MRI of the brain in children and adults
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is a diagnostic procedure that allows you to assess the condition of brain structures and identify all kinds of diseases.
This procedure is absolutely harmless to the health of the body, painless, and is highly informative. There are the following types of MRI:
- standard, which is performed without the introduction of a contrast agent;
- with contrast, before the procedure the patient is given intravenous medications containing gadolinium salts. The substance penetrates the bloodstream and, falling into the rays of the MRI scanner, better illuminates the resulting picture, which greatly simplifies the interpretation of the study.
In the finished images, only soft tissues are visible; the bones of the skull do not interfere with the diagnosis in any way.
In what cases is it necessary to do an MRI?
Timely diagnosis will help identify abnormalities in the development of any brain structure, this will help avoid possible mental and physical developmental disorders in the baby in the future.
Also, this procedure may be prescribed by a doctor if your child has suffered a head injury or is involved in sports where injuries are possible (wrestling, boxing, extreme sports). In such cases, the consequences of a blow or concussion may not appear immediately, so a control procedure will help avoid possible complications later.
Make an appointment now!
Indications for diagnosis using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner may include the following symptoms:
- infectious diseases;
- periodic occurrence of convulsive syndrome;
- frequent dizziness or headaches;
- periodic fainting without apparent external causes;
- progressive hearing loss;
- noticeable blurred vision;
- changes in behavior;
- severely delayed development.
For such indications, your doctor may refer you for an examination to find out what an MRI of the child's brain shows, identify the cause of the symptoms, and prescribe appropriate treatment.
When is EEG indicated for children?
The technique allows you to determine the state of the baby’s nervous system. It is based on the transmission of electrical impulses by neurons that create bioelectrical activity in the brain. What is it - EEG for children? The electroencelograph displays the received information in the form of curved lines during different periods of activity. If the doctor has sent your child for examination, you should not refuse to conduct the examination. It is painless and at the same time quite informative for identifying brain pathologies of various types.
The doctor prescribes an EEG for the child in the following cases:
- with periodically recurring loss of consciousness;
- if the child falls out of reality;
- after moderate traumatic brain injury;
- in an epileptic clinic;
- persistent sleep disorders;
- if oncological processes are suspected;
- to monitor the rehabilitation process after undergoing neurosurgery;
- in case of congenital pathology (eg hydrocephalus);
- for cerebrovascular accidents;
- for disorders in the neurological status (cerebral palsy, other motor disorders);
- for autism spectrum disorders;
- developmental delay, both in the mental and physical spheres.
Electroencephalography shows the localization of foci of epileptiform activity, the degree and dynamics of the disease, and the effectiveness of the selected therapy. Therefore, the scope of its application is very wide.
Sometimes the doctor sends the child for an EEG even in the absence of certain somatic pathologies. Indications for its implementation are deviations in behavior, development inappropriate for age, poor memory and lack of concentration, hyperactivity. At school age, in case of excessively rapid fatigue, an electroencephalogram of the brain may also be prescribed for children.
The method is widely used to diagnose epilepsy.
What can tomography reveal?
Head tomography for children will help identify the following problems:
- the presence of a cyst or intrauterine infection;
- ischemia (pressure of the tumor on the blood vessels of the brain);
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland;
- problems with the inner ear or eye function;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypoxia;
- deviations in the development of brain structures.
Deciphering the tomogram will help to timely diagnose any of the above diseases and treat it at an early stage.
How to prepare for the examination?
The research algorithm differs depending on the age of the child. The general rule is to wash your hair the day before the electroencephalogram is taken to remove sebum from its surface.
An EEG of an infant is often done primarily during sleep, so the selected time for the study should coincide with the sleep schedule. Before the study, you need to feed the baby.
If the baby is over a year old, an important condition is to comply with all the doctor’s requests. Parents must first have a conversation with their children, preparing them psychologically for the session:
- For children 2-3 years old, you can try to imagine research in the form of an exciting journey, let them be superheroes.
- An assiduous child is recommended to take his favorite toy or picture book with him.
- Teach your baby to open and close his eyes, while keeping his breathing even and without fear.
If a child is prescribed medications, they cannot be refused. An exception is when anticonvulsants are discontinued 1-3 days before the examination at the request of the attending physician. Ask to reschedule the study if it coincides with a respiratory disease accompanied by severe catarrhal symptoms (runny nose, cough).
