Echoencephalography: what is it?
Echoencephalography (Echo EG) is an ultrasound diagnosis of the brain. It allows you to examine the state of cerebral (brain) structures and indirectly assess the state of the blood vessels of the head.
The basis of the method can be described as follows: the tissues of the human body have different densities and structures, therefore sound waves, passing through different types of tissues of the brain, are reflected differently. The structures involved in signal reflection produce different waves. By the reflected wave, you can understand where the source of pathology is located. The type and extent of damage to nerve cells is also determined.
Echo EG is a non-invasive method, it takes place without intervention inside the head, without anesthesia. During the examination, the body is not irradiated. No contrast agent is used, there will be no allergies. It is not painful and you do not need to specially prepare for the test.
Indications and contraindications
A child’s brain echo is prescribed for the following conditions:
- Delayed mental and physical development.
- Sleep disorders.
- Muscle hypertonicity.
- Cramps.
- Urinary incontinence (enuresis).
- Logoneurosis (stuttering).
- Head injuries and bruises.
- Nervous tics.
- Hydrocephalus.
Echoencephalography is also performed for frequent intense headaches, dizziness, nausea regardless of food intake, fainting, a feeling of lack of air, decreased concentration and other neurological symptoms.
Echoencephalography of the brain in children is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to monitor the patient’s condition. In case of severe pathology, Echo EG data is taken to make a preliminary diagnosis.
The procedure has no contraindications, except for open wounds, infections, skin defects at the site of application of the sensors. If there are open wounds on the head, it is better to do a CT scan.
Summary for parents
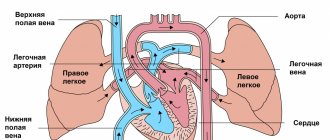
Echocardiography is one of the important and reliable methods for diagnosing pathology of the cardiovascular system. This painless and safe test, which does not involve radiation, can be carried out from birth and even during fetal development. If pathology is detected, the study can be repeated several times.
The technique allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and helps the cardiologist select the right treatment. Parents should not try to understand all the indicators and numbers on their own - this can lead to erroneous conclusions.
Union of Pediatricians of Russia, ultrasound diagnostics doctor Revunenkov G.V. talks about echocardiography and congenital heart defects:
How to prepare
Echoencephalography can be done on patients of any age, women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The procedure does not require preparation. There is no need to follow a special diet, take a contrast agent or carry out additional manipulations. It is best to conduct the examination after sleep.
Contact gel is applied to the scalp where the sensors are attached. The doctor moves the sensor. After the procedure, the gel must be wiped off, so you should take a towel for the examination.
Benefits of EchoCG
Echocardiography has a number of advantages over other types of cardiac examination.
First of all, this is an absolutely painless and non-invasive procedure that does not cause any discomfort to the patient. It is performed like a regular ultrasound. No injections or any other similar manipulations are performed before the procedure.
In addition, the procedure is completely safe for patients of any age group. It can be performed on children, adolescents, and pregnant women, since ultrasound does not have any negative effect on the fetus.
EchoCG is accessible, since the equipment for its implementation is available in almost any medical institution. The cost of echocardiography is much lower compared to MRI.
And the most important advantage of this type of examination is its excellent information content, which will allow the doctor to obtain the maximum necessary information and choose the right therapy.
How is a head echo performed on a child and in what ways?
The doctor should tell you how to prepare your baby for an Echo EG of the brain and what are the features of the examination of the child.
There are two ways to conduct an Echo EG:
- Transmission. Two sensors are used. They are applied on both sides of the head at the level of the temporal bone above the ears. One sensor sends a signal, the other receives. It is necessary that the sensors converge in one axis.
- Emission. This method uses only one sensor.
For young children, neurosonography is performed instead of echoencephalography. This is a scan through the large fontanel. In infants, the fontanelles have not yet ossified, so the ultrasound wave easily passes through the tissue.
The manipulation is carried out without anesthesia. The only difficulty is that it is difficult for children to remain still during the examination. The parents' task is to hold the head and calm the baby.
The procedure takes 10-15 minutes. After this, decryption is done.
Echo EG is often used to monitor the patient's condition during treatment.
Fetal echocardiography
Congenital heart disease can be diagnosed in the prenatal period using fetal echocardiography. The study allows you to study intracardiac blood flow and provide dynamic monitoring of indicators throughout pregnancy.
The examination technique provides the doctor with information on the condition of the heart and blood vessels and identifies congenital defects. It is carried out within 18-22 weeks. pregnancy. The study allows the obstetrician-gynecologist to plan the birth, and micropediatricians and cardiologists to begin treatment of the child immediately after birth.
Indications for fetal echocardiography are:
- murmurs noted by the doctor when listening to the fetal heartbeat;
- congenital heart disease in close relatives;
- diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother;
- taking antibiotics or anticonvulsants in the 1st trimester of pregnancy;
- miscarriages in the past in a pregnant woman;
- detection of abnormalities by ultrasound at 20 weeks.
