Causes of pain
The head in the forehead area can hurt without damage to the internal organs. The cause may be mental fatigue. For knowledge workers, tension accumulates in the center of the forehead. At the end of the working day, a pressing feeling arises. A light massage of a point in the center of the forehead, and then upward, to the sides, will help to remove it.
Head pain in the forehead area may occur due to poisoning by toxic fumes. Such sensations often haunt employees of household chemicals and building materials stores. Low-quality products have a strong odor and emit fumes that cause pain, dizziness, and nausea. People who are sensitive to this should change their job or profession, and wear a respirator before leaving.
Severe headaches are sometimes caused by cerebral vasospasm. This condition manifests itself against the background of smoking, alcohol abuse, and sometimes due to changes in climate zones. Pain can also be triggered by physical or emotional stress.
Read also: Sweating head
Exacerbations of sinusitis
If therapeutic actions were started at the wrong time, the symptoms of the disease intensify and the intoxication of the body increases. Hyperthermia, a feeling of exhaustion, and general poor health can coexist with dizziness and autonomic disorders.
Secondary inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs (dacryocystitis). Polyps, fistulas, tumor-like formations (cholesteatomas) and mucous cysts (mucoceles) may appear in the frontal sinuses.
All this contributes to the appearance of ulcers on the walls of the sinuses, and the infection can penetrate the periosteum and bone.
Possible diseases
In some cases, the head hurts in the forehead and there is pressure due to pathologies of the internal organs. Associated diseases:
- infections: acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections (cause a rise in temperature and intoxication, which is why the head hurts and puts pressure on the forehead);
- ENT diseases: sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis (a characteristic symptom is severe nasal congestion);
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain: encephalitis, meningitis (accompanied by fever);
- pathologies of the nervous system: migraine (pain intensifies due to sounds, bright light, and recedes in silence and darkness), neuralgia (sharp, severe pain);
- injuries: concussions, skull fractures, bruises of the soft tissues of the head;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system: changes in intracranial pressure, hypertension, atherosclerosis, neurocirculatory dystonia;
- endocrine disorders: pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- ophthalmological diseases: changes in intraocular pressure, uveitis, inflammation of the optic nerve, myopia;
- oncological pathologies: brain tumor, neoplasms in the sinuses or pituitary gland.
Headaches in the forehead area can occur against the background of a large number of diseases. A comprehensive examination of the body will allow you to identify and eliminate the provoking factor.
Inflammation of the frontal sinus
The causes of inflammation can be viruses (rhinovirus, adenovirus, coronavirus), bacteria (staphylococcus, streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae) or fungi that penetrate from the nasal cavity.
Past rhinitis, infection from the nasopharynx, inflammation in other sinuses (for example, in the maxillary sinuses), ozena, seasonal allergies, decreased immunity due to hypothermia or stress, nasal injuries, deviated nasal septum, foreign body entry, polyps, cysts in the nasal cavity - all this can cause frontal sinusitis.
Frontal sinusitis also occurs in the presence of certain factors associated with human living conditions and activities. Thus, a polluted atmosphere, especially in the area of industrial enterprises, dusty and gas-filled premises, hazardous industries or occupational injuries (for example, barotrauma of divers, submariners, pilots) lead to malfunctions of the body’s immune system and, as a result, to frontal sinusitis.
The development of frontal sinusitis can be caused by hypothermia of the head in the autumn-winter period due to reluctance to wear a hat, inability to blow the nose correctly, or even general exhaustion of the body.
The development of frontal sinusitis is characterized by the accumulation of pus in the sinuses, and this, in turn, is fraught with serious complications.
Diagnostics
People come to a therapist and neurologist with headaches. Additionally, patients are asked to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist to assess the condition of the fundus. Further testing to determine the cause of headaches includes:
- complete blood count to rule out infections;
- EEG - determines the electrical activity of the brain, detects epileptic activity, migraine;
- ECG - checking the state of the cardiovascular system;
- analysis of thyroid hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- X-ray of the cranial sinuses - to determine ENT diseases.
Even a complete examination does not guarantee that the cause of the pain will be discovered. But it allows you to exclude serious diseases or identify them and select therapy.
Read also: Headaches in the temple area
Varieties of frontitis
Types of frontal sinusitis vary depending on the route of infection, the type and time of development of the pathology.
Experts distinguish:
- Acute frontal sinusitis. It is characterized by the sudden onset of the inflammatory process, the development is rapid, and the end of the disease is complete.
- Chronic frontal sinusitis. Occurs as a consequence of a poorly treated acute form of the disease; with it, long periods of exacerbation are replaced by short pauses of easing symptoms.
