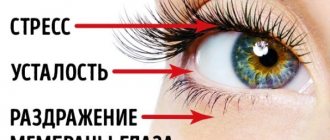
Based on the location and nature of pain in the eyes, an ophthalmologist can often suggest the likely cause of the symptom. What diseases may indicate pain that occurs when moving the eyes, we will talk in this article.
A healthy person does not experience painful sensations when he moves his eyeballs - looks down or up, watches moving objects. If your eyes hurt when you move, then there is a problem. This may be severe fatigue of the visual organs, an ophthalmological or general disease. A doctor can determine the exact cause.
Ophthalmopathologies in which it is painful to move the eyes
The cause of pain that occurs when moving the eyeballs is often directly related to diseases of the visual system.
- Blepharitis.
Usually, pain when moving appears in the late stages of inflammation, when the pathological process has spread from the eyelids to the entire eyeball. In this case, the patient can hardly move his eyes, which are very festered and look reddened.
- Neuritis of the oculomotor nerve.
The disease does not occur very often, but one of its characteristic signs is the difficult movement of the eyeballs and the resulting pain.
- Ocular myositis.
With this disease, the external eye muscles become inflamed, which naturally leads to pain when trying to change the direction of gaze. The inflammatory process in the extraocular muscles can be caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases, injuries, intoxications and a number of other reasons.
- Glaucoma.
Sometimes a patient who goes to the doctor with the complaint “it hurts to move the eyes” is diagnosed with “glaucoma.” With this disease, pain in the eye area can “radiate” to the head, accompanied by swelling of the eyelids, vomiting, decreased visual acuity, and changes in pupil size. If a person experiences such symptoms, one should not delay contacting a doctor. Glaucoma is dangerous, first of all, due to irreversible vision loss.
Pathological causes of headaches when moving the eyes
They can be caused by both eye diseases and pathologies of other organs and systems of the body. Among the ophthalmological reasons:
- Glaucoma. This is a disease associated with increased intraocular pressure. One of the symptoms of glaucoma is pain in the head and eyes, when the intraocular fluid begins to put strong pressure on the organs of vision. The disease is accompanied by vomiting, photophobia, and decreased vision.
- Hordeolum, known as barley. This is inflammation of the eyelid gland. The headache is localized on the side of the injured eye.
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. There are various forms of this pathology. One of them is viral. When it occurs, the head hurts when turning the eyes, the sclera turns red, and there is a feeling of sand in the eyes.
- Refractive errors (astigmatism, myopia and farsightedness) and incorrectly selected correction tools.
- Ophthalmic migraine. The disease affects one eye and the corresponding part of the head, and vision may be lost for several seconds or even hours. Pain in the head intensifies when turning the eyes to the sides and moving them upward.
- Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by a painful condition of the eyes and head.
- Diseases of the optic nerve, the common symptoms of which are throbbing eye pain and headache.
- Myositis is inflammation of the extraocular muscles.
- Mechanical injuries of the visual apparatus.
Other causes of the symptom
In addition to ophthalmological diseases, pain during eye movement can also be caused by general pathologies.
- Respiratory viral infections.
Any ARVI, cold, or flu contribute to the accumulation of toxins in the body. One of the forms of intoxication is pain when rotating the eyeballs.
- Sinusitis.
With sinusitis, the sinuses of the nose become inflamed, which are connected to the eye sockets by common walls. The inflammatory process that begins in the ENT organs can lead to compression of muscle tissue, which interferes with the free movement of the eyeballs and causes pain.
- Migraine pain.
Migraine headaches are often accompanied by pain in the eyeball. Since migraine is characterized by unilateral localization, eye pain is also concentrated on one side.
Treatment
Before prescribing treatment, the ophthalmologist will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. As a rule, the main stages are measuring intraocular pressure, examining the fundus, and examining with a slit lamp. This set of examinations allows you to identify the main and most common eye diseases.
In the case of glaucoma, special medications will need to be dripped into the eyes to reduce intraocular pressure. In most cases, you will need to prepare for surgery - glaucoma does not respond to conservative treatment.
If the pain is caused by an inflammatory disease, then you will need to identify the pathogen and start taking appropriate medications: antibacterial or antiviral.
Treatment for pain caused by fatigue involves following basic visual hygiene recommendations. The patient will have to be more attentive to his health. This pathology is most often found among office workers, and it has even been called visual fatigue syndrome. An ophthalmologist may prescribe eye exercises and recommend coming for preventive examinations.
