A pediatric neurologist is a very important specialist who monitors the central and peripheral nervous system of a child, from birth to 18 years of age. What does a pediatric neurologist treat and what does a pediatric neurologist do? The primary task of this specialist is periodic observations of the stages of formation and development of the nervous system of a small patient, during which many progressive pathologies can be prevented. If it is impossible to prevent them and prevention does not help, an experienced pediatric neurologist determines the diagnosis and prescribes appropriate comprehensive treatment, which in most cases successfully cures the disease.
Today, there are many different diseases of the nervous system that differ from each other, which are classified according to a certain order. Let's list the main lesions of the nervous system and answer the question - what does a pediatric neurologist treat.
- Pathology associated with infection caused by exposure to harmful viruses and bacteria. A newborn child is most susceptible to such infectious diseases due to insufficiently developed immunity. That is why doctors do not recommend that parents visit crowded establishments with a small child.
- Epilepsy. It can be formed either as a result of injury or congenitally. Consultation and treatment with a neurologist are simply mandatory here.
- Diseases associated with severe bruises of the head area, traumatic injuries.
- Toxic pathology. Some drugs and medicines, namely their incorrect prescription and use, can provoke such damage to the nervous system.
- Genetic pathology. Passed on from parents or relatives due to appropriate heredity.
- Hypoxia, which in turn was observed in utero in the fetus.
A pediatric neurologist is very important for the formation of the normal functioning of the nervous system of a small child; he is able to carry out effective prevention of common pathologies.
What is the difference between a pediatric neurologist and a neurologist?
Very often, many parents ask a common question - is there a difference between a pediatric neurologist and a pediatric neurologist? In fact, these two definitions are absolutely identical, and their definitions are equivalent to each other. Why are both terms still used?
The fact is that the term pediatric neurologist is a rather outdated name for a specialist doctor, used in medicine until 1980, which has now taken on a different name - pediatric neurologist.
As for medical workers abroad, there is still a difference in terms:
A neurologist is a specialist who deals with diseases of the nervous system.
A neurologist is a specialist who carefully studies pathomorphology.
What does a baby examination involve?
As already mentioned, examinations of infants are carried out throughout the first year of life. Each visit to a pediatric neurologist in Ufa has a specific purpose:
- Check-up at 1 month. Attention is drawn to the baby’s posture, the presence and severity of unconditioned reflexes. Here, muscle tone is assessed - with normal development, it should be the same on both sides. The child’s movements are chaotic, but at 1 month of life he is already able to focus his gaze on an object and follow its movement. At the same time, a smile appears. In the first months, much attention is paid to the growth of head circumference, which at birth is approximately 34-35.5 cm.
- Check-up at 3 months. Considered one of the most important. By this time, the baby is able to identify his own hands - looking at them or putting them in his mouth is considered a typical action. At 3 months, the process of extinction of most reflexes begins, a revival complex appears, the ability to hold one’s head develops, etc.
- Check-up at 6 months. The baby’s skills are assessed: the ability to roll over onto his stomach and take his original position, raise his head, hold a toy, carry it, etc. During this period, the child must recognize his mother, while he may react differently to other people. Many babies are already sitting by this age. Emotional manifestations at this stage of development become more diverse.
- Examination at 9 months. Attention is paid to the physical development of the child. The baby sits, crawls and stands on his own legs. His brain and mental abilities are also intensively developing: he understands the meaning of spoken words, chooses familiar objects among many others. Please note that at this age the child must understand and respond adequately to prohibitions.
- Check-up at 12 months. Age is characterized by an intensive growth in the number of skills. Some children at this age begin to walk - if this is not the case, there is no need to worry until they are 1.5 years old, but a consultation with a neurologist is necessary. The child knows how to drink from a cup, holds a spoon independently and identifies not only parents, but also other family members, as well as people who often enter the house. Over the course of a year of life, a child's head increases by about 12 cm.
As you can see, each age has its own characteristics. Timely consultation with a specialist allows problems to be identified at an early stage, which makes the prescribed treatment as effective and safe as possible for the little patient. Here you can also get recommendations on the daily development of your baby: intensive parent-child activities in the first year of his life are the key to your baby’s physical and moral health!
Reception of a neurologist in Ufa is carried out at the address: Ufa, st. Revolutionary, 70. You can make an appointment by calling or leaving a request on the website.