- Allergic frontal sinusitis. Immediate reaction to allergens: frequent sneezing, itching of the nose and eyes, there may be no increase in temperature or it may be low;
- Viral frontal sinusitis. When exposed to the virus, a rapid rise in temperature begins, complaints of sore throat, sneezing, and liquid translucent mucus appears.
- Bacterial frontitis. During a bacterial attack, the temperature rises, but slowly; the patient does not sneeze, and the mucus forms thick, with a characteristic tint.
- Catarrhal frontitis. It manifests itself with heaviness in the frontal region, nasal congestion; may not cause complications, or may progress to a more acute stage.
- Purulent frontal sinusitis. The formation and accumulation of purulent contents in the frontal sinuses has a detrimental effect on the patient’s condition; Even loss of consciousness is possible.
- Pneumosinus. A special form of frontal sinusitis, which is characterized by stretching of the frontal sinus; at the same time, air enters the sinus, but there is no exit for it. In this case, there may be no inflammation, but pain in the frontal region will be felt.
Regardless of the type of sinusitis, it can affect either one sinus (right or left) or be bilateral, when both sinuses are involved in the inflammatory process.
Treatment
Headaches cannot be tolerated, so during attacks you should take analgesics. These can be drugs based on paracetamol, ibuprofen, ketorol and others that help a particular patient.
The main treatment for headaches is always aimed at their cause. If there are serious pathologies of internal organs, hormone or chemotherapy, drugs for migraines or epilepsy, and drugs for heart disease are prescribed. Treatment is selected individually, taking into account the results of the examination and the general condition of the patient.
Dear patients!
Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33 Be healthy and happy!
Cephalgia and pregnancy
Most often, girls in this position suffer from migraines, and the illness appears from physical activity, food, lack of sleep, stress, and fatigue. There are also other reasons that cause throbbing pain in women in the position:
- VSD;
- blood pressure problems;
- problems with blood supply;
- voltage;
- disorders in the brain;
- sinus inflammation;
- glaucoma.
For pregnant women suffering from cephalalgia, there are recommendations to combat discomfort, namely:
- do a light massage;
- restful sleep;
- take a contrast shower.
Regarding pain relief with medications, in this case it is important to consult a specialist, since not all painkillers are approved for pregnant women.
Puncture with frontal sinusitis
Without a puncture, you can clear the sinuses and administer medications using a special Yamik catheter. If frontal sinusitis progresses to a severe, protracted stage, a puncture is required. This will clear the sinuses of pus.
In more advanced cases, a trephine puncture operation is required, in which a special tube (cannula) is inserted into the sinus opening. With its help, the sinuses are washed and the necessary antibiotic is administered.
Such surgical interventions are performed under local anesthesia.
In especially severe cases, open surgery is prescribed.
Frontitis: complications and consequences
The chronic stage of frontal sinusitis is dangerous due to its complications. A history of acute respiratory viral infection or a simple cold often causes an exacerbation of the disease, which lasts about three weeks.
When sinusitis passes into the chronic stage, there is a danger of purulent contents of the sinuses penetrating through the back walls into the skull. The consequence of this can be severe purulent meningitis or an abscess.
If a purulent infection penetrates through the thin lower wall of the sinus, the eye sockets will be seriously damaged.
These complications are very dangerous as they can be fatal.
The consequences of untreated frontal sinusitis affect other organs and lead to inflammatory processes in the tonsils, bone tissue and heart muscle tissue, conjunctivitis and damage to the optic nerve, otitis media or pneumonia.
Reasons why the left side of the head hurts
Headache on the left side can be caused by various reasons. It does not necessarily occur in diseases - painful sensations can also appear in healthy people due to stress or fatigue. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain advise you to go for an examination if the pain continues for more than 2-3 days in a row or bothers you too often. It is impossible to determine the exact cause at home or during a simple examination, but the doctor will need information about how the pain began, how long it lasts, in what area it occurs and with what intensity.
Physiological reasons
Even a healthy person, without any disorders or chronic diseases, can have a headache in the left area. If this symptom occurs once, is not very intense and goes away quickly, including after taking painkillers, there is no reason for concern. However, it is important to understand what can trigger a headache attack on the left side of the head in order to avoid such manifestations.
- Intense physical activity is the reason for accelerating blood circulation and activating the central nervous system. As a result, symptoms such as headache, dizziness and dark circles before the eyes, shortness of breath and tingling in the heart area may appear. To relieve them, a good rest is often enough; if the left side of your head hurts badly, you should take a painkiller tablet.
- Stress is one of the most common headaches. They arise as a result of increased concentrations of the hormones adrenaline, cortisol, angiotensin and others. They provoke vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. To relieve pain, it is recommended to rest and resolve stressful situations, otherwise dangerous consequences are possible: chronic headaches, increased risks of stroke.