The patient’s behavior during the session affects the information content of the data obtained, so take your preparation seriously.
Try, if possible, to reduce the load on the nervous system on the eve of the examination. This applies not only to emotional overexcitation, but also to errors in nutrition. You should not give your child tonic drinks the day before. At the same time, it is better to feed him two hours before electroencephalography so that the child can better tolerate the study.
How to prepare your baby for an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is good because it does not require special preparation.
On the day of the diagnosis, choose loose clothing without metal elements for your baby; do not wear anything that contains metal (watches, glasses, chains, earrings, bracelets).
Before the procedure, you will need to talk to your child in advance and prepare him mentally. It is recommended to explain to him why this diagnosis is needed and what the tomograph shows, to convey to him the information that he will need to not move during the procedure, otherwise the pictures will not be obtained.
You can invite him to play a game, for example, call it space flight. Since the tomograph has a built-in two-way intercom, it will not be difficult to beat this.
Most children are not afraid of the device; rather, it arouses their interest and curiosity, so there is no need to worry about the device causing fear in the child.
If the baby is too small to lie still, then the anesthesiologist selects a drug that is absolutely harmless to his body and puts the patient into medicated sleep. Anesthesia is selected by the anesthesiologist, taking into account existing contraindications and possible allergic reactions.
Is MRI harmful for children: how often can the procedure be repeated?
Due to its absolute harmlessness, tomography can be repeated as many times as desired (in the absence of contraindications). Repeated diagnostics are also prescribed by the attending physician. This may be necessary if you need to monitor the course of the disease over time, if you want to monitor the treatment process before and after surgery, if previous results turned out to be ineffective or controversial for various reasons.
Children's MRI may be prohibited if there is:
- the presence of foreign metal objects in the child’s body (implants, prostheses, retainers, clamps);
- electronic devices and stimulants;
- severe allergic reactions to medications (with planned administration of contrast).
How are brain MRIs done for children?
If necessary, the baby is changed into a hospital gown (if the clothing you choose does not meet the requirements) and placed on a pull-out table.
After this, the table is pushed into the magnetic capsule and diagnostics begin. If the procedure takes place without medicinal immersion in sleep, then during it it is recommended to talk with the child so that he does not get nervous.
If a child begins to feel unwell, notices nausea, dizziness, or other strange sensations, he can immediately inform the doctor about this via the built-in intercom to stop the tomograph.
During the procedure, the device scans the body and transmits all data to a special computerized device. After performing a tomography and obtaining an image, the radiologist interprets the image. If the patient was under the influence of medications, then after the tomography he should remain in the hospital for about half an hour under the supervision of doctors so that they can monitor his condition after anesthesia.
Deciphering an MRI of a child’s head will take some time; the result and conclusion will be given to you either on the same day or the next day.
Decoding the results
The primary interpretation of the received images is carried out by the doctor on duty - a radiologist, who issues a preliminary conclusion about existing diseases or problems.
But only a doctor who specializes in pediatric anatomy and studies the pathological conditions of “little” patients can give the most accurate diagnosis.
Be sure to take the received package of documents and photographs to your attending physician. Based on the images, he will be able to confirm or refute his initial fears and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Advantages of the method
Many parents are afraid to take their baby for examination when the doctor recommends an MRI for the child. This is due to misconceptions about the procedure and groundless fears that the method is harmful to children.
Parents should know that the magnetic field has no effect on both adults and children. Image formation occurs due to the activation of hydrogen atoms in cells. The impact is so insignificant that it will not even be recorded by the body and will not cause a reaction in the nervous system, and does not affect the immune system.
- The method has no age restrictions, it can be performed at any age;
- the device does not have any effect on brain activity;
- the procedure is absolutely safe and does not affect your well-being in any way;
- there is no radiation dangerous to the body;
- allows you to obtain clear and high-quality high-resolution images;
- will help identify diseases in their infancy;
- identifies injuries and diseases that are invisible during other types of examination.
Thanks to all the advantages, MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast (and the brain as a whole) is deservedly popular as a diagnostic method. And if the attending physician recommends taking your child for magnetic resonance imaging, then you should not ignore his instructions, because it is possible that this will help prevent the development of the disease and preserve the child’s health for many years.
- Why do you need an MRI?