What does a pediatric neurologist check and what are the specifics of his work?
Regardless of the type of appointment with a pediatric neurologist, primary or preventive, the doctor is obliged to carry out a strict examination procedure and give certain advice. What does a pediatric neurologist do and see in the office of a medical institution?
- Checks the stable functioning of the child’s visual reflexes;
- Checks muscle tone and strength level;
- identifies the presence of coordination of the baby’s movements;
- development of speech and memory.
- Determining the level of sensitivity.
After the neurologist examines the child and listens to complaints from the parents, the general picture of the child’s illness will become more or less clear to him. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional tests in the form of:
- Ultrasound of the brain and blood vessels. Dopplerography.
- MRI of the brain.
| Code | Name of service | Price |
| 6.1 | Appointment with neurologist G.M. Chernyaeva (examination, consultation, treatment prescription) | 2500 |
| 6.2 | Consultation with a neurologist Miroshnik E.E. (1-1.5 hours) | 5000 |
| 6.3 | Carrying out additional neurological examination (tests for dizziness, assessment of cognitive functions, study of the autonomic nervous system) | 600 |
| 6.4 | Treatment of paroxysmal positional benign vertigo (Epley maneuver) | 800 |
| 6.7 | Therapeutic drug blockade (excluding the cost of drugs) | 1900 |
| 6.8 | Therapeutic drug blockade (including the cost of drugs) | 2700 |
| 6.10 | Calling a neurologist to your home (Sviblovo) | 5000 |
| 6.11 | Calling a neurologist to your home (SVAO) | 6000 |
View all
How is the reception going?
First, the doctor asks the parents if there are any complaints that are bothering the child or parents. How long has this been observed, whether any treatment has been carried out, etc. At the first appointment (at three months), the doctor clarifies how the birth took place (cesarean or natural birth), how the pregnancy proceeded, and what the mother was ill with during pregnancy.
After consultation, a pediatric neurologist examines the child. The specialist checks the degree of development of visual function and assesses muscle tone. Using simple tests, the doctor checks coordination and analyzes the degree of manifestation of deep and superficial reflexes. If the baby is already old enough, the neurologist checks how his speech and memory are developed, and how he perceives information.
When should you show your child to a neurologist?
At the birth of a child, a visit to the office of a pediatric neurologist for preventive purposes is simply mandatory. Records are kept in the children's medical history card. Reception is held:
- When the baby is one month old.
- Next at 3 months.
- After six months.
- After one year of age.
- at 4-5 years old (preschool period)
- at 7 years old (before school);
- at 13-14. (adolescence period of growing up)
In addition, if there is even the slightest complaint or suspicion of a disorder in the nervous system of your little child, it is urgently recommended to consult a doctor, namely:
- sleep disturbance, sudden awakenings during night and daytime sleep with characteristic crying and hysterics. Restless short sleep, capriciousness of actions, increased excitability.
- Trembling of the chin and limbs when crying.
- Regurgitation when feeding, sudden vomiting when capricious.
- Lethargy, fatigue, lack of interest in outdoor games and food.
- Periodic convulsions.
- Throwing the head back during sleep.
- Headache.
- State of fainting.
- Muscle twitching uncontrollable by the baby.
- Deviations in development - the child does not walk, does not sit independently, does not crawl, does not hold his head, does not look to the sides.
- Speech defects, delayed development of speech or its absence.
If these symptoms are detected, you must take your child to the children's neurological department!
From this video you will learn what the consequences of not visiting a neurologist may be:
In what cases is it necessary to urgently visit a pediatric neurologist?
The first signs of pathology in a child can be observed from birth or in the first months of life. An immediate visit to a doctor is required in the following cases:
- When crying, the baby literally turns blue.
- There is trembling of the limbs or chin even at rest.
- The child sleeps very lightly, often wakes up and flinches at literally every rustle.
- The child spits up like a fountain after eating.
- Convulsions in a child.
If you notice at least one of the above symptoms in your baby, this is a reason to visit a pediatric neurologist. In addition, compulsory attendance in the first months of life is indicated for children who have received any trauma during childbirth. The risk group also includes babies whose mothers suffered severe toxicosis or an infectious disease during pregnancy, or took potent medications or alcohol. All this increases the risk of problems with the baby’s central nervous system.