- Prolonged mental stress, including working at a monitor without breaks, can cause severe pain in the left area of the head. Constant concentration and tension, especially in a sitting position, is dangerous to health. Doctors recommend taking breaks of at least 5-10 minutes every hour and doing a light warm-up.
- Abuse of tonic drinks, which include tea and coffee, is one of the reasons why a healthy person may have a headache. They contain substances such as caffeine and tannin. These are plant components that cause a constriction of the blood vessels that supply the brain. This effect is often accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
- Alcoholic drinks in large quantities are not a cure for headaches, but the cause that causes them. Ethyl alcohol first dilates blood vessels, and then provokes their sharp narrowing. Jumps in blood pressure are accompanied by pain, weakness and impaired heart function.
- Smoking is a source of nicotine, as well as hot vapors of other harmful compounds. This habit provokes the development of atherosclerosis, in which the lumen of the arteries narrows and they cannot supply enough oxygen to the brain. In addition, smokers often suffer from high blood pressure.
Most of the factors that cause pain in the left hemisphere of the head in a healthy person are related to habits and lifestyle. Doctors recommend completely giving up bad habits and spending time relaxing and walking in the fresh air. As a result, you can notice a significant improvement in your well-being and get rid of headaches.
Pathological conditions in which the left side of the head hurts
Pain on the left side of the head requires examination if it occurs frequently and is of high intensity. There are a number of reasons that can cause this symptom. These diseases can progress, so at the initial stage it is important to determine their cause and select an effective treatment regimen.
Migraine
An acute headache that occurs for no apparent reason and is highly intense is a migraine. During the examination, no functional impairment is observed, but it is known that this type of pain on the left side of the head is vascular in nature. Symptoms last from 4 hours to 3 days, and a migraine aura appears before the attack begins. It includes typical symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased sensitivity to light, smells, auditory and tactile stimuli;
- numbness or tingling sensation on the skin of the face and hands;
- decreased visual acuity.
Statistically, women are more likely to suffer from migraines. Despite the fact that its primary cause has not been discovered, each patient has his own factors that can trigger another attack. This could be certain smells, foods, alcoholic drinks, extreme fatigue or stressful situations. You can relieve symptoms with painkillers, but they are not effective enough for migraines.
Tension headaches
Tension headaches are often symmetrical, but can also occur only on the left side. This is a complex of symptoms that develops due to stress, chronic fatigue, and muscle tension in the neck. One of the reasons why pain in the left head can occur on an ongoing basis is injuries in the cervical spine. The patient is concerned about characteristic manifestations:
- compressive pain that covers the temple and back of the head, spreading to the area behind the eyes;
- muscle tension in the neck and shoulder girdle;
- Symptoms increase towards the end of the day.
To get rid of pain in the head on the left, it is recommended to monitor your posture. Massage therapy can also help, but should be performed by an experienced professional, especially if there has been previous injury in the area.
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are considered the most intense and can significantly affect the patient's daily life. They arise in one part of the head or spread over its entire surface, often affecting the area behind the eyes, forehead and temple. Additional signs also appear:
- nasal congestion, difficulty breathing;
- ptosis - drooping of the eyelid;
- increased sensitivity to light in one eye, watery eyes;
- redness of the facial skin, increased sweating.
Cluster headaches are one of the rarest types. Their exact cause is unknown, but they often occur at regular intervals, in spring or autumn. The attack lasts for 5-10 minutes, and then the pain becomes less acute and persists for up to 3 hours. A characteristic sign of cluster pain is that it begins every day, at a certain time, for 1–3 months.
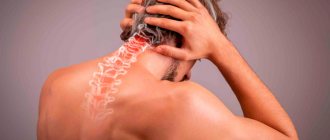
Diseases of the cervical spine
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can be caused by diseases of the cervical spine. Here pass important vessels and nerves that carry blood and impulses to the brain. Their compression or inflammation leads to acute headaches, including unilateral ones.
- Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the cartilage layer between the vertebrae. They become less durable and elastic, and therefore lose their ability to absorb shock during movement. The space between adjacent vertebrae narrows, which leads to compression of blood vessels and nerves. Soreness manifests itself after a long stay in a sitting position or after exercise.
- Displacement of the vertebrae is a dangerous condition that leads to acute pain, inflammation of the nerves and compression of blood vessels. Most often this condition is associated with injuries, falls, or increased stress on the neck area, but in some patients the displacement can also occur in a calm state. In this case, congenital instability of the vertebrae and weakness of the neck muscles are important.
- Protrusion - protrusion of the intervertebral disc, the initial stage of a hernia. The process is accompanied by acute pain in the neck and one part of the head; any movement is difficult. The diagnosis can be made based on analysis of x-rays. The pain in the left hemisphere of the head goes away if the integrity of the spinal column is restored and the compression of blood vessels and nerves is relieved.
