Numbness of the ribs is a clinical symptom and not an independent disease. It appears with the development of numerous pathologies. In some cases, pathology of internal organs (lungs, pleura, myocardium, coronary circulatory system, etc.) signals. Our article will help you understand why the ribs on the left or right side are numb. It talks about the main causes and potential diseases. Also you will learn about the most effective and safe treatment methods.
Rib numbness is a condition that indicates that the conduction of impulses through the sensory network of axons is impaired. It begins in the cells of the epidermis, subcutaneous fat layer and myocytes. There, information is collected about the condition of all tissues, the degree of their blood supply, temperature, interaction with the outside world, etc. All this information is transmitted through sensory axons along large nerves to the root nerves. Through them it enters the spinal cord and cerebral analyzing structures.
If in any of the designated areas there is an obstacle to the passage of a nerve impulse, then the brain does not receive information about the state of this or that part of the body. A person feels this condition as numbness. Those. he does not feel a certain part of the body.
This problem can be either ischemic (impaired blood supply and subsequent atrophy) or neurological (damage to sensory types of nerve fiber) in nature. Rib numbness of traumatic and infectious (herpes zoster) etiology is less common.
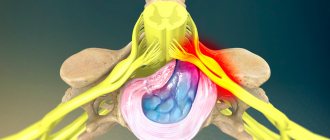
The costal arches are attached to the thoracic vertebral bodies using joints. For this purpose, the vertebral bodies have special processes. The costovertebral joints allow the chest to expand when inhaling and contract when exhaling.
Between the vertebral bodies, the radicular nerves extend from the structure of the spinal cord. Each of them carries sensory (sensitive) and motor (motor) types of axons. The first ones are responsible for sensitivity. The second - for physical activity. The radicular nerves branch and some of the branches are directed along the costal arches. They innervate the intercostal muscles (part of the respiratory muscles). They are also partially responsible for the innervation of the skin of the chest.
The radicular nerves are protected from compression by intervertebral cartilaginous discs. Therefore, when making any movements, a person does not have a traumatic effect on them. But in some cases, when degenerative dystrophic pathology of cartilage tissue is observed, a decrease in the height of the discs occurs. This provokes compression of the radicular nerves. Often the first sign of this condition is numbness in the area of one or another rib (depending on which radicular nerve is under pressure).
Also, such a sensation may be a consequence of mechanical pressure on more distant parts of the innervation network. This may be a consequence of intercostal neuralgia or tumor development. We will talk in more detail about the potential causes of numbness in the area of the costal arches below.
In the meantime, we want to warn you against engaging in self-diagnosis and treatment. If you experience rib numbness, immediately seek medical help from a neurologist. This specialist will help make an accurate diagnosis and tell you which treatment will help in your individual situation.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced doctors work here. They will provide you with the full range of necessary medical care.
Why does it hurt in the pubic area in women?
Traumatic injuries
The cause of sudden pain can be bruises of the pubic symphysis and fractures of the anterior pelvis.
With bruises, the pain syndrome develops after a blow or fall, is moderate, can be accompanied by local swelling, and sometimes bruising. The range of motion is preserved completely or almost completely, the support function is not impaired. All symptoms disappear within 1-2 weeks. With fractures, there are limitations in movement, impaired support of varying degrees, and the inability to raise the straight leg on the side of the injury from a lying position. In women with damage to the superior branch of the pubic bone and the anterior pelvic semi-ring, the pain increases with palpation, compression, and movements of the lower limb on the affected side. In case of ruptures of the symphysis pubis, the patient takes a forced position with the limbs slightly bent and brought together. The pain increases sharply when you try to spread your legs.
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation of the pubic bone occurs due to infection due to surgical interventions, deep wounds in the pubic area, purulent processes in the surrounding tissues. The pain quickly intensifies against the background of increasing swelling, redness of the skin, and deterioration of the general condition. The amount of discharge increases, it becomes purulent in nature. With osteomyelitis, a woman complains of tugging, tearing, throbbing pain in the pubic area. Fever and signs of severe intoxication are detected.
New growths of the pubic bone
The pelvic bones are a common location for benign and malignant tumors. With chondroblastomas, osteomas and osteochondromas, the pain is not intense, slowly increasing over a long time. Chondrosarcomas and metastatic neoplasia are characterized by rapid progression of pain. Initially, the woman complains of minor aching or nagging pain in the pubic area. After a few months, the pain becomes severe, constant, unbearable, and can only be eliminated with narcotic analgesics.