An older child should be taken to a neurologist if:
- The child often complains of headache, dizziness;
- He is bothered by back pain;
- He had epileptic seizures;
- There is a lack of coordination of movements;
- The child has difficulty concentrating and remembering anything;
- The baby stutters;
- The child behaves strangely and shows aggression;
- He has bedwetting.
- He is very anxious and often panics;
- There is a significant lag in development compared to age norms.
What is mmd in neurology in children
MMD is a minimal brain dysfunction caused by acute failure of the central nervous system, disturbances in the child’s mental state, as well as a number of other dangerous symptoms.
How does mmd manifest itself in neurology in children?
- Overly active behavior, namely constant movements of both arms and legs, lack of perseverance.
- Quick distraction to the presence of any irritants.
- Inability to play alone.
- He talks incessantly, interrupts adults, and does not hear others when they ask him questions.
- Moves from one task to another without completing the first.
- Losing things in kindergarten, school, absent-mindedness.
Effective assistance from a pediatric neurologist
At the initial appointment with a neurologist at the children's clinic "RebenOK", the doctor will get acquainted with the existing complaints and the history of the baby's development, examine him, check his reflexes and the functioning of the autonomic and nervous systems. Based on the information received, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis, and if necessary, prescribe additional examination.
At the RebenOK clinic, a neurologist with extensive experience in treating various pathologies in young patients, including epilepsy, works with children.
Also in our pediatric neurology center, children can undergo physiotherapeutic procedures such as laser therapy and Bioptron light therapy, and sign up for general massage and therapeutic exercises.
What is neurology in children?
Neurology in children is a complex, multifaceted medical discipline that deals with diseases of the nervous system of a small patient. If a qualified doctor still detects neurology in a child, this can be explained by the following most common reasons:
- Receiving a birth mechanical injury;
- fetal hypoxia, as well as insufficient oxygen supply due to possible repeated entanglement in utero;
- complex process of childbirth and labor;
- acute toxicosis of pregnant women throughout the entire period;
- genetic inheritance.
What is neurology in eight-year-old children?
The child’s psyche is like plasticine; it is very susceptible to stress and any circumstances; parents, in turn, are advised to ensure that it is not damaged. In what cases does neurology occur in school-age children, namely 8 years old?
- Excessively heavy loads on the child’s body.
- A feeling of constant fear caused by the behavior of parents, as well as their pressure.
- Adaptation period at school.
Such neurosis is accompanied by anxiety, sometimes stuttering, tics, and fainting. At the slightest manifestation of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
If any pathological process is suspected, a pediatric neurologist may refer for instrumental diagnostics, for example:
- Ultrasound examination with additional Doppler sonography;
- Electroencephalography;
- Computed tomography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging
Additionally, general urine and blood tests may be prescribed to exclude possible infectious processes in the child’s body.
To eliminate some abnormalities, the doctor may prescribe medication. In addition, a pediatric neurologist may recommend techniques such as:
- Manual therapy, the purpose of which is to normalize the functioning of certain organs.
- Craniosacral technique. This technique is aimed at aligning the bones of the skull, which improves blood circulation and brain function. In most cases, this technique is relevant for young children.
- Muscle relaxation. Helps get rid of muscle hypertonicity, which has a positive effect on the condition of bones, vertebrae and internal organs.
Additionally, other types of treatment may be prescribed, such as exercise therapy, emotional techniques, etc. The duration of treatment and specific prescriptions depend on the diagnosis and its severity. Some abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous central system can only be eliminated in childhood. Therefore, pay close attention to your doctor’s recommendations. Be healthy!
When is it necessary to make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist?
A visit to a doctor of this specialty is mandatory as part of the medical examination program for children aged 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months. After this, the child must undergo a preventive examination with a neurologist before enrolling in kindergarten and school (at 2–3 years and 6–7 years). The established procedure should not be neglected, since psychomotor developmental deviations are more successfully corrected at an early age.