- What diseases can MRI detect?
- MRI of the TMJ and temporal bones.
- MRI of cerebral vessels.
- Features of MRI of the head in the presence of dental implants.
- What to choose for a head examination - MRI or EEG.
At what age are MRIs performed on children?
Magnetic resonance of charged particles does not affect the child’s health, therefore MRI diagnostics of brain diseases is one of the most popular ways to determine cerebral pathologies.
At what age can children have an MRI? The study is prescribed from the second month of the child’s life, but there are certain features of the procedure.
The patient needs to maintain a motionless body position for a sufficiently long time. Movements contribute to the appearance of artifacts in the photo and reduce the information content of the scan.
Since babies cannot lie for a long time without moving, general anesthesia is used. For children under 5 years of age and with increased excitability of the nervous system, the study is carried out under anesthesia, in a hospital setting. The baby is being observed by an anesthesiologist.
At an early age, MRI under general anesthesia is performed when alternative diagnostic methods (ultrasound, EEG, etc.) are insufficiently informative.
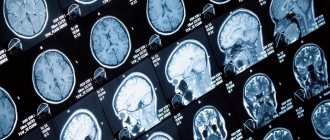
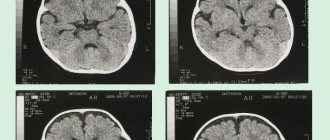
Hydrocephalus on MRI images
After 5 years of age, children can have an MRI scan at any diagnostic center. If desired, one of the parents can be present at the procedure. No special conditions are required for native research. Contrast tomography for children under 12 years of age is performed in a hospital. Intravenous administration of the drug and the nuances associated with this manipulation make it necessary for the child to remain under supervision. Adolescents are examined with an intensifier in all diagnostic clinics that have the appropriate license.
Preparing for the brain MRI procedure - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What is an MRI of the brain?
- When is a brain MRI necessary for an adult?
- When is a brain MRI necessary for a child?
- Preliminary preparation
- Preparation in the MRI room
- Features of preparation for the procedure with the introduction of contrast
- In what cases is anesthesia required?
- Strict contraindications
- Relative contraindications
- Who is not recommended to undergo an MRI of the brain?
- Are there possible complications with an MRI of the brain?
- We invite you to undergo an MRI of the brain at MEDSI!
What is an MRI of the brain?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic method that is designed to search for and identify damage in various organs.
To carry it out, special equipment is used - a tomograph. The doctor orders an MRI of the brain to determine whether the patient has any disease or damage to this organ. The research is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance. Each human organ consists of matter of varying density and structure. During the diagnostic process, signals are recorded that, under the influence of a magnetic field, emanate from each point of the organs being examined. Due to the dissimilarity of their properties, organs are displayed differently on a tomogram. Each section has its own meaning. The data is recorded on a digital medium. As a result of the examination, the doctor receives projections of brain slices from different sides. This allows you to most accurately diagnose the problem and select treatment.
When is a brain MRI necessary for an adult?
The doctor orders an MRI to find out if there are pathologies or abnormalities in the patient's brain, diagnose the disease at an early stage, and then choose and monitor treatment. For MRI of the brain, indications may be as follows:
- Severe and frequent headaches
- Stroke
- Epileptic seizures
- Head injuries
- Pain and discomfort in the eyes and ears
- Dizziness
MRI of the brain is used to identify or confirm a number of diseases and disorders associated with the functioning of the brain, circulatory system, and nervous system, including chronic ones. These are diseases such as:
- Epilepsy
- Multiple sclerosis
- Oncology
- Hemorrhage
- Aneurysm
- Eye and/or ear diseases
- Infection
- Cyst
- Arterial obstruction or venous thrombosis
- Congenital defects in the structure of the brain
- Hydrocephalus
- Chronic diseases of the nervous system
- Intracranial hypertension
The doctor may order an MRI before surgery to determine the condition of the tissues and cerebral cortex and localize the lesion due to injury or disease. A tomogram helps to identify not only tumors or recently emerging brain problems, but also chronic ailments.
The procedure is completely safe, so not only adults, but also children are prescribed MRI of the brain.
When is a brain MRI necessary for a child?
