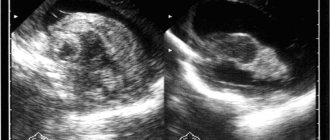
In premature babies
Most often, premature babies suffer from central apnea. Therefore, neurosonography becomes the main diagnostic method. Otherwise - ultrasound examination of the brain. The brain stem, where the respiratory center is located, is especially carefully studied. The doctor analyzes the nature and dynamics of brain processes and makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathologies.
If abnormalities are detected, a lumbar puncture is prescribed. With its help, they look for hemorrhages or inflammation in the brain.
Possible consequences
Sleep apnea in children is a serious disease that causes great harm to health. As a result of constant holding of breath, the body lacks oxygen, and the brain primarily suffers from this. The result is dangerous and irreversible pathologies.
Constant lack of sleep as a result of regular awakenings from lack of air leads to drowsiness, apathy and lethargy during the day, which increases the risk of injury. Added to this is the lack of concentration, attention, nervousness, and capriciousness of the baby.
Due to lack of rest, the body's protective functions are reduced, the immune system weakens, and the tendency to catch colds increases, which, in turn, leads to increased apnea and, in severe cases, the death of the baby.
The following diseases can result from regularly holding your breath during sleep:
- Sudden awakenings from lack of oxygen, which can be up to a hundred during the night with severe apnea, lead to sleep disorders and the risk of developing chronic insomnia.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Cardiovascular diseases, hypertension.
- Ischemic disease, heart failure.
What to do for apnea: first aid
During an attack, parents should provide first aid to the baby by following simple steps:
- Take the baby in your arms, stroke or pat him on the back, rub his arms, legs, earlobes, tickle his heels or pat them.
- Spray your baby with cool water.
- To make breathing easier, place your baby on his tummy with his head turned to the side.
If the baby's breathing has not returned, perform artificial respiration:
- Place your baby on a hard surface on his back.
- Place a cushion from a sheet or towel under the shoulder blades so that the head tilts back slightly.
- Hold your head and inhale air into your mouth and nose at the same time. The air portions should be very small.
- If the child does not wake up after 6-8 breaths, perform chest compressions.
Recommendations for parents
If, as a result of examining the baby, no serious developmental pathologies were identified, the following tips will help ease breathing at night:
- Ventilate the children's room before going to bed, and use a humidifier during the heating season.
- Do wet cleaning in the house twice a week, create a hypoallergenic environment around the child, minimizing the presence of dust.
- Monitor the correct position of the child's head and body during sleep, choose an orthopedic pillow and mattress for him.
- Don't forget about hygiene procedures. If necessary, rinse your child's nose with saline to clear the nasal passages.
All of the above preventive measures are easy to implement and will help your child get proper rest during sleep.
In addition, we remind Kaliningrad residents that it is necessary to monitor the baby’s weight, adhere to a balanced diet and avoid overeating.
To strengthen the muscles of the larynx and pharynx, the child can perform simple articulatory exercises: stretching the vowels “i” and “s”, as well as inflating balloons, singing and playing wind instruments.
If, despite taking all preventive measures, your child’s sleep and behavior during the day causes you anxiety and concern, make an appointment with an ENT doctor by calling the numbers listed on our website. Do not ignore the consultation, because the child’s health is above all!
Treatment
During hospitalization, doctors perform the necessary manipulations to stabilize the baby’s condition. Premature babies are placed in an incubator. If the attacks recur there, the child is connected to a ventilator.
Medication prescriptions and clinical recommendations are made taking into account the causes of the disease. For example, to treat infant apnea caused by excessively enlarged adenoids, an ENT specialist prescribes surgery to remove them.
Prevention
Simple recommendations will help prevent the development of apnea in infancy:
- it is necessary to regularly ventilate the room where the child sleeps;
- the air in the children's bedroom should not be excessively dry;
- Before going to bed, the child should not be overheated;
- bedding must be selected correctly: a hard thin mattress, a low pillow, pillow filling and blankets made from natural materials (filling made from natural bird feathers is not acceptable);
- It is prohibited to use aerosols (both household products and perfumes) near the baby;
- tobacco smoke is strictly prohibited.
To control a child's sleep in the first months of life, it is worth placing his crib in the parents' bedroom.