In addition, children require a neurological examination in the following cases:
under 1 year of age
- restless behavior;
- shallow sleep, frequent awakenings at night;
- trembling of the chin and limbs when crying;
- frequent regurgitation of food during feeding;
- poor appetite, slow weight gain;
- motor development disorders (a 4-month-old child cannot hold his head up and does not grab a toy, a 7-month-old child does not sit or crawl, etc.).
from 1 year to 6–7 years
- attacks of aggression or fear, frequent hysterics;
- sleep disturbances, throwing back the head when lying down;
- bed-wetting;
- complaints of headaches;
- obsessive involuntary movements and tics (for example, coughing without a cold);
- fatigue, rapid loss of interest in outdoor games;
- speech development disorders.
from 7 to 18 years old
- sudden mood swings;
- complaints of local pain (head, back, arms, legs);
- fainting, tremors, general weakness;
- deterioration of vision and hearing not associated with pathologies of the eyes and ears;
- changes in skin sensitivity;
- forgetfulness, problems concentrating.
A timely visit to specialists at the pediatric neurology department will allow you to determine the causes of the pathology and begin treatment on time. Disturbances in the behavior and movements of a child can be caused by:
- birth injuries;
- bruises to the head and back as a result of outdoor games or falls;
- febrile convulsions due to high fever;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system;
- hereditary predisposition and other reasons.
How does an appointment with a pediatric neurologist go?
Medical specialists strive to find a common language with every little patient. When contacting our pediatric neurology department, you only need to prepare data from previous examinations of the child and, if possible, an extract from the outpatient card. Additionally, you do not need to receive a referral from a pediatrician or general practitioner.
1
Make an appointment
Let us know when it would be convenient for you to see your doctor so we can prepare for your visit. An appointment with a pediatric neurologist can be made by phone or through the “Personal Account” on the website. You can also fill out an online application:
Make an appointment
2
Diagnostics
The doctor talks with the parents, examines the child and makes a diagnosis. A pediatric neurologist at our clinic in Moscow checks the patient’s reflexes, muscle tone, coordination of movements and other functions of the nervous system. If necessary, additional diagnostics are prescribed and a course of treatment is developed.
3
Treatment and observation
During the consultation, the pediatric neurologist indicates which treatment methods will be most effective and how many courses are likely to be needed. You can undergo all the necessary physiotherapeutic, osteopathic, massage and other procedures in our medical center.
What examinations can a pediatric neurologist prescribe?
Laboratory research. The doctor will need general and detailed blood and urine tests, which will help identify inflammatory processes and infectious pathologies in the patient’s body. In addition, a neurologist can prescribe allergological, immunological, hormonal, bacteriological and other studies. The Miracle Doctor clinic has its own laboratory, which performs several thousand types of tests to determine the nature of damage to the nervous system.
Ultrasound Doppler. Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck is one of the safest and most informative methods for diagnosing neurological diseases. Ultrasound ultrasound is prescribed for children with frequent headaches, fatigue, memory and attention problems, and delayed speech development. The examination allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels feeding brain tissue, the lumen of blood vessels and other important parameters. Doppler ultrasound can be prescribed to children of any age.
Duplex scan of the brain. The method combines ultrasound and Dopplerography, thanks to which the doctor is able to obtain images of blood vessels, information about their structure and characteristics of blood flow within one diagnostic procedure. Scanning is indicated for children with minor brain dysfunction, intracranial hypertension and other diseases. For young patients, diagnosis is usually carried out during sleep.
EchoEG. Neurologists at the children's department of the Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow prescribe echoencephalography to young patients to check intracranial pressure, diagnose brain tumors, hemorrhages, abscesses, injuries and other pathologies. The method involves the use of safe and painless ultrasound diagnostics in combination with electroencephalography. Children under one and a half years old usually undergo neurosonography (ultrasound through open fontanelles).
EEG. Electroencephalography is a safe method for recording brain biocurrents. The examination helps determine the causes of fainting, seizures, sleep disorders and other disorders. EEG is prescribed to diagnose the presence of various forms of epilepsy, as well as brain dysfunction resulting from injury or surgery. The procedure is safe and can be performed even on newborn children.
ENMG. Electroneuromyography is intended to assess the bioelectrical activity of muscle fibers and myoneural endings. In the children's neurology department of the Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow, ENMG is performed to determine the possible causes of movement disorders, such as cerebral palsy, perinatal damage to the central nervous system, nervous tics, and polyneuropathy.
MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for children with suspected tumor processes, cerebrovascular accident, or the formation of an intervertebral hernia. MRI is performed for frequent headaches and dizziness, fainting, decreased vision or hearing, sudden changes in behavior, and developmental delays. The method is safe and highly informative.
CT. Computed tomography is used to obtain high-precision images of the skull and spine, as well as areas of the brain and spinal cord. The examination allows you to suspect tumors and metastases, abscesses, infectious pathologies of the central nervous system, and clarify the nature of traumatic injuries. In some cases, CT is performed with contrast - the introduction of a safe hypoallergenic substance that increases the accuracy of diagnosis.
Radiography. The method is used for a comprehensive examination of different parts of the spine and diagnosis of vertebral displacement, osteochondrosis and other pathologies. Pediatric neurologists at the Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow work with modern digital equipment, which allows them to make an accurate diagnosis for various conditions. X-rays are performed quickly and painlessly.
What diseases of the nervous system do the doctors at the Miracle Doctor clinic treat?
Cerebral palsy (lat. paralysis cerebralis)
Cerebral palsy is a group of neurological diseases that are manifested by various movement disorders (impaired coordination of movements, unsteadiness of gait, retardation in psychomotor development, etc.). Pathology usually occurs due to damage to brain structures due to trauma, hypoxia, infections and other reasons. Pediatric neurologists in Moscow offer comprehensive treatment for cerebral palsy.
Epilepsy (lat. epilepsy)
Chronic brain disease causes recurring seizures, headaches, loss of consciousness and other symptoms. In preschool children and adolescents, epilepsy is diagnosed more often than in adults. However, with an integrated approach, this complex disease can be controlled and treated. If the child is shown to a good pediatric neurologist in a timely manner, the situation can be brought under control.
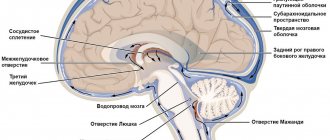
Hydrocephalus (lat. hydrocephalus)
The disease is manifested by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity, an increase in the size of the head, bulging fontanelles, developmental delays and other symptoms. The effectiveness of treatment for hydrocephalus depends primarily on early diagnosis. This is one of the reasons why a child needs to make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist every 3 months during the first year of life.
Vegetovascular dystonia (lat. Vegetovascular dystonia)
Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system is a complex disease affecting various organs and systems. VSD is manifested by arrhythmia, unstable blood pressure, increased fatigue, decreased memory and attention, sleep disorders, mood swings and other symptoms. A child with vegetative-vascular dystonia needs to be regularly examined by a neurologist.
Neuroses (novolat. neurosis)
Neurological disorders in children are often mistaken for whims and manifestations of adolescence. Meanwhile, neurosis is a reversible psychogenic disorder. The pathology can manifest itself as attacks of fear, stuttering, frequent hysterics, a state of stupor, obsessive movements and other symptoms. Neuroses require careful examination and correction.
Neuropathies (lat. Neuropathies)
An inflammatory disease affecting peripheral nerve endings may appear as a result of birth trauma, hypothermia, previous infectious disease and other reasons. Children are usually diagnosed with damage to the facial or auditory nerve. For this reason, any changes in a child’s facial expressions or hearing is a reason to contact not only a pediatrician or therapist, but also a pediatric neurologist.
Enuresis (ancient Greek: enouresis)
Involuntary urination, which can occur in a child during the day or during sleep, is a serious disease caused primarily by neurological disorders. Reflex control over emptying the bladder is formed in a child by the age of 3–4 years. If this moment is missed, long-term complex treatment may be required, including work with a psychologist, medication and physical therapy.
Minimal brain dysfunction (lat. Default dysfunctione cerebri)
MMD is a relatively new term in neurology, meaning minor changes in the central nervous system. In children under 5 years of age, the pathology can manifest itself as neurological abnormalities and mental retardation; in adolescents, hyperactivity, speech disorders, and social maladjustment. MMD is most often caused by birth injuries and requires observation by a pediatric neurologist.
Neuromuscular diseases (lat. neuromuscular morbus)
Paralysis, spinal muscular amyotrophy, dystrophy and other pathologies are most often hereditary. The diseases are manifested by impaired muscle function, replacement of muscle tissue with fat, low physical activity or its absence. Pediatric neurologists working in Moscow successfully practice modern methods of treating the listed pathologies.