Pregnancy period
Minor pain in the pubic area can normally be observed in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. It is caused by an increase in the size of the fetus, preparing the body for the birth of a child. If the pain intensifies at night, during sexual intercourse, walking up stairs, spreading the legs and putting pressure on the pubic area, symphysitis should be suspected. Intense pain, inability to stand, walk and lift legs indicate the development of symphiolysis - damage to the ligaments and separation of the pubic bones.
Pelvic fractures in pregnant women develop as a result of trauma in half of the cases. In other women, they become a consequence of systemic diseases (osteoporosis, osteodystrophy) or local processes (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis). In the absence of provoking pathologies, spontaneous damage occurs extremely rarely. The classic clinical picture of a fracture is observed: intense pain in the projection of the pubis or other areas of the pelvis, forced position, limited function of the limbs.
Pain in the pubic area
Gynecological diseases
Pain in the pubis and suprapubic region is mainly noted when the uterus is affected, which, like the symphysis pubis, is located in the midline. Determined for the following pathologies:
- Acute endometritis.
The pain syndrome occurs acutely simultaneously with the appearance of leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor, chills, general hyperthermia, tachycardia, and pain when urinating. It is especially difficult in the presence of an intrauterine device. - Chronic endometritis.
The pain is not intense, aching. Often combined with dyspareunia. They are supplemented by uterine bleeding, menstrual disorders, bloody or serous-purulent discharge from the genital tract. - Postpartum endometritis.
In mild cases it develops within 5-10 days. Low-grade fever, pain above the womb, slight tachycardia, moderate lochia mixed with blood are noted. In severe cases, it manifests itself within 2-3 days. Chills, fever, severe pain above the pubis, profuse bloody-purulent cloudy lochia with a fishy odor are detected. - Endometriosis.
Painful sensations are found in 15-25% of women and can be localized only above the pubis or be diffuse. They are permanent or worsen in the premenstrual period. Other possible symptoms are dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, pain during sexual intercourse, urination and defecation.
Patients with adnexitis, salpingitis and ovarian cysts more often complain of pain in the right or left iliac zone. Possible irradiation into the womb and suprapubic region. In women with cysts, pain increases with internal bleeding, suppuration, rupture of the membrane or torsion of the leg of the cystic formation.
Nagging pain in the suprapubic region with delayed menstruation and engorgement of the mammary glands may indicate an ectopic pregnancy with the attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterine part of the fallopian tube, the rudimentary horn of the uterus or the abdominal cavity. When the ovum ruptures, the pain increases sharply, radiates to the lower back, legs and anus, and is accompanied by bleeding or spotting, weakness, tachycardia, and loss of consciousness.
With cancer and sarcoma of the uterus in the early stages, bleeding and menstrual irregularities are observed. Subsequently, paroxysmal cramping pain occurs over the womb, followed by the discharge of pathological discharge from the vagina. In the later stages, the pain becomes intense and constant. There are dysfunctions of neighboring organs and cancer cachexia.
Pathologies of the urinary system
Pain above the pubis is typical for bladder diseases. Observed in diseases such as:
- Acute cystitis.
Cutting and aching pains appear suddenly. An increased frequency of urges, pain, pain and burning during urination, sometimes blood in the urine, lower back pain, and an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels are detected. - Chronic cystitis.
Diagnosed with 3 or more exacerbations in a year or 2 or more exacerbations in six months. It is accompanied by the same symptoms as acute cystitis, but the manifestations persist longer and often have a wave-like character. - Bladder cancer.
Dysuria, pain in the pubic area, groin and sacrum is preceded by hematuria. The pain syndrome is initially insignificant or moderate, observed only when the detrusor is filled, and subsequently becomes intense, painful, and constant. - Bladder tuberculosis.
Develops against the background of kidney tuberculosis. It manifests itself as constant aching pain in the suprapubic area, frequent painful urination with a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, imperative urges, periodic blood in the urine, malaise, increased fatigue, low-grade fever, and loss of body weight. - Bladder stones.
Pain in the lower abdomen and above the pubis is minor at rest. They increase sharply when changing body position, during urination, which is associated with the movement of stones and traumatization of the mucous membrane. Possible irradiation to the perineum, labia, upper thighs.