Fatigue and overexertion
If you have a headache and a feeling of tension in the eyes, which increases with pressure, this may be the result of fatigue and prolonged overexertion. Most often, such side effects occur in a person who spends a long time in front of a computer monitor or tries to focus his gaze on a specific object.
For pain that occurs due to fatigue and overexertion, special treatment is not required. It is enough to take a break from the computer and relax a little, turn off the lights and sit with your eyes closed. In some cases, an unpleasant symptom may occur with physical fatigue.
As a result, muscles throughout the body become overstrained, including the muscle tissue that holds the eyeballs. When you try to move your eyes, you feel pain and discomfort.
In addition, the muscle tissue of the eyeballs is “responsible” for focusing, so pain and pain can be combined with blurred vision.
Such problems with the organs of vision can manifest themselves as a result of chronic fatigue syndrome and regular stress. An effective solution in such cases will be special gymnastics - blinking frequently for several seconds, then looking into the distance and to the side.
Injuries to the organs of vision
The appearance of sharp pain, burning and stinging in one eye is a common sign of injury to the eyeball. Damage can be caused by various wounds, thermal and chemical burns, and impacts to the organs of vision. Without timely medical care, injuries lead to complicated inflammatory processes and partial or complete loss of vision. Most often, self-determination of injury is not particularly difficult.
Damage to the eyeball in most cases is accompanied by the formation of a dark circle or hematoma under the eye, redness of the eye and other signs of conjunctivitis, and rapid deterioration of vision.
If you have injuries or damage to your eyes, you should not hesitate to visit a traumatologist or ophthalmologist.
Without appropriate treatment, you can completely lose your vision. The formation of a blood clot under the mucous membrane is considered no less dangerous. This greatly increases the chance of retinal detachment and causing a blood clot to break off, which can lead to blockage or narrowing of blood vessels.
Diagnosis and treatment
A consultative examination by an ophthalmologist will help determine the exact cause of pain in the eyes when moving. At an appointment with a specialist, a physical examination is performed and a comprehensive examination is prescribed. It includes laboratory and hardware diagnostics, which consists of:
- General analyses.
- Blood biochemistry.
- Analysis for the presence of a fungal infection of the eye mucosa.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye media.
- Measurement of pressure inside the eye.
- Determination of the boundaries of the field of view.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball
- Confocal microscopy
Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the etiology of the development of pain in the eyes during movement is determined and appropriate treatment is selected.
If minor pain suddenly appears, first aid at home is allowed. For this it is recommended:
- Limit or completely eliminate eye strain.
- Make a light head massage in the direction from the temples to the back of the head, and from the back of the head to the forehead.
- Massage the muscles of the collar area.
- Rinse the eyeballs with tea leaves or a light solution of chamomile.
- If pain increases, painkillers may be taken.
If the pain does not stop and its intensity increases, methods of official medicine are used to relieve it. The most effective complex treatment includes taking medications from the following groups:
- Painkillers.
- Antispasmodics.
- Antihypertensive.
- Vasodilators.
- Antibacterial.
- Antifungal.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Preparations for moisturizing the mucous membrane.
- Immunomodulators.
- Antiviral.
- Vitamin complexes for the eyes.
- Diuretics.
- Antihistamines.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When treating pain in the eyes of any etiology, topical medications are predominantly used. Also, as prescribed by a doctor, general medications are taken.
Traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary treatment. The most effective natural medicines are infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs.
- A decoction of mint leaves. It is used to relieve increased muscle tone, reduce visual tension, stabilize blood pressure and restore the psycho-emotional state, strengthens the body's protective functions.
- Infusion of chamomile. Allows you to quickly get rid of inflammatory processes when applied topically, reduces the severity of symptoms, and alleviates burning and stinging sensations in the eyes.
- Compresses and lotions made from aloe juice, honey and yogurt are also effective. Dandelion root juice and mature honey are used as drops. Ice cubes made from brown algae quickly relieve inflammation and pain in the eyes.
The use of traditional medicine should only be done after consultation with the attending physician. Self-medication in this case threatens to deteriorate the health of not only the eyes, but also chronic pathologies in general.
Treatment of pain in the eyes when moving is prescribed by an ophthalmologist, taking into account their etiology. The selection of drugs, the regimen for their administration and the duration of the therapeutic course are made in each case individually and depend on the physiological parameters of the patient.
Contact lenses and glasses
Advertising:
The causes of pain in the eyes when trying to look to the side can be associated not only with various diseases, but also with harmless factors - for example, wearing incorrectly selected glasses or prolonged use of contact lenses. Glasses should be selected only after a diagnosis by an ophthalmologist, based on his recommendations. Selecting glasses on your own causes regular headaches and difficulty moving the eyeballs. Wearing such glasses only aggravates the ophthalmological problem and further impairs vision.