Interpretation of results: norm and possible diseases
To make a correct diagnosis, the results of the Echo EG and the patient’s complaints are compared. The decoding is carried out either by a neurologist or a laboratory specialist. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. When interpreting data, the doctor’s experience and precise adjustment of the equipment are important.
To decipher Echo EG data, the doctor looks at three indicators of the echo signal:
- Initial complex. The signal is reflected from the bone, soft tissue, meninges and lateral ventricle on the side where the scanning occurs.
- Ultimate complex. This is the reflection of an ultrasonic wave from the bones of the skull and soft tissues of the head of the opposite hemisphere.
- Between them, a stable M-echo signal is recorded, which is reflected from the middle parts of the brain: epiphysis, pineal gland, septum pellucidum, and others. M-echo is essential for diagnosis.
Echoencephalography can be performed in two modes:
- M-method. One-dimensional scanning in which a graph is displayed on the screen
- Ultrasound scanning. 2D scanning. The brain is imaged in two planes.
Normally, the M-echo distance should be the same on one side and the other of the head. If the deviation is more than 1-2 mm (in children up to 3 mm), then this may be a sign of conditions such as hematoma, cerebral edema, abscess (accumulation of pus), intracerebral tumors, bruises and neoplasms. An increase in the volume of the lateral ventricles and the 3rd ventricle indicates the presence of hydrocephalus.
In a state of wakefulness, sleep, anxiety, the EG echo shows its rhythm: alpha, beta, delta or theta rhythm. Normal frequency is alpha rhythm, 8-13 Hz, beta rhythm, 13-30 Hz, theta rhythm, 4-7 Hz, delta rhythm, 0.5-3 Hz.
In case of severe disorders, electroencephalography is used as a preliminary diagnostic method. Additional research methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging, may be needed.
Research methodology
For transthoracic echocardiography, the patient is placed in the left lateral position. When a person lies in this position, the apex of the heart and the left side of the chest are brought closer together. This makes it possible to provide the most accurate visualization of the heart - as a result, all four of its chambers are visible on the monitor at once.
The doctor applies a gel to the sensor, which improves contact between the electrode and the body. After this, the sensor is alternately installed first in the jugular fossa, then in the area of the fifth intercostal space, where the apex beat of the heart can be monitored as clearly as possible, and then under the xiphoid process.
Of course, every doctor strives to ensure that the results of the study are as accurate as possible. It should be noted that how informative the procedure will be depends on three main factors.
First of all, the anatomical features of the patient should be taken into account. Serious obstacles to ultrasound are obesity, chest deformation and other similar factors. As a result, the resulting image may not be clear and cannot be interpreted properly. In order to clarify the diagnosis, doctors in such cases offer a transesophageal examination or MRI.
The quality of the equipment should also be taken into account. Of course, more modern equipment will provide the doctor with more opportunities to obtain sufficient information about the patient's heart.
Finally, the competence of the person conducting the examination should be taken into account. In this case, not only his technical skills are important (the ability to position the patient in the correct position and place the sensor at the right point), but also the ability to analyze the data obtained.
When performing stress echocardiography, the patient first undergoes a regular echocardiography, and then special sensors are applied that record parameters during physical activity. For this purpose, bicycle ergometers, treadmill test, transesophageal electrical stimulation or medications are used. In this case, the initial load is minimal, and then it is gradually increased, monitoring blood pressure and pulse indicators. If the patient's health worsens, the examination is stopped.
All this time, an electrocardiogram is continuously performed, which makes it possible to quickly respond if any extreme situations arise. During exercise, the patient may feel dizziness, increased heart rate, and discomfort in the heart area. After stopping the exercise, the heart rate slows down. Sometimes, in order for the heart to function completely back to normal, it is necessary to administer other medications. In this case, the patient's condition is carefully monitored until complete recovery.
Typically, the entire procedure lasts about an hour.
Transesophageal echocardiography begins with irrigating the patient's mouth and pharynx with lidocaine solution. This is intended to reduce the gag reflex during insertion of the endoscope. After this, the patient is asked to lie on his left side, a mouthpiece is inserted into his mouth and an endoscope is inserted through which ultrasound will be received and delivered.
What pathologies can echoencephalography reveal?
Echo EG shows the brain parts and large blood vessels. This diagnostic method allows timely detection of diseases such as meningoencephalitis, hydrocephalus, neoplasms and strokes. The procedure is available for all categories of patients: children, adults, nursing mothers, and also during pregnancy.
Using echoencephalography, you can identify not only the localization of the pathological process, but also understand how large the lesion is.
Neoplasms, meningoencephalitis, dropsy, intracerebral hemorrhage
In patients with long-term illness, a large shift in the M-echo may indicate the appearance of a tumor. The size of the displacement depends on the exact location of the tumor in the hemisphere. If the tumor is located in the middle sections, the displacement may be 2 mm, or may not be observed at all.
Meningoencephalitis is an inflammation of the brain and meninges. The disease is caused by microorganisms. The carriers are ixodid ticks.