Problem No. 6. Short-term change in habitual odors in the absence of ARVI
Root cause of change
Smells change if there are problems in the ENT organs or pathological changes in the brain - tumors, circulatory disorders, traumatic brain injuries. The cause may also be irritation of the nasal mucosa by vapors of caustic substances (bleach, ammonia, etc.). In addition, a change in smells can be a harbinger of an epileptic attack and the onset of a migraine attack.
The degree of manifestation is within normal limits
If odors disappear for a short time after inhaling vapors of caustic substances or if you have nasal diseases, then there is no need to panic. If odors disappear for no apparent reason or the sense of smell is persistent, you should consult a specialist.
Solving the problem when it occurs
The only thing that can be done before contacting a specialist is to treat the nasal mucosa with a solution of sea water (Aquamaris, Aqualor) or saline solution.
Where to go?
First, you should contact an ENT doctor, who, if necessary, will refer you to another specialist. If smells change or disappear before an attack of headaches, or if this is followed by disorientation in the surrounding space, numbness of the torso or convulsions, then immediately go to a neurologist.
Diagnostics
Women with suspected injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system are examined by an orthopedic traumatologist. Patients with signs of gynecological pathologies require consultation with a gynecologist. If there are symptoms of damage to the urinary system, an examination by a urologist is necessary. At the initial stage, the specialist establishes the circumstances of the appearance, the nature and duration of the pain syndrome, its connection with various factors, and the presence of other manifestations. The diagnostic program may include the following procedures:
- Visual inspection.
Allows you to localize the source of pain (bones, internal organs). During the physical examination, the doctor identifies redness, swelling, wounds, purulent foci, bone deformities, space-occupying formations, and detects symptoms that are pathognomonic for certain pathological conditions. - Gynecological examination.
Makes it possible to determine the presence and nature of discharge, the size and tone of the uterus, and the condition of the appendages. It is used in assessing the duration and course of pregnancy, during the primary diagnosis of endometritis, endometriosis, adnexitis, ovarian cysts, and other gynecological pathologies. - X-ray of the pelvis.
In case of fractures, survey photographs are recommended to study all the pelvic bones and fully visualize possible severe and complex injuries. For osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, and tumors, radiographs of the symphysis and pubic bones are taken. For women with symphysitis, the technique is prescribed in the postpartum period. - Ultrasonography.
In case of symphysitis, an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis is performed to assess the severity of the pathology and select the method of delivery. For gynecological diseases, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed. The best option in most cases is the method with the simultaneous use of vaginal and abdominal sensors. For detrusor lesions, an ultrasound of the bladder is performed. Some women are advised to have a kidney ultrasound. - Other imaging methods.
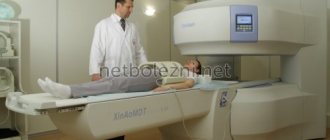
For stones, urography is informative. Patients with neoplasms can undergo cystography, pelvic venography, and lymphadenography. Women with urolithiasis are prescribed a CT scan of the kidneys, ureters and bladder. Victims with traumatic injuries with insufficient radiographic information require a CT scan of the pelvis. - Endoscopic studies.
They are an important part of tumor diagnosis. For malignant neoplasia of the uterus, hysteroscopy is performed, and for neoplasms of the bladder, cystoscopy is performed. They provide detailed visualization of space-occupying formations and provide for the collection of biopsy samples for subsequent histological analysis. - Lab tests.
Leukocytosis and increased ESR in the CBC indicate the presence of inflammation. Urine, discharge from wounds and genitals are examined by culture to identify the causative agent of infection. With symphysitis, a decrease in the amount of calcium and magnesium in the LHC is determined. To confirm an ectopic pregnancy, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin is examined. As part of the morphological analysis of biopsy specimens, the type and degree of malignancy of tumors is clarified.
Ultrasound of the bladder
Problem #8: Shaky hands for no apparent reason
Root cause of change
The cause of trembling in the hands can be diseases of the nervous system, such as essential tremor, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, damage to the cerebellum (the part of the brain responsible for balance. - Author's note.
), acquired dementia (dementia), alcoholism, consequences of tick-borne encephalitis, peripheral nerve injury and some others. This condition can also be observed with pathology of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), poisoning with toxic substances, excessive coffee consumption, lack of vitamin B12, stress, excessive physical strain.