Indications for examining a child are as follows:
- Tumor recognition
- The need to identify pathologies and disorders of the brain structure
- Study of the cerebral cortex and blood vessels
- Examination of his sinuses and ventricles
It must be remembered that a doctor should prescribe an MRI of the brain, since he is the one who knows whether the procedure is necessary and what nuances of the examination should be taken into account. Therefore, if the patient independently wants to obtain such a study, the results may be less accurate than if the process is supervised by an experienced physician.
Preliminary preparation
MRI of the brain requires preparation. First of all, it is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of implants, because with some of them it is impossible to undergo an MRI of the brain, despite the indications for the procedure. The doctor should also be warned if the patient has claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces). Then the study can be carried out under sedation (putting the patient into medicated sleep). A pregnant woman needs to warn doctors about this, as there are some restrictions.
Before the MRI, you can take medications that the patient usually uses. No special diet is required, except in individual cases determined by the doctor.
Preparation in the MRI room
If there are no contraindications, immediately before the brain MRI procedure, preparation is minimal. You should:
- Remove all metal and magnetic objects, including jewelry, hairpins, etc.
- Remove plastic cards, phones, keys, etc. from your pockets
- Remove clothing with metal elements
- Remove those prostheses that are possible: hearing aids, dentures
Features of preparation for the procedure with the introduction of contrast
Separately, preparation for MRI of the brain is required if the patient is undergoing an MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent. This is required if it is necessary to obtain even more accurate analysis results. A special gadolinium-based substance is injected into the patient through a catheter. It makes the human body more sensitive to magnetic resonance.
In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor - an allergist-immunologist, in order to exclude possible allergic reactions to the administered medicine.
In what cases is anesthesia required?
Young children cannot remain still and control themselves, so an MRI of the child's brain may be performed under sedation. An older child who is not afraid and understands the importance of the procedure will be able to undergo it independently.
Thus, examination under sedation can be carried out in the following cases:
- the patient has claustrophobia
- a small child is being examined
- possible panic attacks
- severe pain does not allow lying still
- have mental disorders
- antisocial behavior of the patient
If you require a study under sedation, you must notify the administrator when registering. He will provide up-to-date information about the centers where this service is available on the day of registration.
When the basic preparations are completed, the patient is placed on a sliding table and then placed in the tomograph chamber. The tomograph is a cylinder around which there is a magnet. The latest machines allow you to scan the brain in 15 minutes. After the examination, the patient will receive a disk or image with a transcript.
Strict contraindications
The magnetic field is harmless to humans, unlike X-ray radiation. Therefore, most of the contraindications for MRI of the brain apply to patients who have any metal implants. This is due to the nature of the procedure: it is carried out using a magnet, which can attract or distort the operation of the mechanism. Dangerous items include:
- pacemakers
- defibrillators
- ear implants
- metal prostheses
- clips on vessels
Relative contraindications
Other items are not prohibited during the procedure, but may distort the results. Here they are:
- nerve stimulants
- non-metallic prostheses
- staples, plates, pins
- artificial heart valves
- dental implants
- braces
Who is not recommended to undergo an MRI of the brain?
It is not recommended to undergo MRI if the patient
- has a body diameter greater than 150 cm
- overstimulated and unable to remain still
It must be remembered that MRI is used with caution for pregnant women and is not recommended in the first trimester.
Are there possible complications with an MRI of the brain?
As a rule, there are no complications when undergoing MRI of the brain. But strange sensations may arise. If the study is carried out using a contrast agent, then during its administration such unpleasant reactions of the body as:
- pain at the injection site
- nausea
- rush of blood
- allergic reaction
The first three symptoms usually pass quickly, and in the latter case it is necessary to immediately inform the doctor about the deviations so that he can take the necessary measures.
You may feel warm during the scan. If this bothers the patient greatly, he needs to tell the doctor about it.
In rare cases, after undergoing an MRI of the brain, the patient may feel unwell. Therefore, if the following symptoms occur, you should immediately report them to your doctor:
- headache
- dizziness
- vision problems
We invite you to undergo an MRI of the brain at MEDSI!
At MEDSI clinical diagnostic centers you can undergo an MRI of the brain quickly and painlessly.
MRI at MEDSI is:
- Urgent examinations in case of injury or sudden illness
- Performing tomography under sedation (for those suffering from claustrophobia and panic attacks)
- Equipment from well-known manufacturers (Siemens, Philips)
- Research for adults and children
- Interpretation of results exclusively by qualified radiologists