A similar problem occurs when wearing contact lenses for a long time. Even if they are correctly selected, lenses cannot be worn for a long time. The eyeballs must rest, otherwise they will become overstrained and irritated.
In addition, when wearing contact lenses for a long time, there is a high risk of infection, which will lead to various eye problems.
To check the cause of the problem, you can stop wearing contact lenses or glasses for a while. If after this the condition of the visual organs improves, the cause of the pain lies precisely in this.
Treatment of noise in the head with cervical osteochondrosis
Without eliminating the underlying disease, it is impossible to get rid of noise in the head. But osteochondrosis is a chronic progressive pathology that is problematic to cure, especially if the pathological process has been going on for several years and is in an advanced stage.
Note! Only the initial stages of cervical osteochondrosis are treated. In other cases, treatment is aimed at inhibiting degenerative processes.
To reduce the manifestations of osteochondrosis, complex therapy is required, which includes:
- use of medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massage;
- therapeutic exercises;
- wearing orthopedic devices (Schants collar).
In case of displacement of the vertebrae, formation of osteophytes, hernias, or severe narrowing of the lumen of the spinal column, surgery is performed. All defects that cannot be removed conservatively are removed surgically.
Drug therapy
To treat noise in the head, the following groups of drugs are used:
- analgesics;
- muscle relaxants;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- chondroprotectors;
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- sedatives;
- diuretics, decongestants;
- medications to improve cerebral circulation (some of them are contraindicated for low blood pressure);
- antihypertensive drugs;
- nootropics.
The course of drug treatment for noise in the head with cervical osteochondrosis can last several months, depending on the severity of the patient. Throughout the entire therapy, the neurologist monitors the patient’s condition and adjusts the treatment regimen.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
To reduce muscle spasm and tension, the following procedures are used:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- UHF;
- electrical stimulation;
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- mud therapy.
To reduce noise in the head, manual techniques, acupuncture, and underwater traction are used.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Note! All physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out strictly according to indications, according to the schedule.
Massage
It is an obligatory part of the treatment of headaches and noise in the head due to osteochondrosis, but there are contraindications to massage:
- severe pain syndrome;
- severe compression of the nerve roots;
- hypertonicity of the muscles of the cervical-collar area;
- acute inflammatory process;
- hypertension;
- thrombosis;
- aneurysm;
- oncological diseases.
Massage relaxes muscles, improves blood circulation and reduces neurological symptoms. It is performed by a physical therapist or chiropractor. Treatment must be combined with neck exercises.
Note! Some therapeutic massage techniques are available only to qualified specialists, so they cannot be repeated at home.
Physiotherapy
The first training sessions should take place with an instructor, since exercises are selected individually for each patient. They help strengthen muscles, eliminate tension and normalize blood circulation.
Gymnastics is also a mandatory preventive measure for the occurrence of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. A set of exercises should be performed daily, 3-4 times a day. When working at a computer, warm-up is required every 1.5-2 hours.
Note! For osteochondrosis in the cervical spine, swimming and water aerobics are useful. Water relieves the spine, and physical activity helps strengthen the muscle frame.
Features of drug therapy
Advertising:
The occurrence of pain in the eyes when turning your gaze to the side can have many reasons, depending on which drug therapy is selected.
| Causes of the problem | Pharmacological group | Medications |
| Bacterial diseases | Antibacterial drugs | Amoxicillin tablets, Levomycetin and Tobrex drops |
| Viral lesions of the organs of vision | Antiviral and antiseptic agents | Acyclovir ointment, local antiseptic Okomistin |
| Allergic reactions | Antihistamines | Tablets Suprastin, Loratadine, Tavigil, Allergodil drops, hormones Hexamethasone |
| Fatigue and eye strain | Means for moisturizing mucous membranes | Systane, Visine, drugs based on artificial tears |
| Dry eye syndrome | Means for moisturizing mucous membranes | Systane Ultra, Emoxipin |
| Increased eye pressure | Medicines to normalize blood pressure | Irifrin drops |
| Long-term wearing of contact lenses | Means for relieving irritability of the mucous membranes | Visoptic drops |
To quickly eliminate pain after injury or damage to the eyeball, you can take a tablet of Ibuprofen, Analgin, Solpadeine. Additionally, you can instill pain-relieving drops Diclofenac or Inocaine.