The degree of manifestation is within normal limits
It can be considered normal if tremor occurs during anxiety (if this does not interfere with a person’s professional and personal life) or after excessive physical exertion.
Addiction to the problem
We must not forget that tremor can occur in people who abuse alcohol. The tendency to essential tremor is inherited.
Solving the problem when it occurs
Find out the cause, if possible eliminate the provoking factor, take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Where to go?
If you are concerned about this problem, consult a neurologist. Sometimes a therapist can deal with the problem if the cause is not a pathology of the nervous system.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
A woman with a suspected pelvic fracture should be placed on a backboard with her legs bent and a pillow placed under them. The pelvic bones should be secured by wrapping a scarf or sheet. To prevent traumatic shock, it is recommended to warm up with a blanket, drink plenty of warm drinks, and take an anesthetic. Fractures and suspicion of an interrupted tubal pregnancy are indications for immediately calling an ambulance.
Conservative therapy
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the cause of the development of pain in the pubis:
- Injuries.
Upon admission, intrapelvic anesthesia is administered; in the case of isolated pubic bone fractures, local anesthetic administration is possible. The fixation option is chosen taking into account the type of injury; a shield or a hammock is used, or in severe cases, skeletal traction. Painkillers are used, and antibiotics are prescribed for open injuries. During the rehabilitation period, patients are referred to exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy. - Osteomyelitis.
The basis of therapy is antibiotics, which are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen and administered intramuscularly or intravenously. Analgesics are used. In case of severe intoxication, infusion therapy is carried out. Dressings are carried out, the wound is washed and drained. - Symphysitis.
To eliminate hypocalcemia, calcium supplements are prescribed, and vitamin D and magnesium supplements are used to improve the absorption of the microelement. To eliminate aseptic inflammation, NSAIDs are recommended. Non-drug methods include magnetic therapy, wearing a bandage, and special exercise therapy complexes. An adequate choice of obstetric care tactics is required, taking into account the severity of the pathology. - Endometritis.
The first priority is to fight the infection with antibacterial agents. In case of severe intoxication, protein and saline solutions are administered intravenously. Immunomodulators, antihistamines, and multivitamin complexes are prescribed. To eliminate bleeding and reduce pain in the acute period, cold and hormonal drugs are used. After the condition improves, medicinal electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy, and ultrasound therapy are useful. - Endometriosis.
Conservative treatment is carried out in case of asymptomatic or mild symptoms during premenopause, if it is necessary to restore or preserve reproductive function. Hormone therapy is carried out with combined estrogen-progestogen agents, gestagens, antigonadotropic drugs, gonadotropic releasing hormone agonists. - Cystitis.
The treatment regimen includes antibiotics from the groups of fluoroquinolones, nitrofurans, macrolides, cephalosporins and non-fluorinated quinolones. Uroseptics, NSAIDs, and combined herbal remedies are used. Intravesical instillations are performed. Inductothermy, UHF, and iontophoresis are performed. - Detrusor tuberculosis.
Treatment is carried out with anti-tuberculosis drugs and fluoroquinolones. Additionally, NSAIDs and angioprotectors are prescribed to reduce the severity of inflammation and prevent cicatricial changes in the urinary tract.
For adnexitis and salpingitis, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapy are used. For oncological lesions alone or as part of combination therapy, including radiation therapy and chemotherapy in the pre- and postoperative period.
Problem No. 10. Dizziness when rising from a chair
Root cause of change
This occurs with orthostatic hypotension - redistribution of blood from the head to the lower extremities.
The degree of manifestation is within normal limits
This can be normal or pathological. The norm is if a person was sitting and suddenly jumped up; tall and thin people are especially prone to this condition. In diseases of the endocrine system, as well as in the elderly, this is an additional factor in falls and requires treatment. This condition can be caused by medications.
Addiction to the problem
This problem more often occurs in older people, as well as tall and thin people (due to the fact that the blood does not quickly have time to be redistributed among the vessels).
Solving the problem when it occurs
The doctor recommends controlling your actions and trying not to get up suddenly. If you still feel dizzy, then take a comfortable position - sit back or lie down and raise your legs at an angle of 45 degrees.
Where to go?
If the problem occurs frequently, then your specialist is a cardiologist; if necessary, and if cardiac pathology is excluded, he will redirect you to a neurologist.