Chronic neck diseases require timely treatment as they can progress. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions for a full diagnosis, as well as treatment and recovery from injuries, osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement and intervertebral hernias.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic vascular disease that occurs when fat metabolism is impaired. Some products, including cholesterol, are not excreted, but accumulate in the blood and settle on the walls of the arteries. The vessels become fragile, insufficiently elastic, and cannot fully narrow or expand in response to increases and decreases in pressure. There are a large number of factors that can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, including:
- frequent consumption of fatty foods of animal origin (the main source of cholesterol);
- disruption of the secretion of enzymes that are involved in fat metabolism;
- liver diseases;
- overweight and sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
With atherosclerosis, a headache may occur on the left or right due to impaired blood supply to the brain. Painful sensations are often associated with increased blood pressure. The inability of the blood vessels to dilate and compensate for this condition leads to acute pain, dizziness, nausea and other alarming symptoms.
Traumatic brain injuries
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can appear even long after injury. Concussions, bruises, open and closed craniocerebral injuries cause disruption of the blood supply to certain areas of the brain. Even in patients whose nervous activity is completely restored, pain may be felt after exercise and due to changes in weather. Injuries often trigger chronic migraines. The pain can be relieved with painkillers, and the doctor will help you choose the most suitable option.
Stroke
An acute headache on the left side of the head is one of the first signs of a stroke. In this condition, a sudden disruption of cerebral circulation occurs, resulting in areas of ischemia. The process can be determined at home, but it is important not to miss its first manifestations:
- acute headache, often one-sided;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- pain in the heart area;
- asymmetry of movements of facial muscles and limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
The most common type is ischemic stroke. It occurs when there is an acute disturbance of cerebral circulation due to vascular disease or blockage. Atherosclerosis, stress and other factors can lead to an attack. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but is more life-threatening. It is accompanied by rupture of the vessel and the release of blood into the brain. It can accumulate in the brain ventricles or meninges, thereby provoking the appearance of areas of necrosis. Help for a stroke can only be obtained in a hospital, in an inpatient setting. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain emphasize that the highest probability of a favorable outcome remains if you seek help in the first 2 hours.
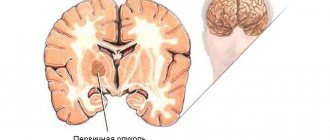
Neoplasms in the brain
Tumors and cysts can cause acute headaches, including unilateral ones. Neoplasms disrupt the processes of cerebral circulation, compress blood vessels and nerve tissue. The pain is chronic and always appears in the same area, but can spread to the entire surface of the head. The diagnosis is made based on CT or MRI data, and treatment tactics are selected individually. Early diagnosis of lumps is important because over time they can grow in size and cause more dangerous symptoms.
Colds
Colds and flu are common infectious diseases that appear more often during the cold season and in the off-season. The virus infects the upper respiratory tract and causes a persistent increase in temperature. Headache is also considered one of the characteristic symptoms. It is associated with pressure changes, high temperature, and also with the accumulation of exudate in the nasal sinuses. It decreases after rest and taking antipyretic drugs.
Arterial hypertension
Increased blood pressure is one of the main causes of headaches in the left area of the head. With hypertension, it is one-sided, pulsating, and can spread to the temple area or the back of the head. At home, you can measure your blood pressure using a tonometer. Normally, the result is about 120/80 mmHg; hypertension can be considered when the result is 140/90 mmHg. and more. An attack of hypertension may also be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- tinnitus, temporary deterioration in hearing and vision;
- rapid heartbeat;
- redness of the facial skin;
- painful sensations and discomfort behind the sternum.
Attacks of hypertension are often triggered by intense physical activity, stress and nervous tension. They appear more often in hot weather and in poorly ventilated areas. The pressure increases due to the need to increase the supply of oxygen to the cells. To normalize blood pressure, it is recommended to ventilate the room and take medicine.
Prevention
To avoid such a serious disease as frontal sinusitis, you must:
- take treatment of any runny nose seriously;
- pay the same attention to the treatment of colds, as well as diseases of the nasopharynx;
- constantly rinse your nose with sea water;
- proper nutrition, adherence to drinking regime, consumption of the necessary set of vitamins;
- dress according to the season, avoiding hypothermia and drafts;
- maintain immunity (sleep 8 hours, adhere to a work-rest schedule);
- avoid injuries to the head and nasal septum;
- spend time in the fresh air, especially in a coniferous forest, maintain physical fitness;
- maintain a healthy microclimate in the house: constant ventilation, air humidification, especially during the heating season;
- Spa treatment;
- If you suspect an illness, immediately contact an otolaryngologist.