Hydrocephalus (water on the brain) is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. EchoEG data should alert you if the index of the third ventricle is less than 22. Normally, 22-24.
During a stroke, if the M-echo is displaced by 5 mm or more in the first days, then this is a hemorrhagic type. If it moves by 2.5 mm, then the disease is ischemic.
Preparation for echo-CG
As a rule, when performing one- and two-dimensional echocardiography, as well as Doppler echocardiography, there is no need for any special preparation. If a transesophageal study is prescribed, there are a number of limitations.
So, the last meal should be no later than six hours before the procedure. Drinking is also not recommended. Immediately before the procedure, dentures should be removed.
On the eve of a transesophageal examination, persons with a labile nervous system are recommended to take a mild sedative. After the procedure, the patient will need some time to recover, so you should not overload yourself with work until the end of the day. It is also necessary to refrain from driving.
About echolocation
Everyone knows that bats and dolphins use echolocation to navigate in space. However, few people can answer the question: how does it all work? And it works something like this. First of all, the mouse emits ultrasound. Then she catches the echo of the same sound emitted to her, reflected from objects. The bat has the ability to recognize the ultra-short intervals that pass from the emission of a sound signal to the return of the echo. In this way, the mouse determines the distance between trees or other objects, and also sees how far this or that insect is from it. What is surprising is that the bat perfectly distinguishes the echo from a static (immovable) object from a moving object.
Echolocation was discovered in dolphins more than half a century ago. Dolphins, like bats, use ultrasound, mainly at frequencies of 80-100 gHz . The signals emitted by dolphins are incredibly powerful: for example, they can see a school of fish more than one kilometer away!
Anechoic chamber
There is a room where there is no echo at all. It's called an anechoic chamber. There are two types of anechoic chambers. Each type serves to dampen one or another type of echo. Simply put, in such a chamber, sound (or radio waves) simply do not reflect from the walls. The first acoustic type. It, as the name implies, serves to suppress ordinary sound echo. The second, accordingly, is radio frequency and is necessary to suppress the reflection of radio waves.
Additional diagnostic methods
We list additional ways to recognize various brain diseases:
- X-ray
Doctors usually send the patient for an x-ray to confirm or refute the diagnosis. If the disease affects the child, then craniography is performed, while the body receives minimal radiation exposure, because of this the negative impact on the body is minimized.
But in order to send a child for an x-ray, there must be important reasons for this. This will allow us to identify various pathologies, microcephaly, possible injuries during childbirth, concussions, and more.
- CT scan
Includes instrumental examination of various parts of the body, the brain; computed tomography is based on examination using x-rays. Patients are prescribed a CT scan when there is a suspicion of a tumor in the brain, with increased intracranial pressure, head injuries, etc. At the same time, the level of radiation is minimal, so this method is safe for the child’s body.
Meningoencephalitis
This disease can be contracted if you are exposed to a virus, bacteria or protozoan organism. When a patient is diagnosed with such a pathology, the protective membranes and substance in the center of the nervous system become inflamed.
A person experiences symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, severe headache, chills, and the body temperature rises and the person begins to become delirious.
Patients who are infected with this infection experience severe inflammation of the M-echo. If the inflamed area exceeds 7-8 millimeters, this is a direct indicator of a brain abscess. The acute form is characterized by the accumulation of a large amount of pus in the central nervous system.
Dropsy (hydrocephalus)
This disease begins due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull. Why does it accumulate:
- cerebrospinal fluid is produced too quickly,
- fluid circulation is impaired,
- absorption deteriorates.
What symptoms appear in newborns:
- the head grows too quickly,
- eyes go down
- the fontanel swells greatly,
- on the head, where the bones have not yet fused, there are pulsating, round-shaped swellings.
If you check the center of the nervous system during this illness, then the M-echo breaks into 2 parts. The distance level will be approximately 5-6 millimeters.
If you check the echogram, you will notice a bunch of other signals that have high amplitude; they are located at a distance between the initial, middle and final complexes.
Small interesting facts
- If the distance from the noise source to the nearest obstacle (wall or rock), then no echo is formed.
- The famous German river Rhine is full of surprises. For example, there is a place where the echo repeats 20 times
- In the city of Verdun, in France, there are two towers. If you shout while standing between them, you will hear the echo of your voice up to 11 times.
- The Ear of Dionysus is a real record holder in the field of echo. This is a grotto in Syracuse, shaped like a human ear. But that’s not what makes him interesting. Due to its shape, the grotto makes the echo incredibly strong. Throwing a stone or a simple clap will echo out of the darkness with real thunder
Sources:
- https://otomkak.ru/chto-takoe-eho/
- https://interneturok.ru/lesson/physics/9-klass/mehanicheskie-kolebaniya-i-volny/skorost-zvuka-otrazhenie-zvuka-eho-eryutkin-es
- https://vivareit.ru/eho-interesnye-dannye-i-fakty/